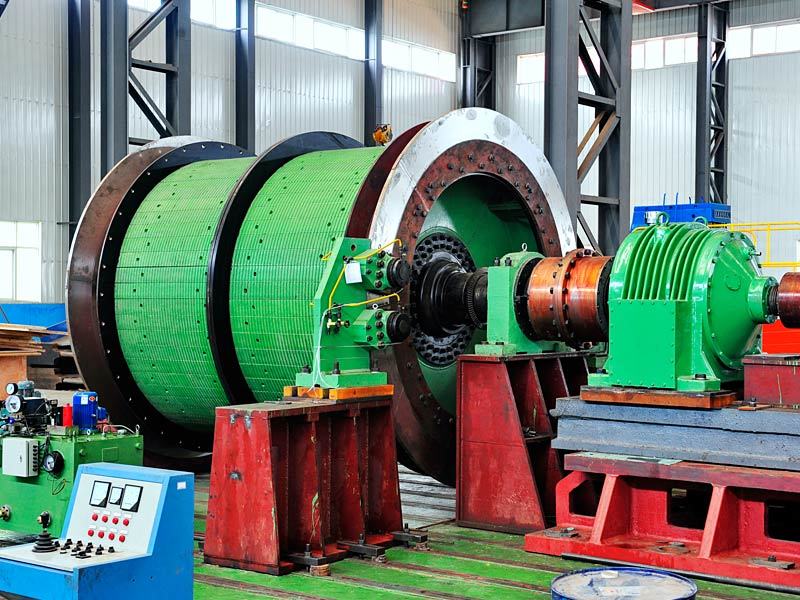
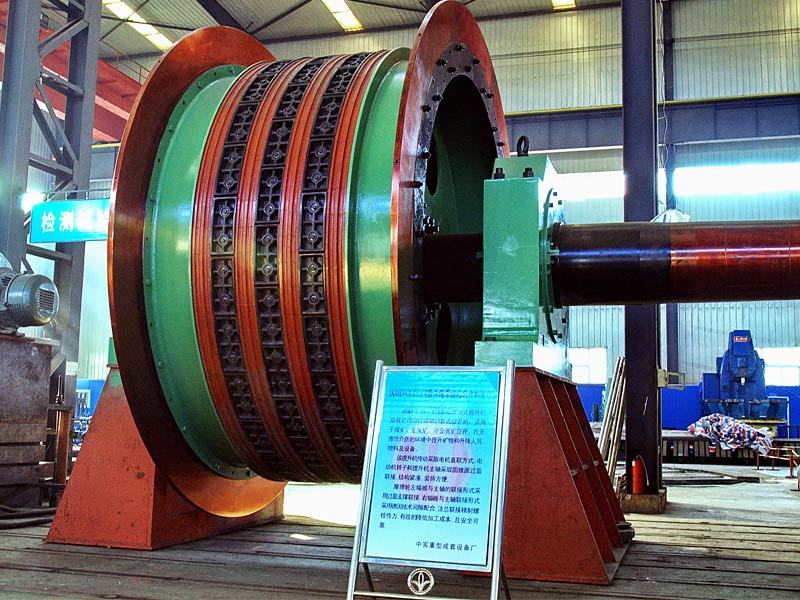
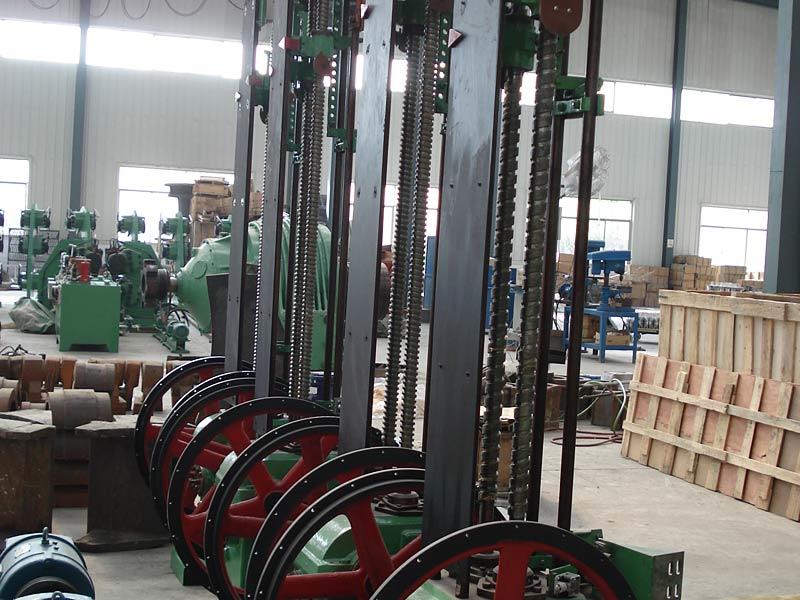
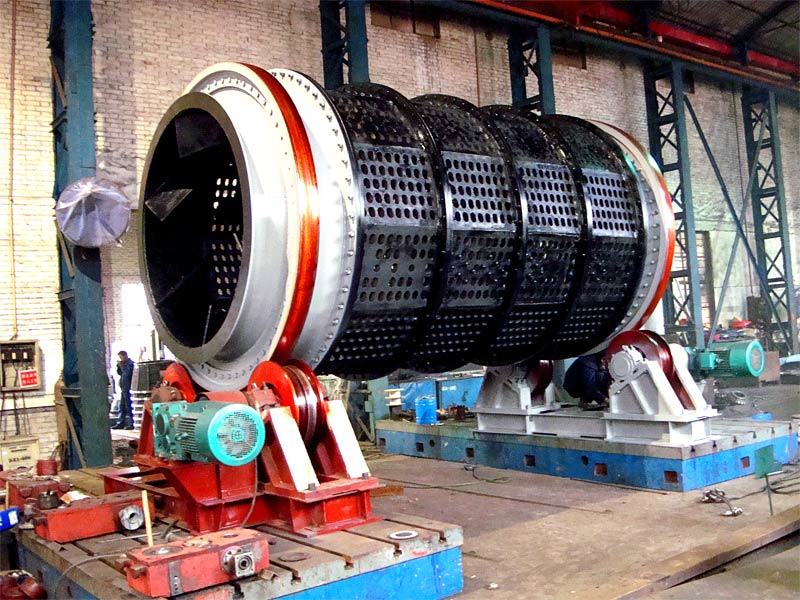
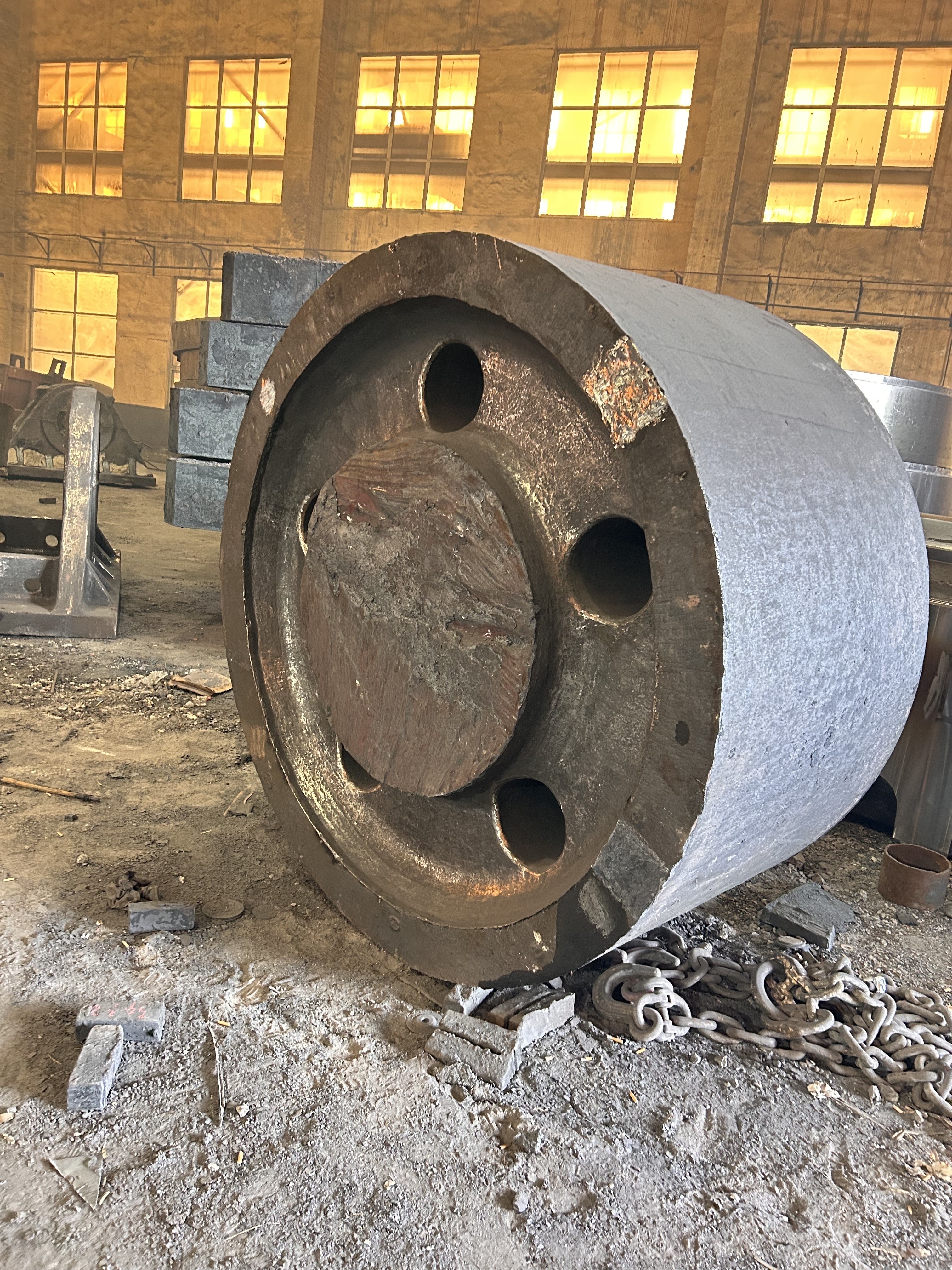
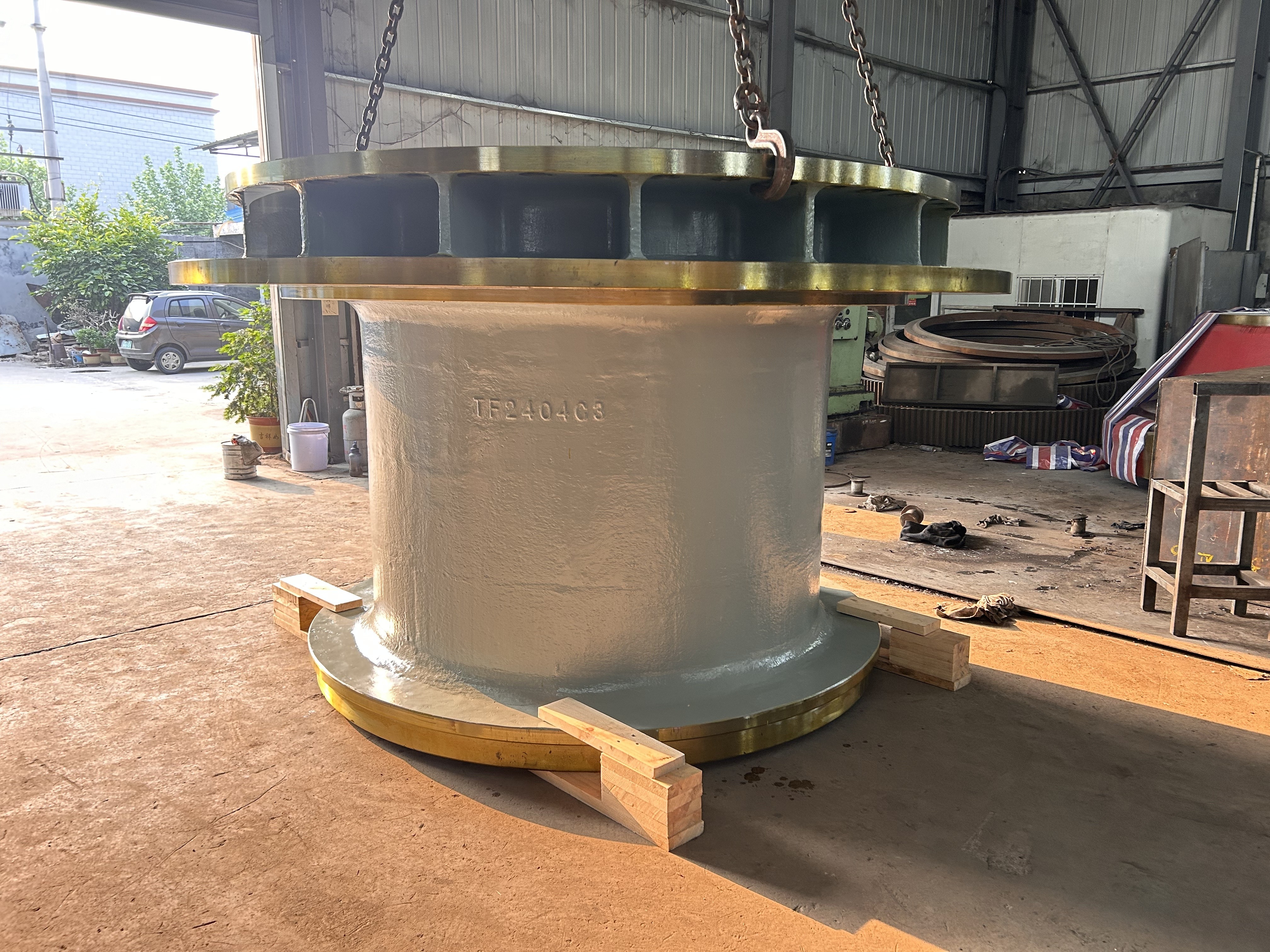
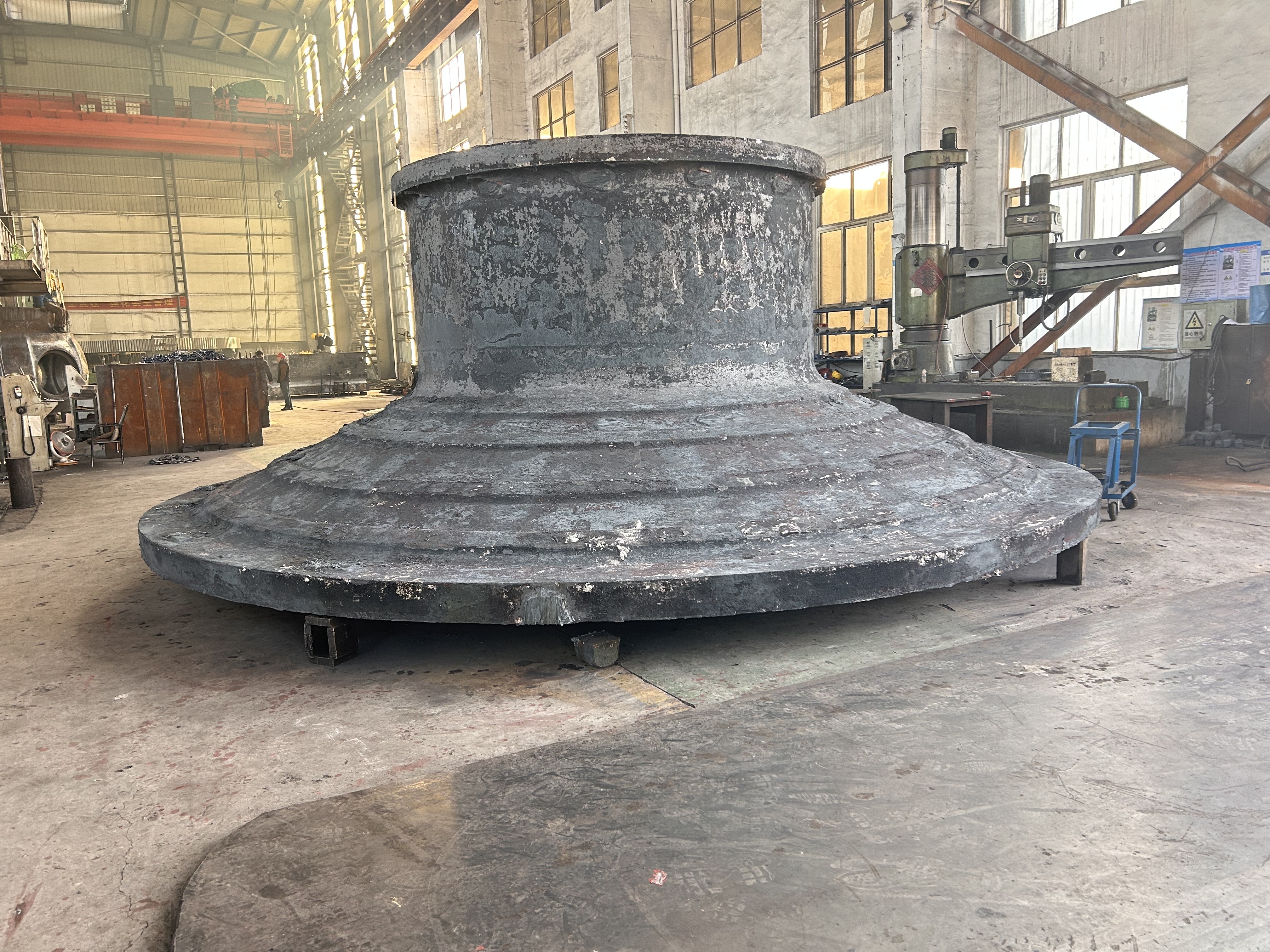
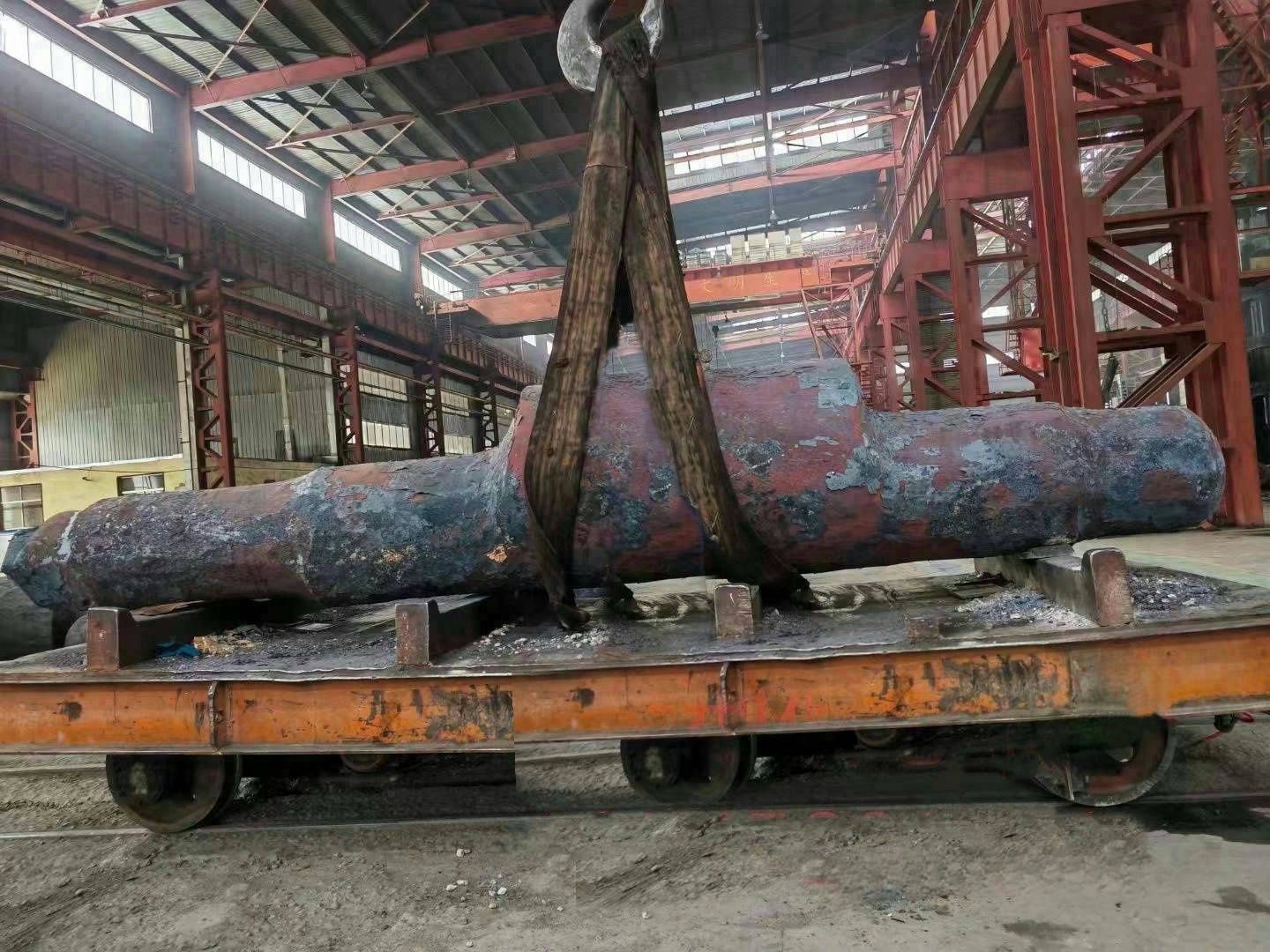
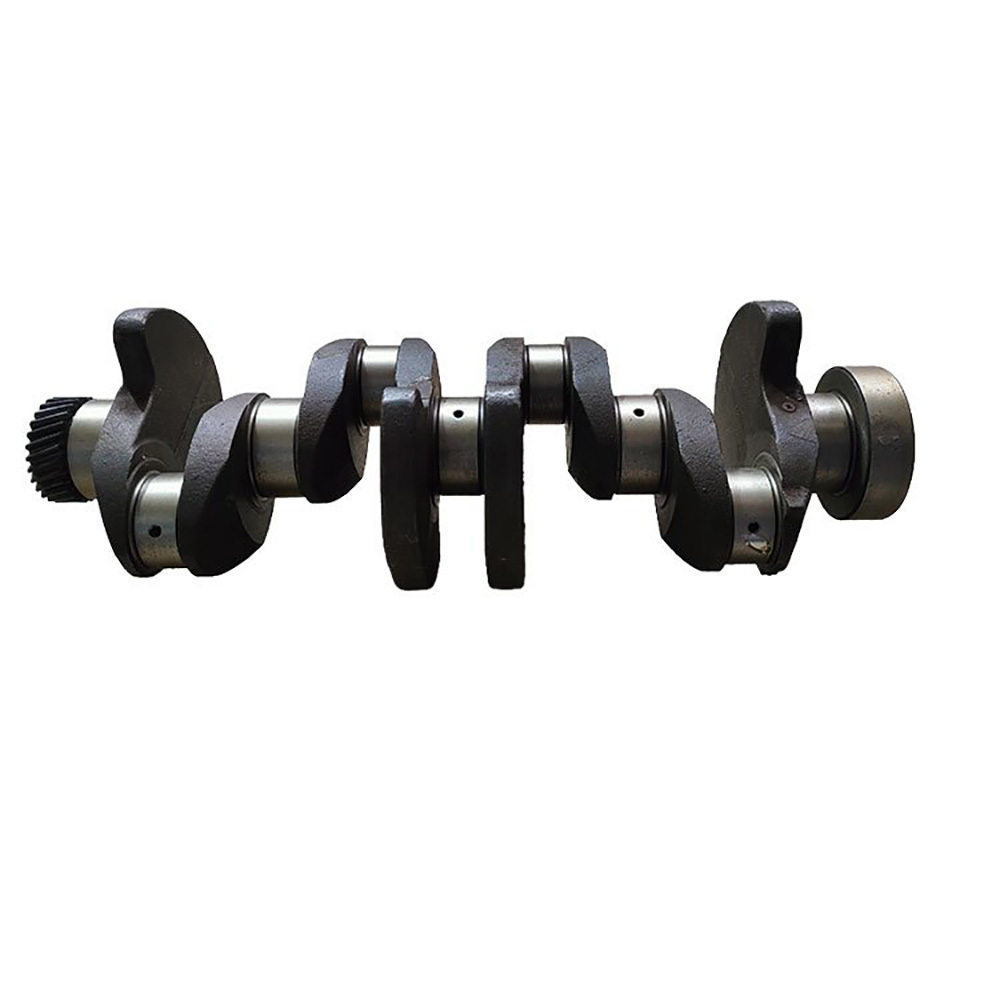
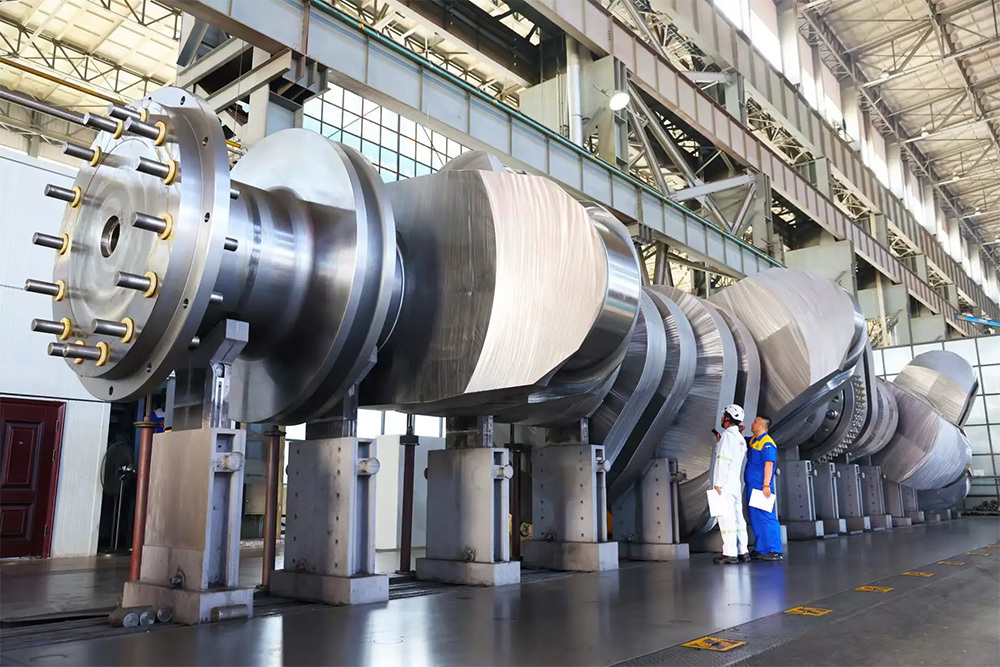
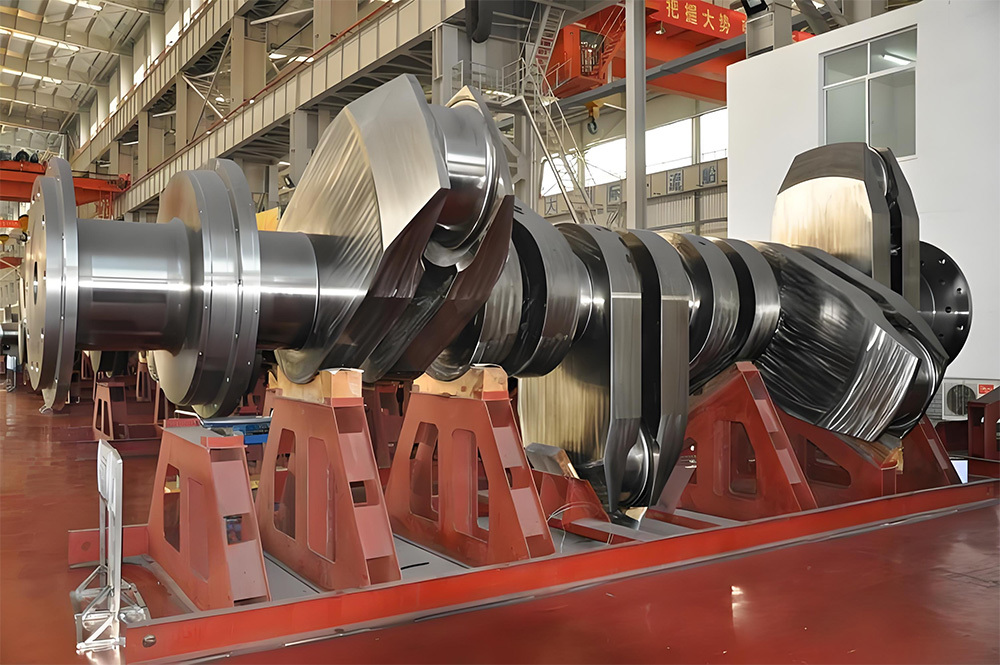
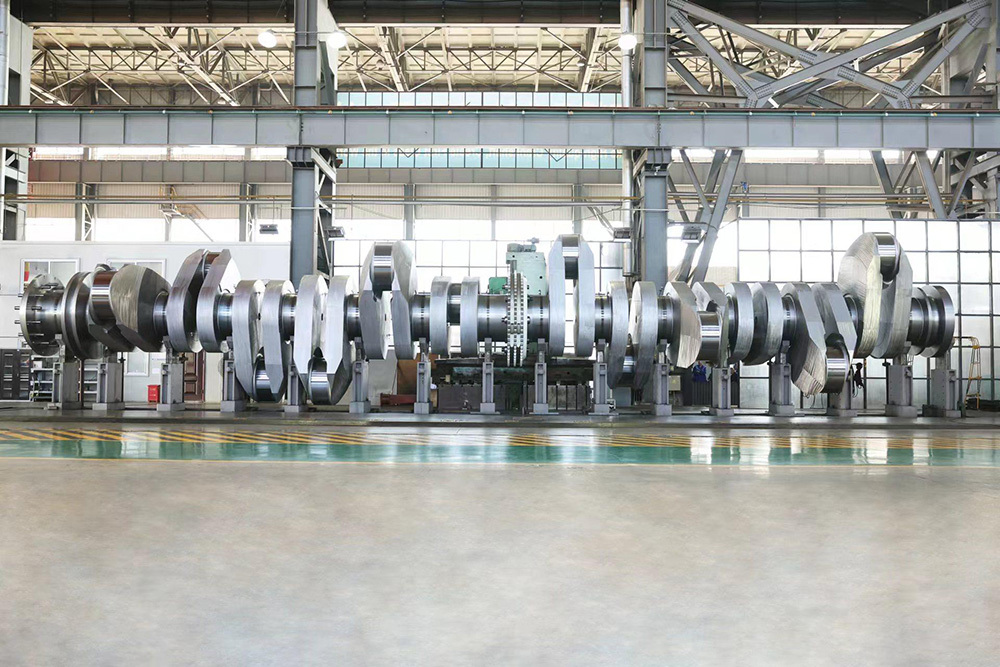
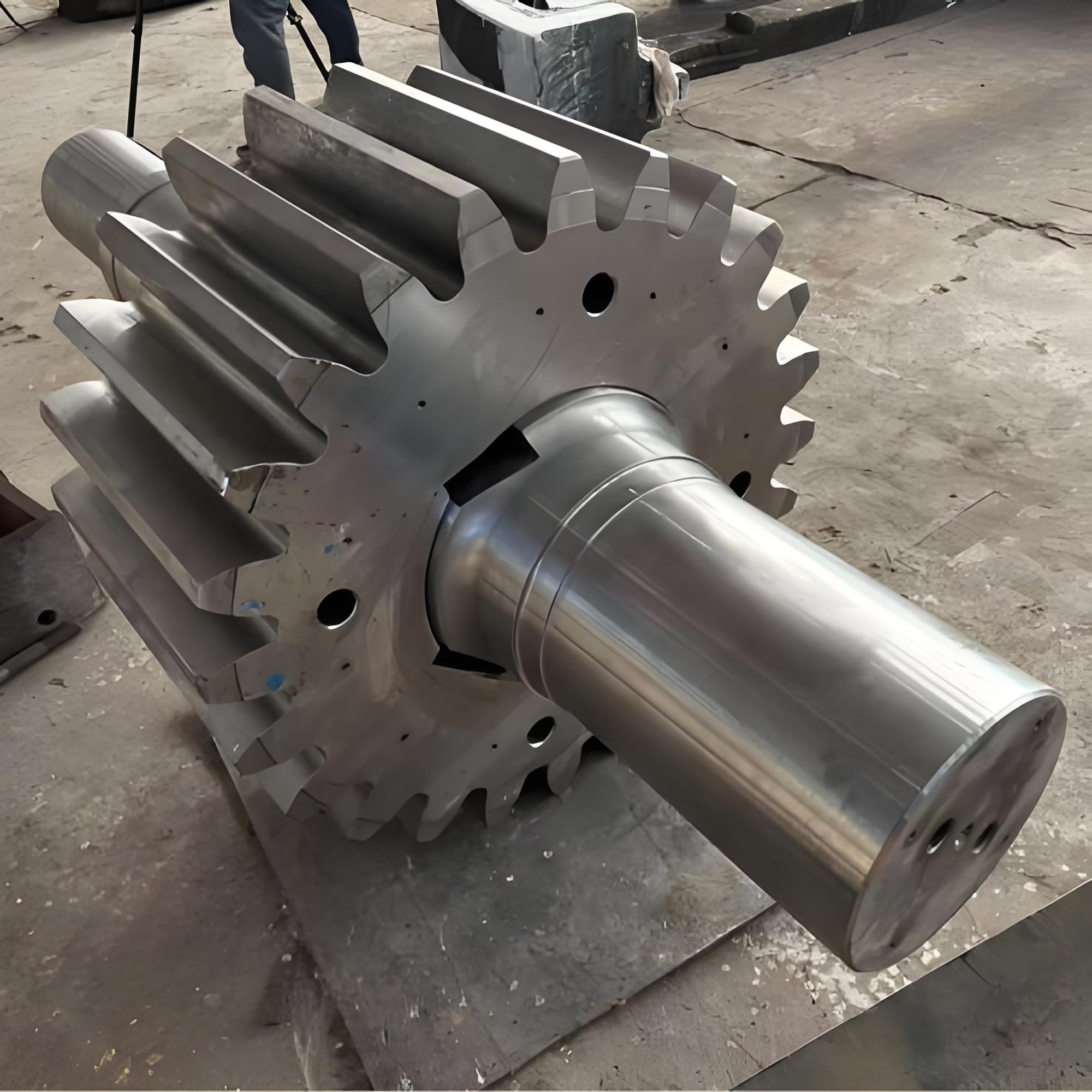
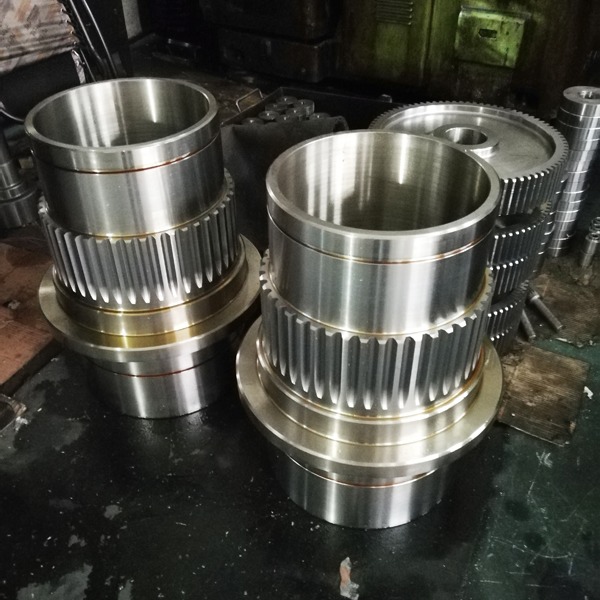
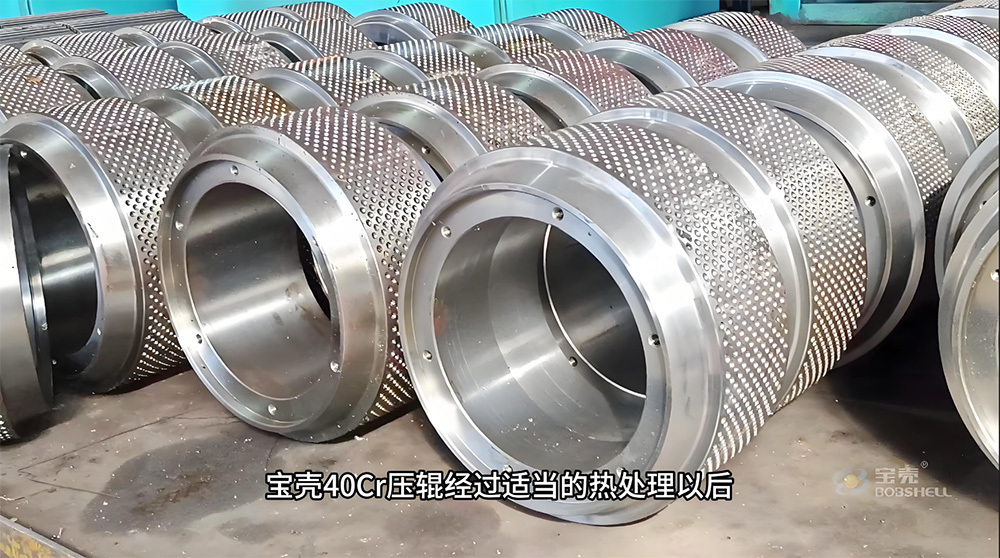
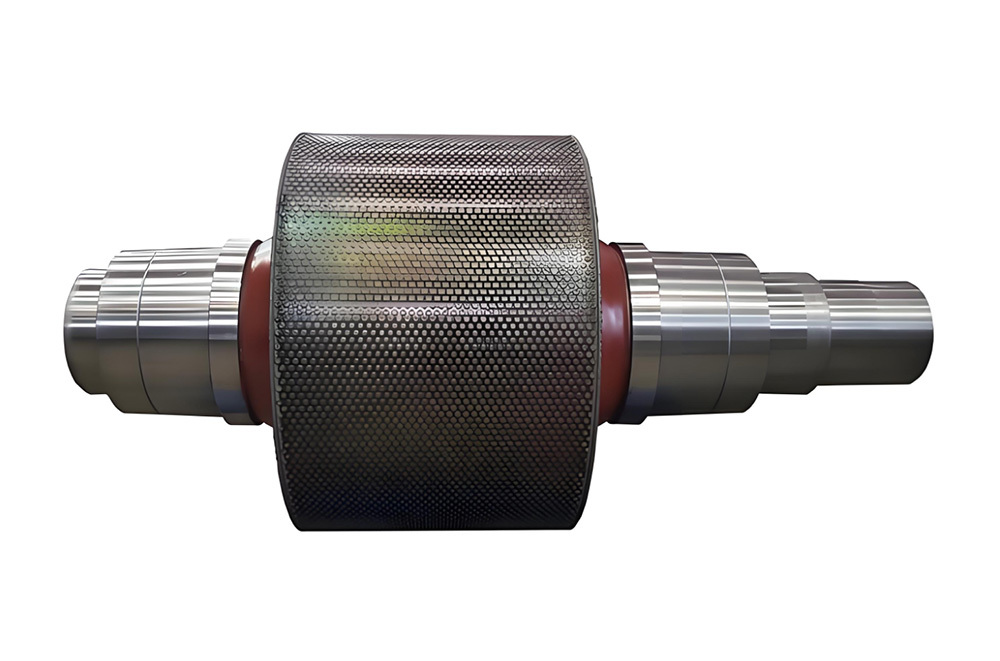
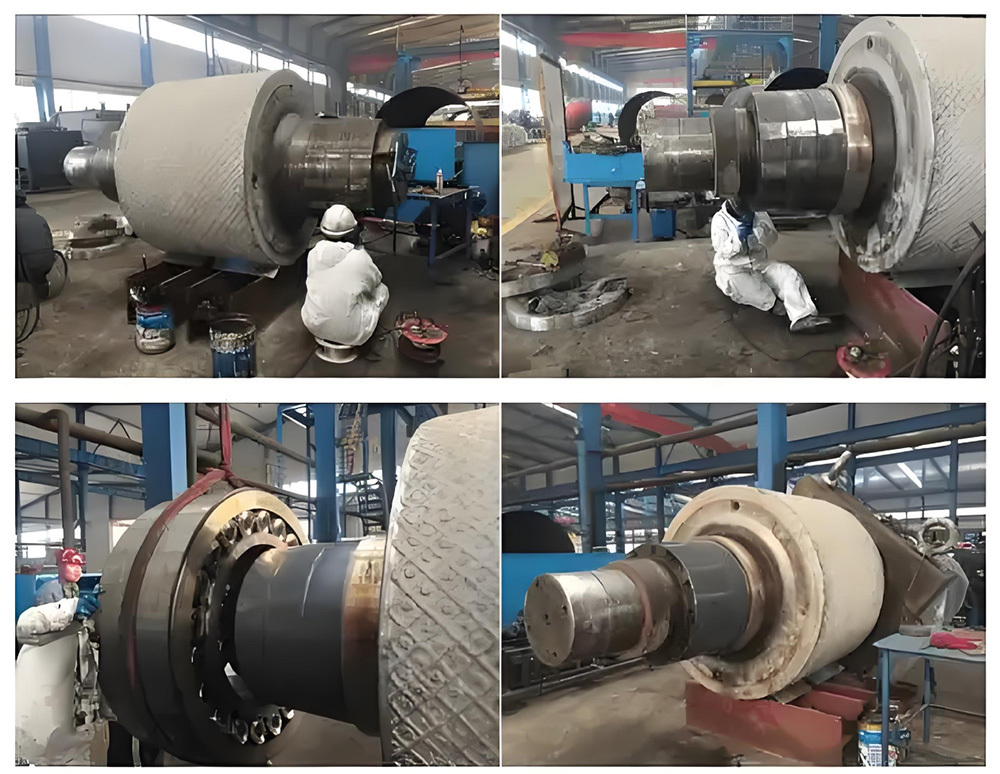
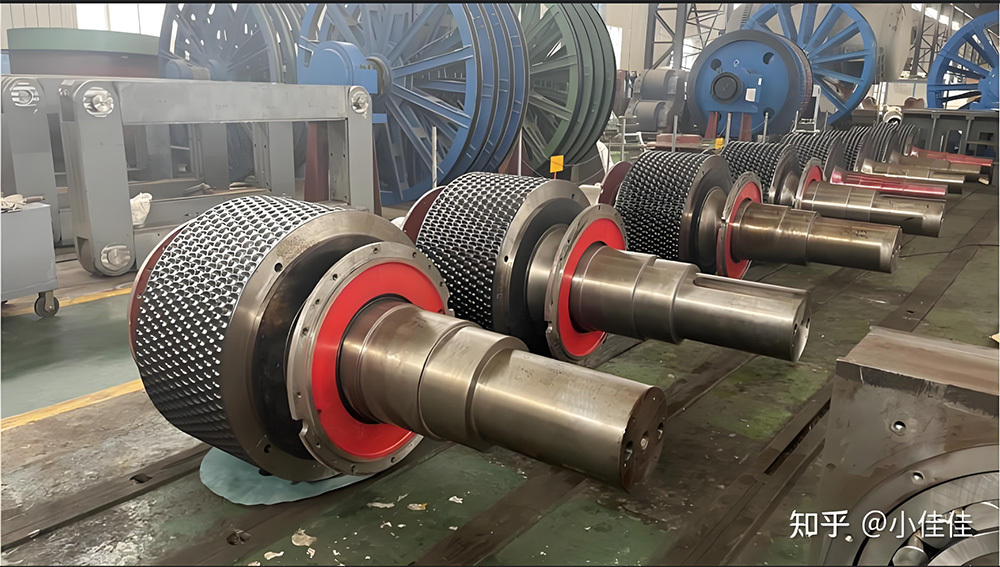
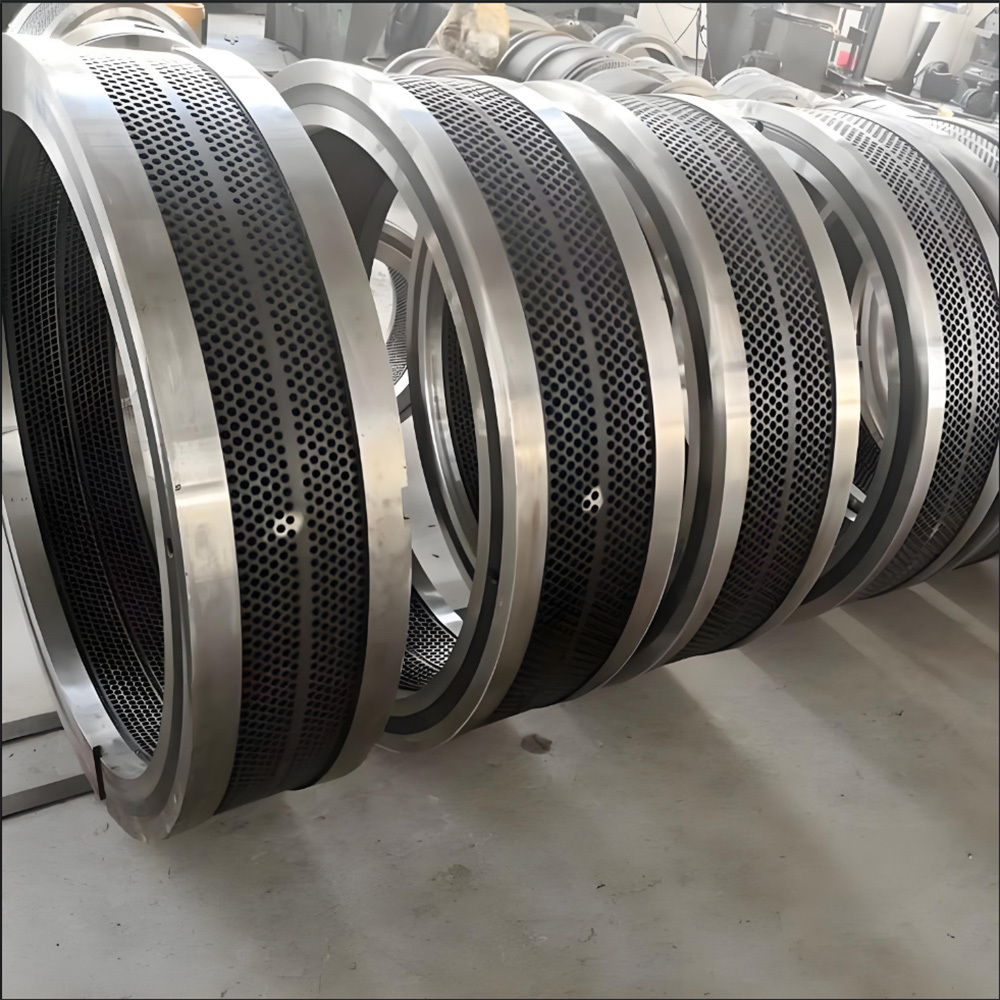
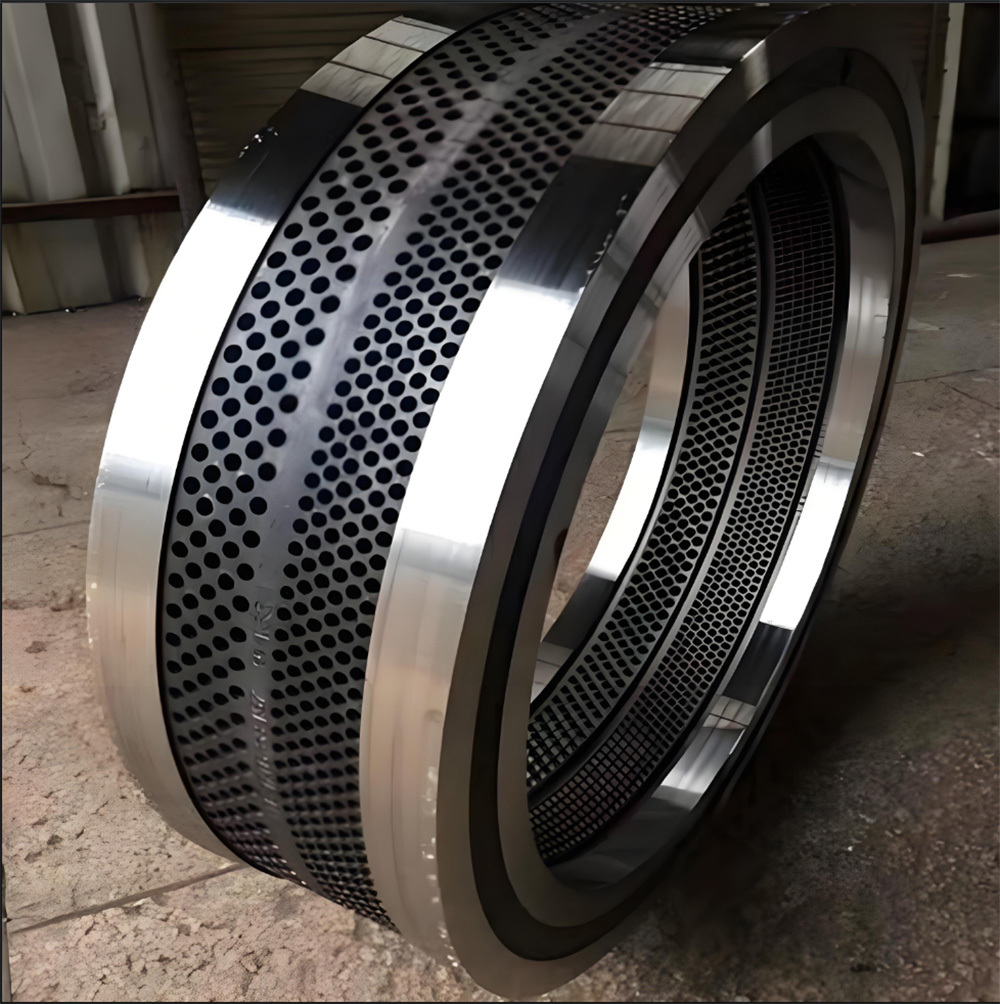
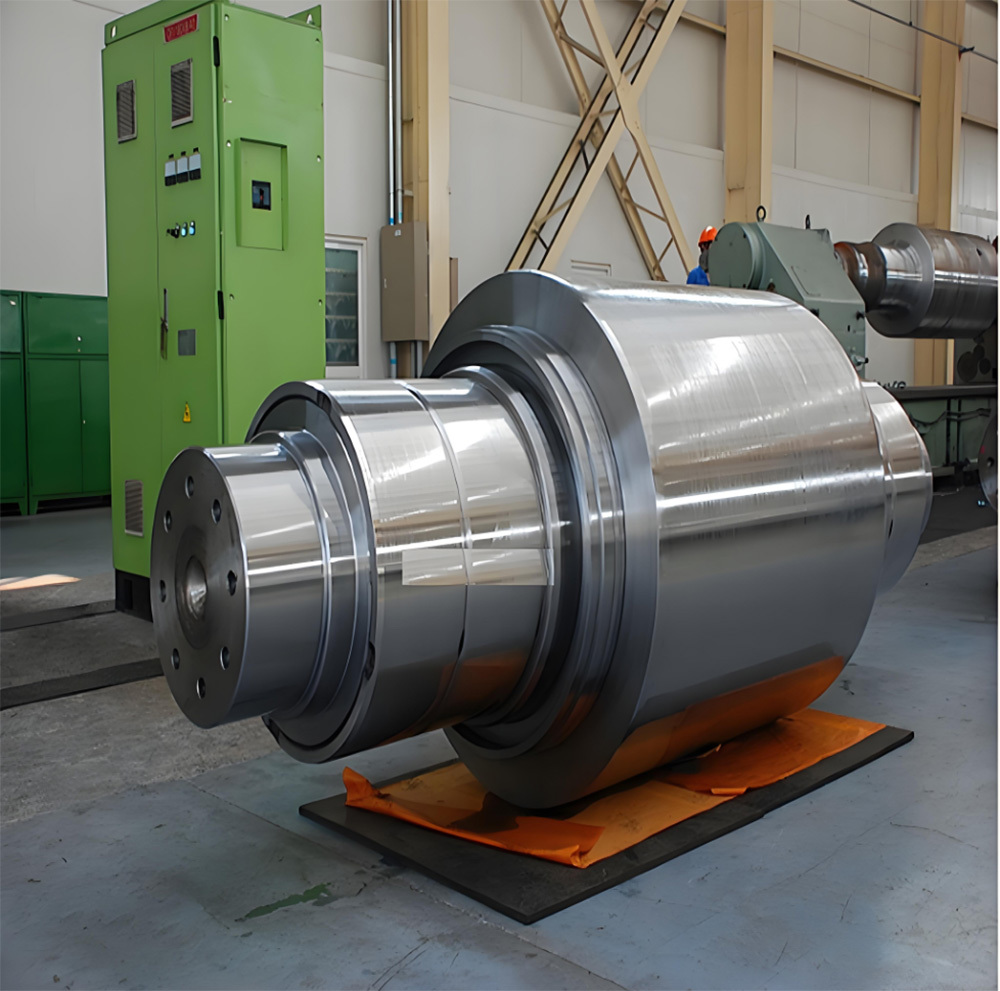
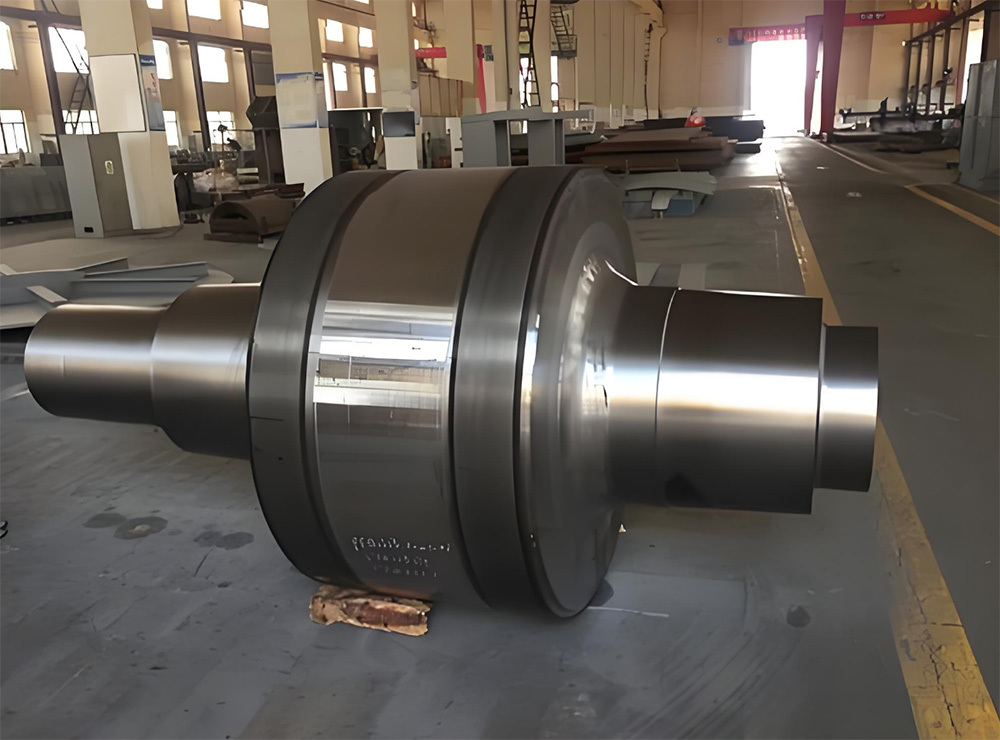
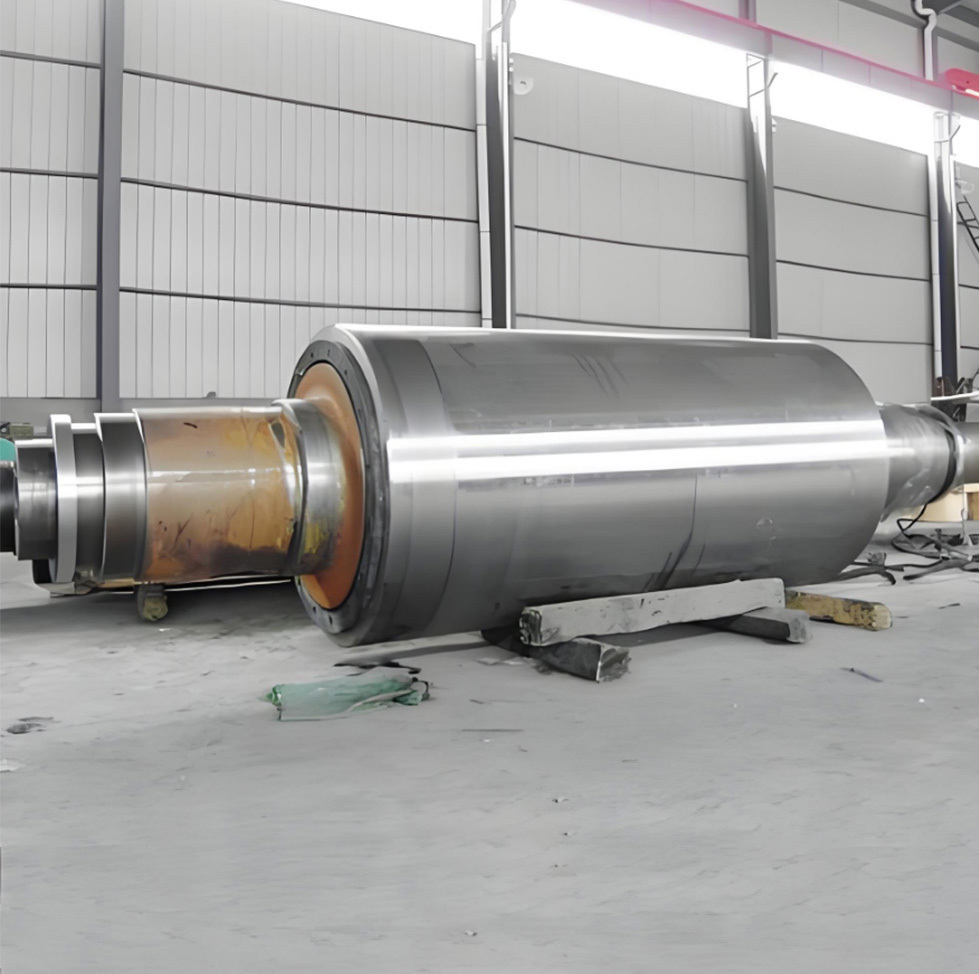
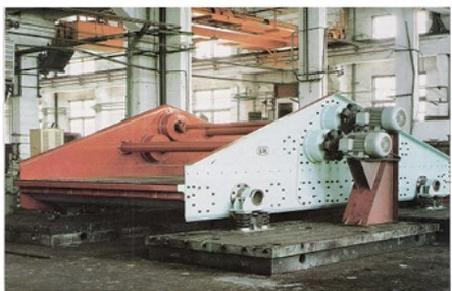
Mining crankshafts are core transmission components in mining machinery equipment, primarily used to convert reciprocating motion into rotary motion, driving key equipment such as slurry pumps, drilling rigs, compressors, and crushing equipment. Mining crankshafts must operate stably under high temperature, high dust, high vibration, heavy load, and harsh conditions. Their design must balance high strength, impact resistance, wear resistance, and long service life, making them critical elements to ensure continuous production and efficiency in mining operations.
Classification of Mining Crankshafts
1. By structural form:
- Integral crankshaft: Suitable for small to medium-sized mining equipment, forged or cast as a whole, simple structure, easy maintenance.
- Composite crankshaft: Composed of multiple main shaft journals and crank throws assembled by bolts, welding, or shrink fitting, suitable for large equipment, facilitating manufacturing and transportation.
2. By material and process:
- Forged steel crankshaft: Made from high-strength alloy steel (such as 42CrMo, 35CrMo), with excellent fatigue resistance, suitable for high impact load scenarios.
- Ductile iron crankshaft (e.g., QT700-2): Lower cost, suitable for medium to low load or medium speed equipment.
3. By application scenario:
- Slurry pump dedicated crankshaft: For example, the old Hengyang BW320 slurry pump crankshaft, which must withstand the impact of high pressure and large volume slurry.
- Drilling rig crankshaft: Suitable for geological exploration drilling rigs, needing to adapt to frequent start-stop and complex formation loads.
Specifications
1. Size range:
- Length: Ranges from several hundred millimeters to several meters, depending on equipment scale.
- Diameter: Main shaft journal diameter usually between φ80mm and φ300mm; crank pin diameter matches connecting rod load.
- Weight: From tens of kilograms to several tons (crankshafts for large drilling rigs can exceed 10 tons).
2. Material characteristics:
- Forged steel yield strength ≥ 800MPa, surface hardness HRC 50-60; ductile iron tensile strength ≥ 700MPa.
- Surface roughness: Key shaft journals Ra ≤ 1.6μm to reduce friction and wear.
Design parameters
1. Material selection:
- Ductile iron: Such as QT700-3, QT800-2, QT900-2, with high tensile strength and wear resistance, suitable for the high-strength working environment of mining crankshafts.
2. Dimensional parameters:
- Crank pin diameter (d1): Usually between 64-82 mm, affecting the crankshaft's load capacity and strength.
- Main shaft journal diameter (d2): Generally 73-82 mm, matching the crank pin diameter to ensure crankshaft balance and stability.
- Crank throw radius (R): Typically within 59-62.5 mm, determining the crankshaft's motion stroke and power output.
- Crank arm thickness (h): About 23-25 mm, affecting crankshaft stiffness and torsional resistance.
3. Strength and stiffness requirements:
- Tensile strength: Should reach 700-900 N/mm² to ensure reliability under high load.
- Elongation: Not less than 2%-4%, ensuring material toughness and impact resistance.
- Impact value: Greater than 14.7 J/cm² to improve crankshaft fatigue resistance.
Scope of application
1. Mining extraction equipment:
- Slurry pumps: Such as BW320 slurry pumps, used for slurry transportation in geological exploration and foundation treatment.
- Drilling rigs: Geological core drilling rigs, crawler drilling rigs, etc., driving drill bit rotation and penetration.
2. Crushing and screening equipment: Power transmission systems for vibrating screens and crushers.
3. Other mining machinery: Mining compressors, transfer pumps, coal mining machines, and other heavy-duty equipment.
Key features
1. High reliability and impact resistance:
- Use of high-strength materials combined with composite strengthening processes to resist extreme loads and vibrations in mining.
2. Wear and corrosion resistance:
- Surface quenching, nitriding treatment, or coating technologies to adapt to high dust and corrosive environments.
3. Long maintenance intervals:
- Designed service life ≥ 10,000 hours, reducing downtime and maintenance costs for mining equipment.
4. Heavy load adaptability:
- Optimized crank throw structural design to enhance bending and torsional stiffness, preventing deformation or fracture.
5. Lubrication and cooling optimization:
- Built-in oil channels and forced lubrication systems to reduce frictional heat accumulation under high-temperature conditions.
Process introduction
1. Forging/Casting process:
- Forged steel crankshaft: High-temperature die forging with full fiber streamline control to ensure material uniformity.
- Ductile iron: Airflow impact molding and electroslag remelting to reduce casting defects.
2. Heat treatment:
- Medium frequency induction quenching: Hardened layer depth of 2-3mm on the journal surface to enhance wear resistance.
- Quenching and tempering treatment: Optimizes the balance between matrix strength and toughness.
3. Precision machining:
- CNC turning + tracking grinding: Ensures journal roundness and coaxiality accuracy.
- Deep hole drilling: Oil channel machining accuracy reaches ±0.1mm to ensure smooth lubrication.
4. Surface strengthening:
- Fillet rolling: Increases fatigue strength by over 120%, eliminating stress concentration.
- Nitriding/coating: Forms a wear-resistant protective layer to extend service life.
5. Inspection technology:
- Ultrasonic flaw detection: Checks for internal cracks and porosity.
- Dynamic balancing test: Simulates actual working conditions and adjusts to optimal balance state.
Outstanding advantages
1. Extreme environment adaptability:
- Specifically designed for high dust, high temperature, and heavy load conditions in mines, significantly reducing failure rates.
2. Maintenance economy:
- Long-life design reduces replacement frequency and lowers the total lifecycle cost of mining equipment.
3. Technological advancement:
- Uses composite strengthening processes and precision manufacturing technology, outperforming traditional mining crankshafts.
4. Customization capability:
- Can customize crank angle and lubrication system according to different mineral types and equipment models to improve adaptability.
5. Domestic breakthrough:
- Domestic mastery of forging and strengthening technology for large mining crankshafts replaces imports and ensures supply chain security.
Keywords
Next: Crankshaft





Mining crankshaft
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-
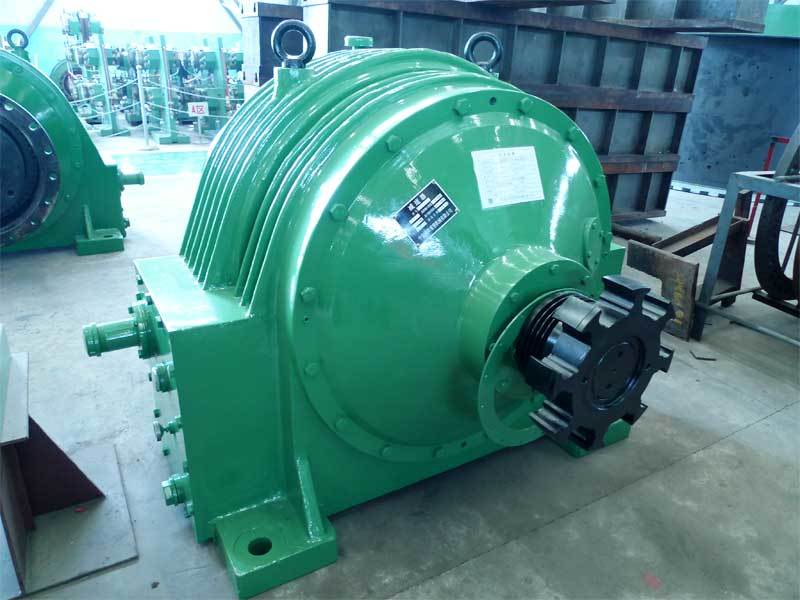

Planetary Gear Reducer
-
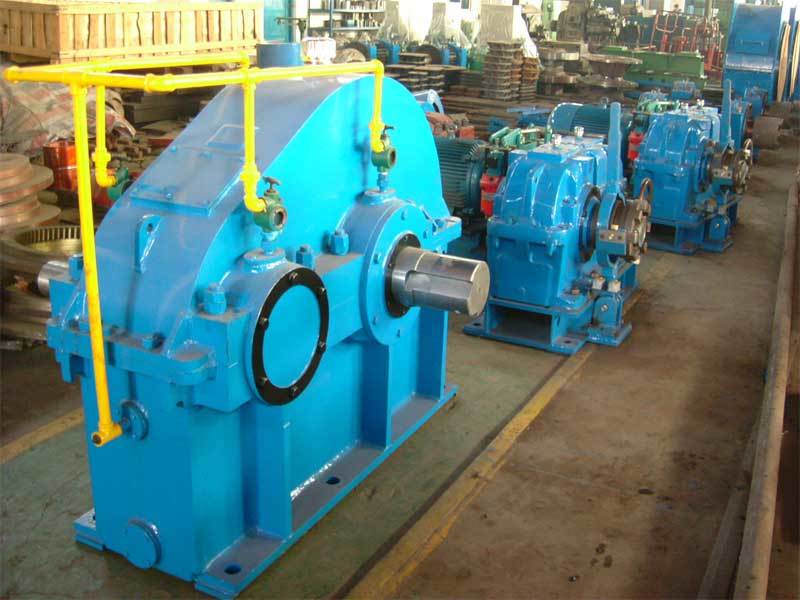

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
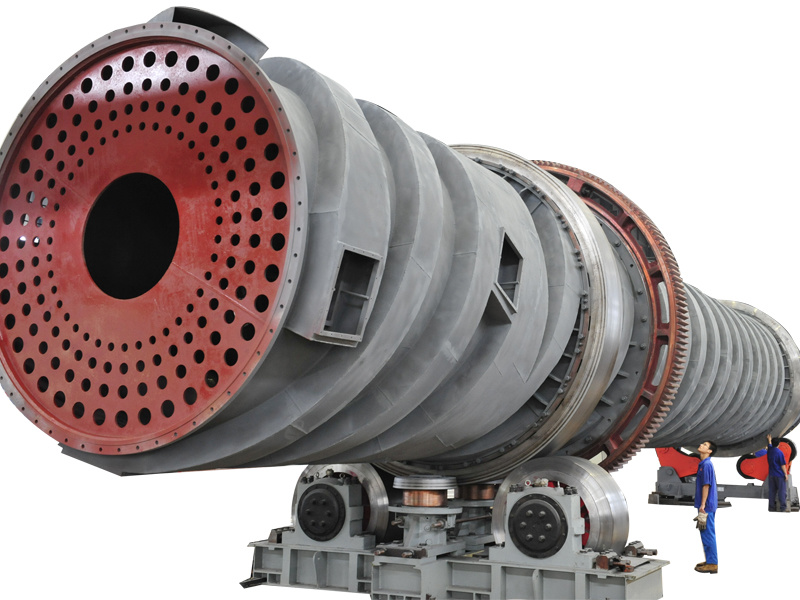
Rotary kiln
-
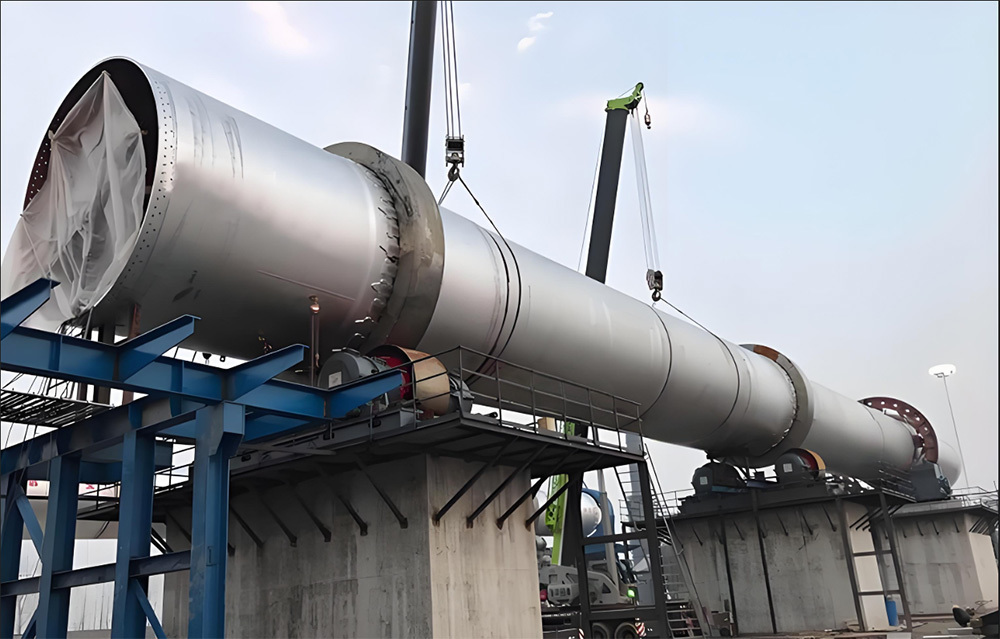

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-
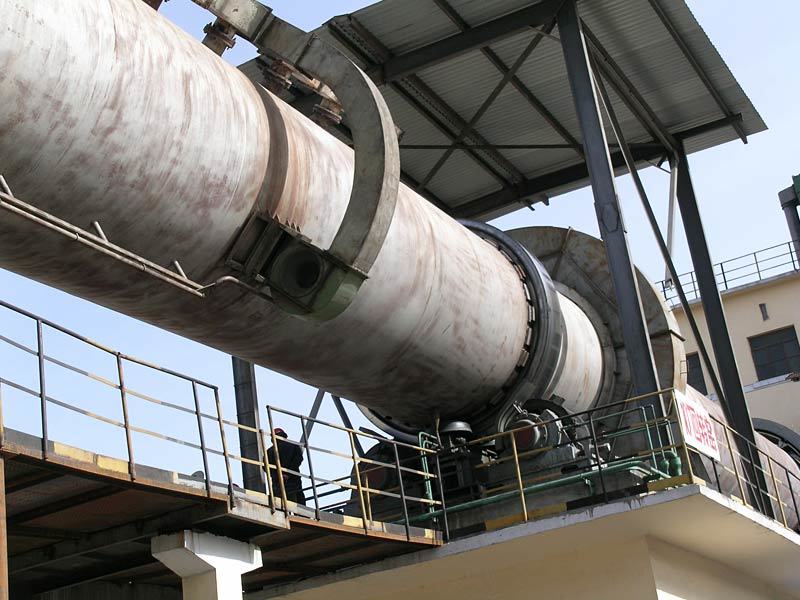

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-
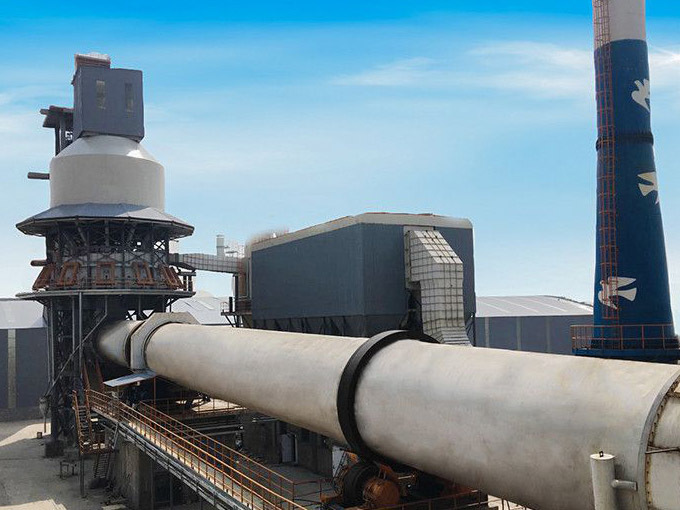

Lime Rotary Kiln
-
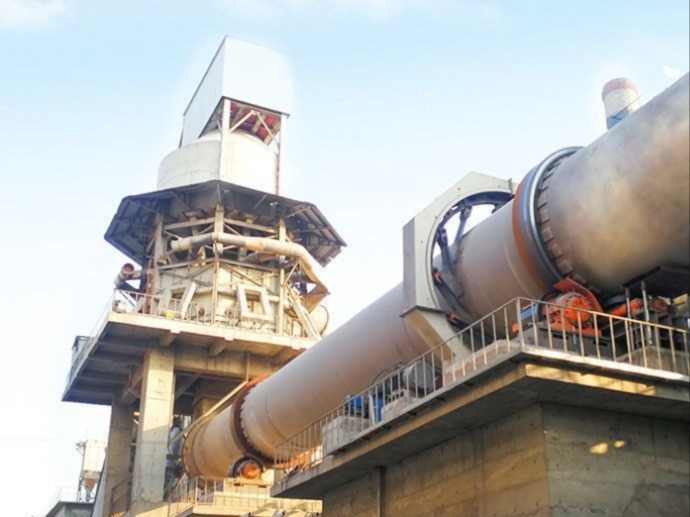

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-
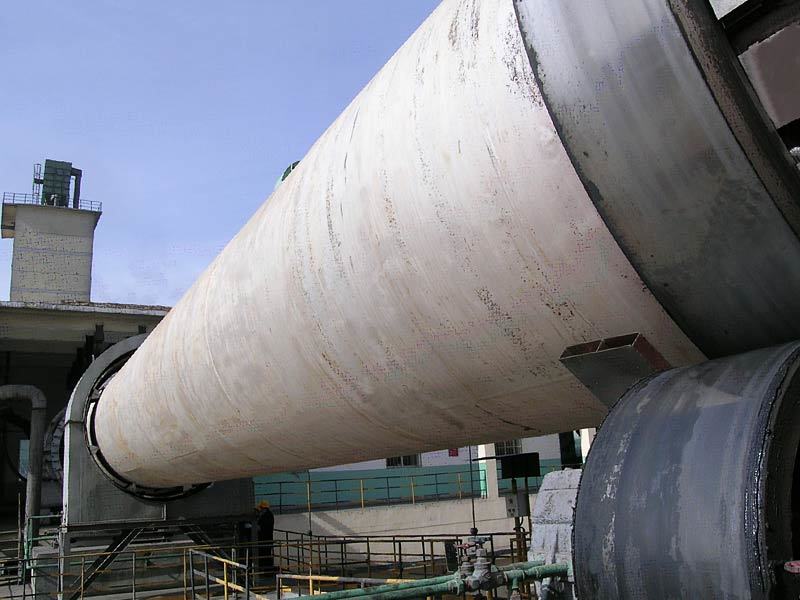

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
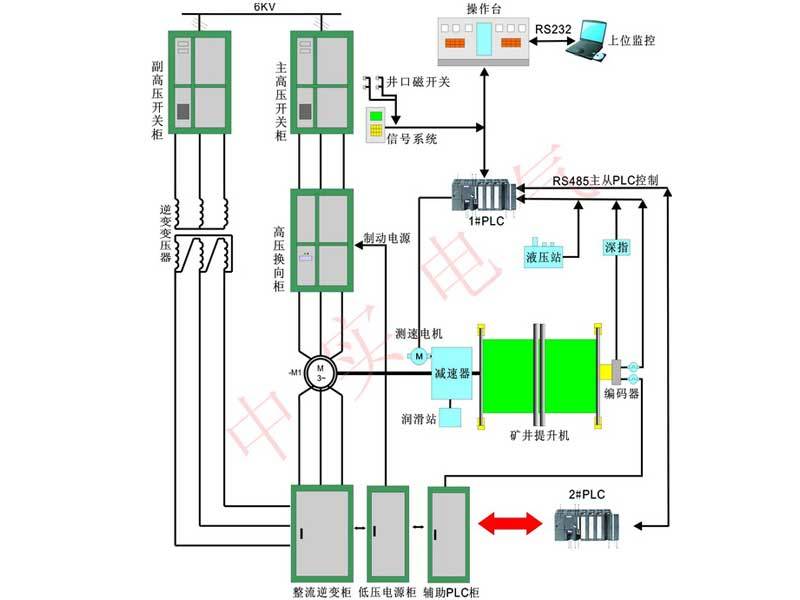
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
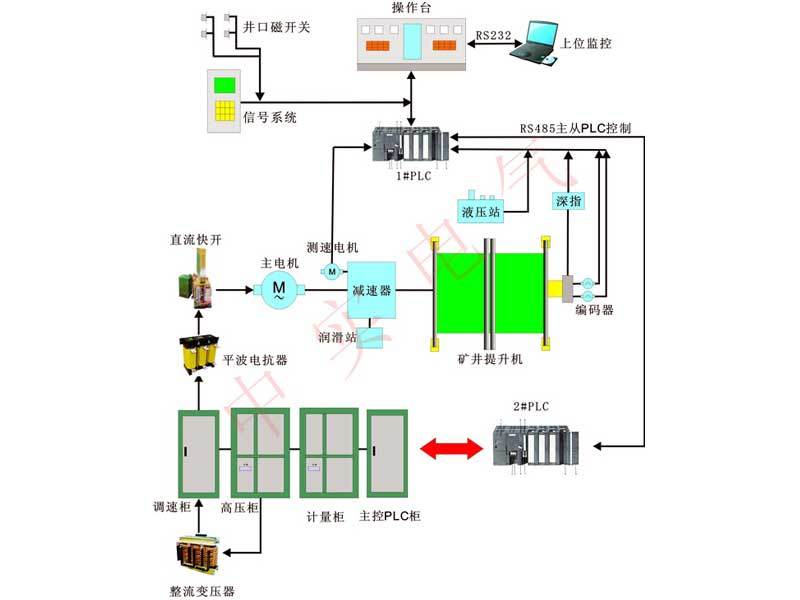
Fully digital DC control system
-
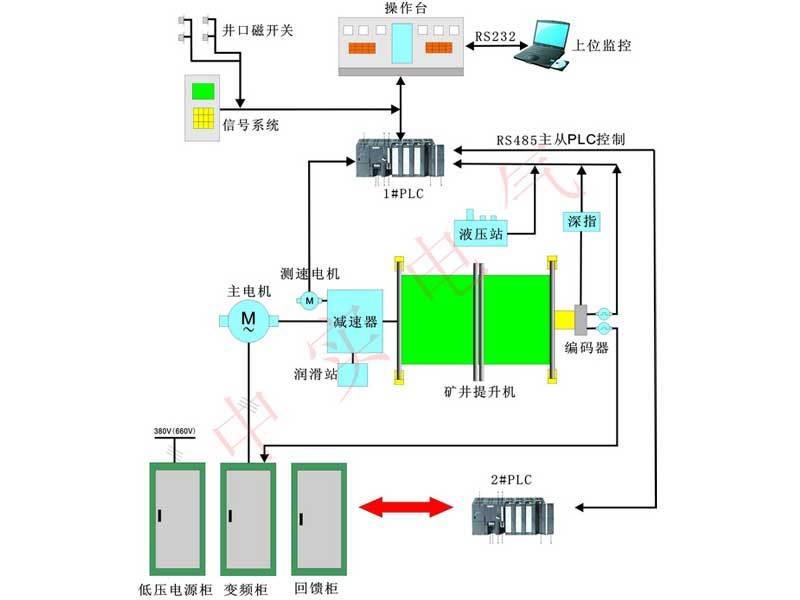
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
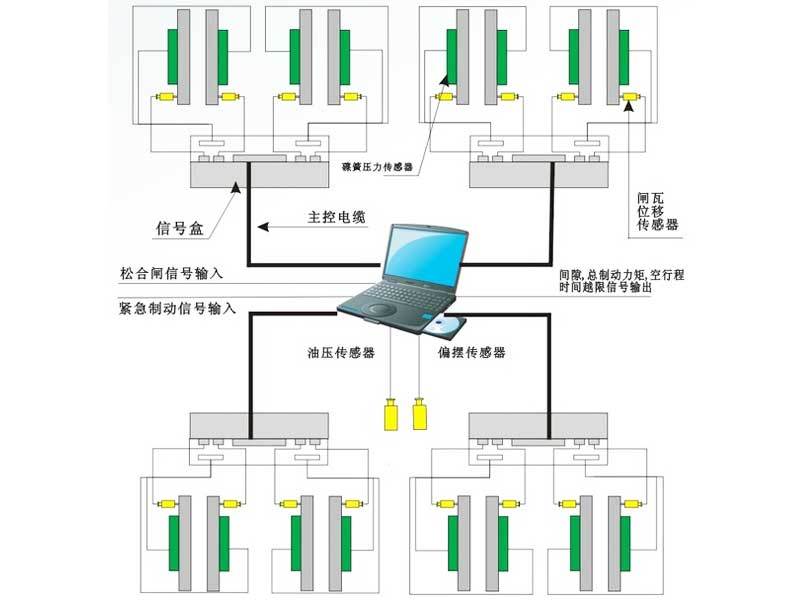
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
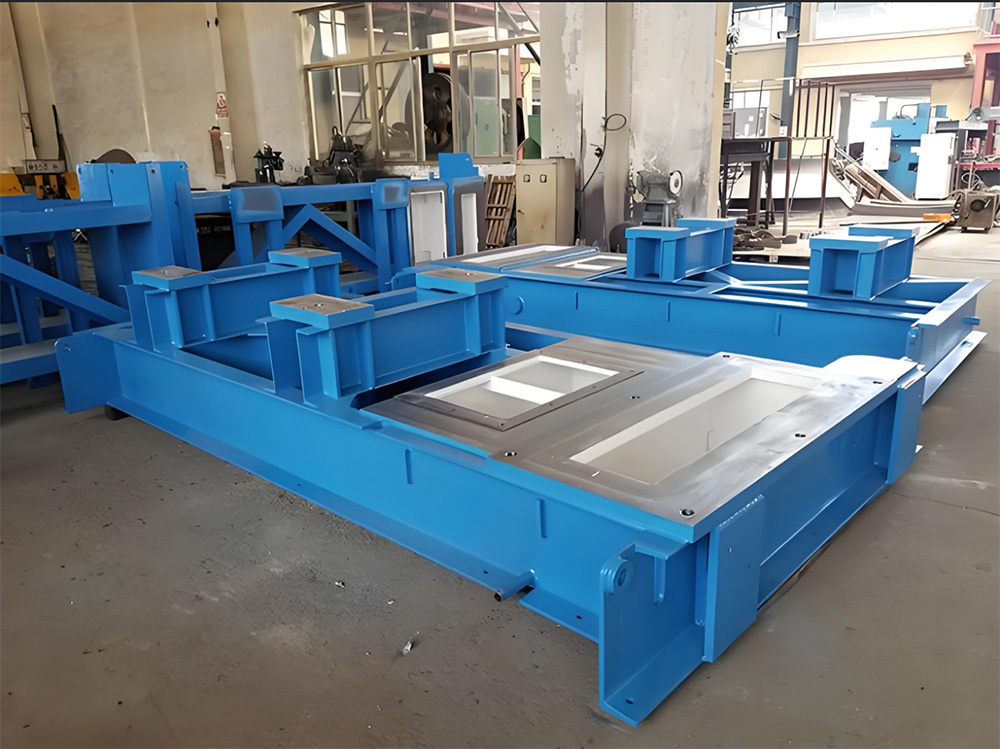

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-
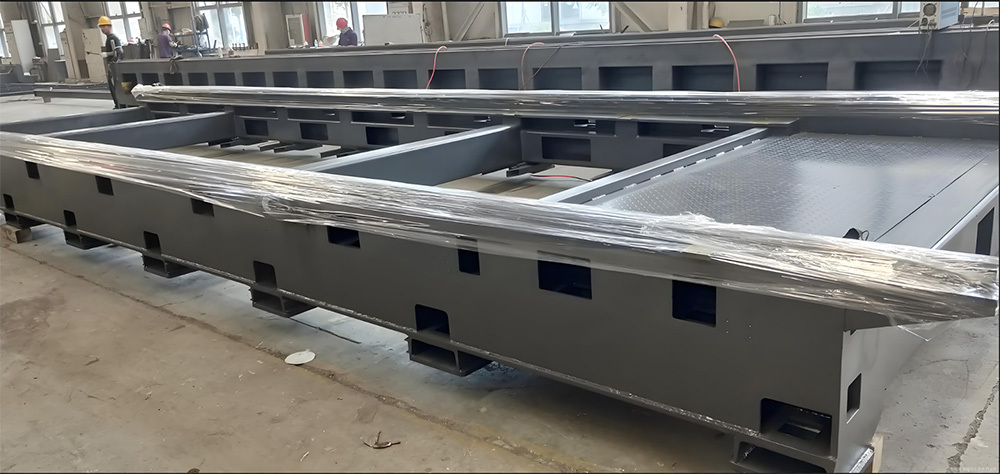

Large base
-
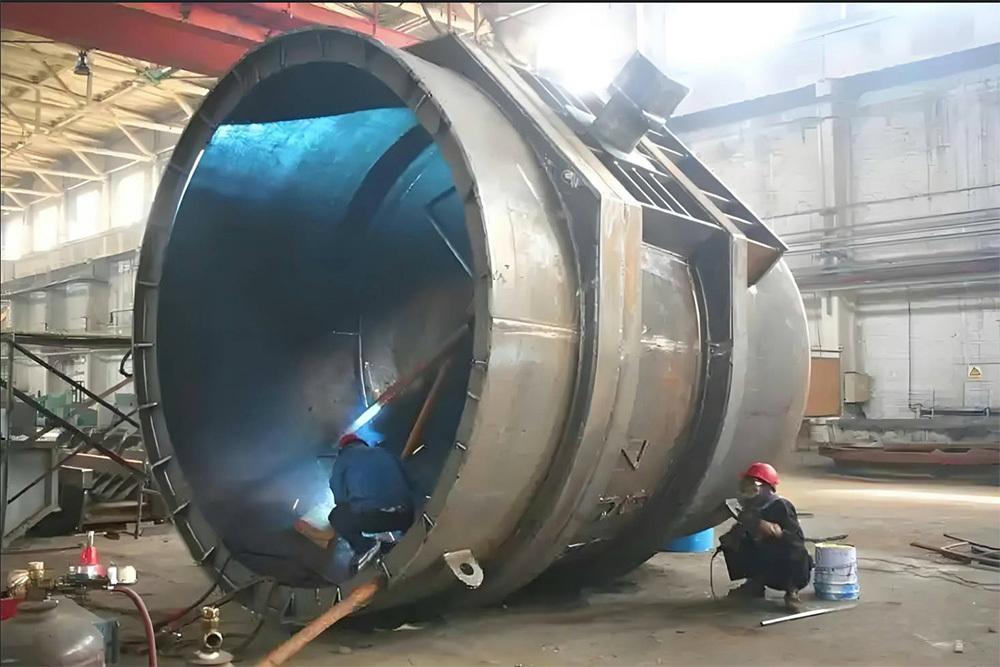

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
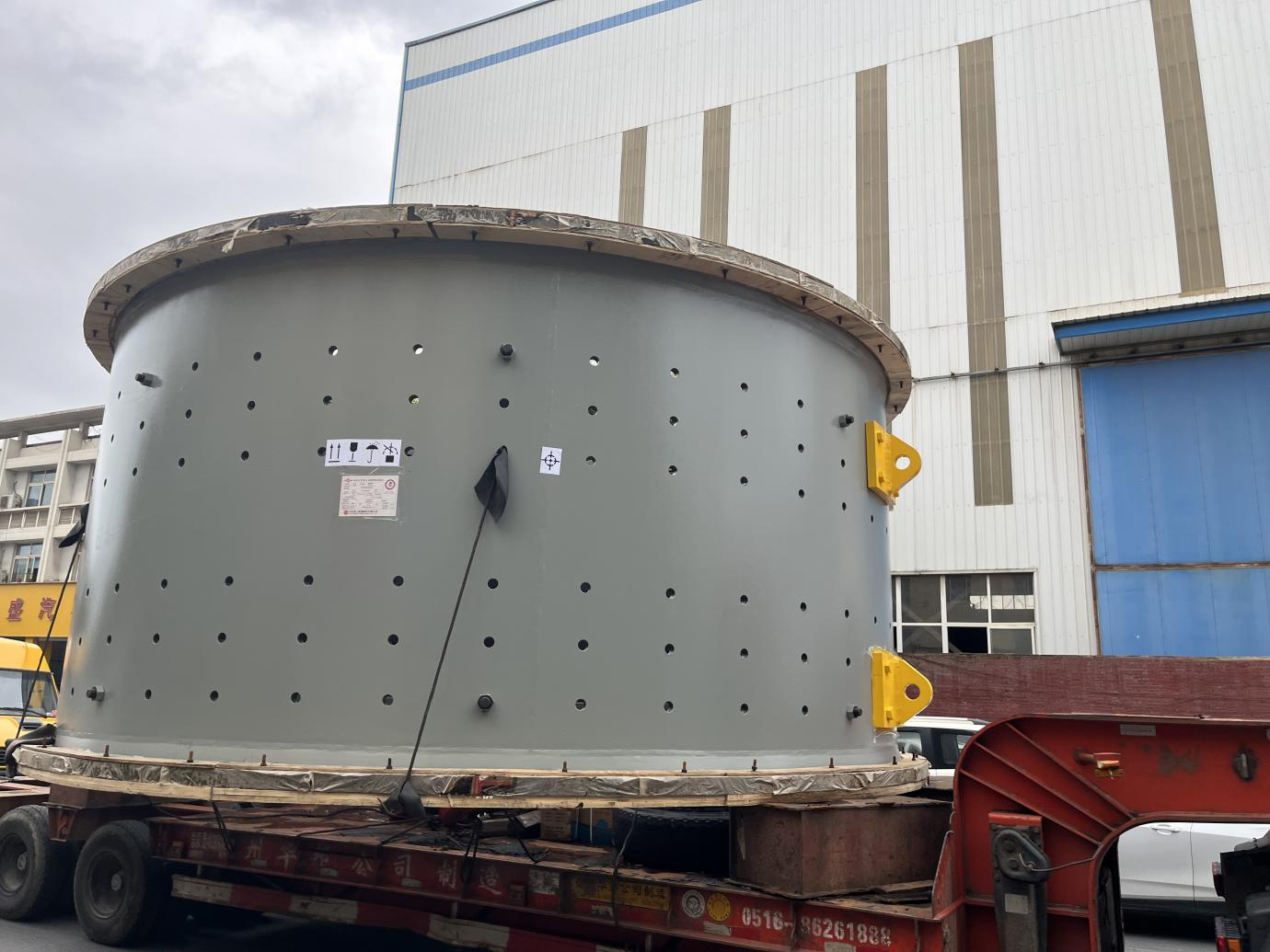

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-

Bus Alloy Bushings
-

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-
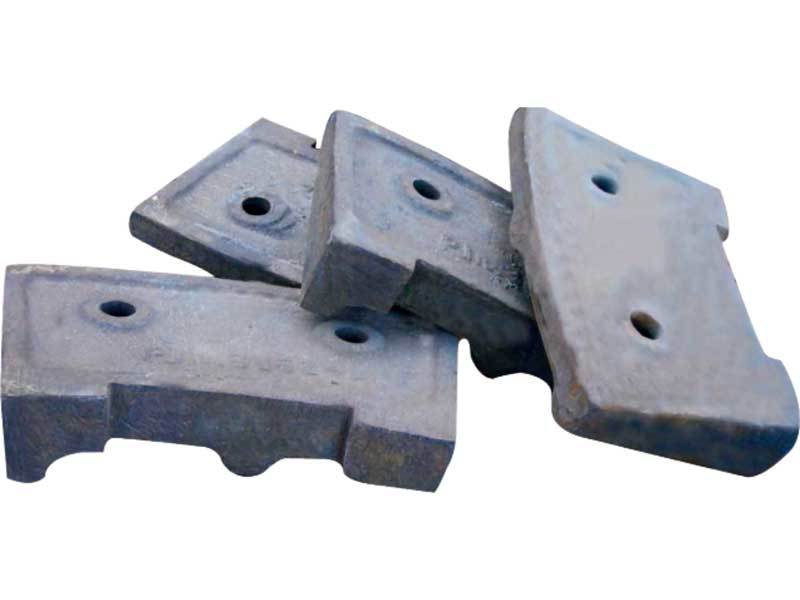

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-
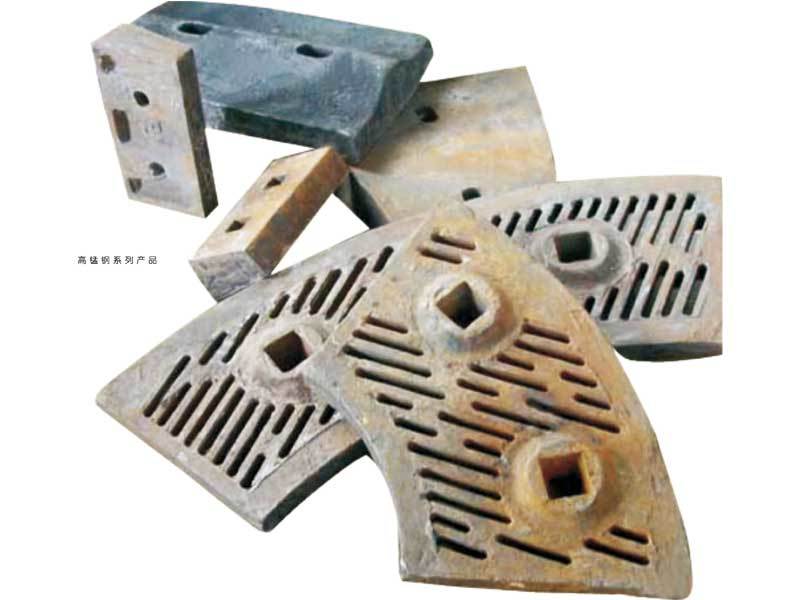

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-
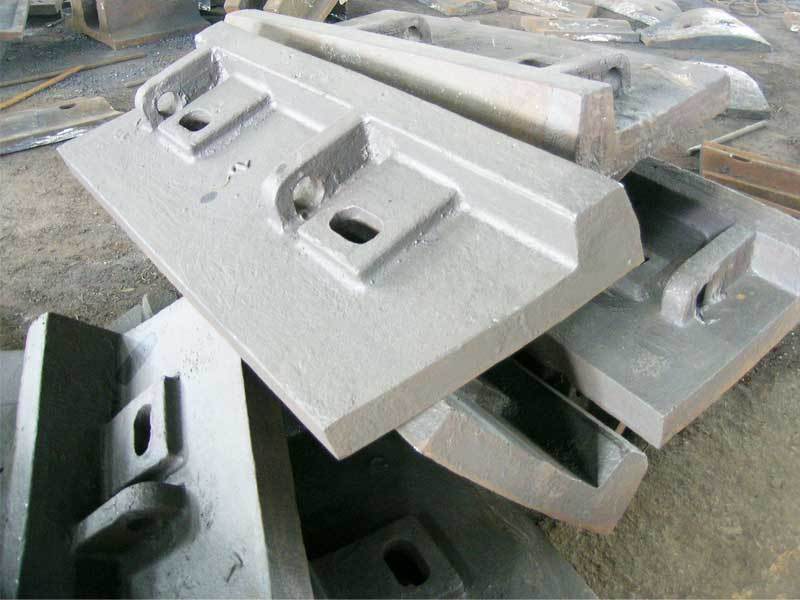

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-
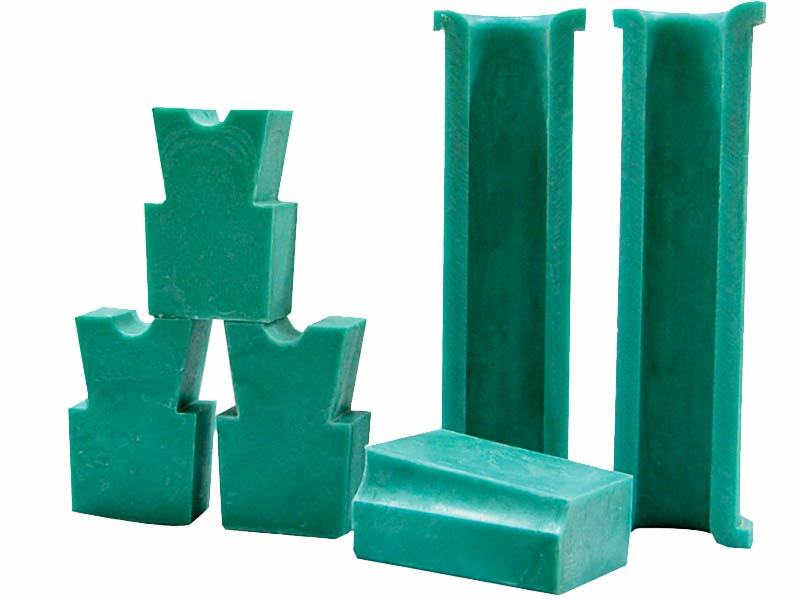

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
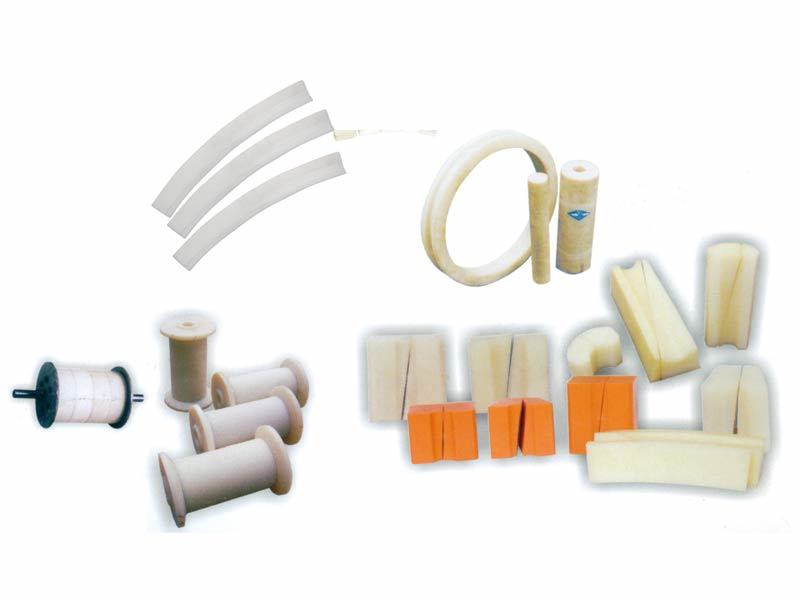

Nylon products
-
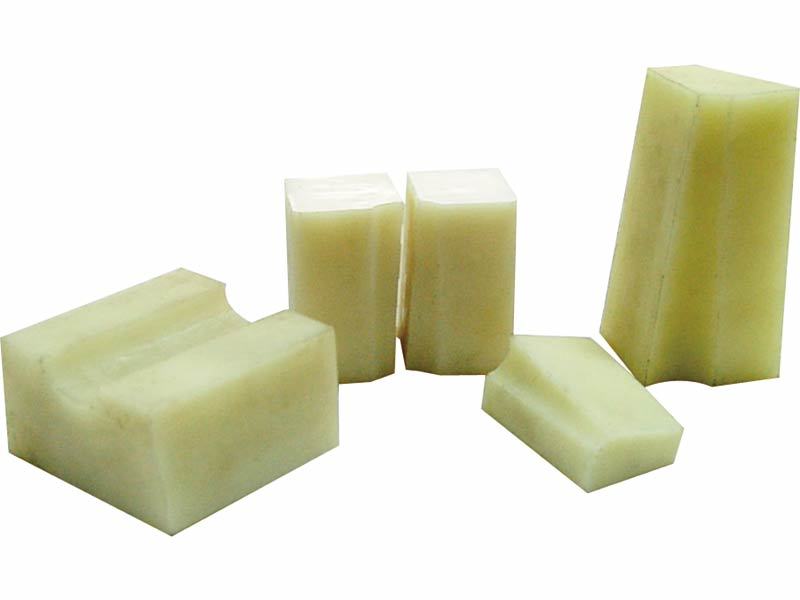

Polyurethane Products
-
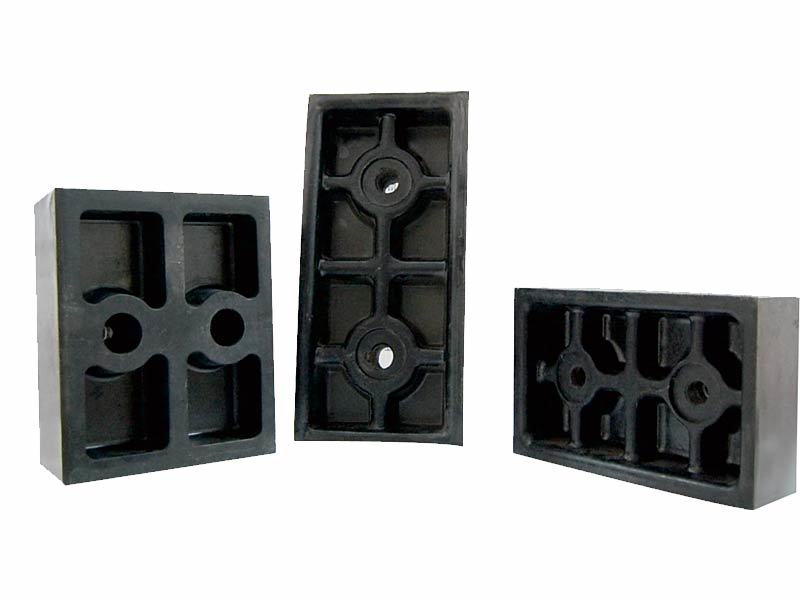

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
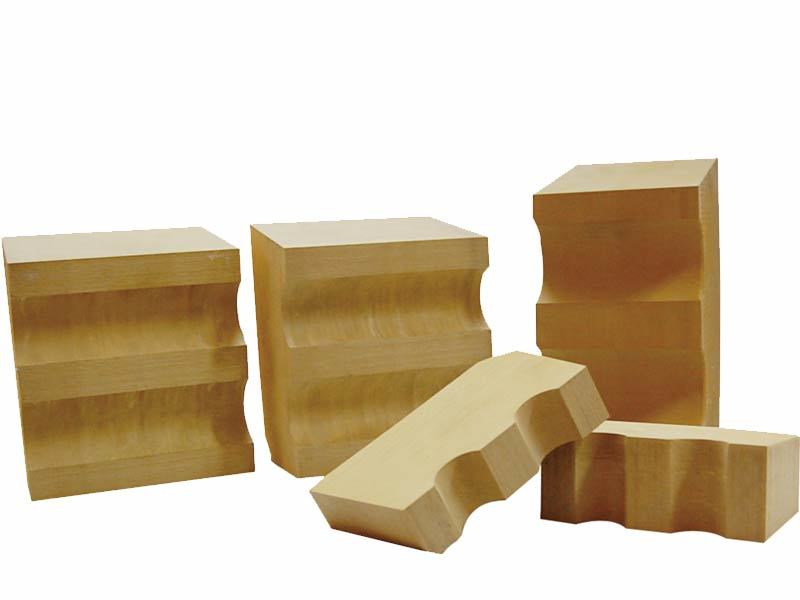

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information