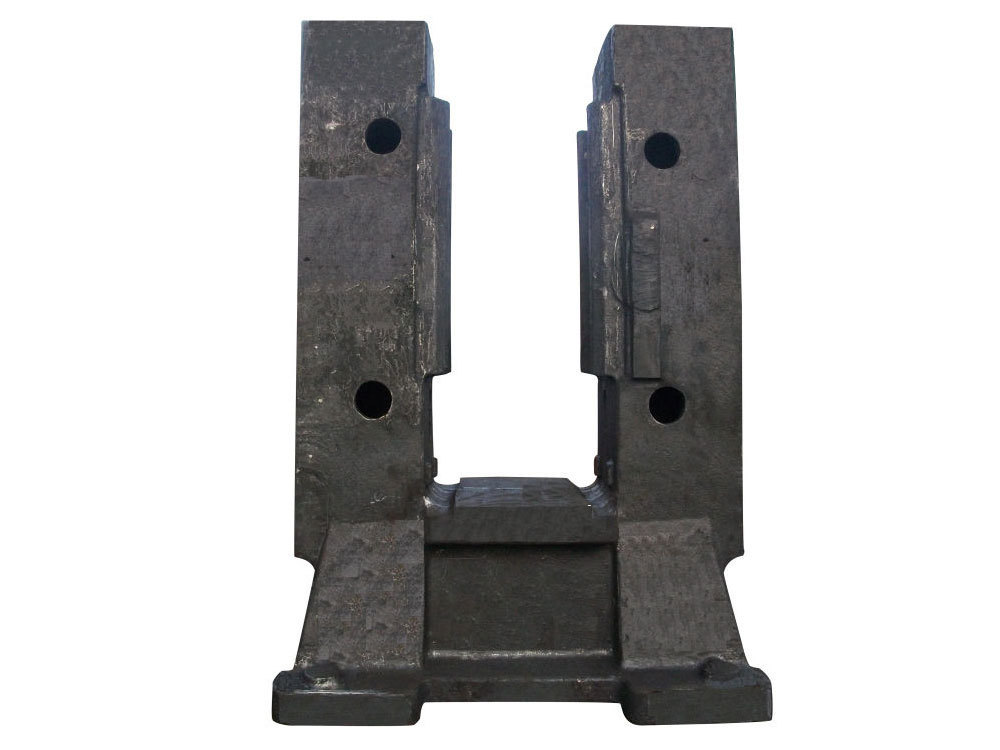
I. Basic Overview and Classification of Crusher Jaw Plates
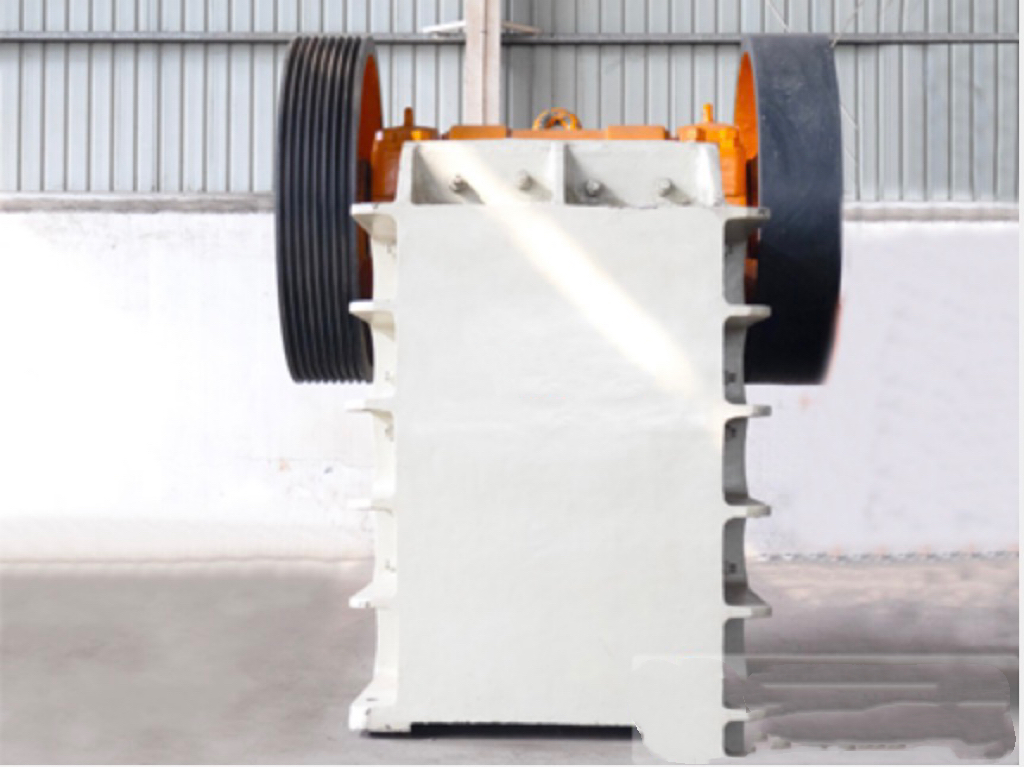
The jaw plate is the core wear-resistant component of a jaw crusher, directly contacting the material and performing the crushing action through compression. It comes in two types: the moving jaw plate and the stationary (fixed) jaw plate—resembling the "upper and lower jaws" of an animal. By combining the periodic swinging motion of the moving jaw plate with the stationary plate, the machine applies compressive and shearing forces to break down the material. Depending on the specific model of the jaw crusher, jaw plates are available in various sizes and specifications. For instance, the 500×750 model crusher is designed to work optimally with a particular-sized jaw plate—and it’s crucial that the plate matches the equipment model precisely to maintain maximum crushing efficiency.
II. Structure, Function, and Working Principle of Crusher Jaw Plates
1. Core structural components
The moving jaw plate: Driven by an eccentric shaft to perform periodic oscillating motion, it is the active crushing component, and its movement trajectory directly affects crushing efficiency.
Fixed jaw plate: Attached to the crusher frame, it forms the crushing chamber with the moving jaw plate and bears the reaction force from the material.
Side lining plates: Installed on both sides of the crushing chamber, typically made of cast steel, they provide auxiliary wear resistance and are classified as chisel-type abrasive wear parts—specifically, part 5.
2. Operating Principle
The electric motor drives the eccentric shaft to rotate via a pulley, causing the moving jaw plate to perform reciprocating up-and-down motion.
Rising phase: The angle between the elbow plate and the moving jaw increases, pushing the moving jaw plate closer to the stationary jaw plate, thereby squeezing and crushing the material.
Descending phase: The angle decreases, and the moving jaw plate returns to its original position under the action of the tie-rod spring. The crushed material is then discharged through the discharge opening.
During this process, the lower part of the鄂 plate typically wears out faster than the upper part due to more frequent contact with the material.
3. Core Material Properties
Metrics |
Parameters |
Comparison of Traditional Materials |
Initial Hardness |
HB 180-220 |
Lower than high-chromium cast iron (HRC 60+) |
Hardness after work hardening |
HB 500–550 |
Increase by more than 2 times |
Tensile strength |
≥800 MPa |
Superior to ordinary carbon steel (450 MPa) |
Elongation |
≥35% |
Impact-resistant and不易断裂 |
Impact toughness |
≥150 J/cm² |
Five times that of high-chromium cast iron |
III. Jaw Plate Structural Design and Manufacturing Process
1. Tooth Profile Optimization
Tooth profile |
Applicable Scenarios |
Breakage Efficiency |
Wavy teeth |
Hard rock (granite, iron ore) |
High biting force, prevents material jamming |
Triangular teeth |
Medium-hard rock (limestone, basalt) |
Balanced Wear Life |
Trapezoidal teeth |
Viscous material (clay ore) |
Anti-blocking material design |
2. Casting Process
Water glass sand mold casting: Ensuring clear contour definition (dimensional tolerance CT10)
Riser Optimization: Computer simulations of the solidification process reduce shrinkage cavities (X-ray inspection meets ASTM E186 standards).
3. Surface Enhancement
Explosive Hardening: Pre-hardened surface up to HB 380–400, extending initial service life by 30%
Overlay welding repair: After wear, local repairs can be performed using high-chromium alloy welding electrodes (D667).
IV. Application Scenarios and Lifespan Reference
Eccentric plates are widely used in fields such as mining, metallurgy, building materials, and construction waste management. They can crush brittle materials—like ores, rocks, and concrete blocks—with compressive strengths not exceeding 320 MPa—and serve as the critical component that enables jaw crushers to perform "primary crushing."
Crushed Materials |
Compressive Strength (MPa) |
Jaw Plate Life (Hours) |
Failure Mode |
Granite |
150–300 |
300–400 |
Tooth root fatigue fracture |
Iron ore |
200–350 |
250–350 |
Impact pitting + spalling |
Limestone |
80–150 |
600–800 |
Uniform wear |
Construction waste |
Mixed metals |
150–250 |
Localized tooth loss |
Life Extension Program:
Pre-screening to remove metal impurities; adjust the discharge opening to be at least 1.3 times the feed particle size (to reduce overload impact).
Design Optimization: Ensure the crushing chamber angles between the moving jaw and stationary jaw are properly aligned to minimize the impact load of material on the jaw plates.
Two-way usage: When the lower part of the jaw plate is severely worn, it can be installed upside down—reversing its position—to continue working with the still-undamaged upper section.
Regular maintenance: Promptly clear any remaining material in the crushing chamber, and check whether the tightening bolts are loose, to prevent excessive wear of the jaw plates due to increased vibration.
5. Maintenance and Inspection
Daily Inspection: Measure tooth height wear weekly (replace if wear exceeds 15% of the original height)
Bolt Pre-tightening Force Inspection (Torque Value ≥ 980 N·m)
Failure Analysis: Metallographic Examination: Check for the presence of grain boundary carbides due to insufficient cooling.
Hardness Gradient Test: Verify the Depth of the Work-Hardened Layer (should be ≥30 mm)
Keywords
Next: New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology






Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
Rotary kiln
-

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-

Lime Rotary Kiln
-

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
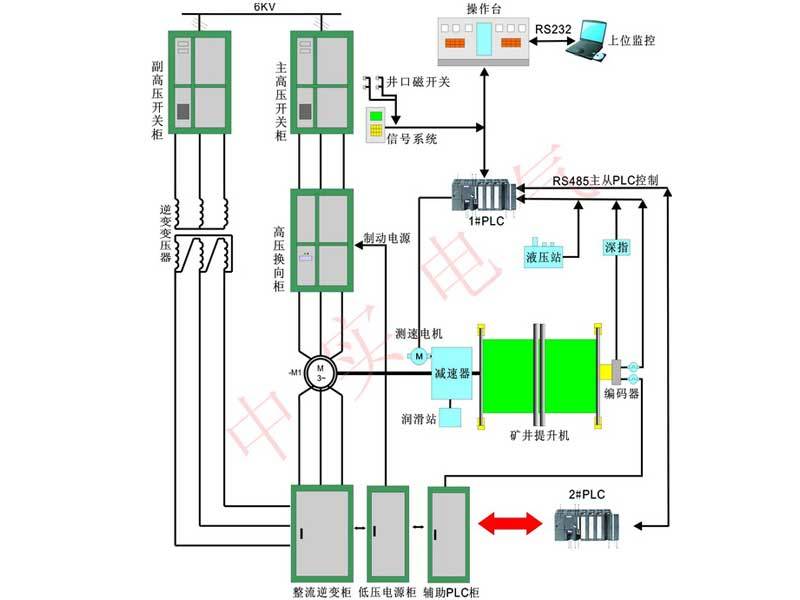
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
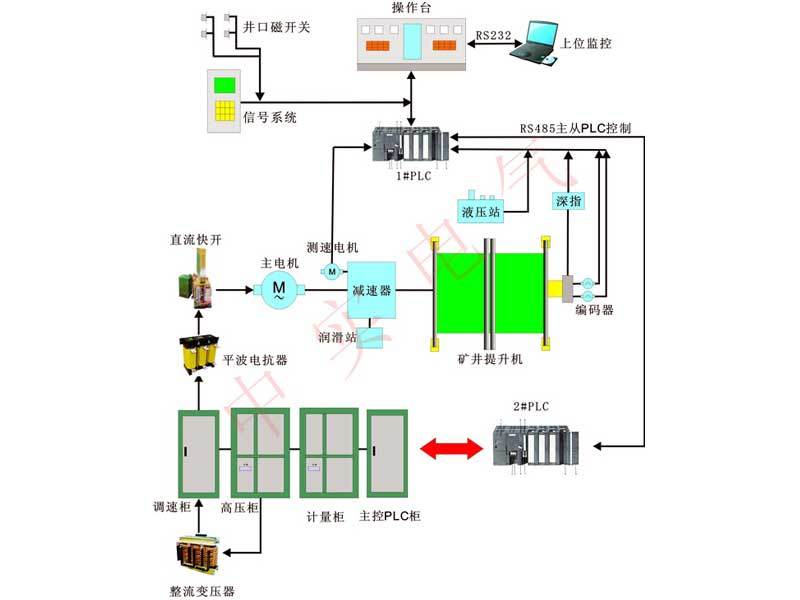
Fully digital DC control system
-
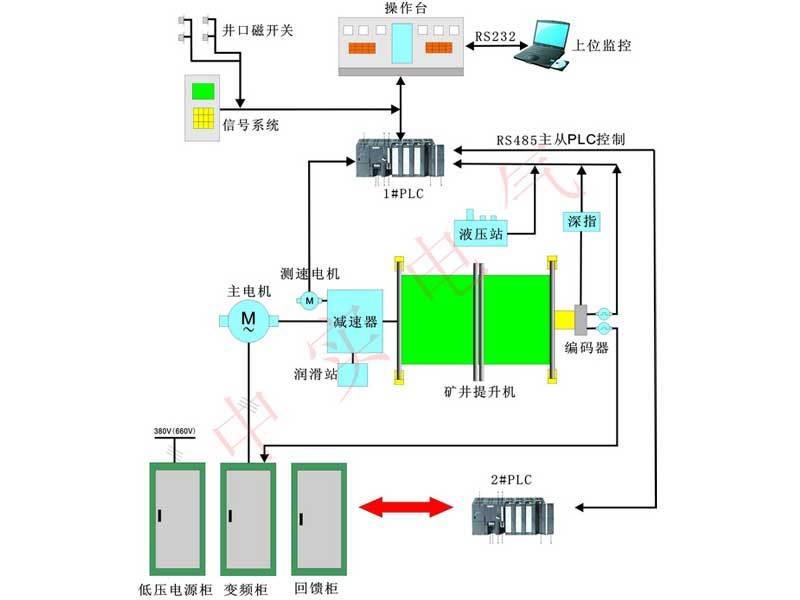
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
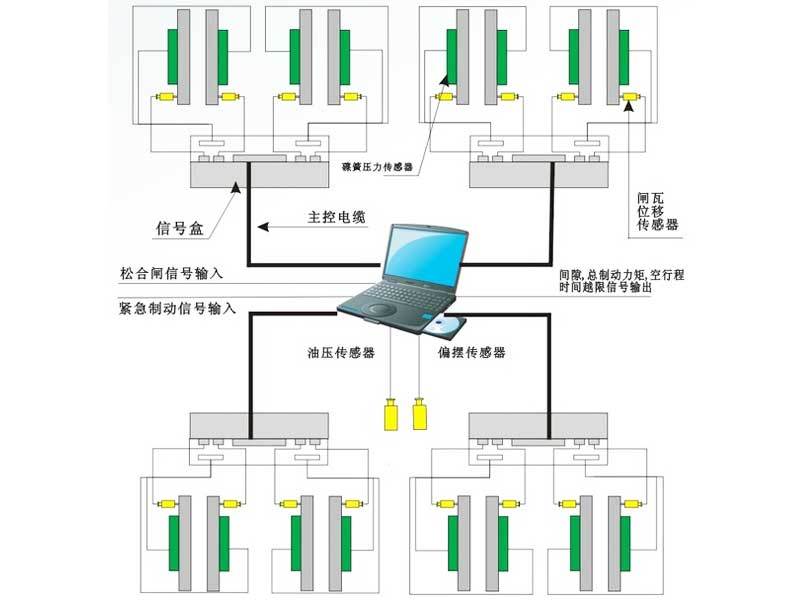
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-

Large base
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-
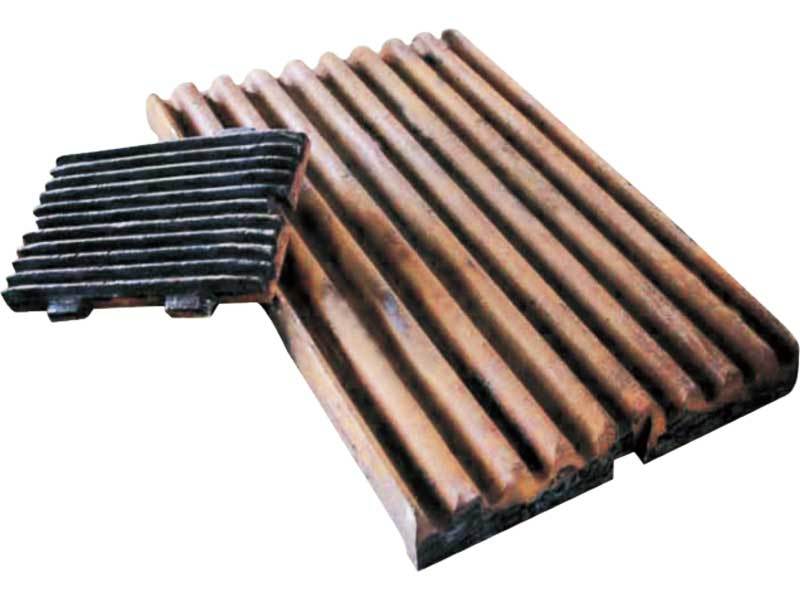

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-
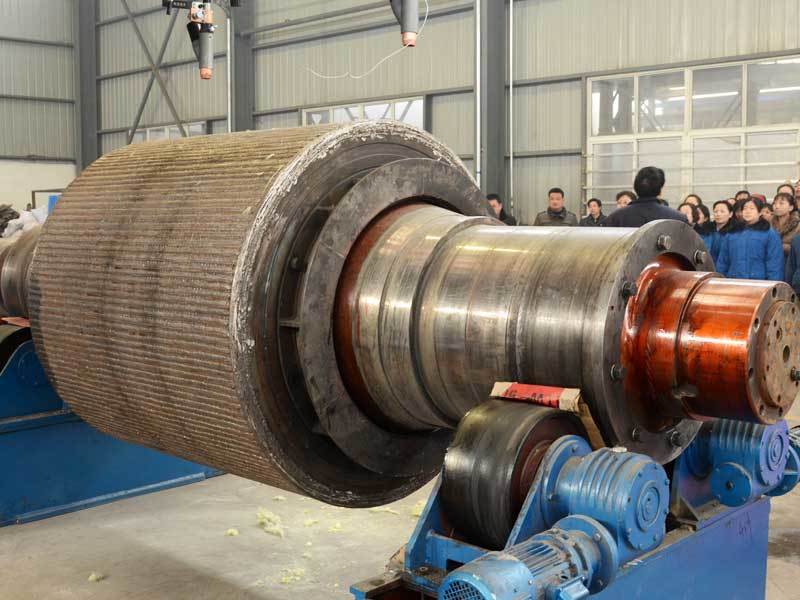

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-
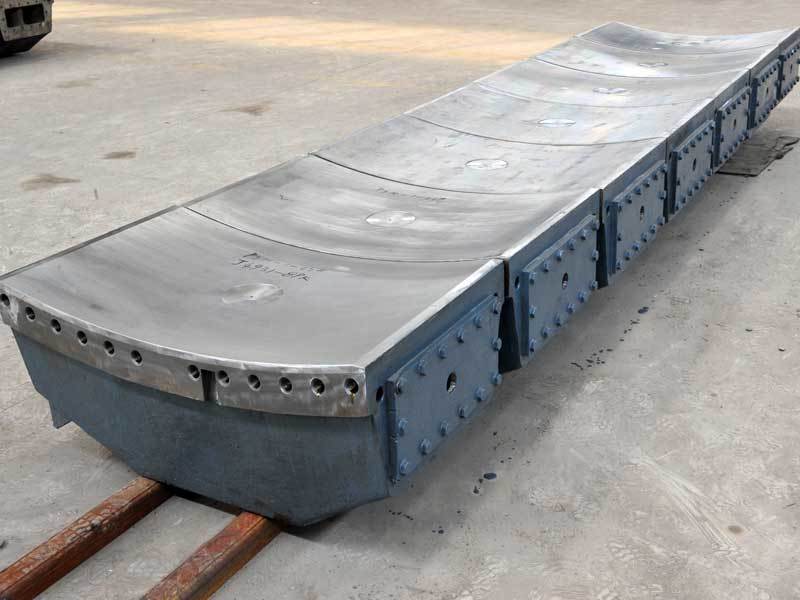

Bus Alloy Bushings
-
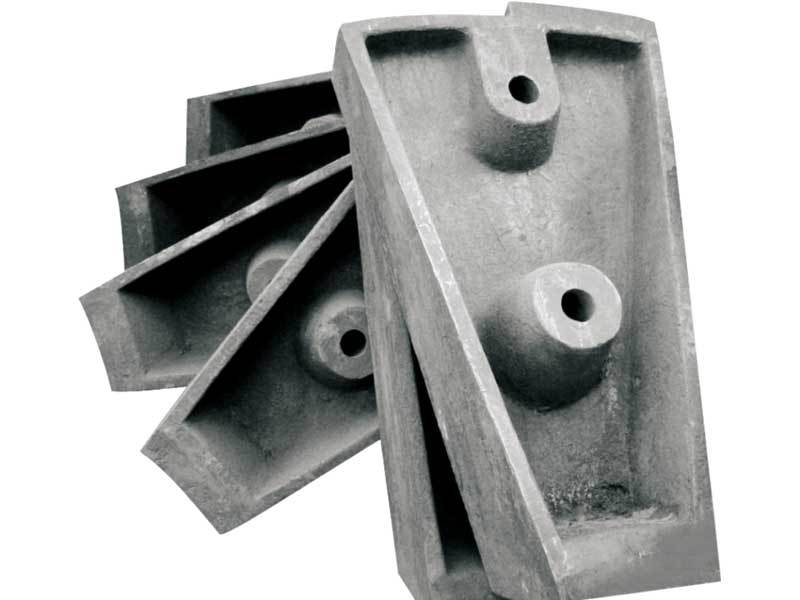

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-

Nylon products
-

Polyurethane Products
-

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information