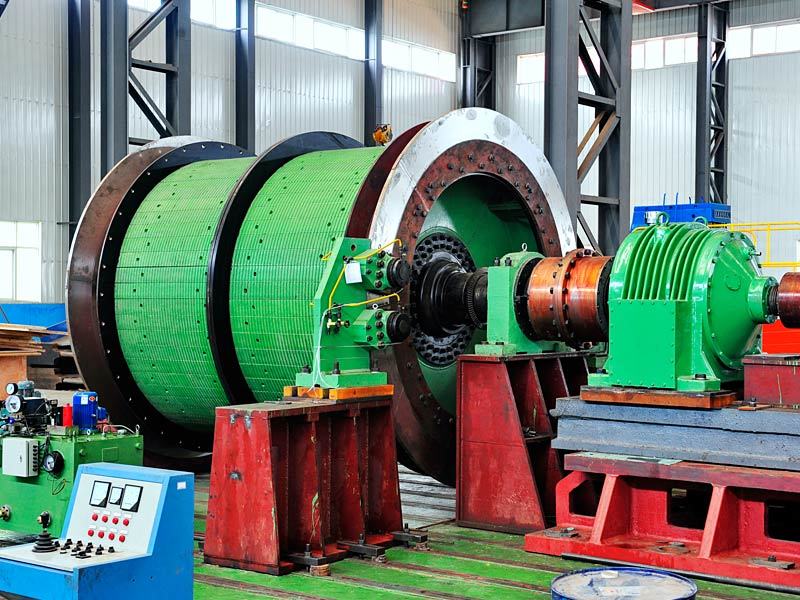
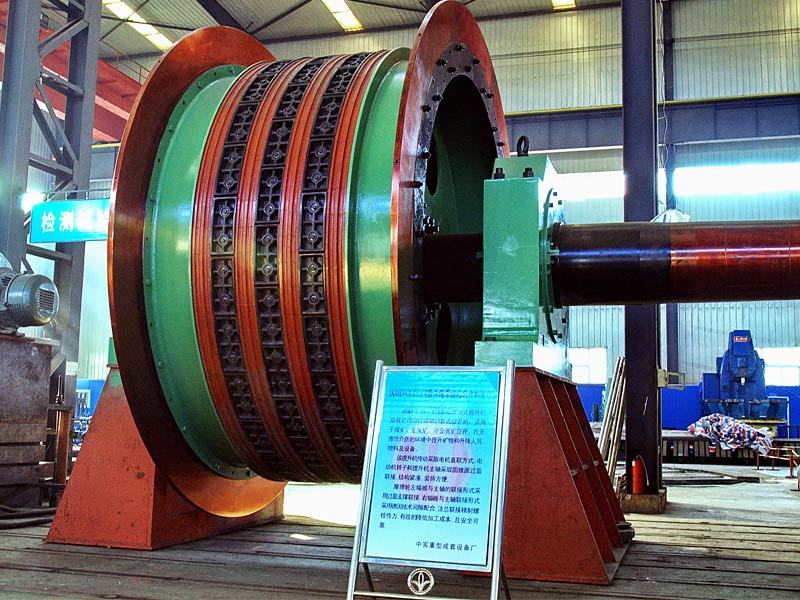
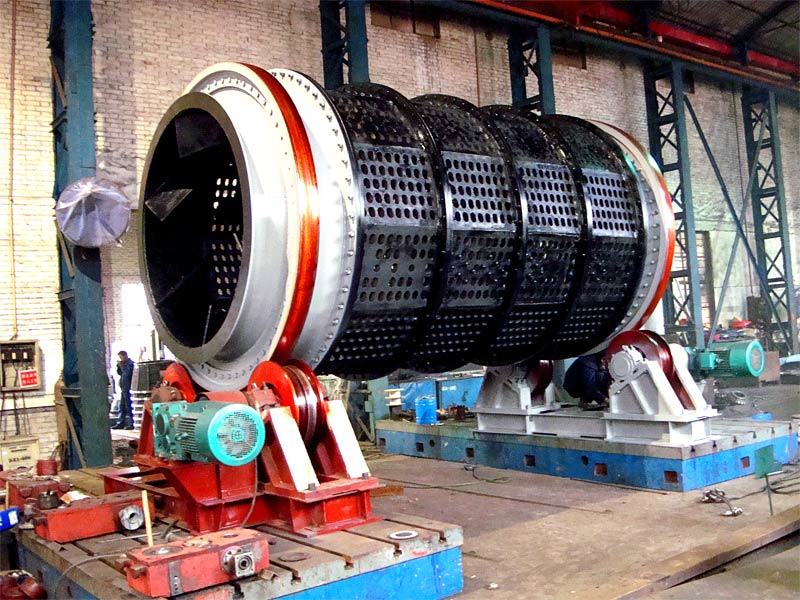
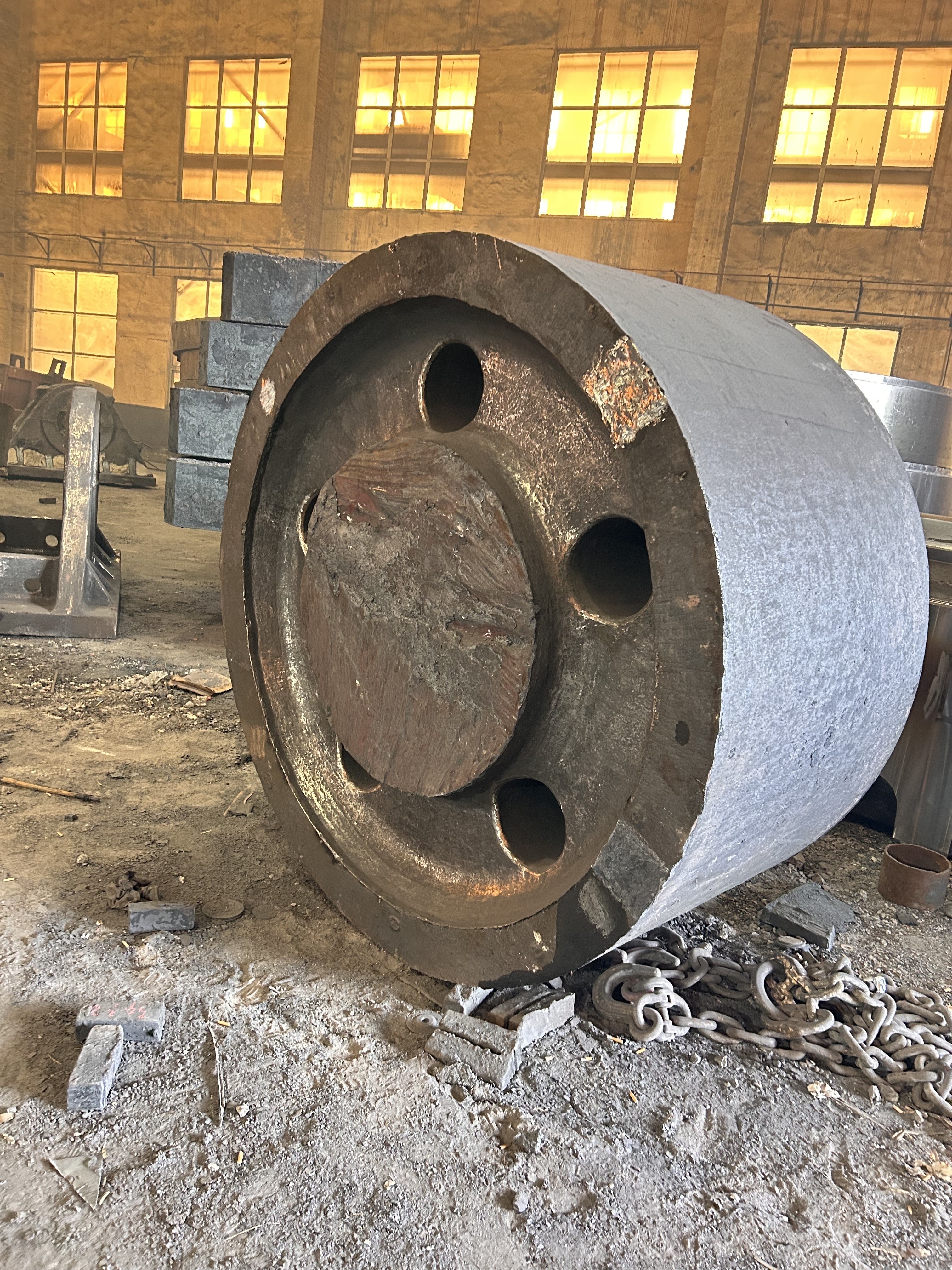
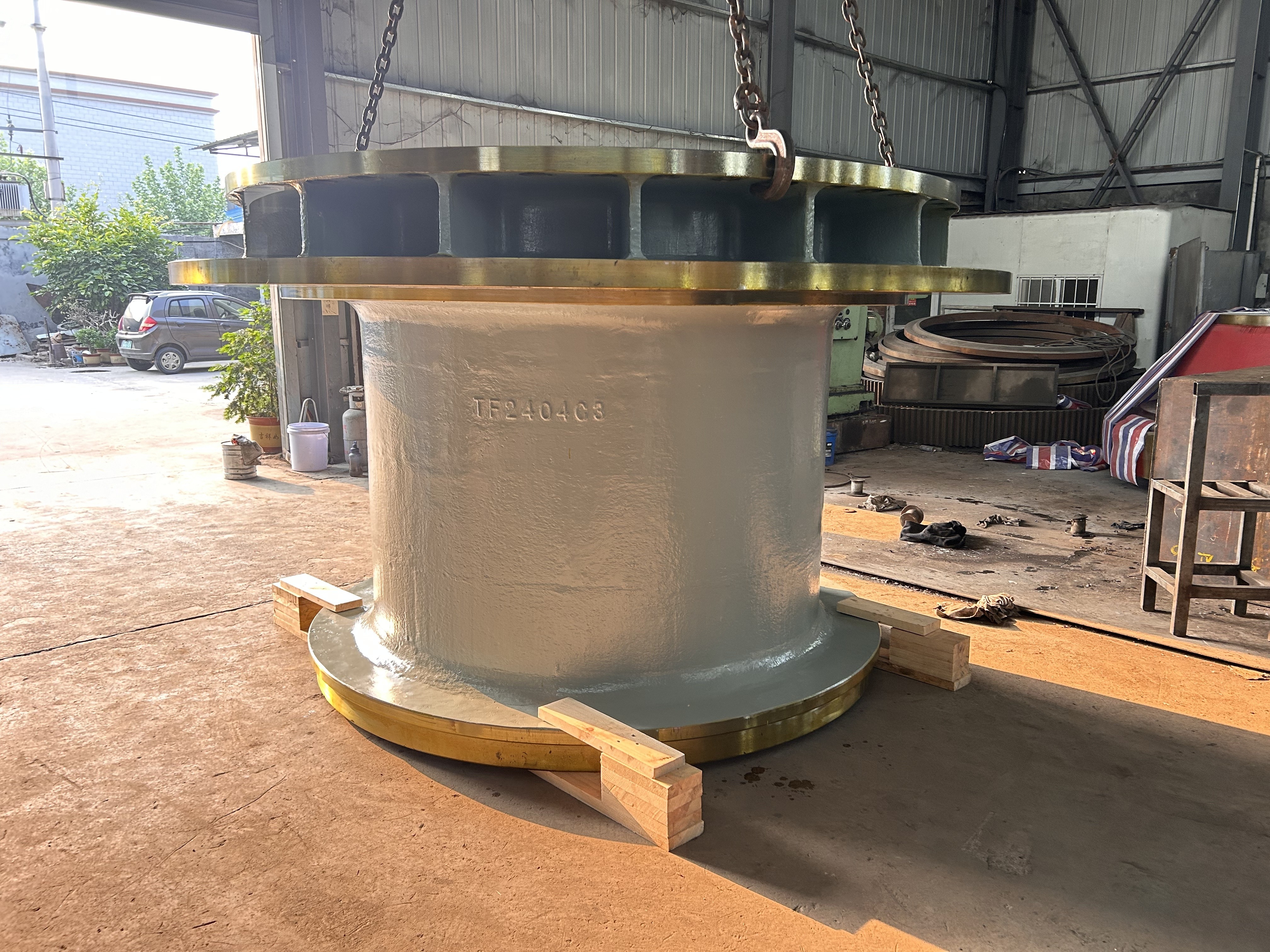
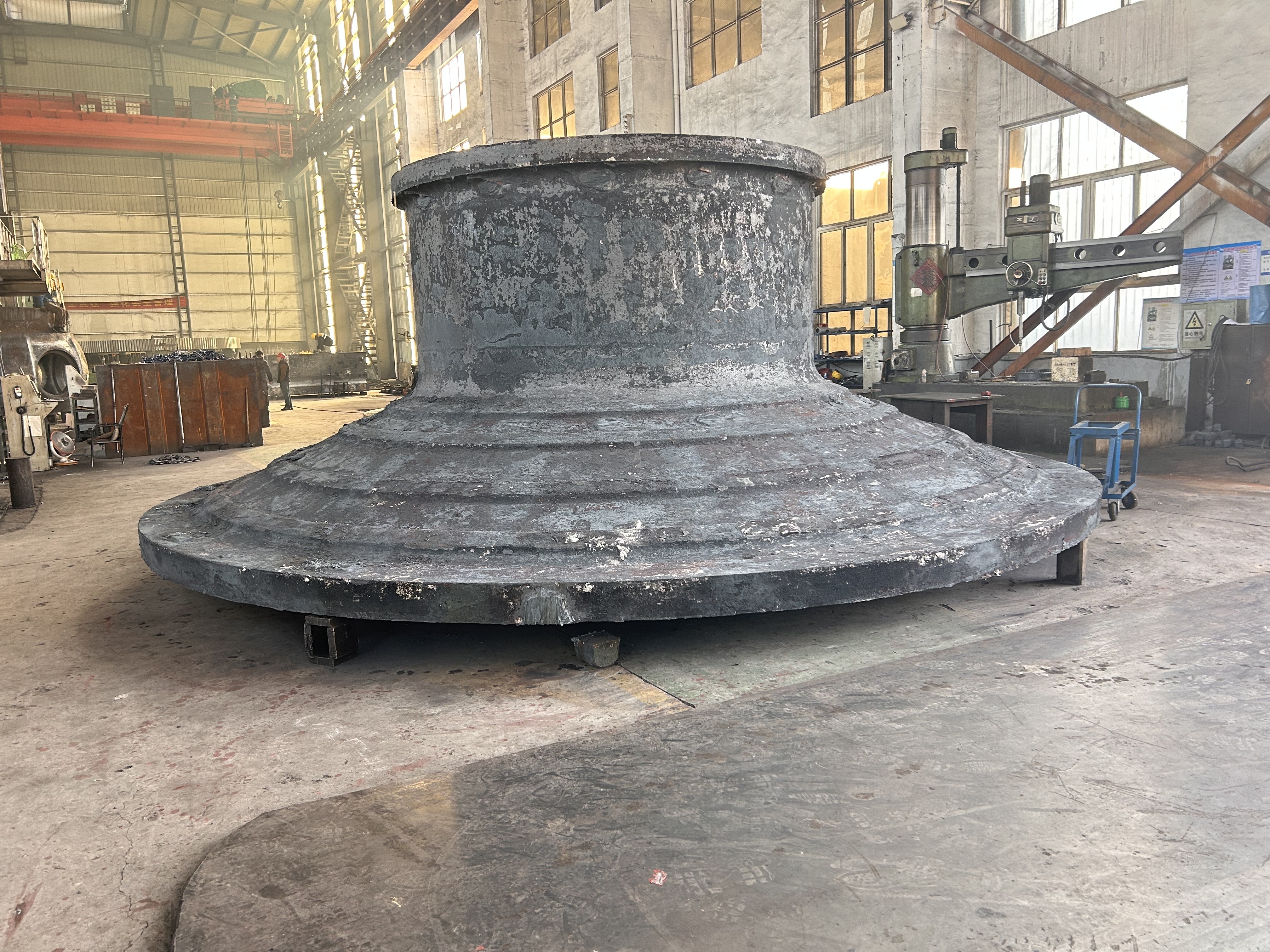
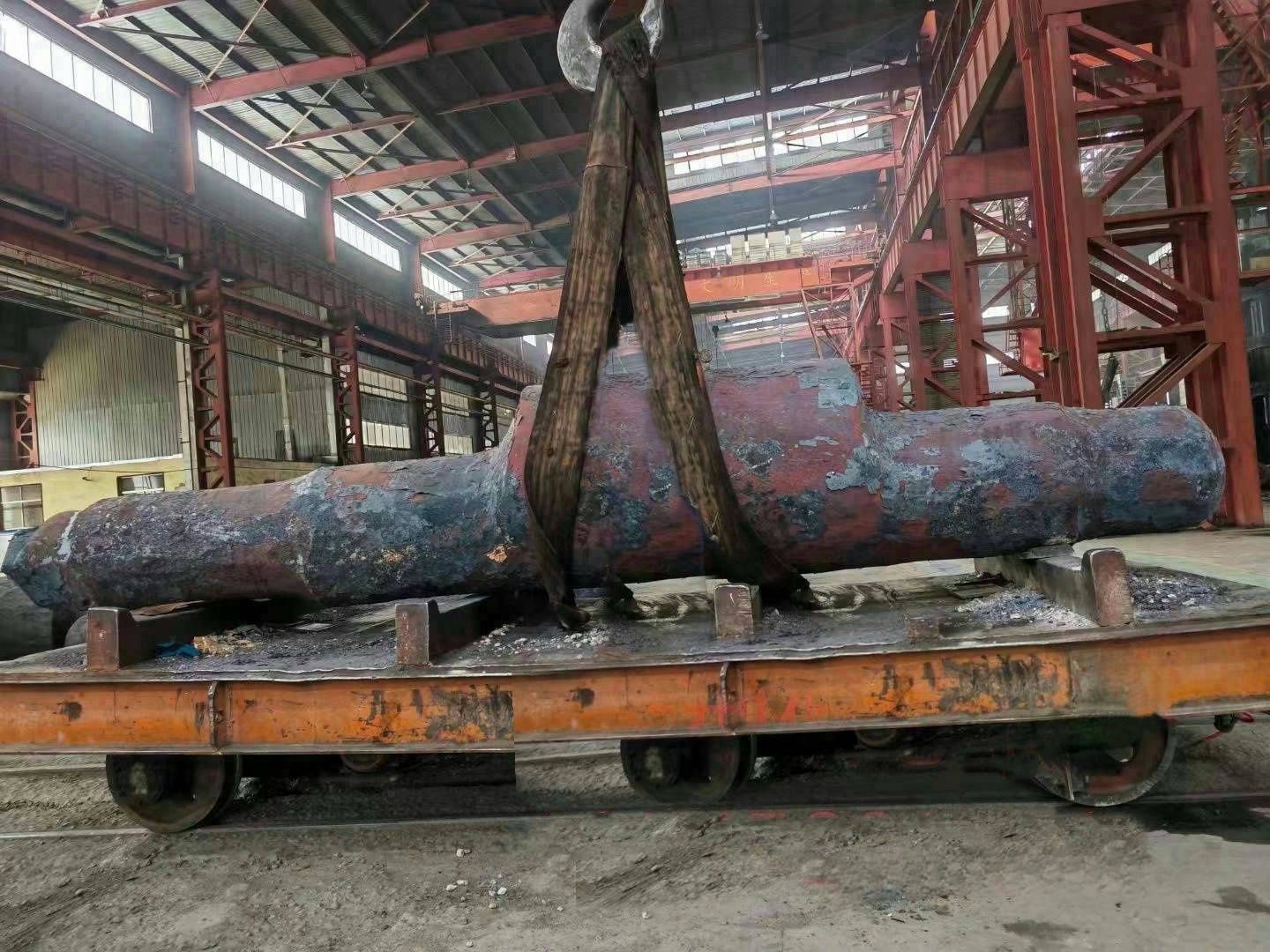
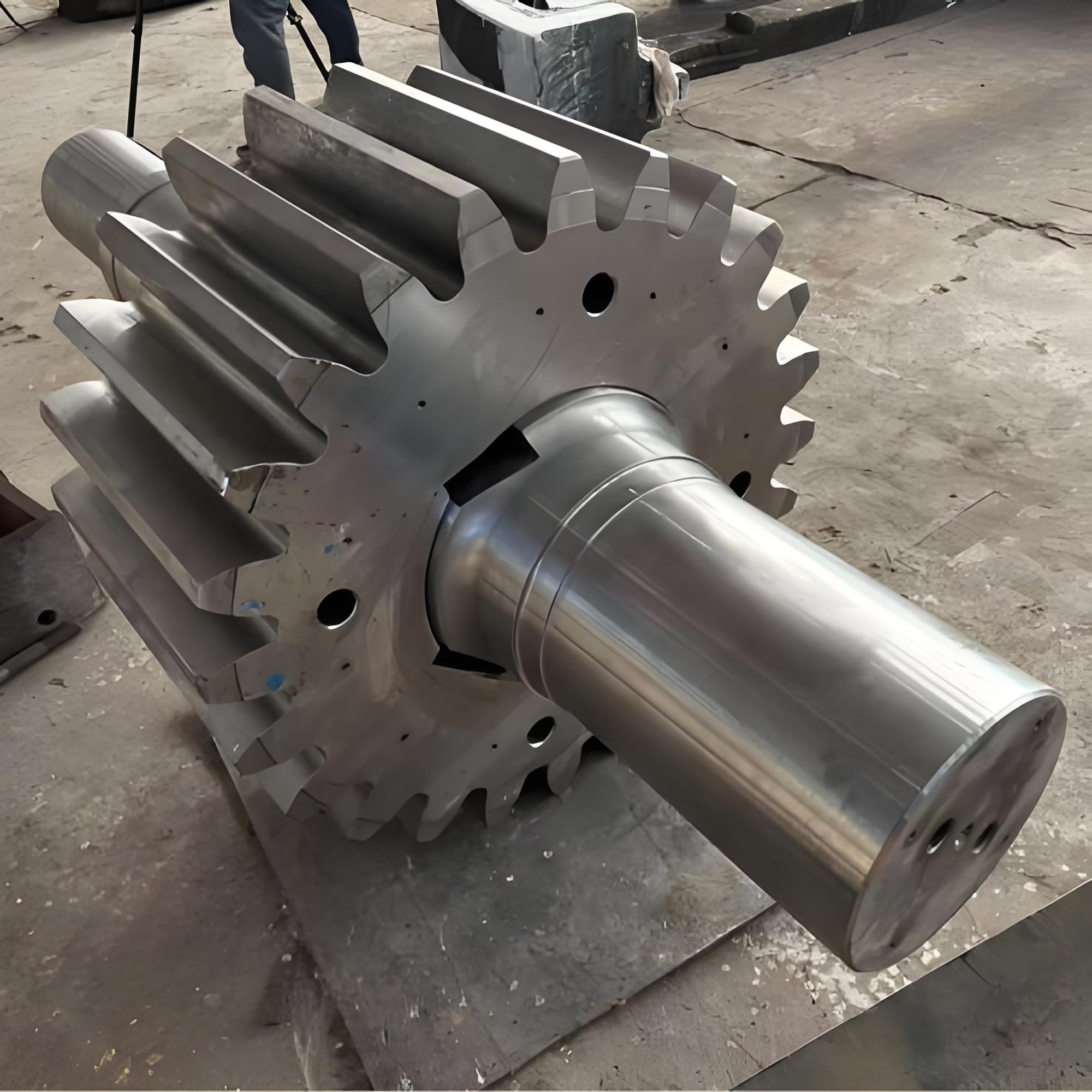
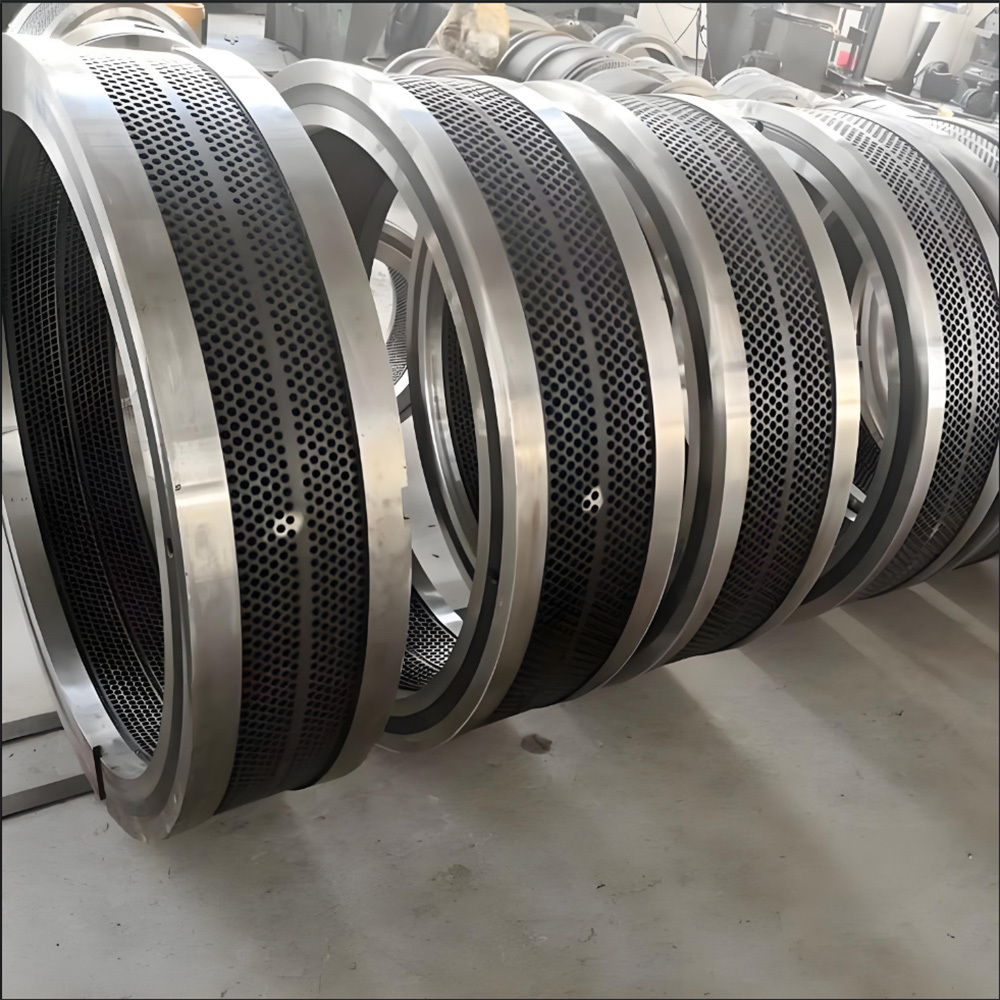
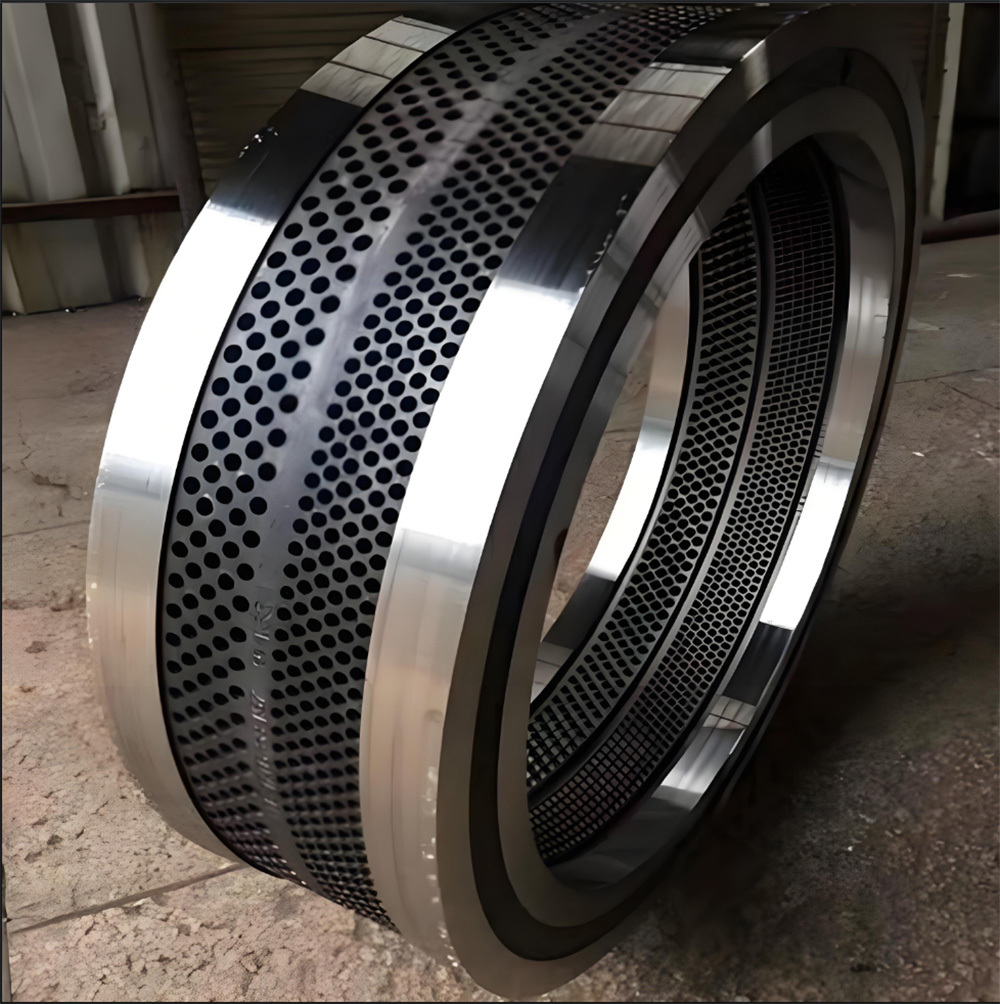
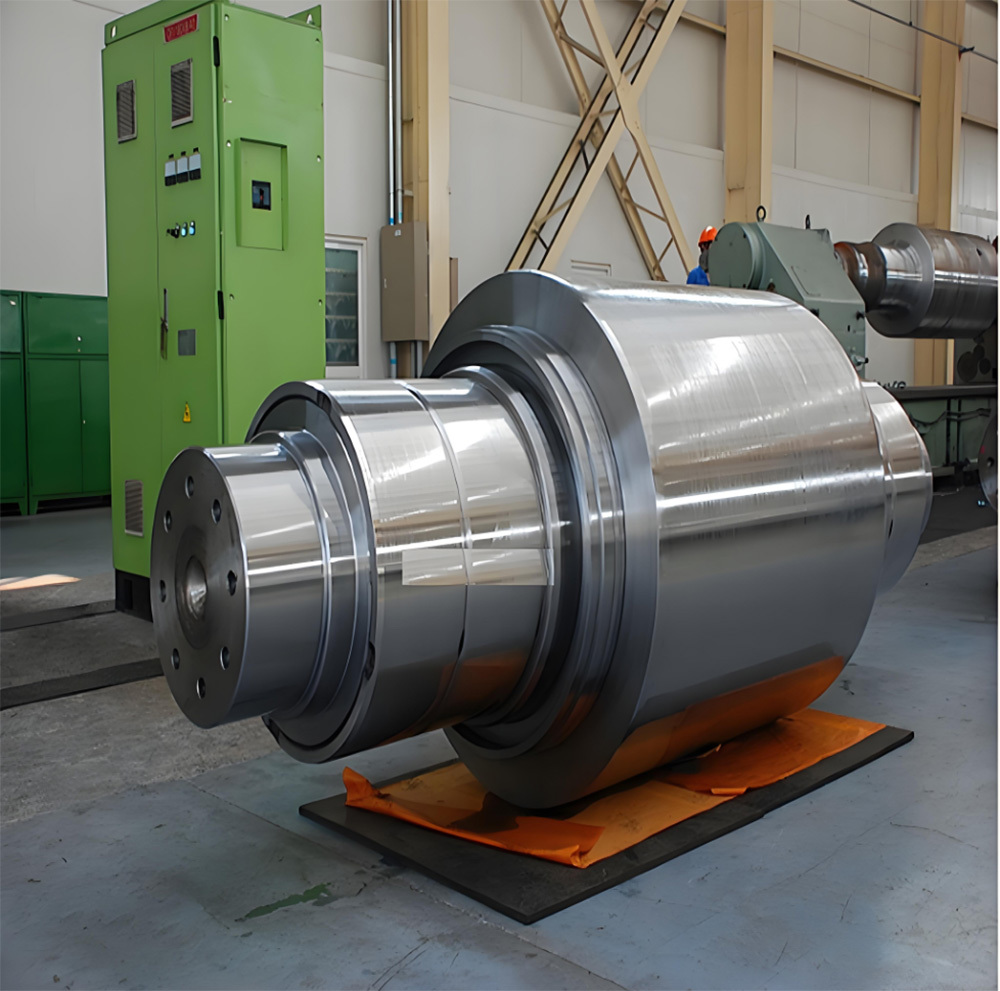
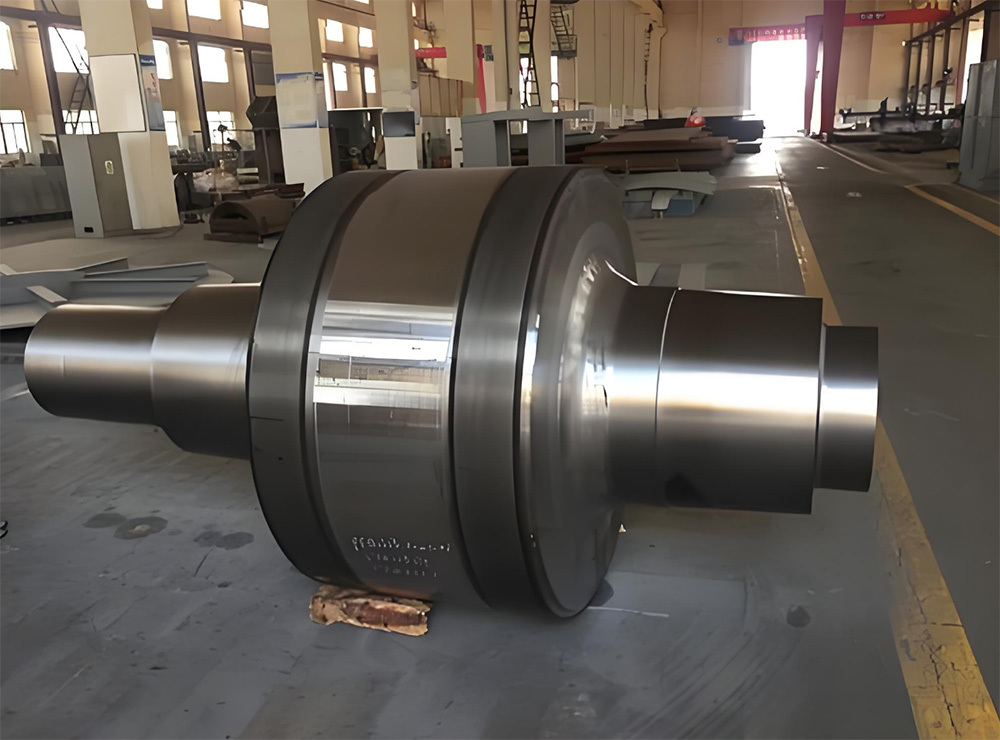
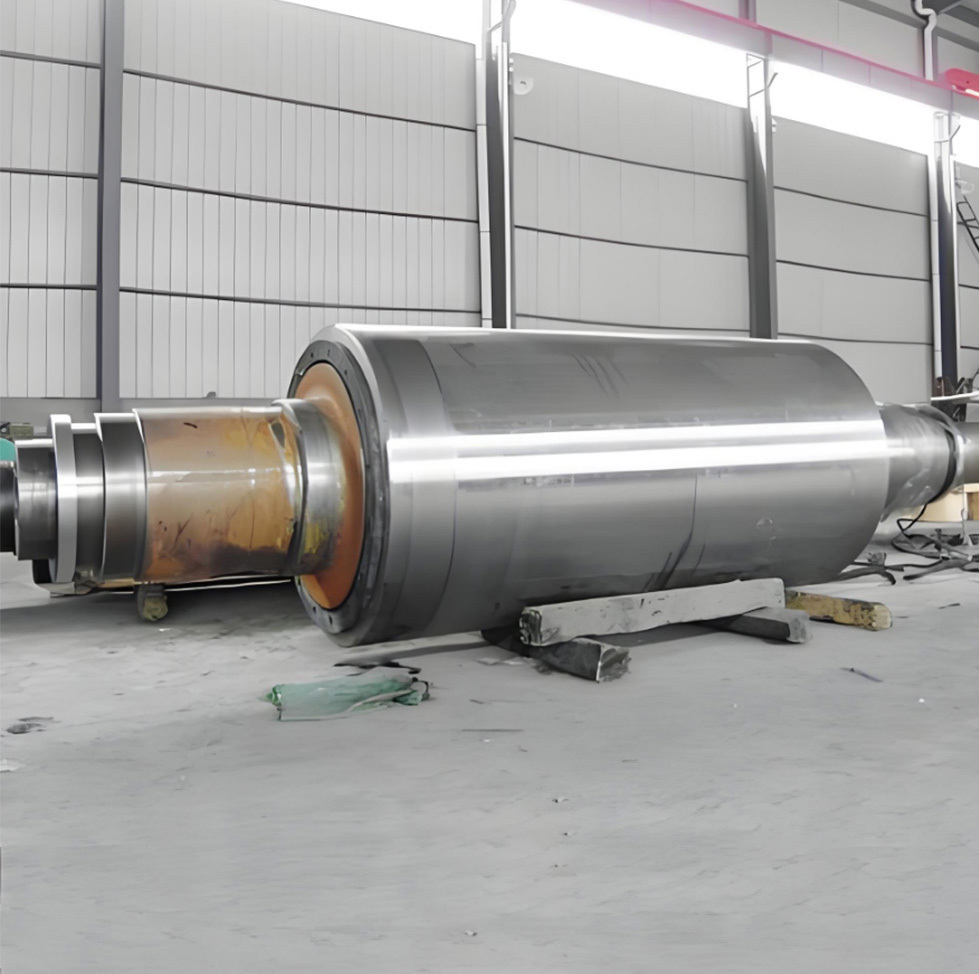
I. Introduction to Bus Alloy Bushings
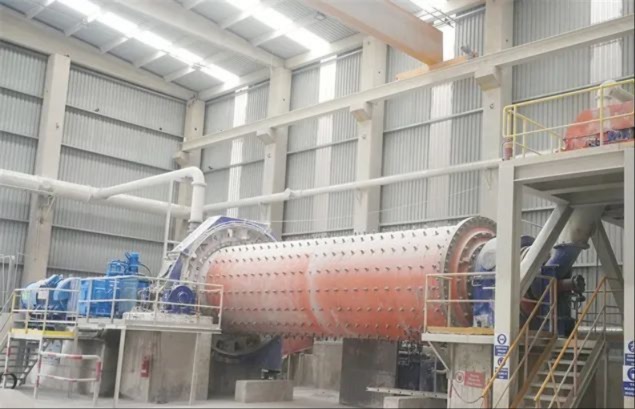
Babbitt bearing bushings are sliding bearing components lined with Babbitt alloy—a type of bearing alloy characterized by a low-melting-point, soft matrix based on tin (Sn) or lead (Pb), uniformly embedded with hard particles. Primarily designed to work in conjunction with journal bearings, they are widely used in the rotating systems of large-scale machinery. Their applications span across various heavy industrial sectors, including cement machinery (such as cement ball mills), steel machinery (like fans in steel plants), chemical processing equipment, paper-making machinery (e.g., drying cylinder machines), petroleum equipment, marine machinery (such as propeller shaft sleeves for ships), compression machinery, coal mining equipment, and mineral-processing systems. Additionally, these bushings are essential components in critical parts like bearings, shaft sleeves, and shaft liners found in large machine tools, hydro turbines, steam turbines, and power generation units.
II. Core Characteristics and Material Classification of Babbitt Alloy Bearings
1. Material Classification and Composition Characteristics
- Tin-based Babbitt alloy: Its main components are tin, antimony, and copper, with trace amounts of lead added in some cases. A typical composition (by mass fraction) includes 3% to 15% antimony, 2% to 6% copper, and 1% cadmium (with the remainder being tin). In China, this alloy is designated by the grade "ZChSnSb," such as ZChSnSb11-6. The microstructure consists of a soft-phase matrix (α solid solution) and hard-phase particles (intermetallic compounds like SnSb, as well as star- or strip-shaped Cu6Sn5 compounds), giving it excellent friction-reducing properties, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It is particularly well-suited for high-speed, heavy-load operating conditions.
- Lead-based Babbitt alloy: Based on lead as the matrix, it contains elements such as antimony and tin, making it relatively low in cost. It is suitable for medium-to-low speed, light-load operating conditions, though its overall performance is slightly inferior to tin-based alloys.
- Cadmium-based Babbitt alloy: Less commonly used, primarily for specific corrosive environments.
2. Performance Advantages
Friction-reducing and wear-resistant properties: After initial running-in when the soft matrix wears down, the hard-phase particles help support the journal, maintaining a low coefficient of friction while also exhibiting excellent conformability and embeddability (capable of accommodating minute impurities).
Mechanics and Environmental Adaptability: Exhibits excellent conformability (adapting to journal eccentricity), anti-galling properties, robust resistance to vibration and compression, as well as superior performance under extreme temperatures and in corrosive environments.
Excellent embeddability: The soft matrix allows tiny hard particles (such as dust or metal debris) to become embedded within it, preventing scratches on the journal bearing.
Good compliance: Capable of slight deformation to accommodate minor shaft deflection or misalignment.
Anti-galling properties: Exhibits a lower coefficient of friction compared to steel journal bearings, making it less prone to cold welding (seizing).
Good oil affinity/wettability: Easily establishes and maintains a lubricating oil film.
Certain fatigue resistance: Capable of withstanding cyclic loads (especially tin-based alloys).
3. Key Points of Manufacturing Process
Bearing Bush Cleaning: Place the steel-shell bearing bush in a 10%-15% cleaning agent solution to remove rust, then rinse thoroughly with 80°C hot water. Finally, use 70°C hot water to eliminate any remaining contaminants. Never touch the cleaned inner surface with your hands.
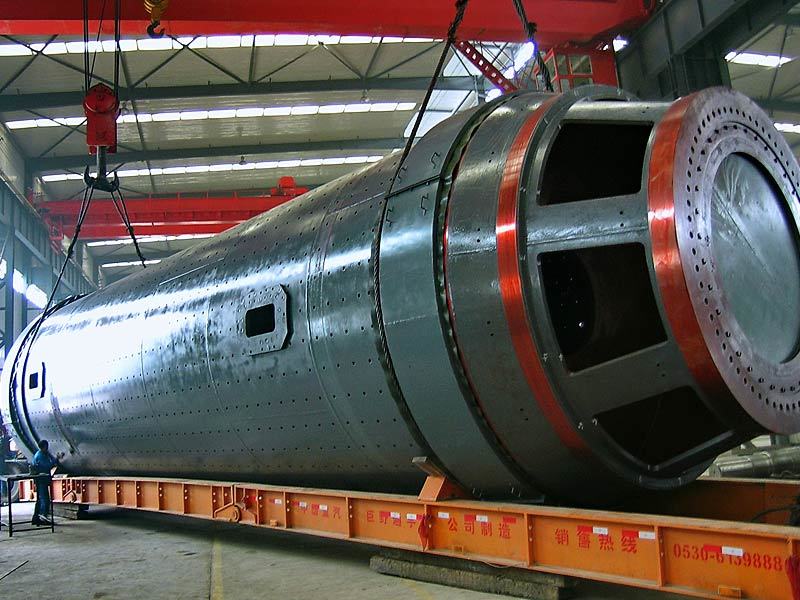
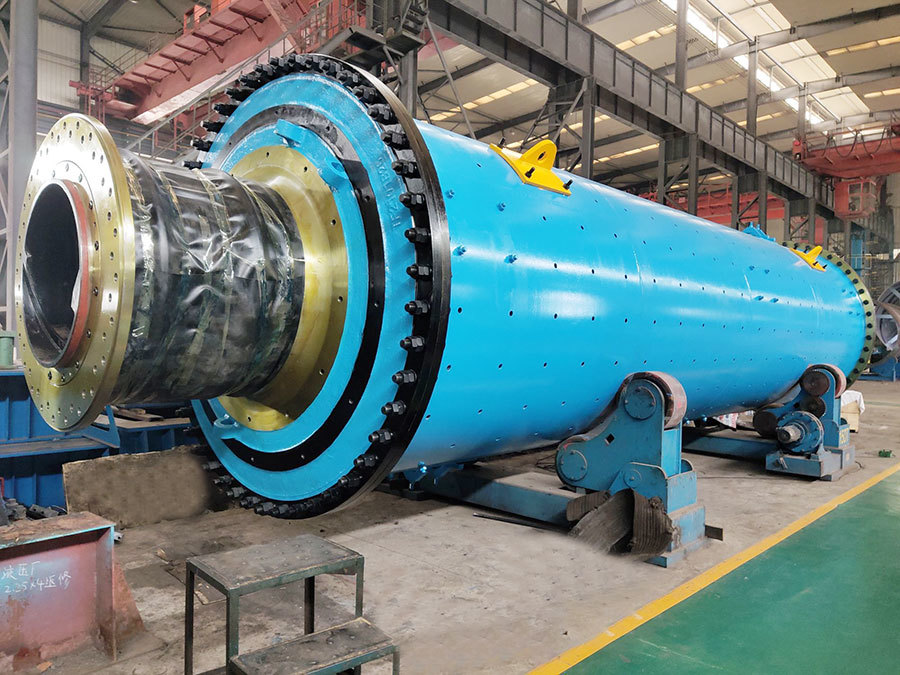
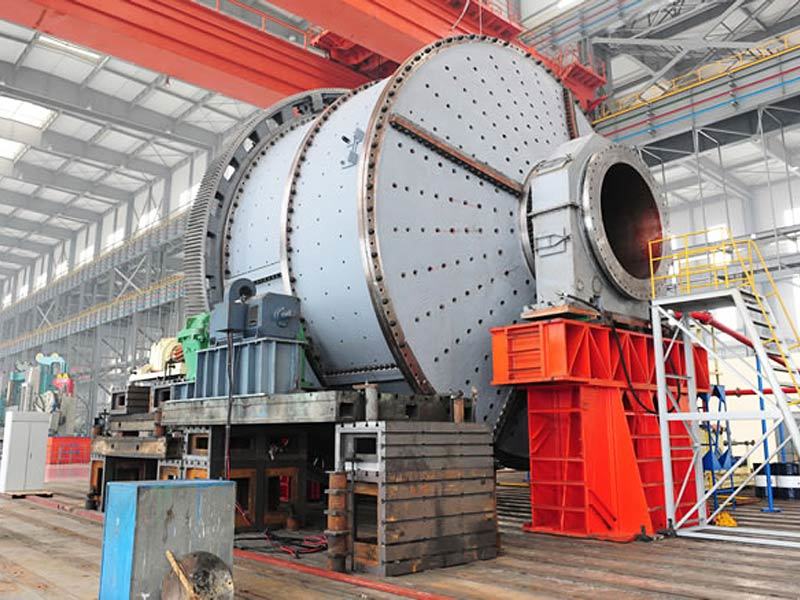
Centrifugal casting: This process uses centrifugal casting technology to ensure an even alloy layer is uniformly bonded to the steel shell, eliminating porosity and shrinkage cavities for a strong, durable bond. The thickness of the alloy layer must be adjusted according to the specific operating conditions: thicker coatings are required for applications involving high loads, high rotational speeds, elevated temperatures, or corrosive environments, while thinner coatings are sufficient under less demanding circumstances.
III. Main Application Scenarios
Babbitt alloy bearings (especially tin-based ones) are widely used in medium-to-high-speed, medium-to-heavy-load sliding bearings that require high reliability, low friction, excellent impact resistance, and effective journal protection.
For example: Large power machinery—such as steam turbines, gas turbines, hydro turbines, main bearings for large generators and compressors, as well as connecting rod bearings.
Marine Power: Diesel engine crankshaft bearings, crosshead bearings, and thrust bearings.
Heavy machinery: Bearings for rolling mills and mining equipment.
Internal combustion engines: (some older or large diesel engines are still in use). Precision machine tool spindle bearings
Common Damages and Repair Methods
- Causes of damage include primarily bearing burn-out (caused by poor lubrication or overload), vibrational wear, and corrosion fatigue; in severe cases, the damaged area can exceed one-third of the total bearing surface.
- Repair method: Cast and refurbish damaged bearing shells by re-casting Babbitt alloy to restore their performance, making it suitable for repairing bearing shells in equipment such as drying cylinders and blowers.
IV. Usage and Maintenance Recommendations
Regular inspections: Monitor the condition of bearing bushings to prevent equipment downtime caused by the escalation of localized damage.
Lubrication Management: Ensure proper lubrication to prevent severe failures such as bearing seizure.
Temperature Control: Avoid prolonged operation in high-temperature environments exceeding the alloy's tolerance range to maintain the stability of its microstructure.
Keywords
Previous: New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology






Bus Alloy Bushings
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
Rotary kiln
-

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-

Lime Rotary Kiln
-

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
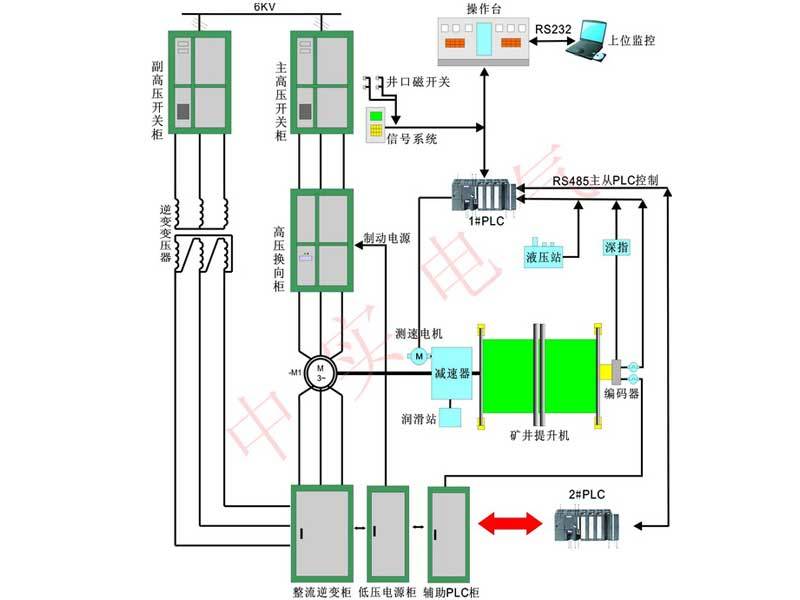
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
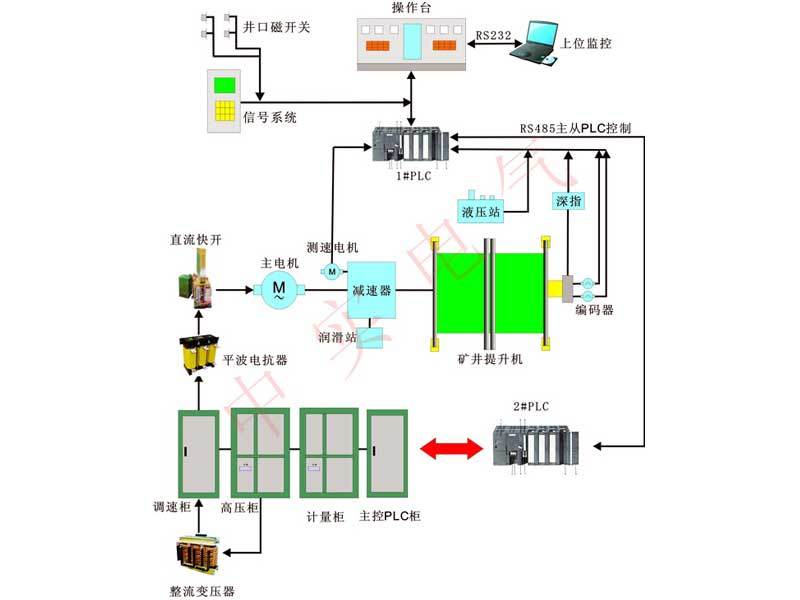
Fully digital DC control system
-
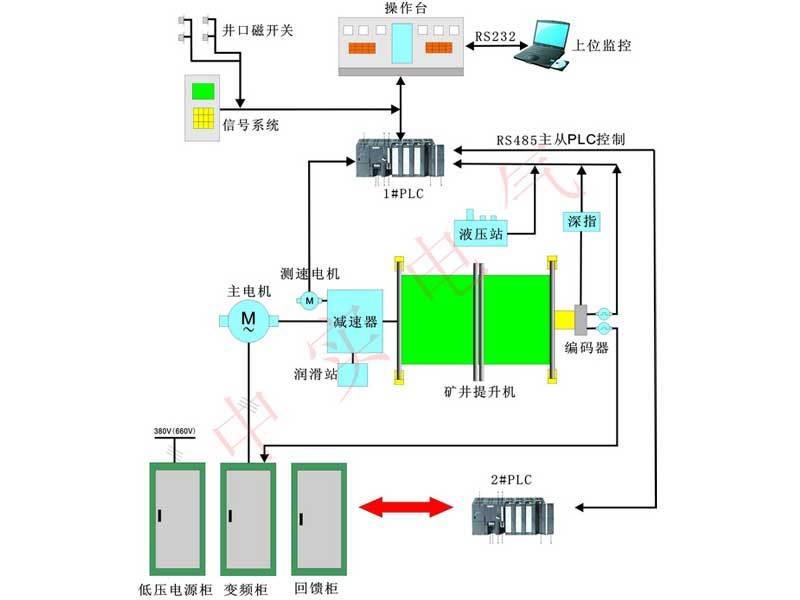
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
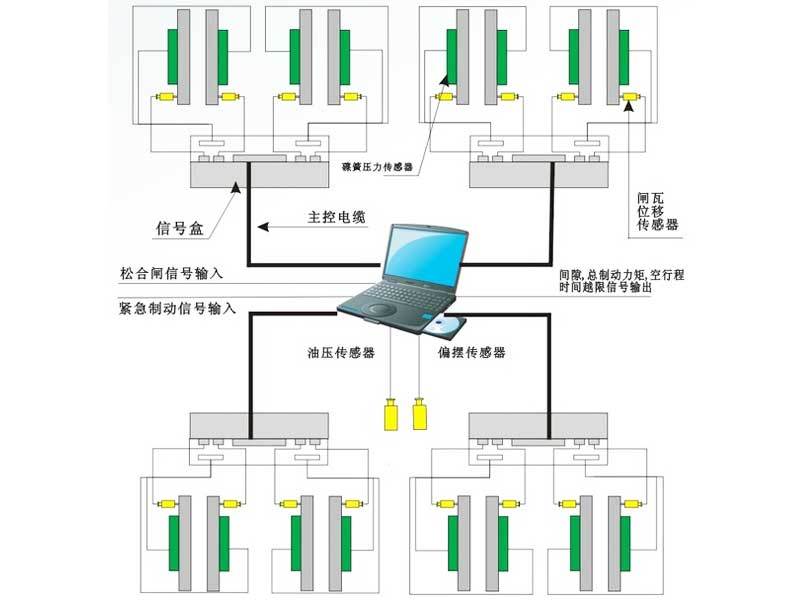
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-

Large base
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-
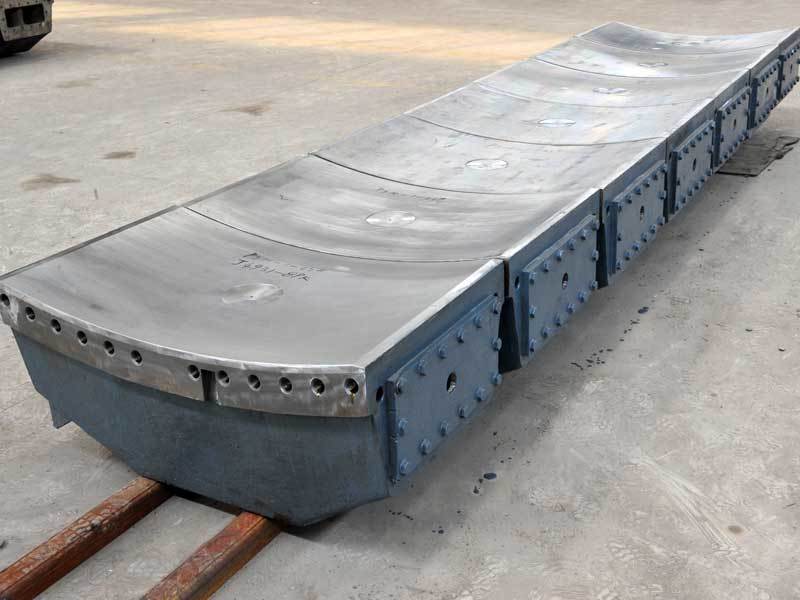

Bus Alloy Bushings
-

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
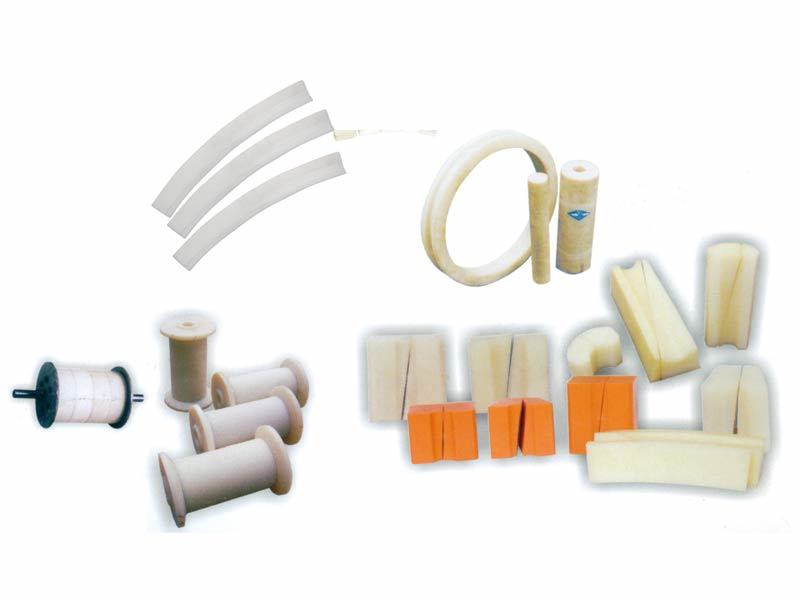

Nylon products
-
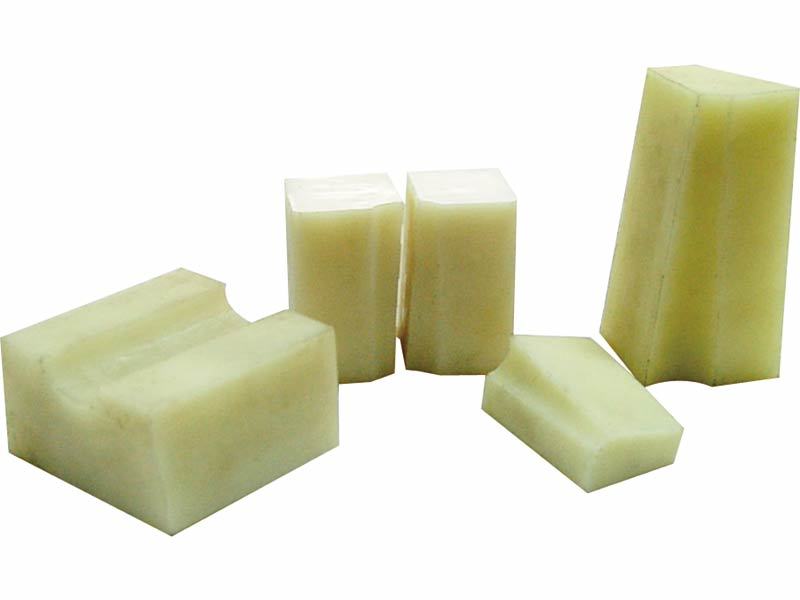

Polyurethane Products
-
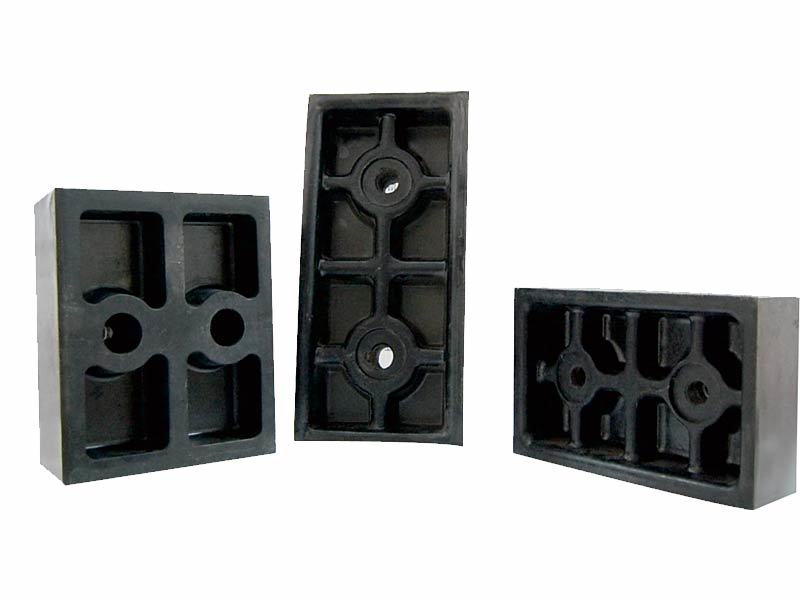

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
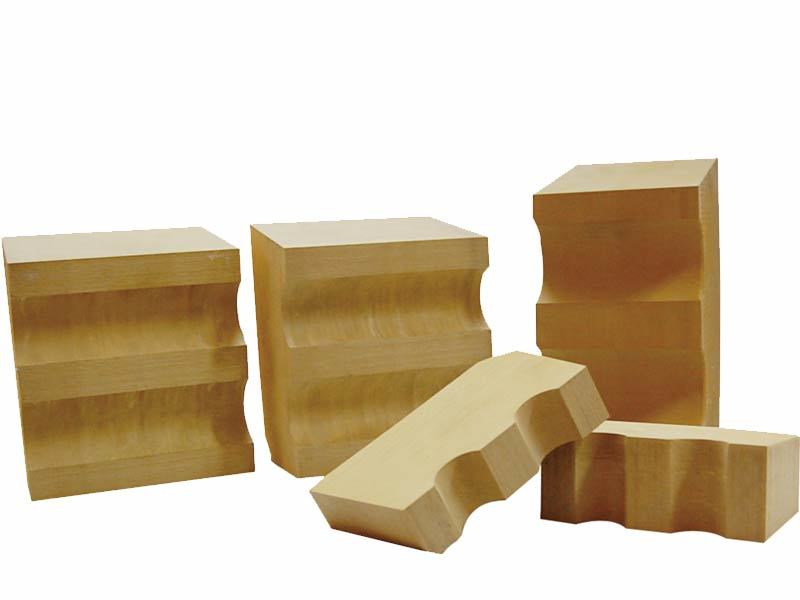

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information