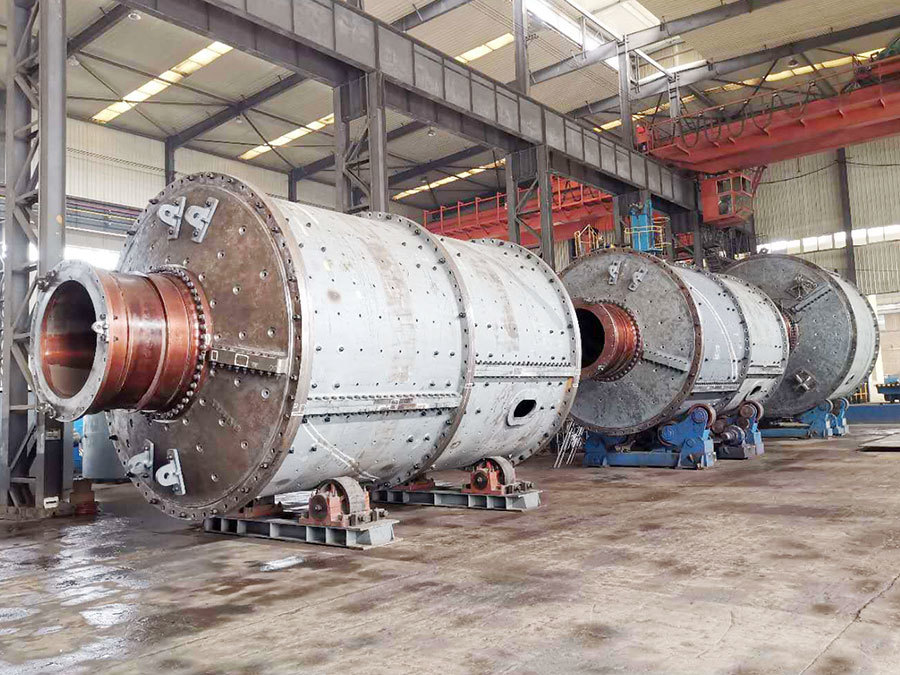
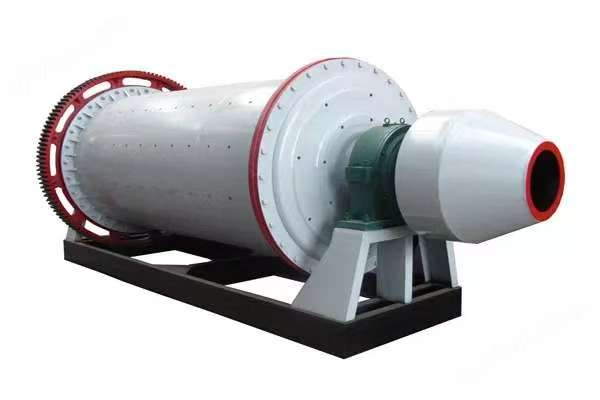
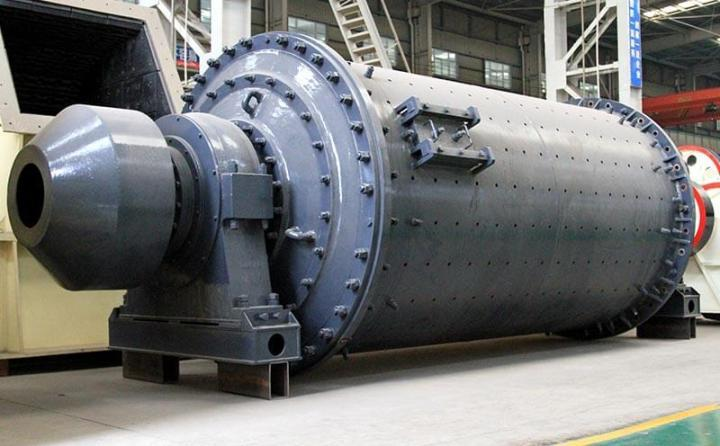
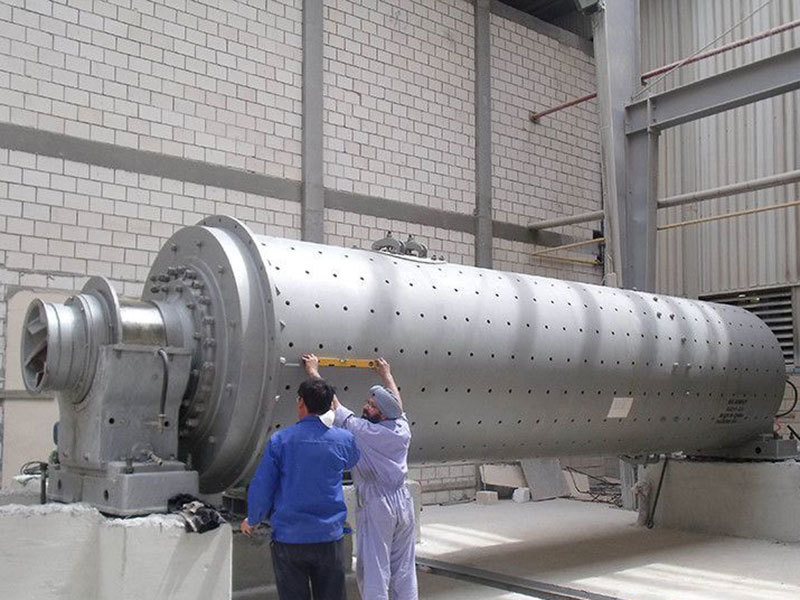
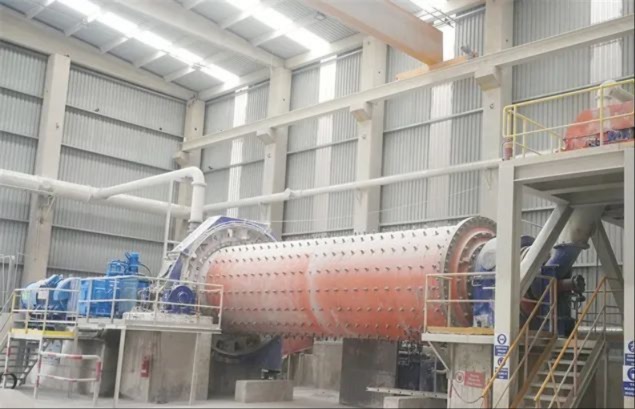
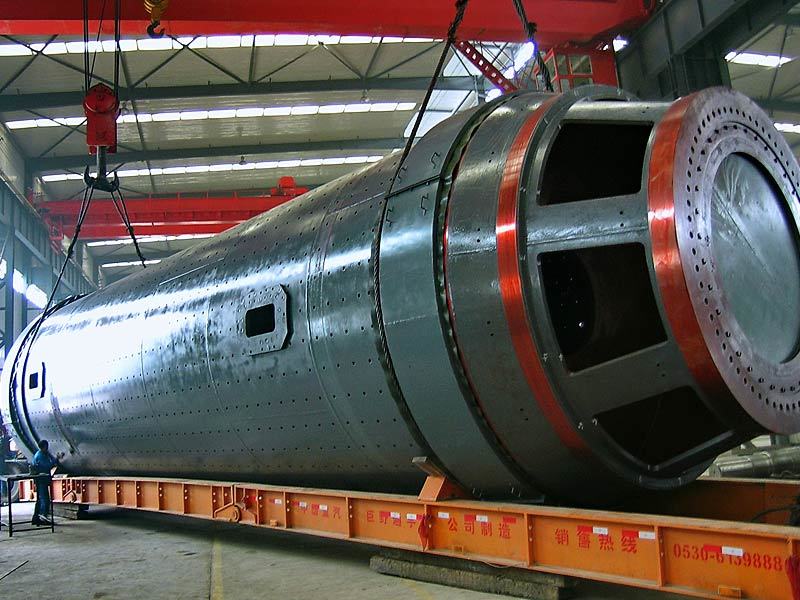
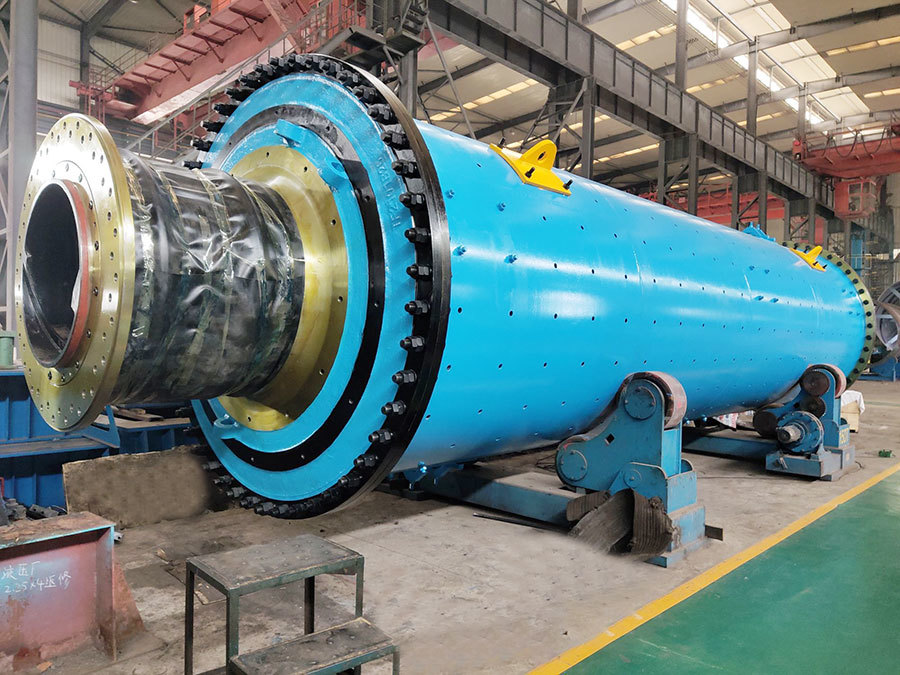
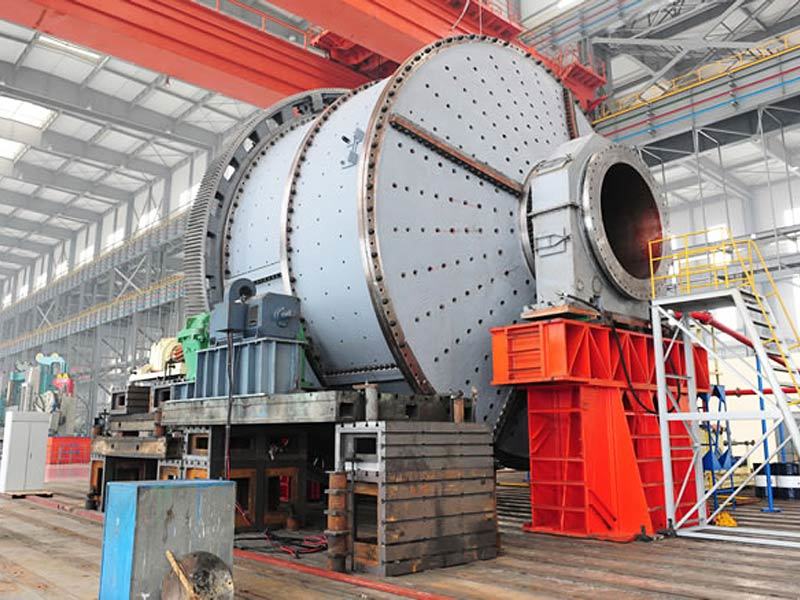
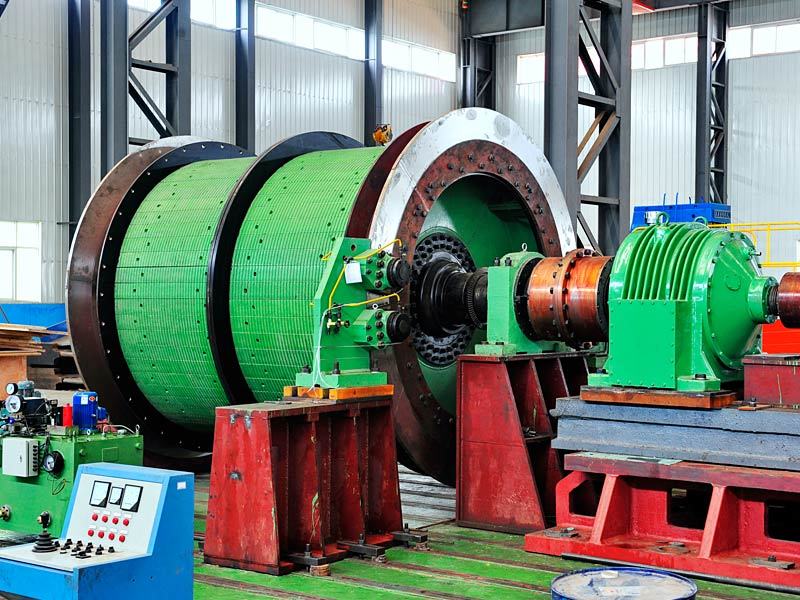
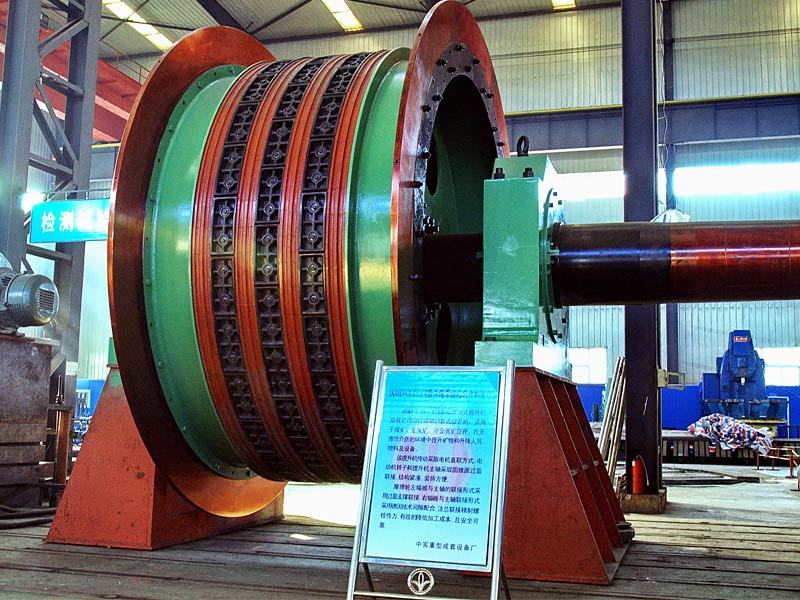
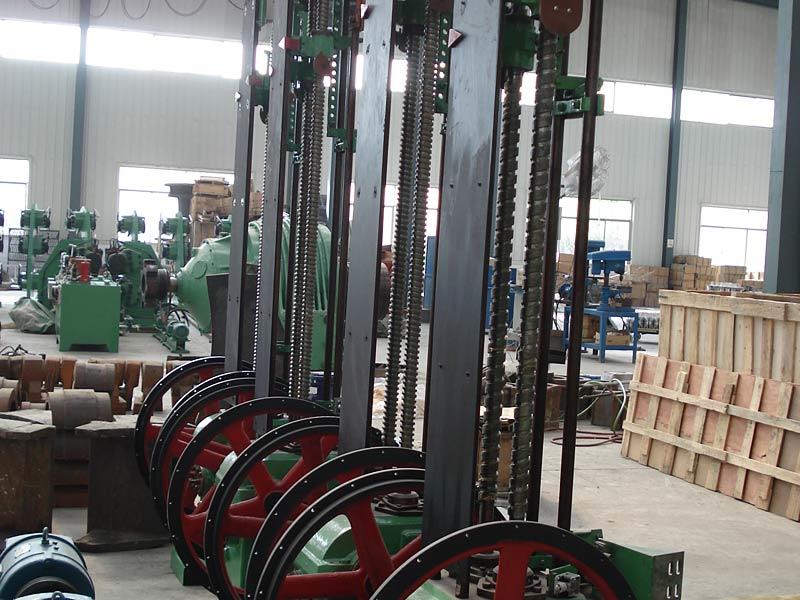
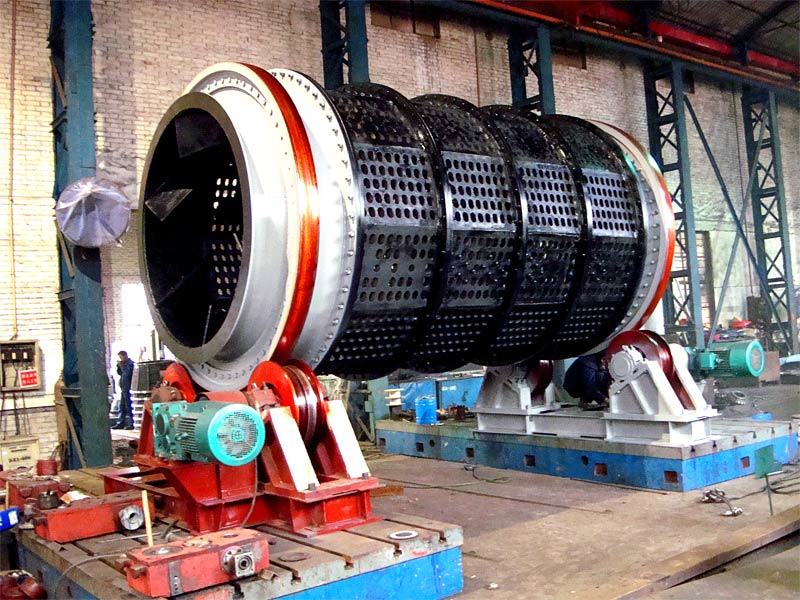
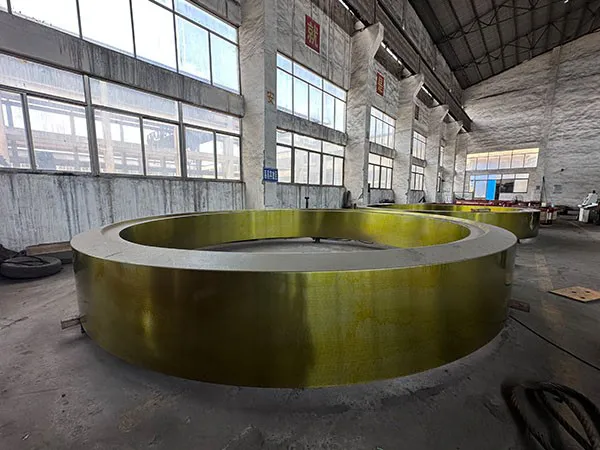
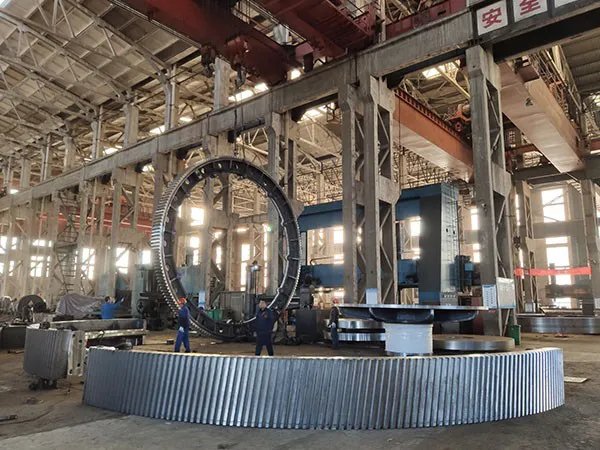
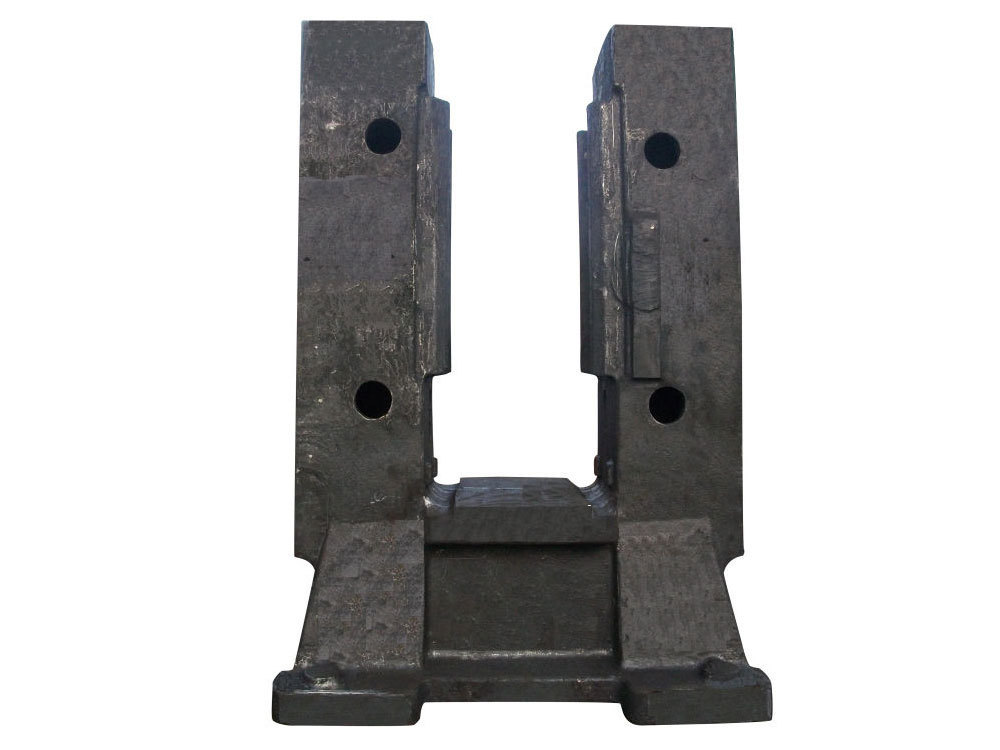
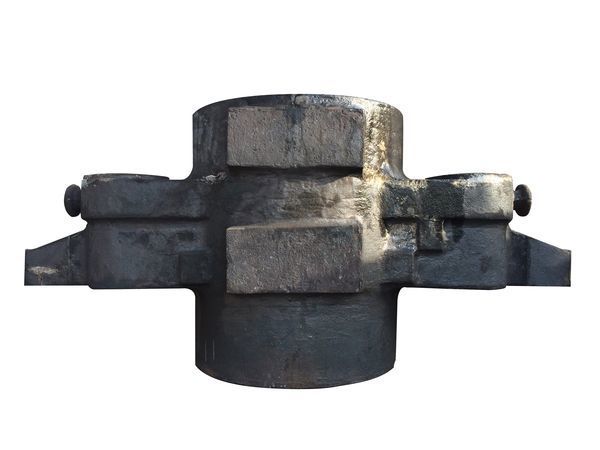
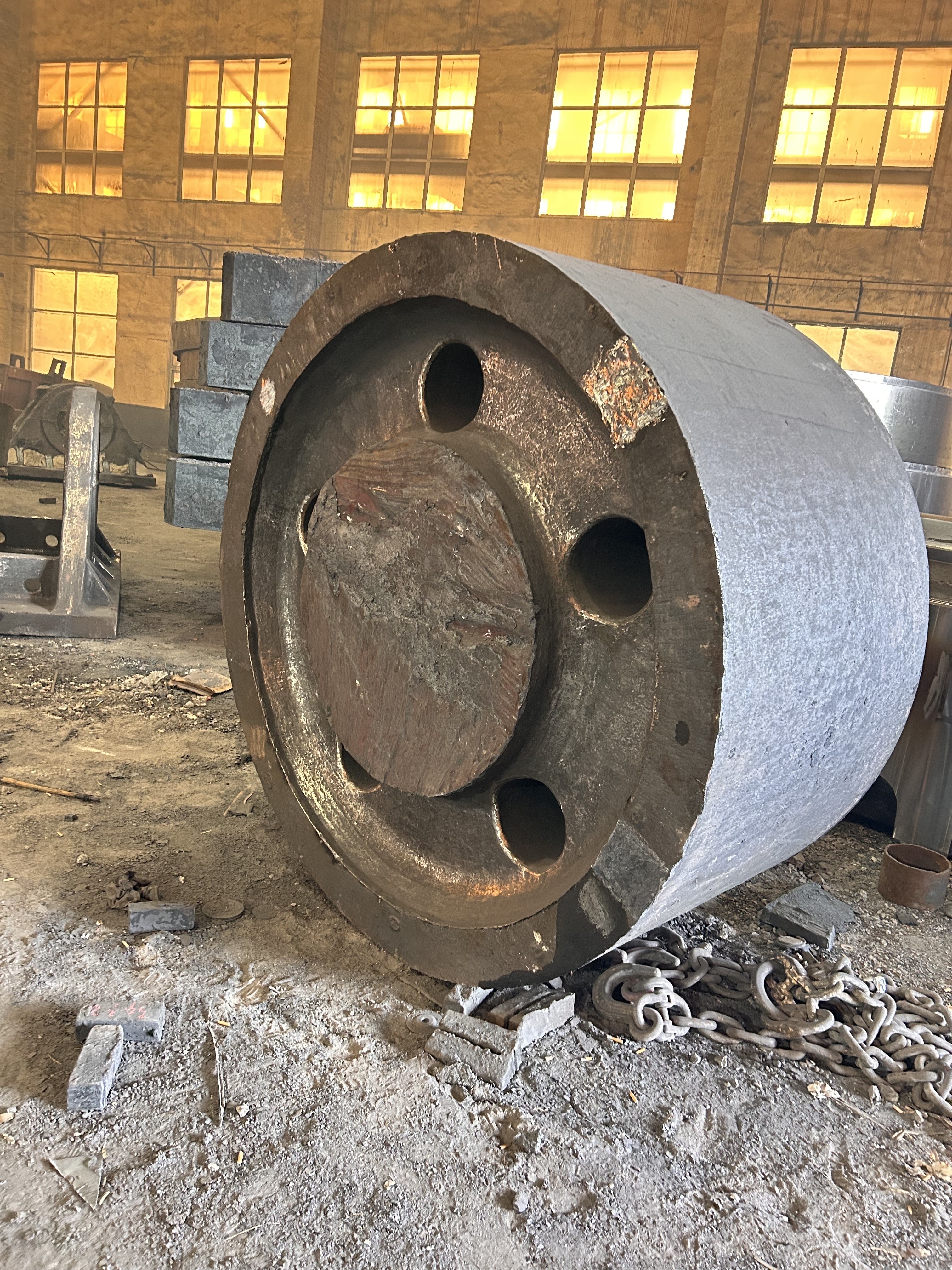
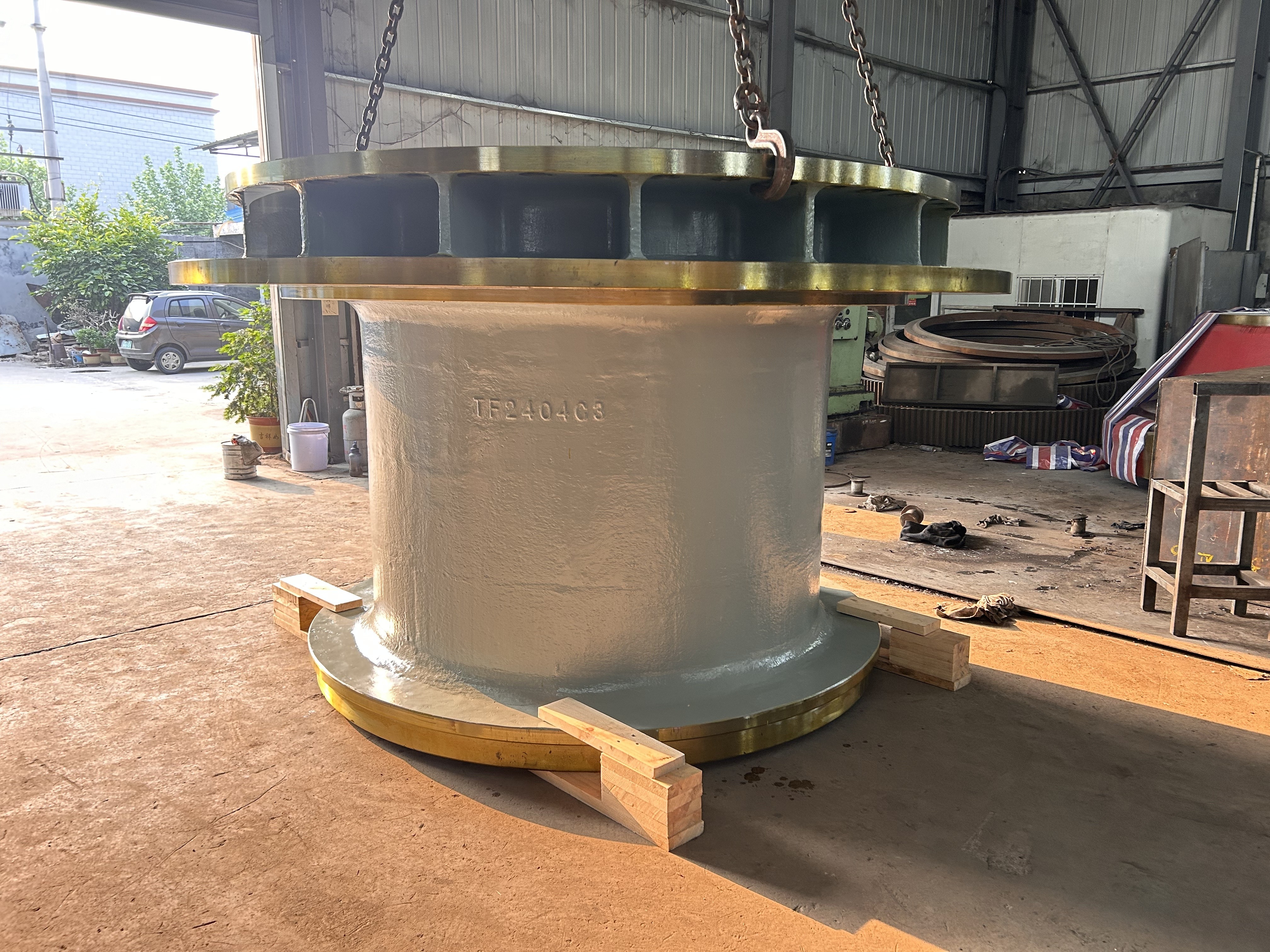
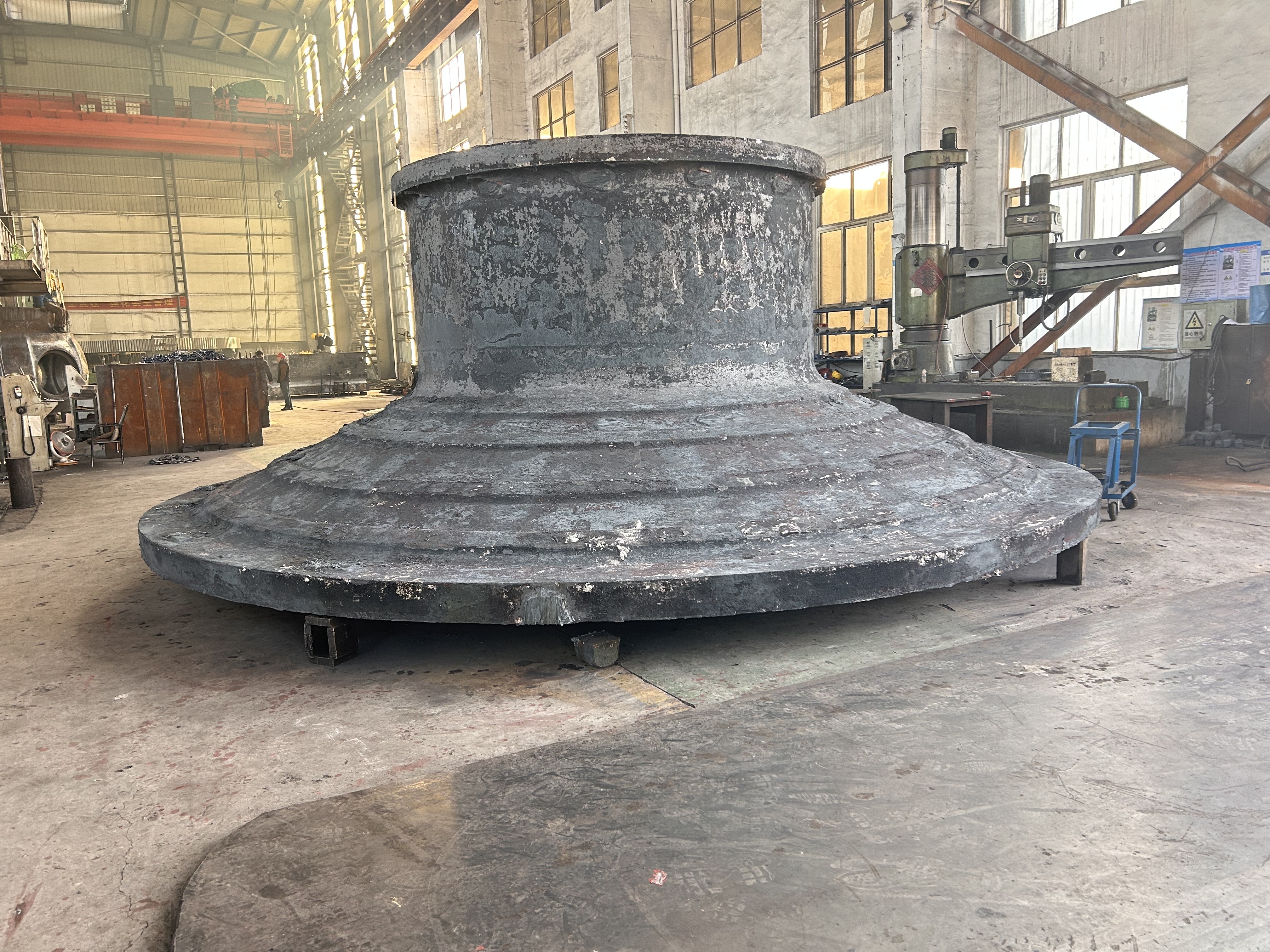
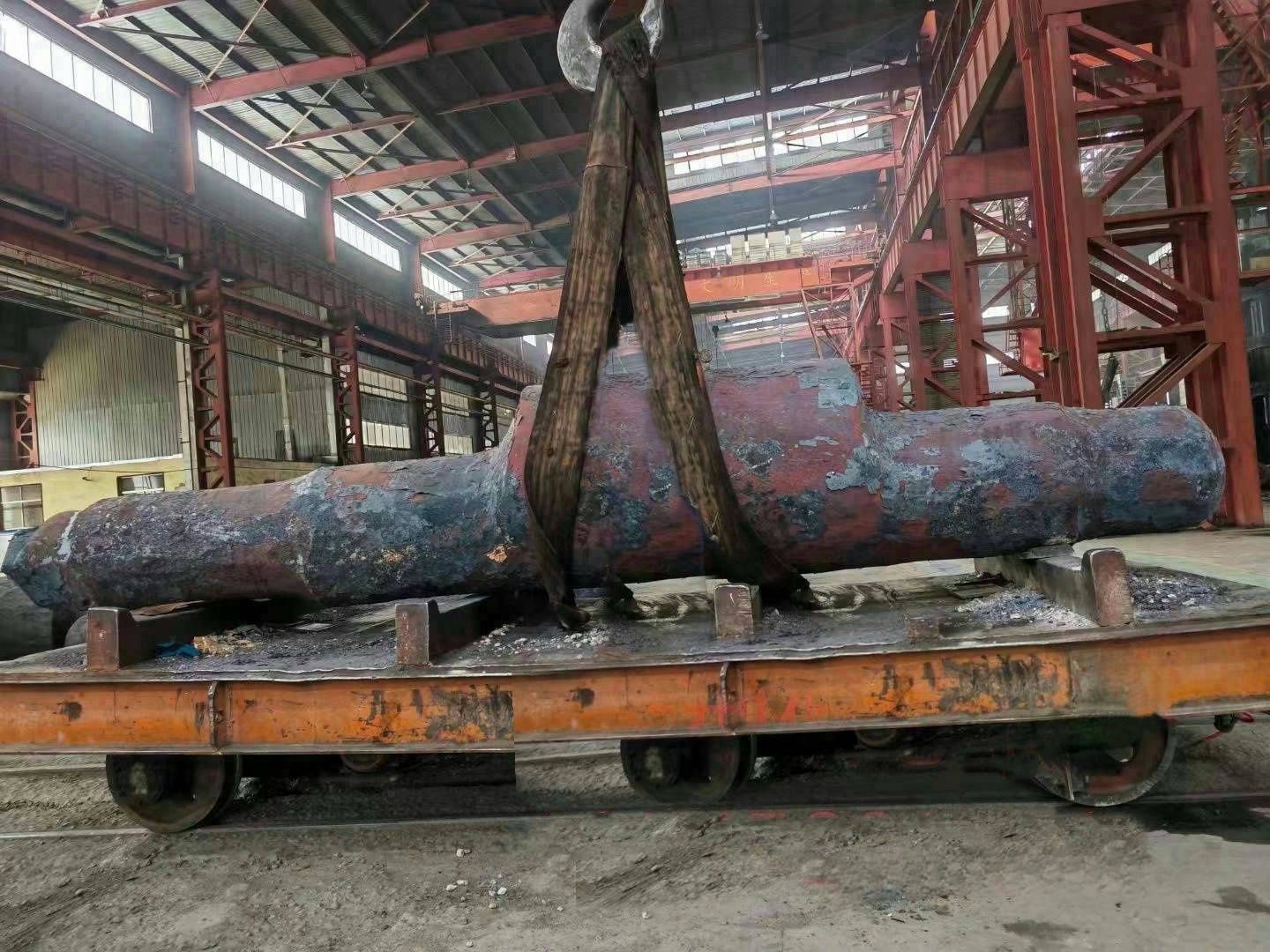
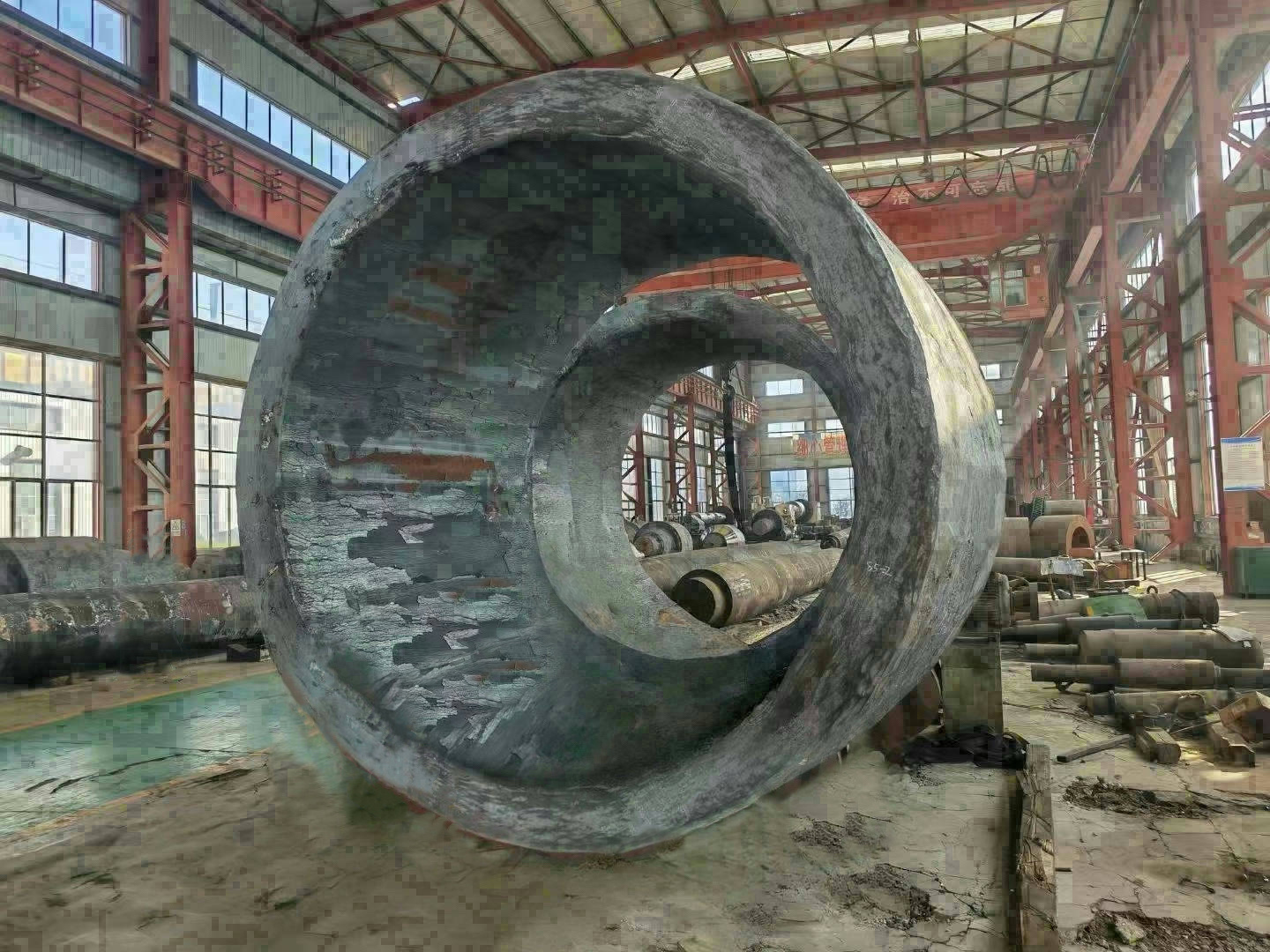
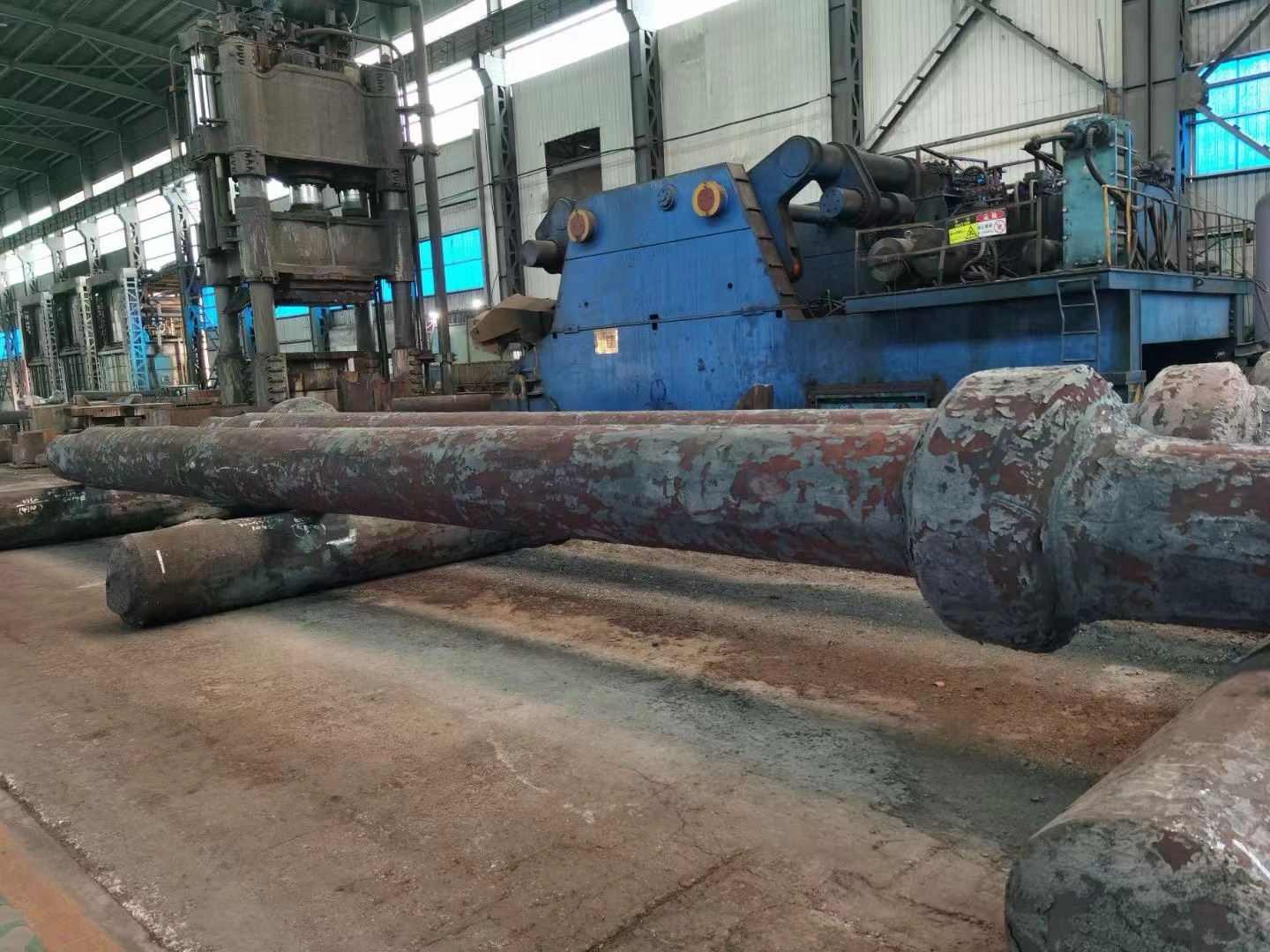
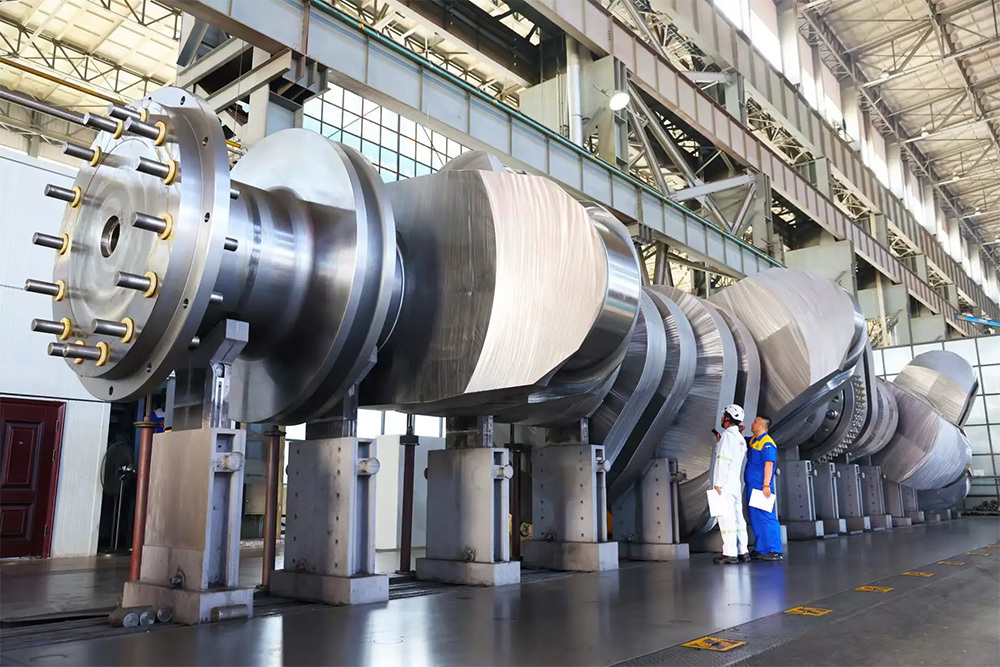
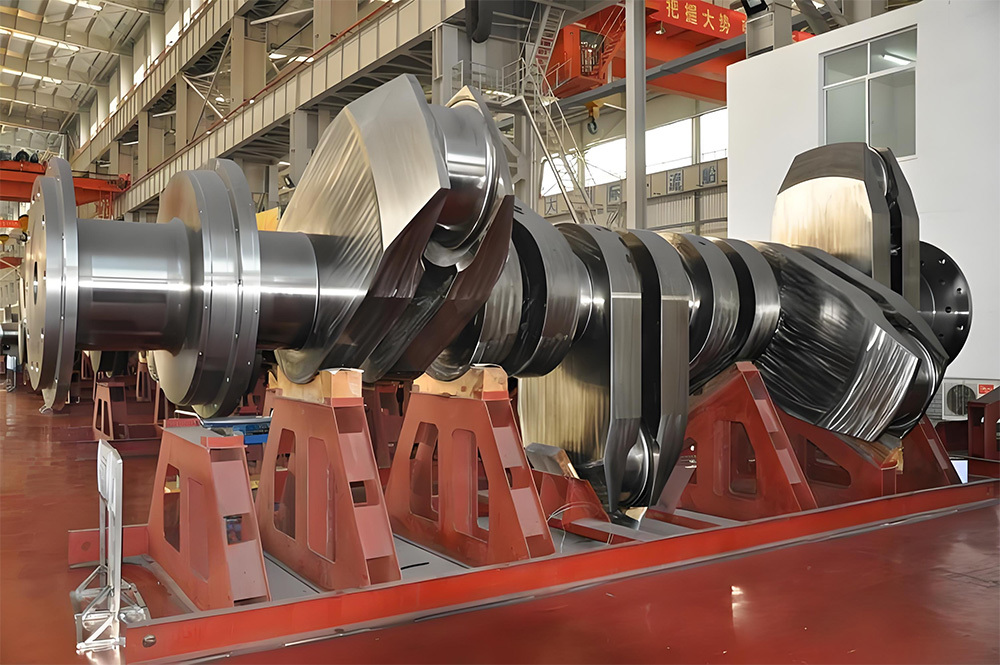
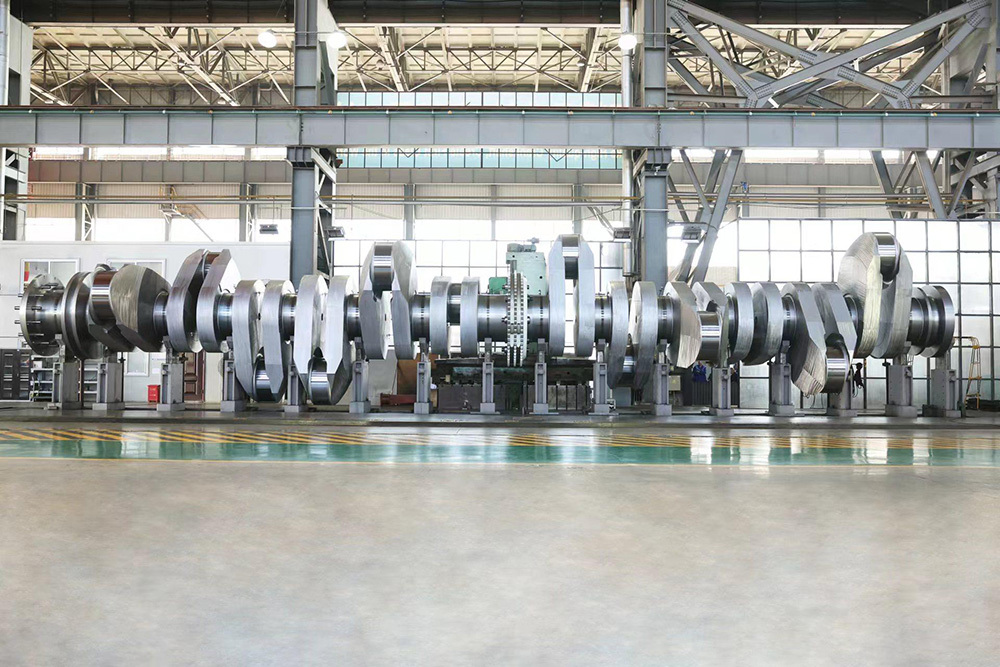
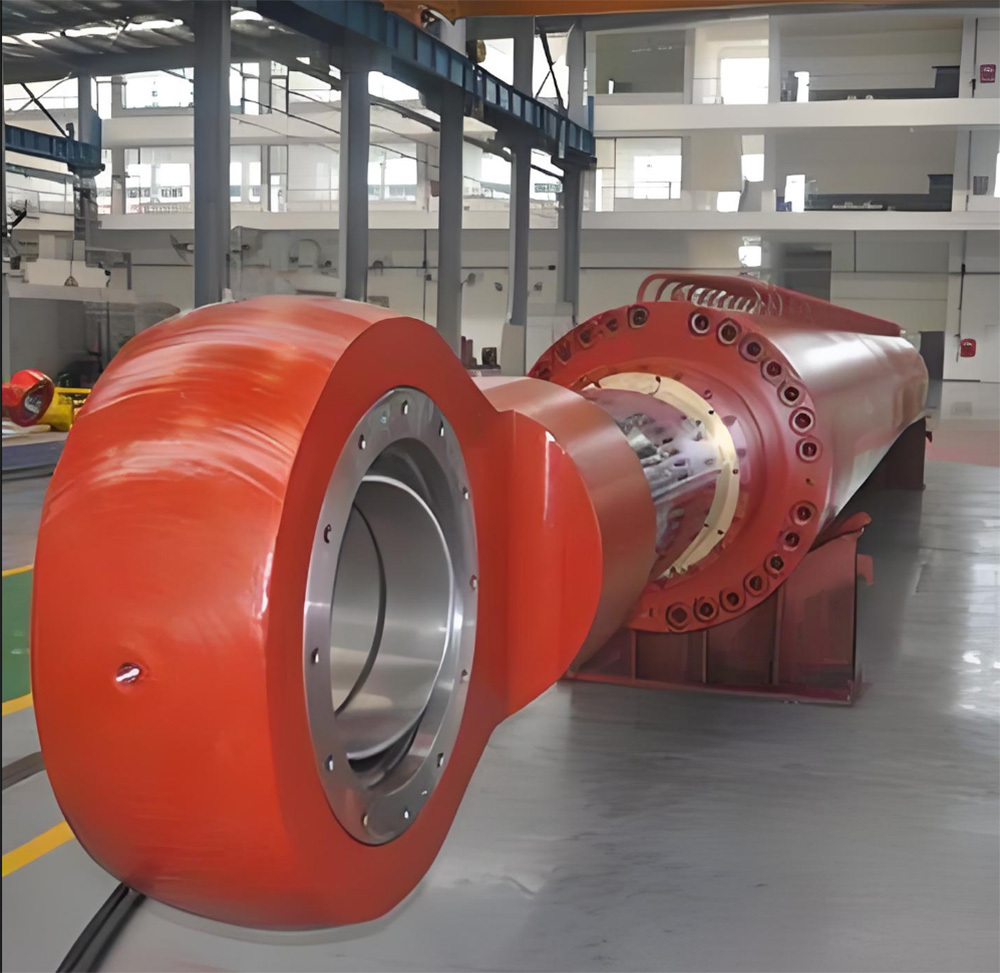
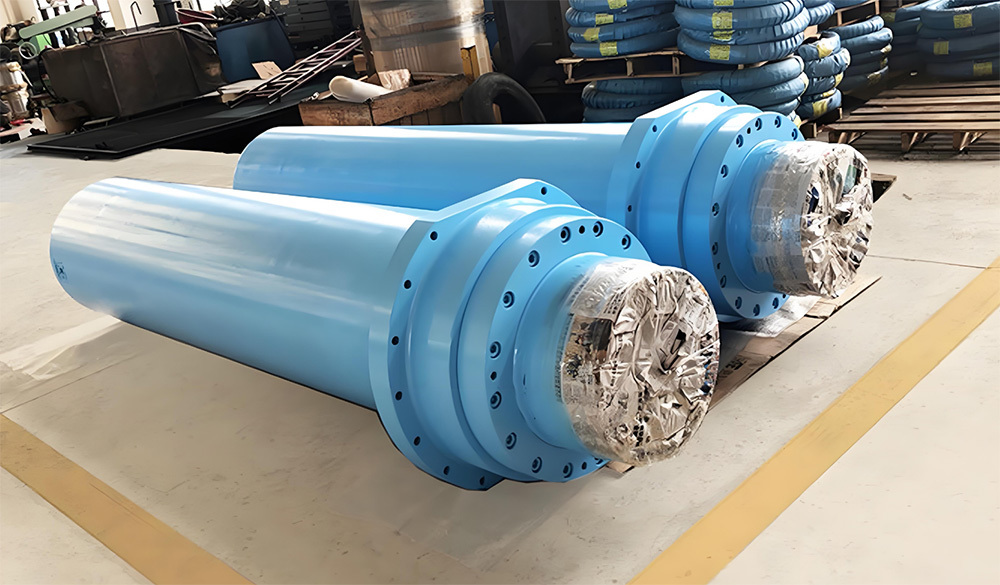
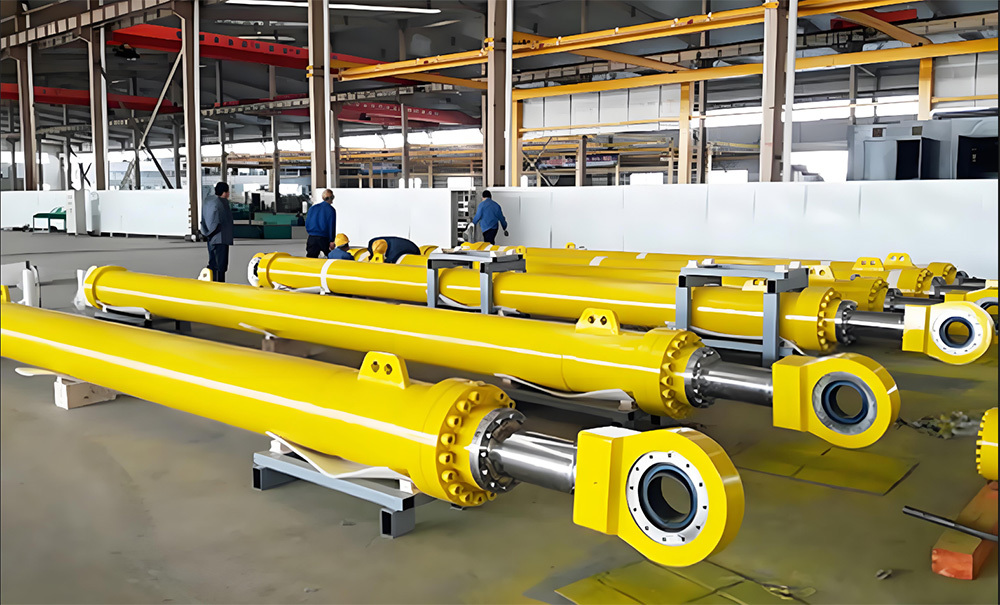
I. Introduction to Large-Scale Riveted and Welded Components
Large riveted and welded components serve as the "skeleton" of industrial heavy-duty equipment and infrastructure. At their core lie the judicious selection of materials—primarily low-alloy high-strength steel—and precision manufacturing, particularly in welding and assembly. Quality control is rigorously implemented throughout the entire process—from material inspection and process monitoring to non-destructive testing. Post-weld heat treatment and anti-corrosion treatments are critical in ensuring long-term reliability and durability. Moreover, design must comprehensively account for factors such as strength, stiffness, fatigue resistance, manufacturability, ease of transportation and installation, as well as the service environment. A thorough understanding of the material properties and intricate manufacturing processes is essential to guarantee product quality, performance, and longevity.
II. Main Materials
Materials commonly used for large riveted and welded components typically include steels that are core-resistant to corrosion, high temperatures, and low temperatures—and are also the most widely used.
Corrosion-resistant steels: 316/316L austenitic stainless steel, 2205 duplex stainless steel
High-temperature-resistant steels (operating temperature > 350°C): 310S (0Cr25Ni20) austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel, Incoloy 800/800H high-alloy special heat-resistant steel
Low-temperature-resistant steels (operating temperature < -20°C): 16MnDR low-temperature carbon-manganese steel, nickel-based low-temperature steel, and austenitic stainless steel
Room-temperature steels (temperature range: -20°C to 350°C): Q235B carbon structural steel, Q355 series low-alloy high-strength steels (HSLA), and Q355NH (national standard) weathering steel.
III. Key Processes in Welding Technology
Pre-weld preparation: Material cutting, forming, and beveling (with precision control).
Strict cleaning: Remove oil, rust, water, oxide scale, and other contaminants from the bevel and surrounding areas on both sides.
Assembly tack welding: Use the same welding materials and processes as for the final welds to ensure high-quality tack welds of appropriate length and spacing. Also, inspect assembly gaps and misalignment.
Preheating (if required): Heat evenly to the specified temperature, and monitor and record accordingly.
Welding process:
Weld strictly according to the WPS and welding sequence.
Control interlayer temperature (monitor and record).
When performing multi-pass, multi-arc welding, carefully clean away interlayer slag and spatter. Ensure proper fusion of the weld beads to prevent defects.
Monitor key parameters (current, voltage, speed, gas flow rate, etc.).
Welding Process |
Application Scenarios |
Material preparation process |
Flame cutting (CNC cutting), plasma cutting, laser cutting, shearing, and sawing. High-precision bevel machining (such as edge milling and bevel cutting machines). |
Forming process adopted |
Rolling (cylindrical and conical shapes), bending (using a bending machine), pressure forming (with large-scale presses), and roll forming. |
Assembly and Alignment |
Using large-scale tooling fixtures and platforms—such as welding positioners and roller stands—ensures the precise positioning and dimensions of each component. This is a critical step in quality control. |
Common Welding Methods |
Application Scenarios |
Submerged Arc Welding |
Suitable for long straight welds and circumferential seams (such as longitudinal and circumferential seams of cylindrical shells). |
Gas-shielded welding |
MAG (CO2 or mixed gas), MIG (inert gas). Widely used and highly versatile (manual, semi-automatic, automatic), suitable for various positions and joint types. |
Shielded Metal Arc Welding |
Suitable for positions that are difficult to automate, short welds, and repair welding. It is less efficient and relies heavily on the welder's skill. |
Electroslag Welding |
Vertical welding for extra-thick plates (such as box-beam diaphragms). |
Narrow-Gap Welding |
Designed for butt joints in extra-thick plates, it offers high efficiency and minimal deformation. |
Post-weld treatment |
|
Stress Relief |
Large components generally require post-weld heat treatment—either overall or localized (typically stress-relief annealing)—to remove weld slag and spatter, followed by grinding of the weld seam and its surrounding areas. This process helps relieve residual welding stresses, preventing deformation, cracking, and improving the material's toughness. |
Orthopedic |
Flame straightening and mechanical correction (using presses and jacks) are employed to control welding deformation. |
Mechanical Processing |
Perform precision machining operations such as milling, boring, and drilling on critical mating surfaces and hole locations. |
We will conduct non-destructive testing, inspection, and testing on the products:
| Project | Content |
Visual Inspection |
Surface defects (cracks, undercut appearance inspection (VT), porosity, arc craters, etc.). |
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) |
Detecting internal defects (such as lack of fusion, incomplete penetration, slag inclusions, and cracks) is especially critical for thick plates. |
Radiographic Testing (RT) |
Intuitively displays internal defects and is commonly used for critical butt joints. |
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) |
Detection of Surface and Near-Surface Defects (Ferromagnetic Materials) |
Penetrant Testing (PT) |
Detecting surface opening defects (non-magnetic materials). |
Destructive Testing (Sampling) |
Such as tensile testing, bending tests, impact tests, hardness tests, and metallography (typically conducted during process qualification or random inspections). |
Dimensional Inspection |
Check whether the overall structural dimensions and key component dimensions meet the drawing requirements. |
Pressure/Leak Test (if required) |
Such as hydraulic tests, pneumatic tests, and leak-tightness tests. |
IV. Typical Application Scenarios
Industry |
Product Cases |
Key Solutions |
Mining machinery |
Crusher frame, ball mill drum, mine car chassis, kiln body, furnace body, and more |
Impact-resistant structural design + locally reinforced welding |
Energy Equipment |
Wind turbine tower sections (diameter Φ4.5m), hydropower station penstock pipes |
Automatic circumferential welding + 100% radiographic inspection |
Engineering Vessels |
Dredger cutterhead frame, port crane boom |
Salt Spray Environment-Resistant Welding (C5-M Level Protection) |
Chemical equipment |
Reactor vessel shell (thickness ≥ 80 mm), hydrogenation reactor |
High-Temperature and High-Pressure Welding (PED 2014/68/EU Certified) |
V. Quality Assurance System
1. Certification Standards:
① EN 1090-2 EXC3 (EU's highest-grade steel structure)
②ASME Section VIII Div.1 (Pressure Vessel Code)
③ISO 3834-2 (Welding Quality Management System)
Specialized material standards:
① The ISO 15614 series of standards, "Welding Procedure Specifications and Qualification for Metallic Materials" (e.g., ISO 15614-1 for steel arc welding, -8 for pipe welding, etc.), supports weld material compatibility testing and verification of process parameters.
②GB/T 19867.1 "Welding Procedure Specifications and Assessment" (China National Standard) is equivalent to ISO 15614, mandating the preparation of detailed Process Working Documents (WPS) and specifying assessment test methods for domestic projects.
3. Inspection and Defect Acceptance Criteria:
① ISO 5817 "Quality Grades for Defects in Fusion Welded Joints of Steel, Nickel, Titanium, and Their Alloys"
② GB/T 11345 "Manual Ultrasonic Testing Methods and Acceptance Criteria for Steel Welds" (China National Standard)
Core Standard for Nondestructive Testing (UT) of Large Structures
Note: Large riveted and welded components often involve dissimilar steel welding (e.g., Q355B with 316L), requiring additional compliance with ISO 18274 (nickel-based welding material standard) or AWS A5.11 (stainless steel electrode specification).
Keywords
Previous: Large Riveted and Welded Components







Large Riveted and Welded Components
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
Rotary kiln
-

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-

Lime Rotary Kiln
-

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
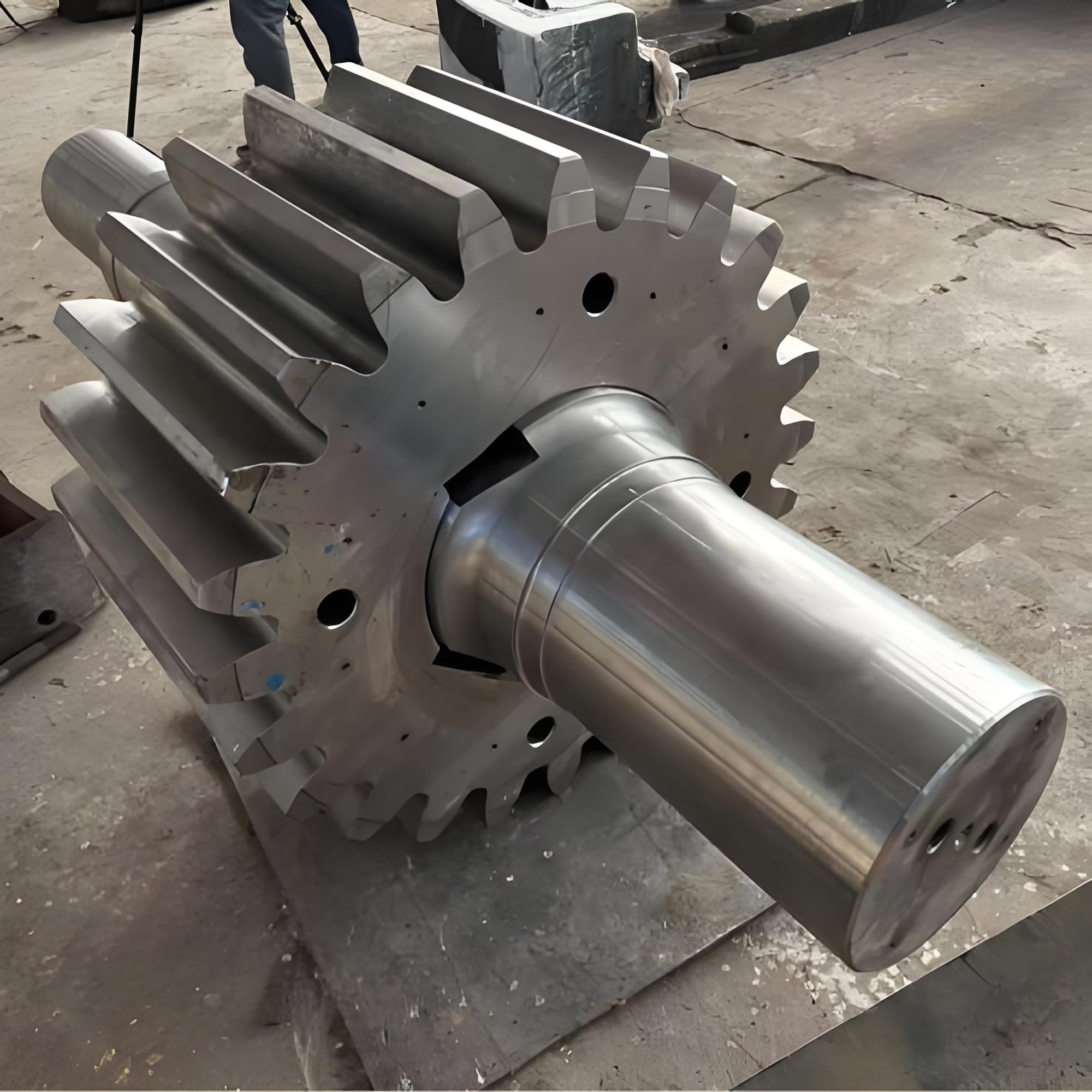
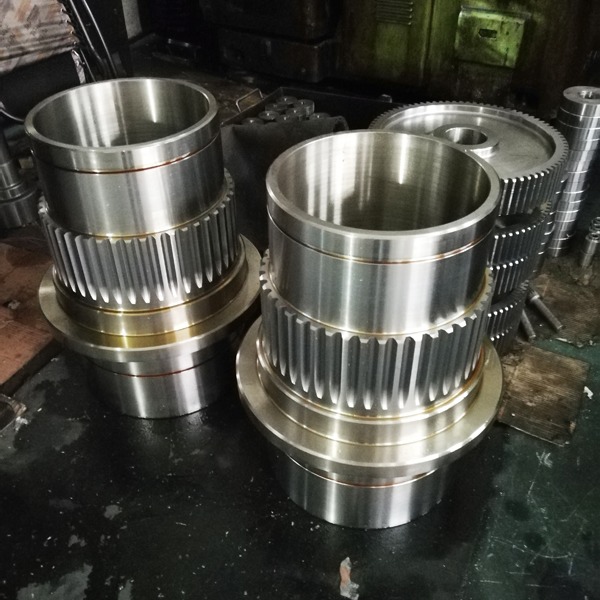
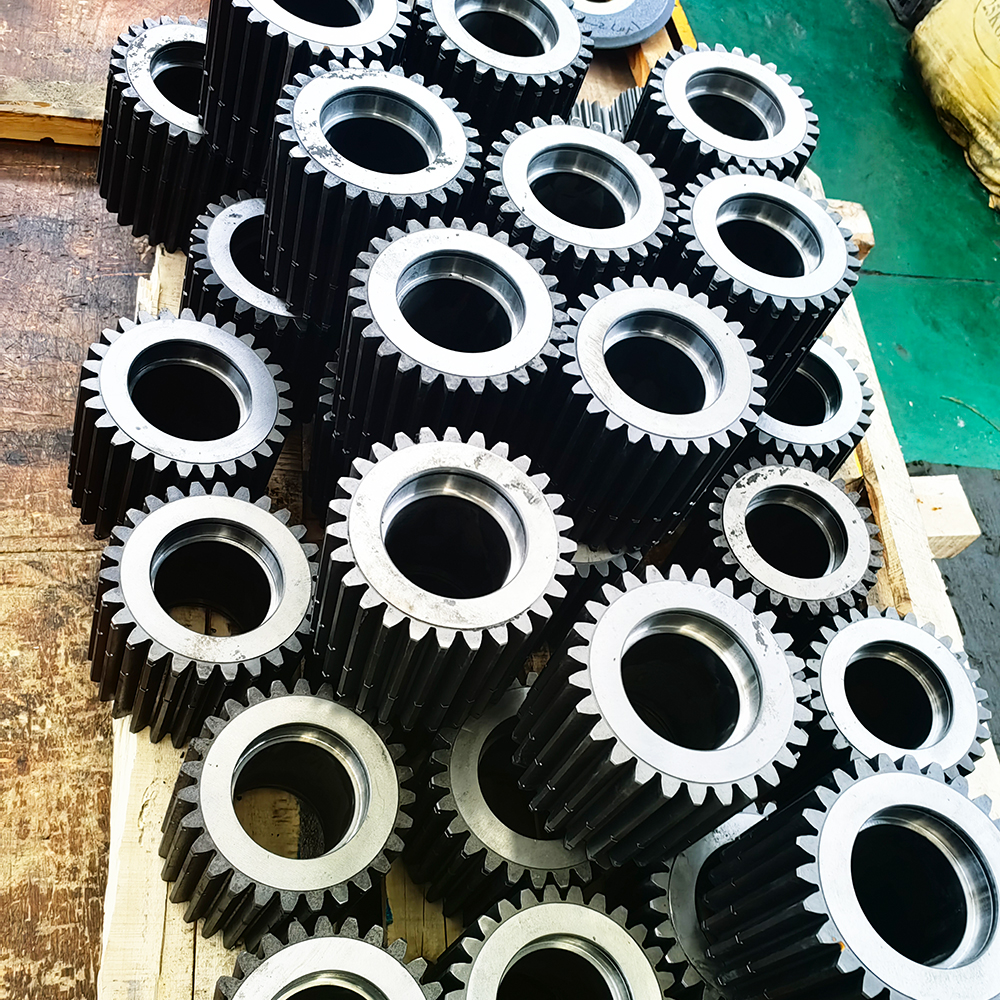
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
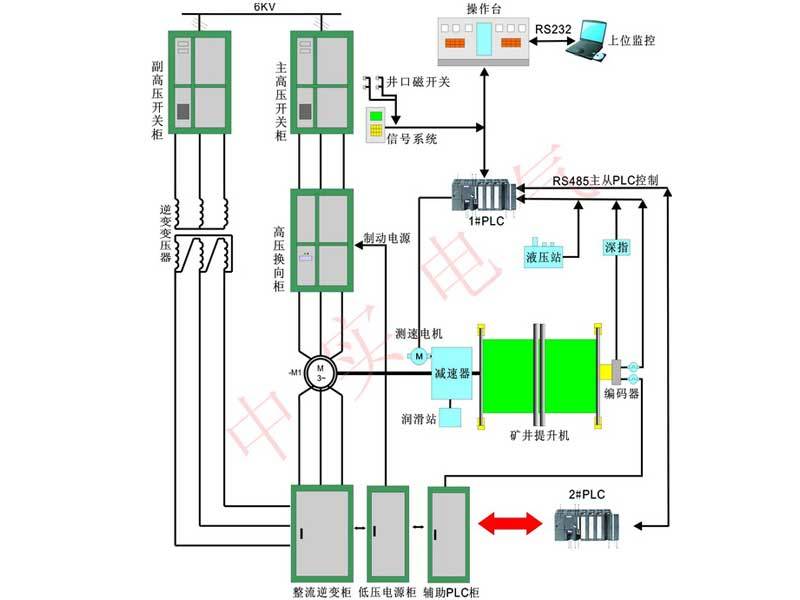
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
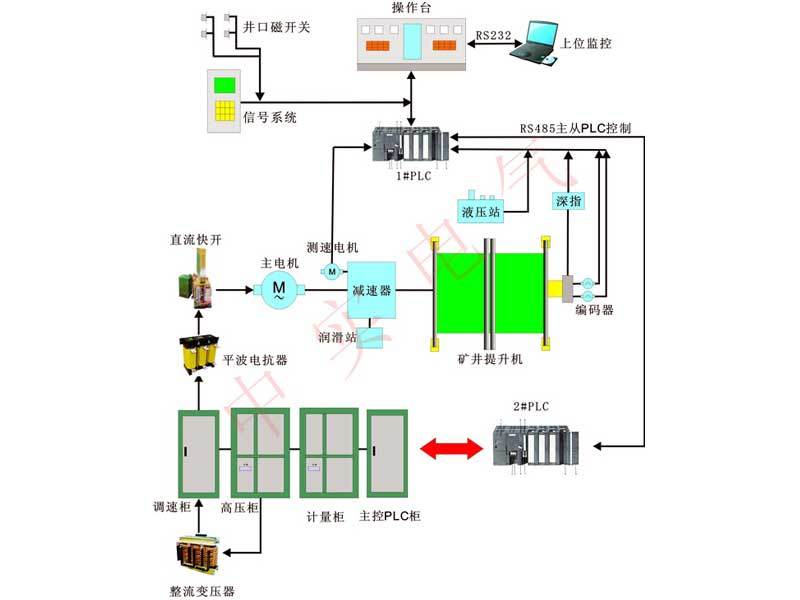
Fully digital DC control system
-
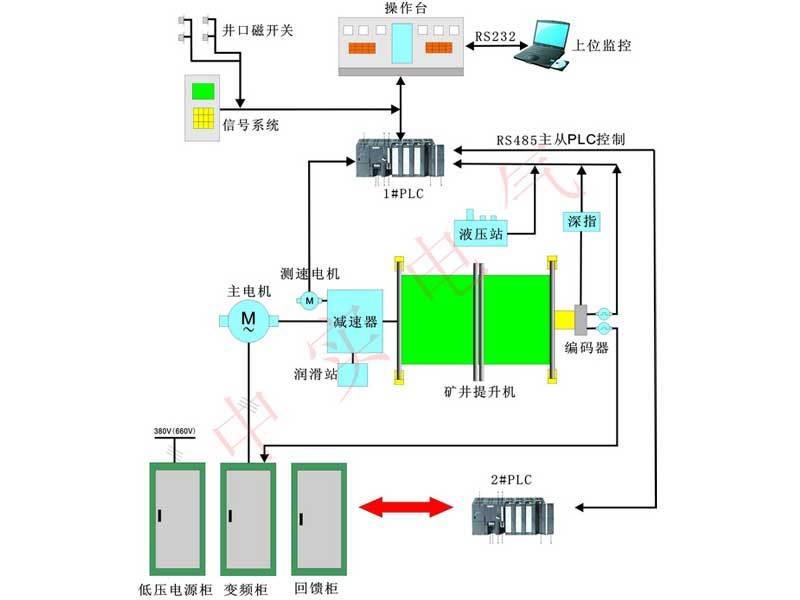
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
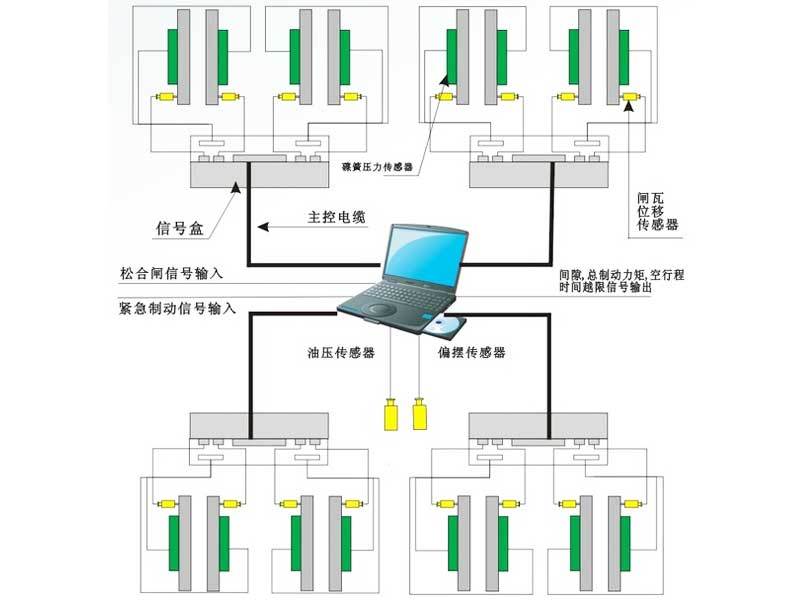
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
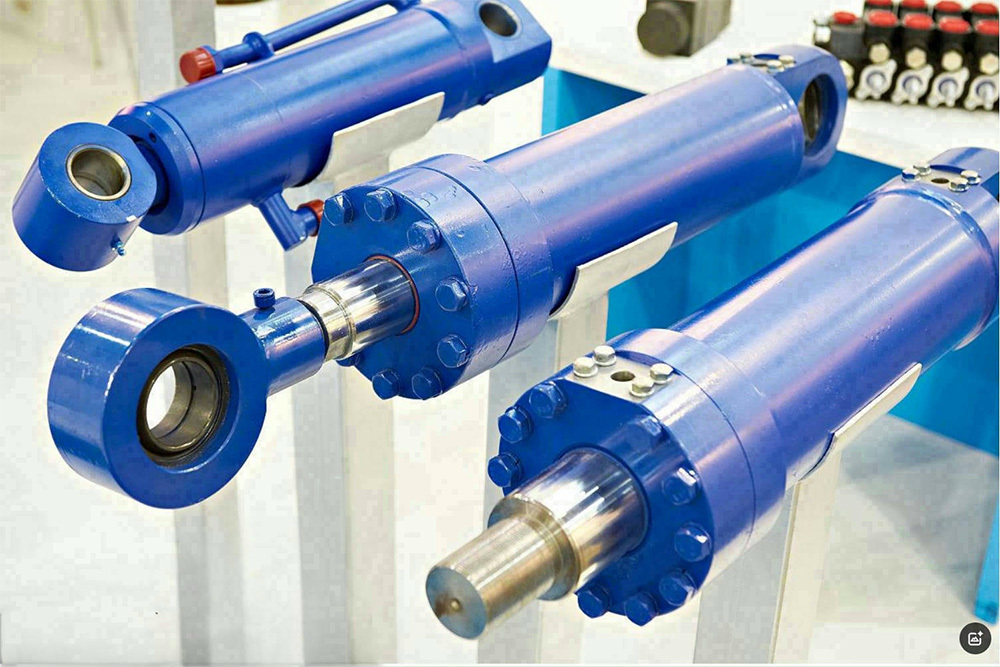
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-
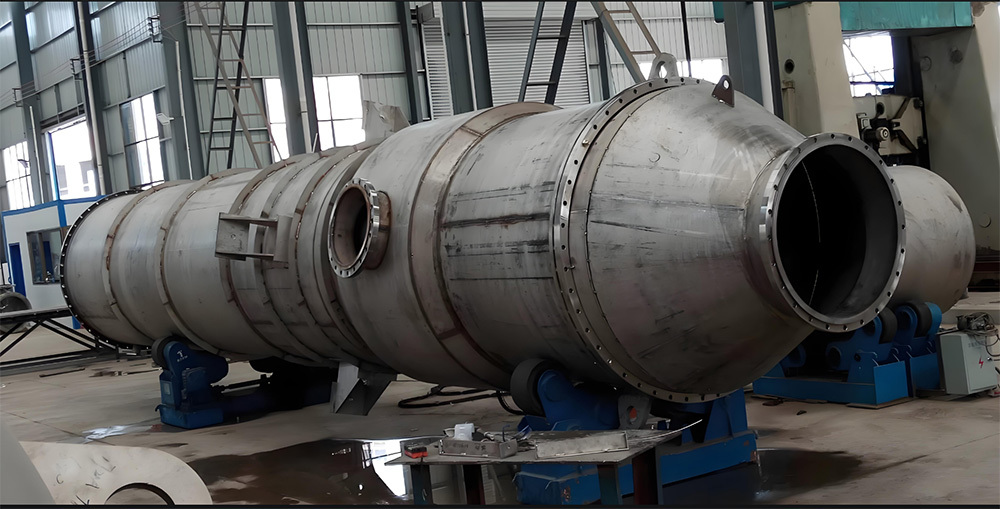

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-
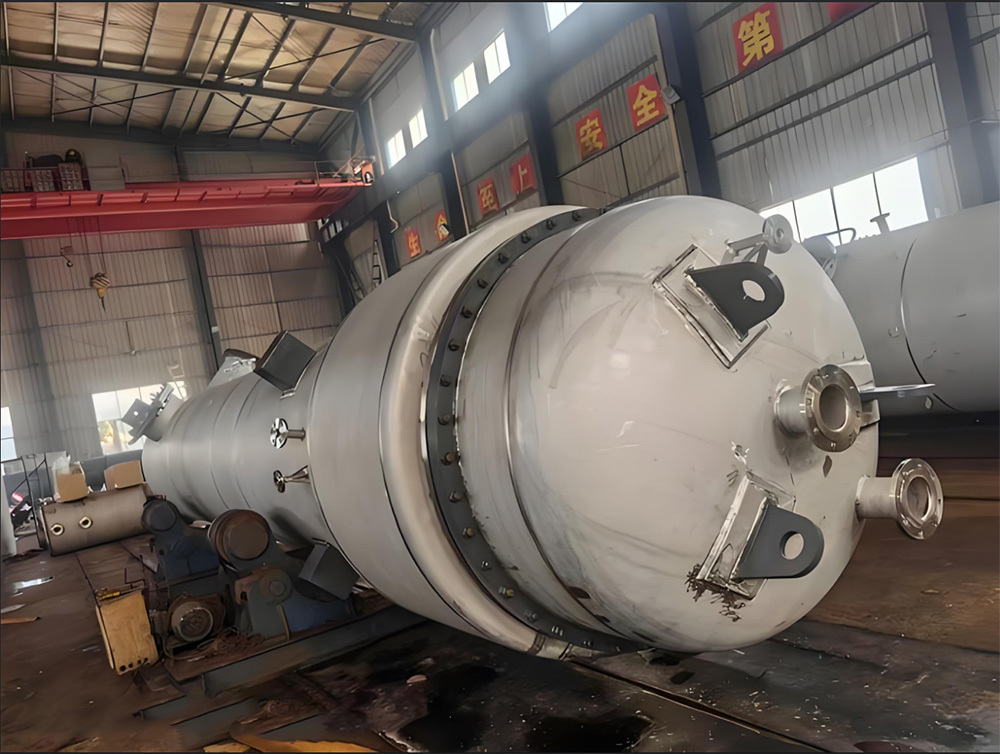

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-
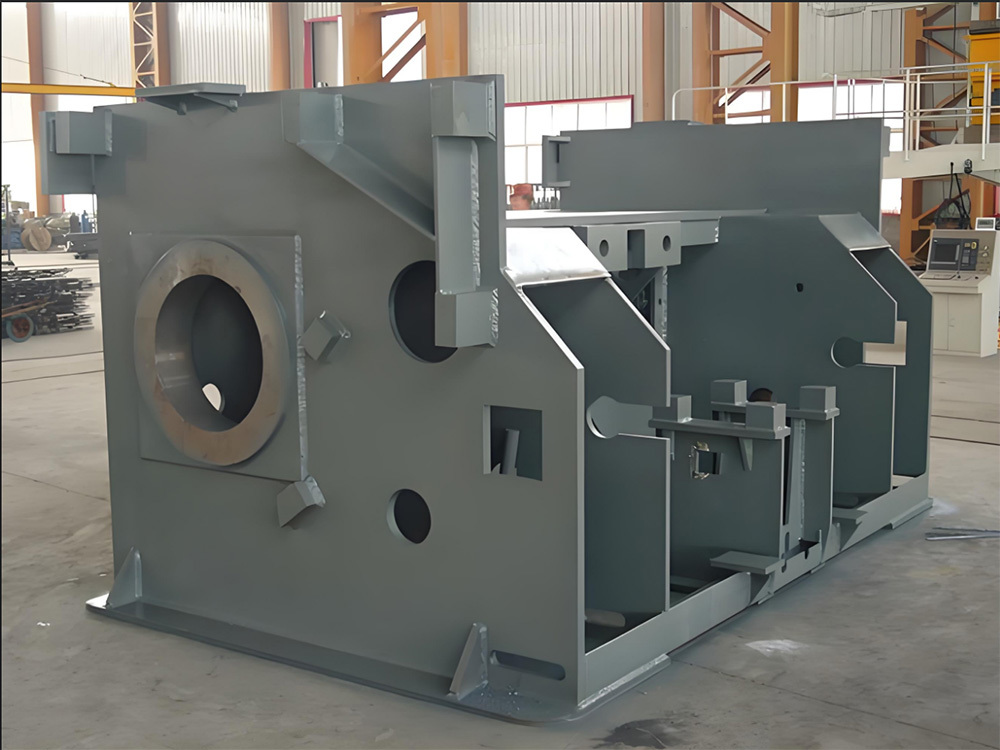

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
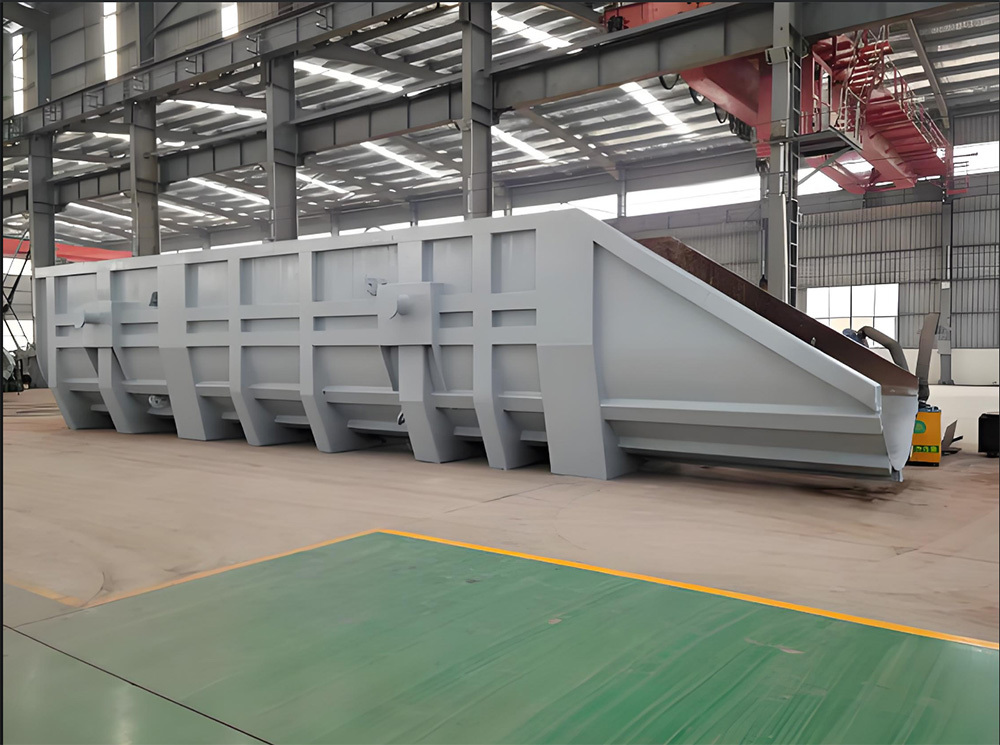

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
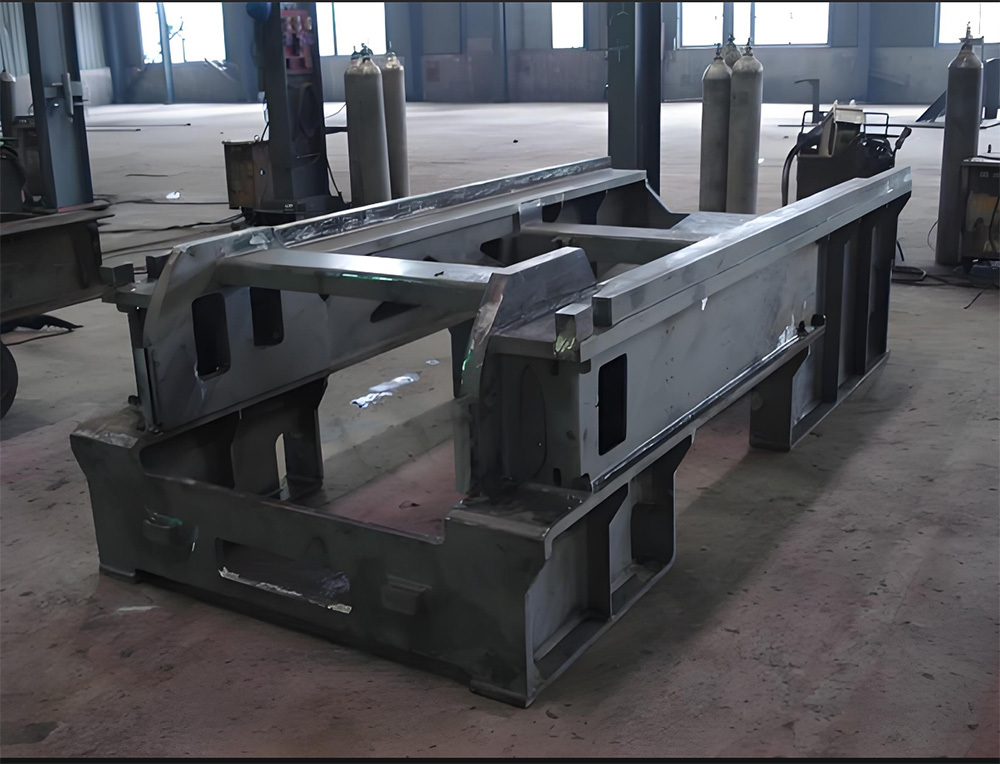

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
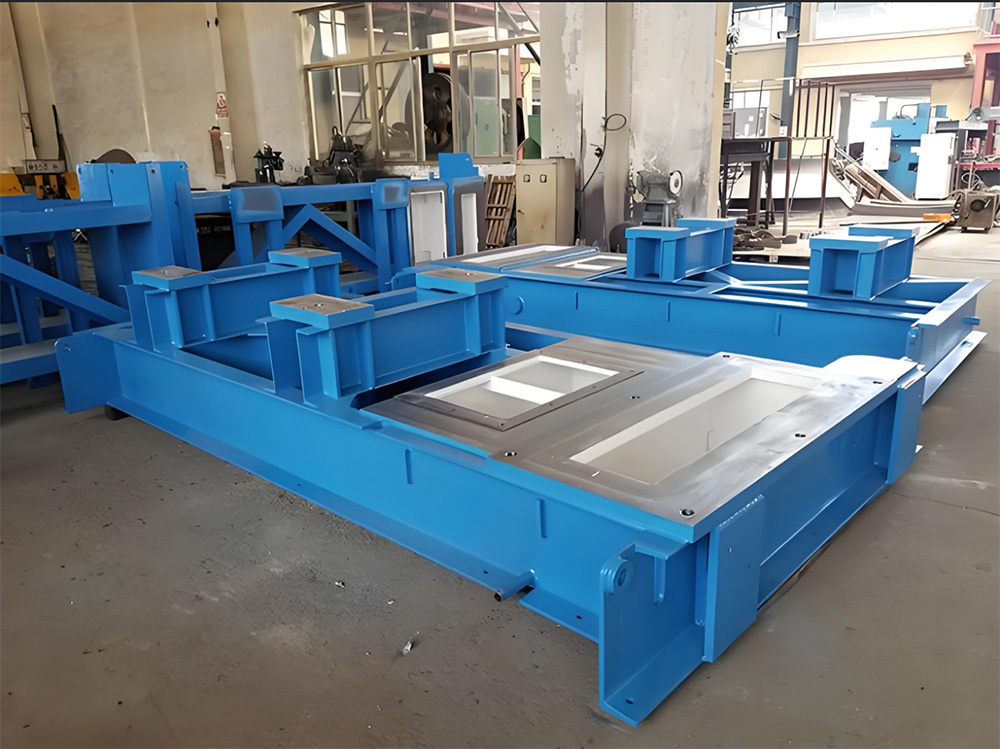

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-

Large base
-
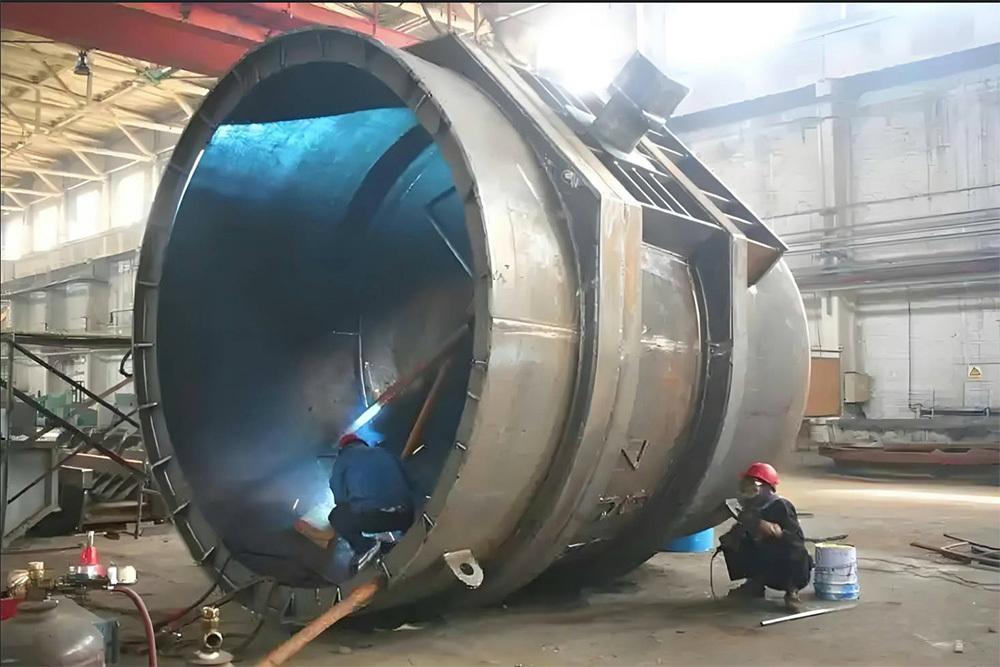

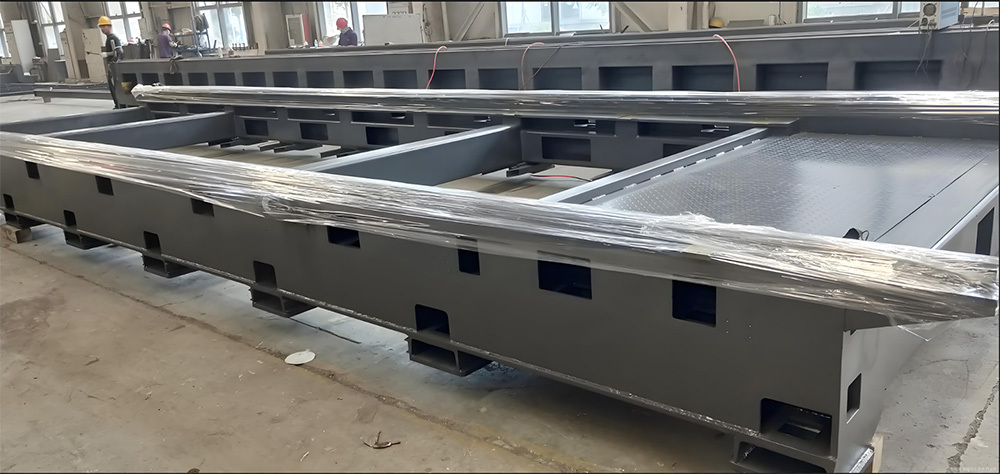
Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
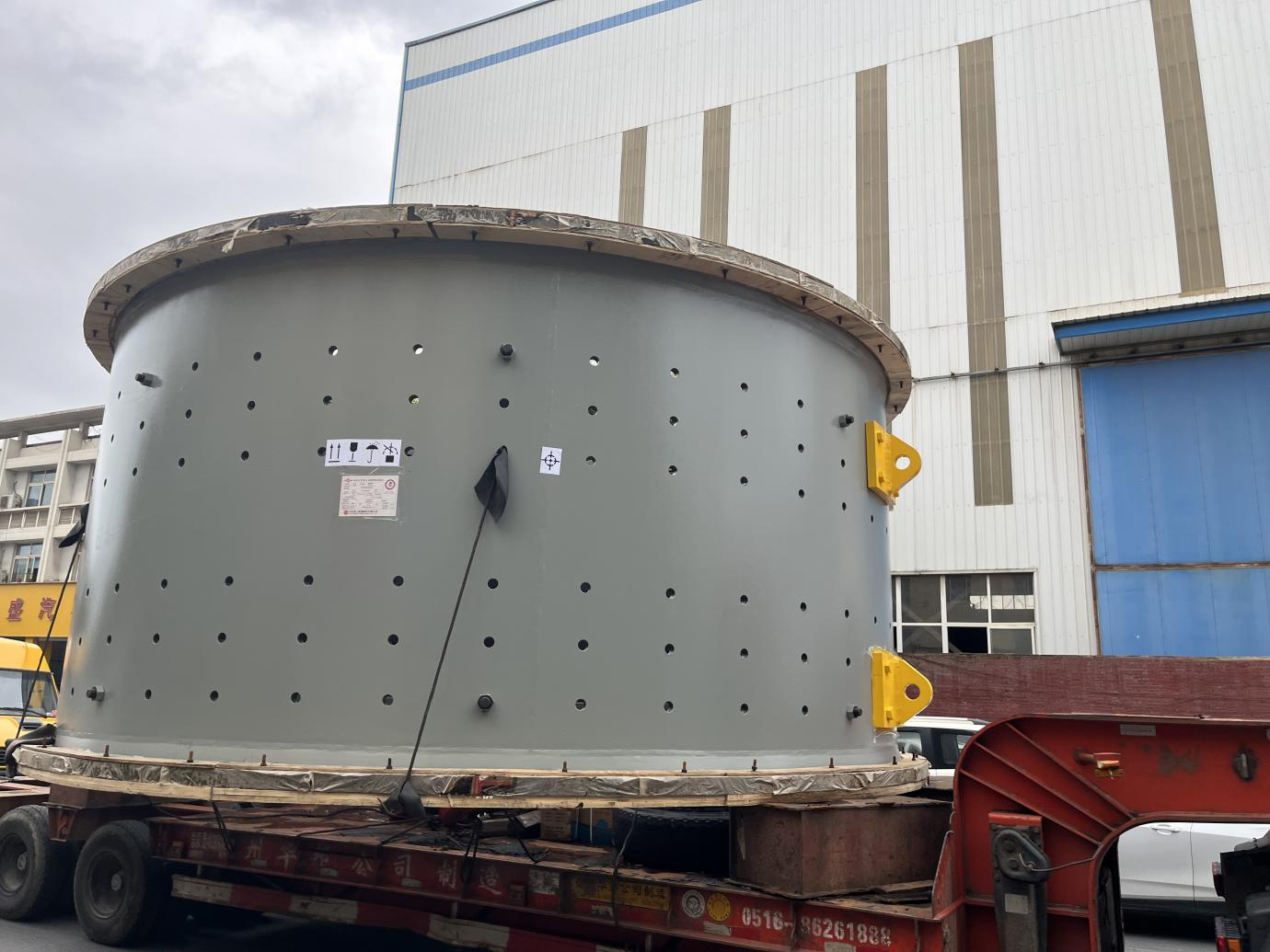

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-

Bus Alloy Bushings
-

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
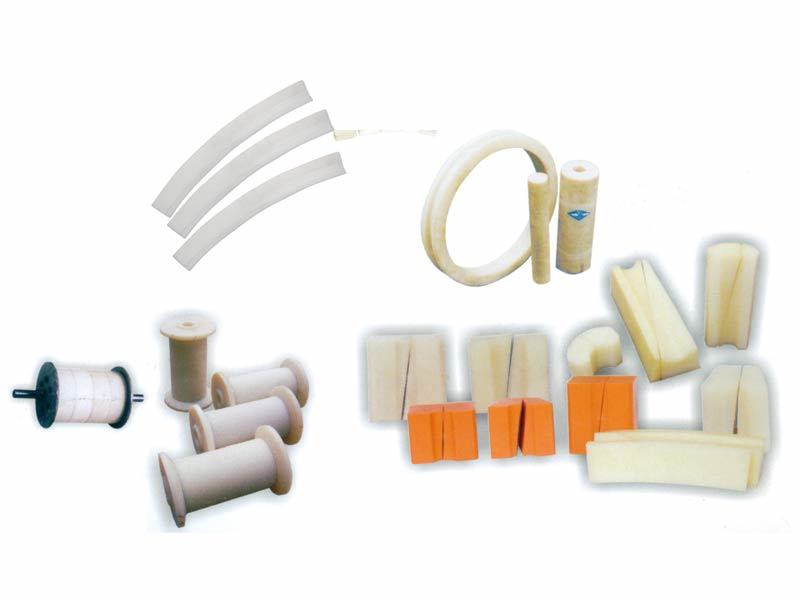

Nylon products
-
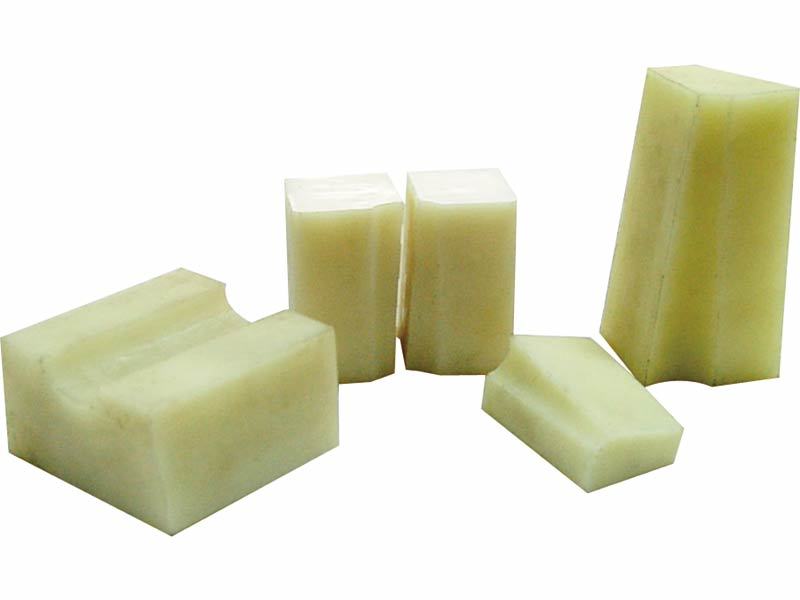

Polyurethane Products
-
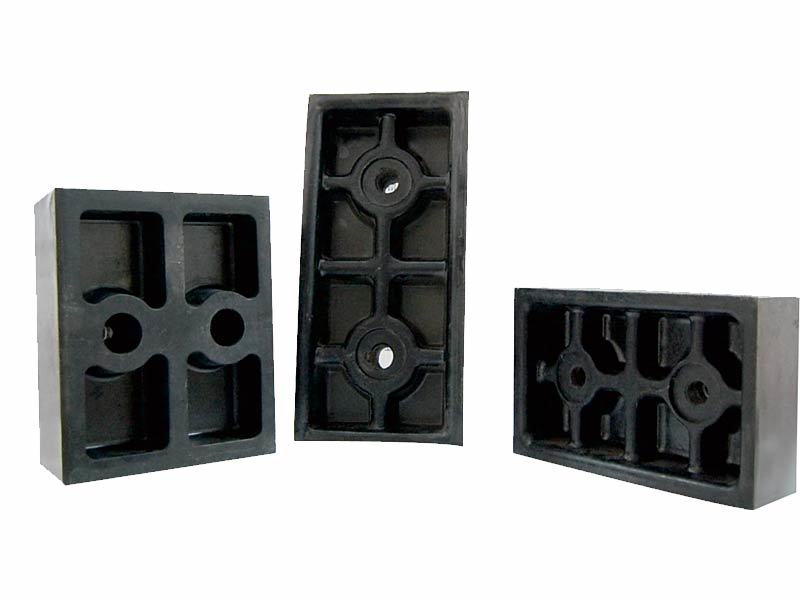

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
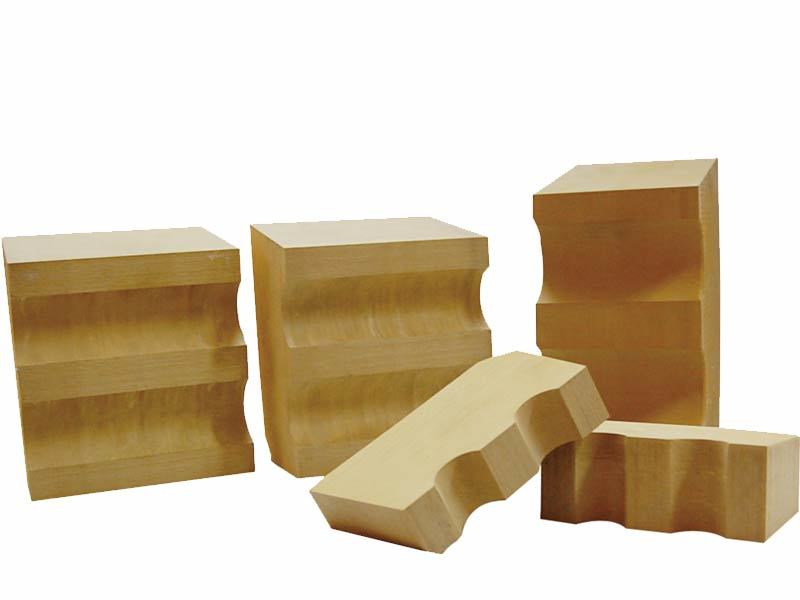

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information