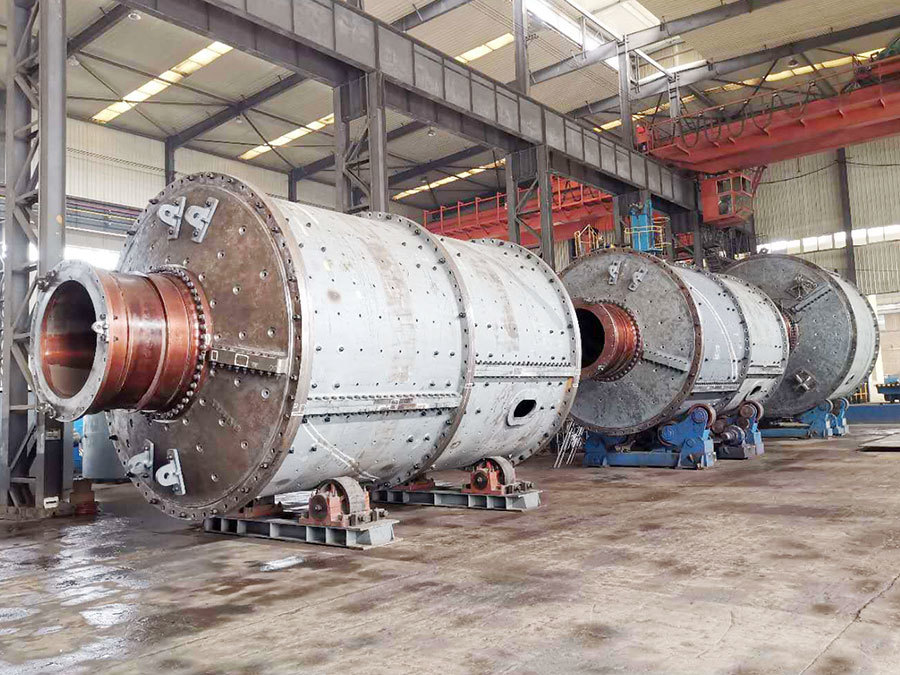
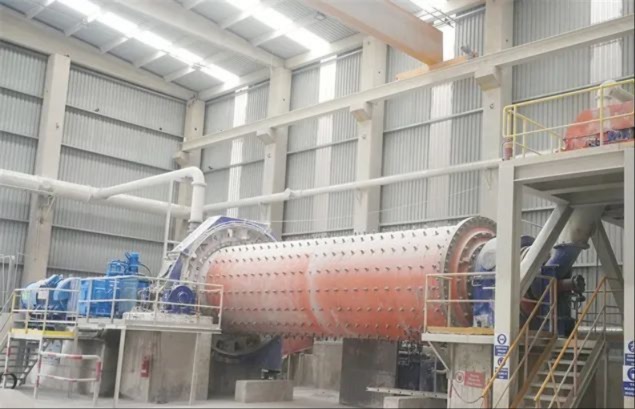
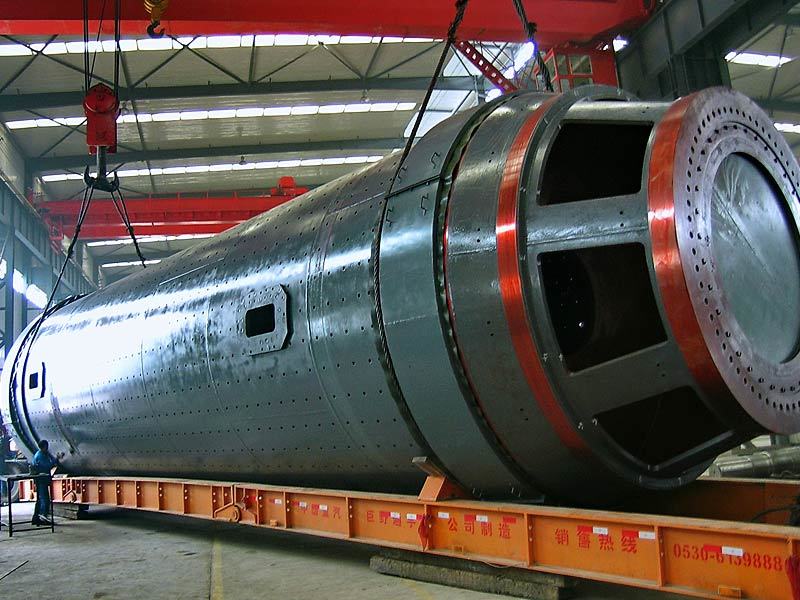
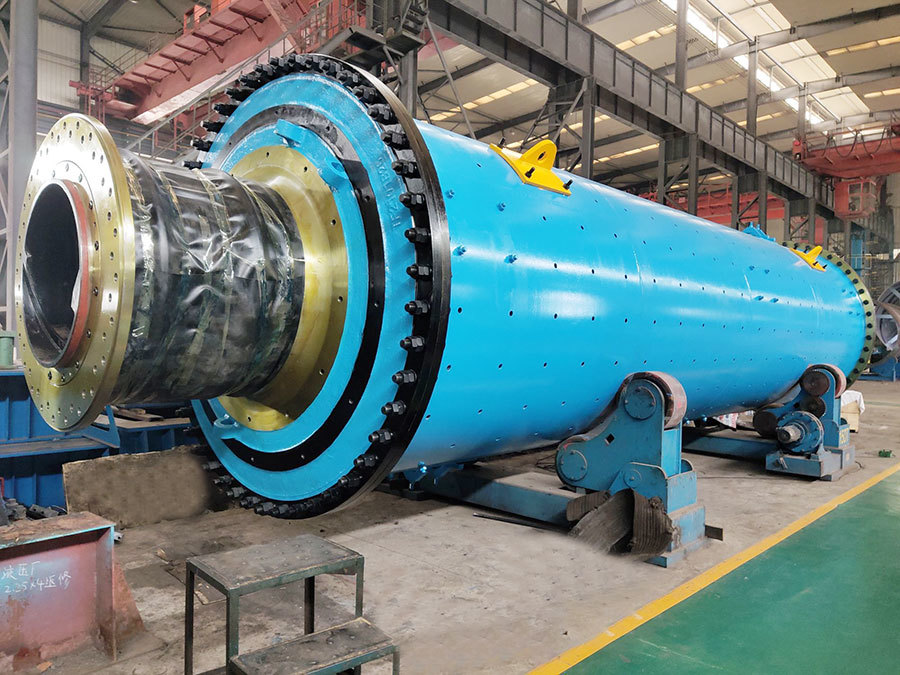
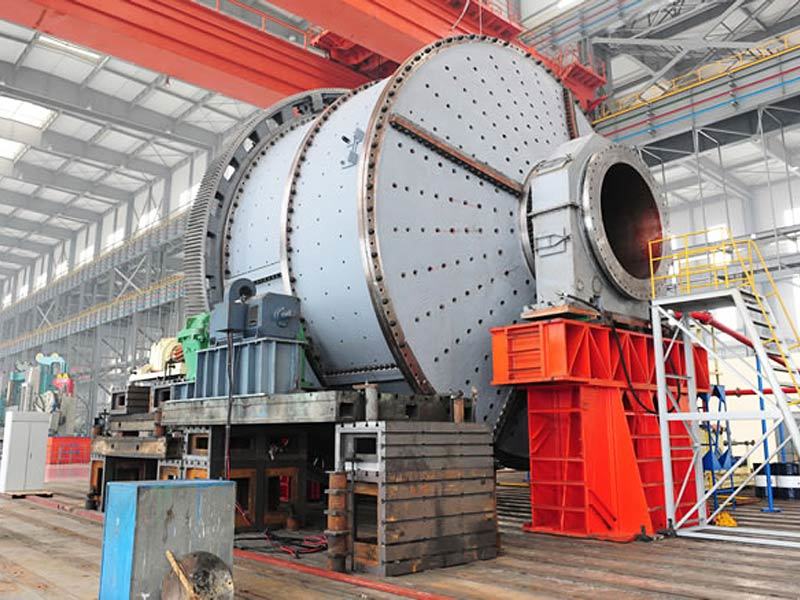
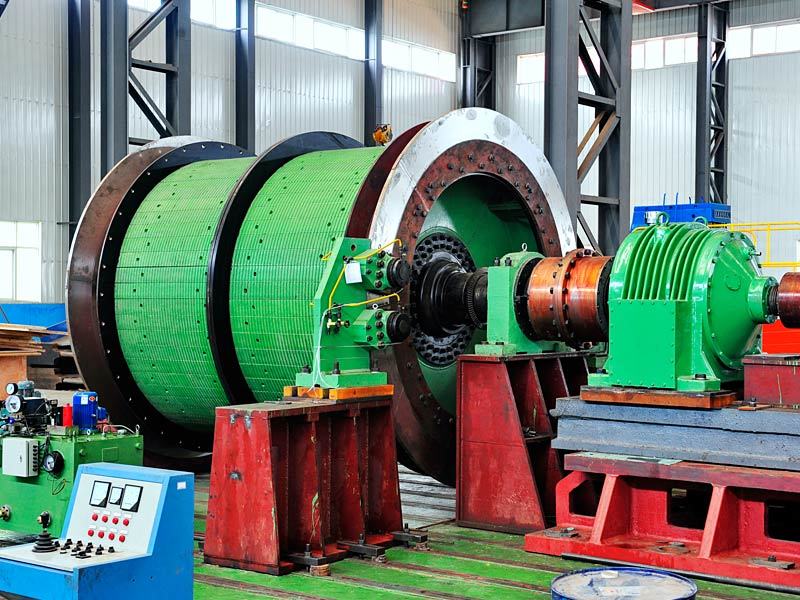
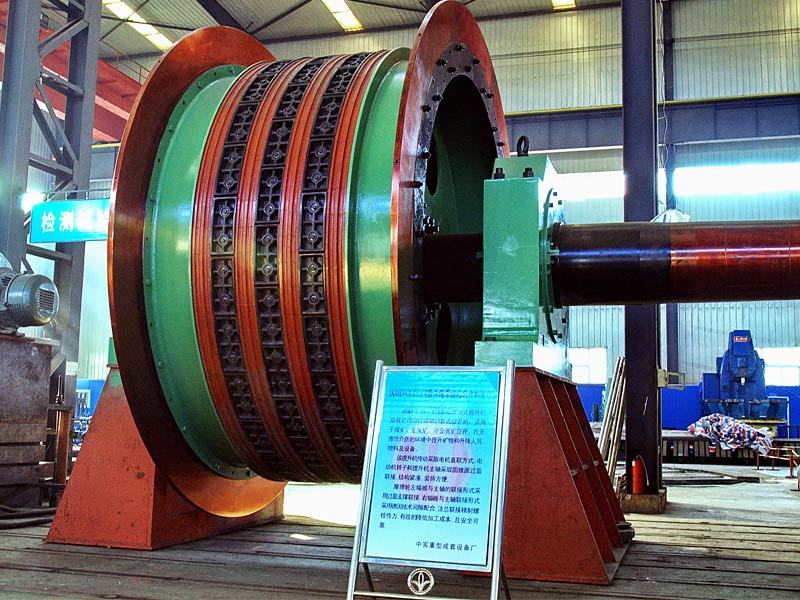
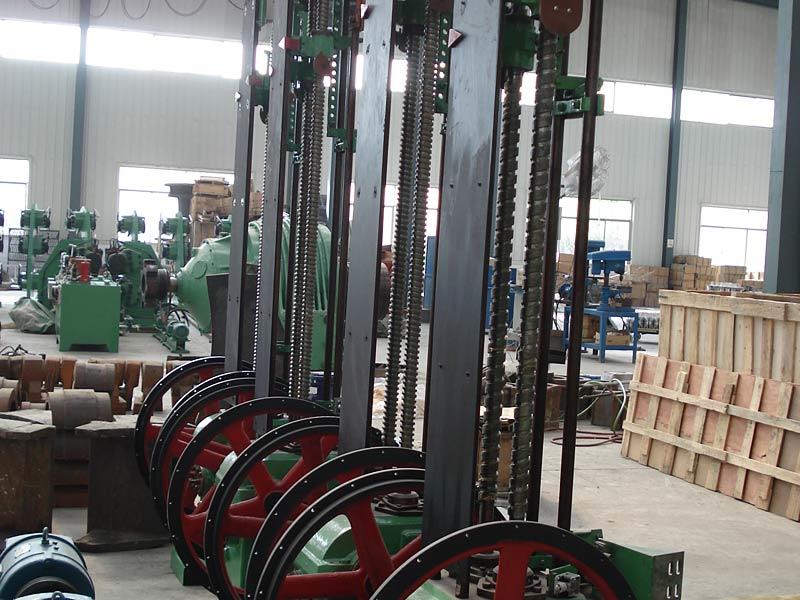
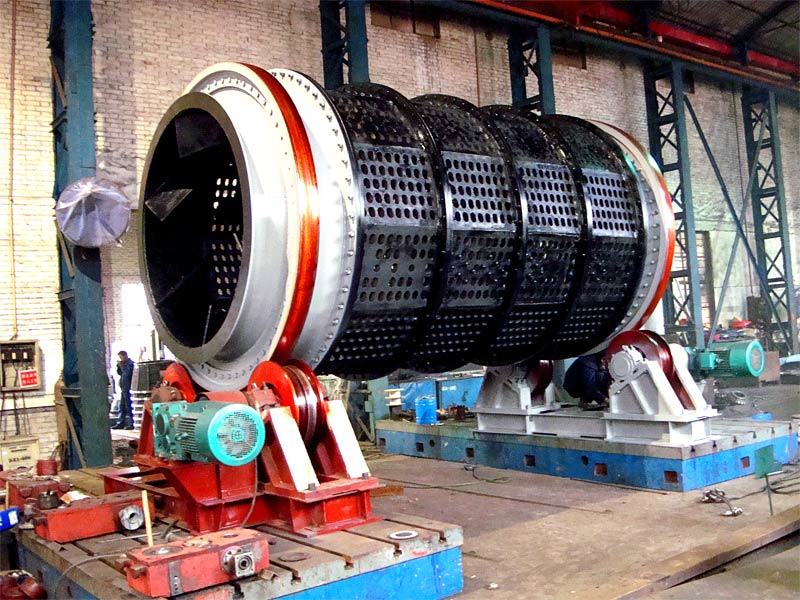
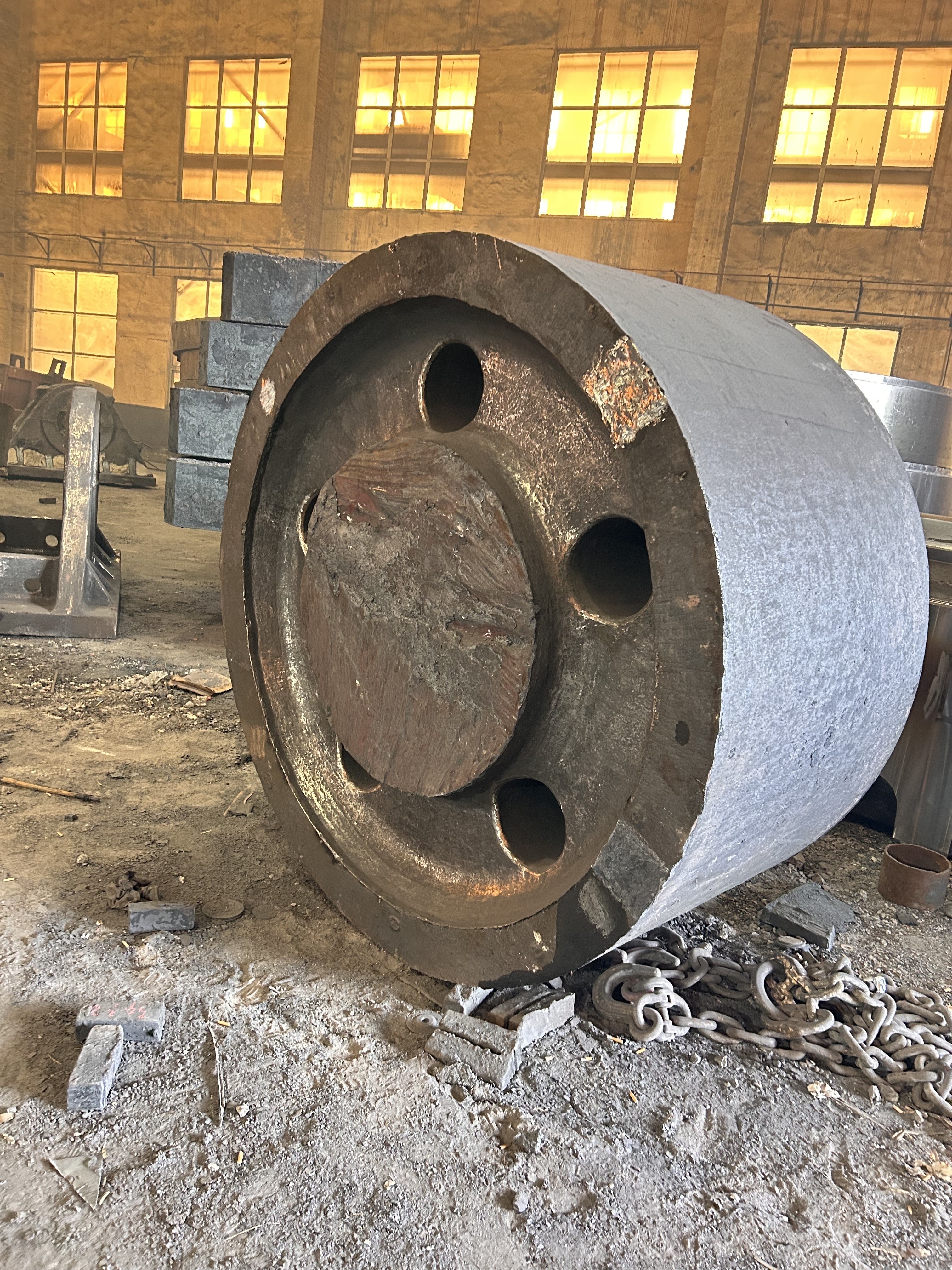
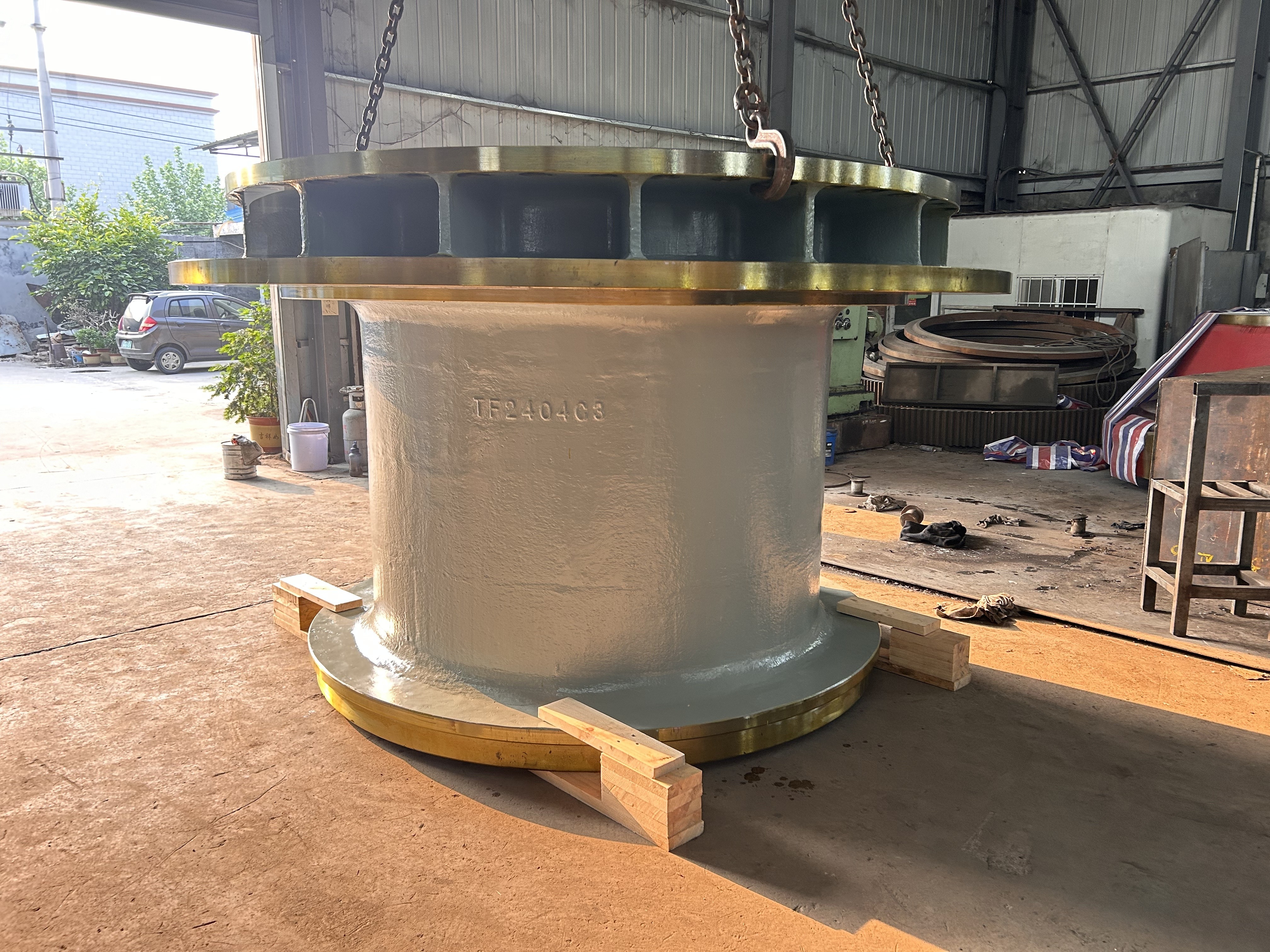
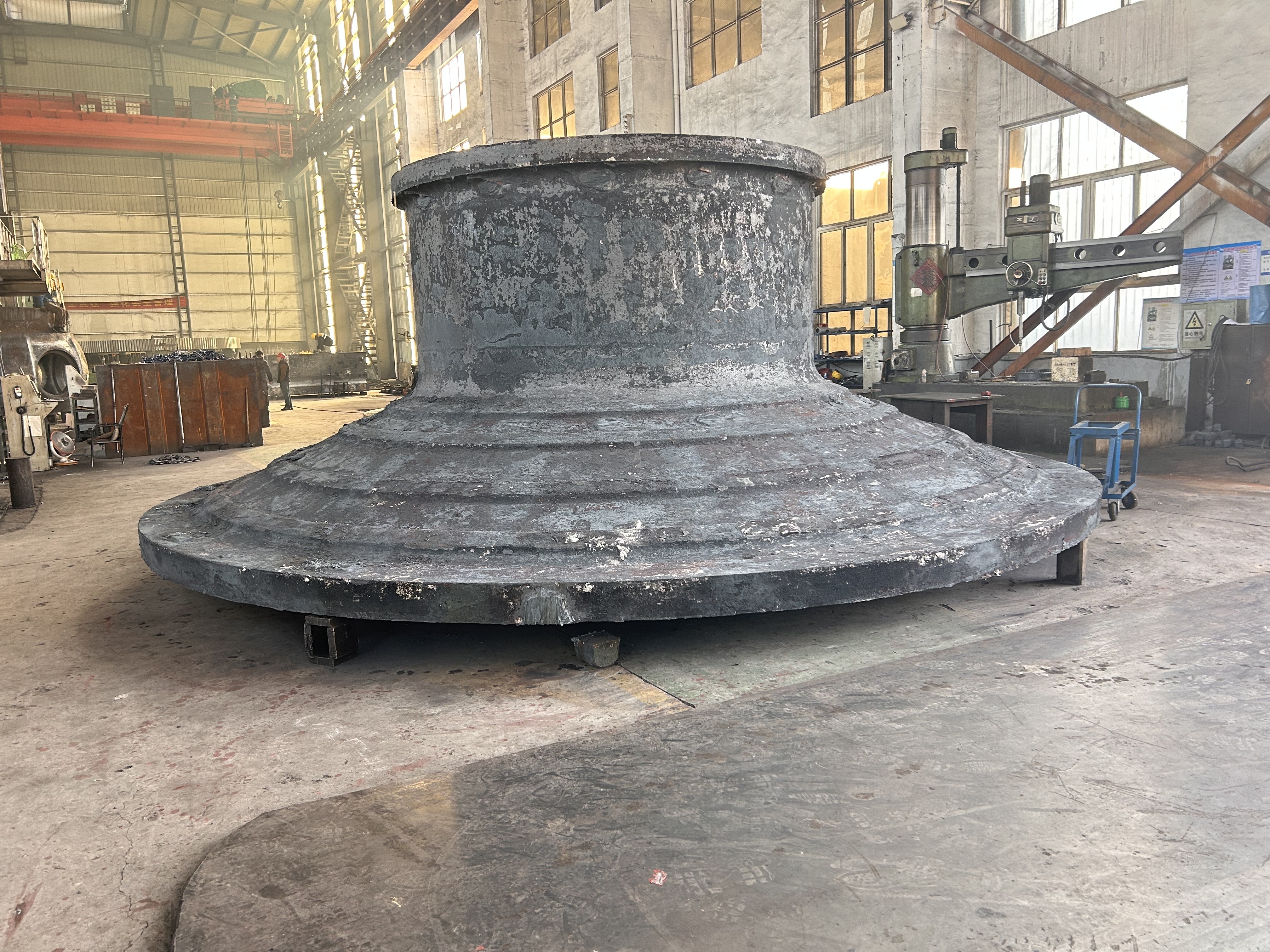
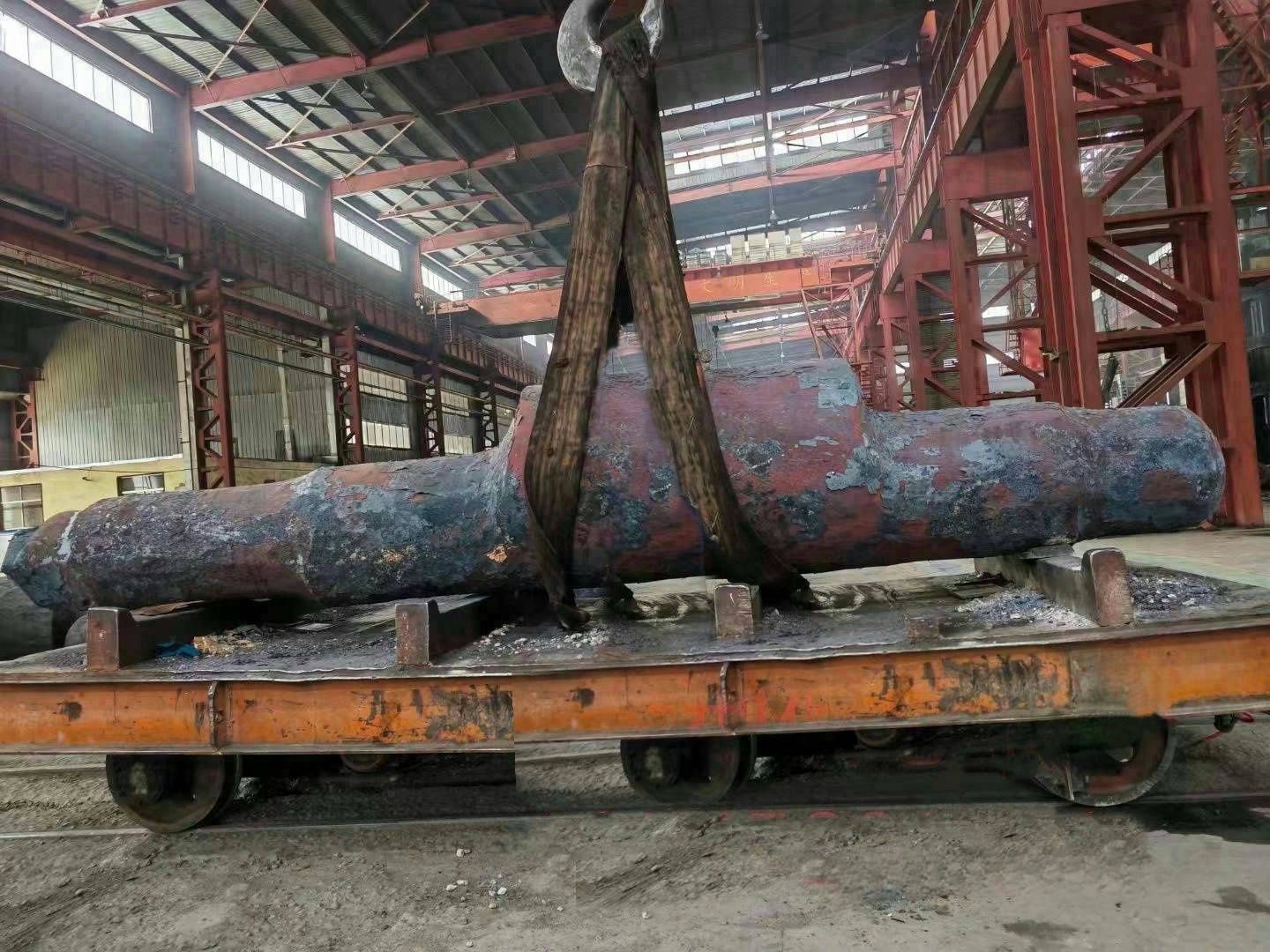
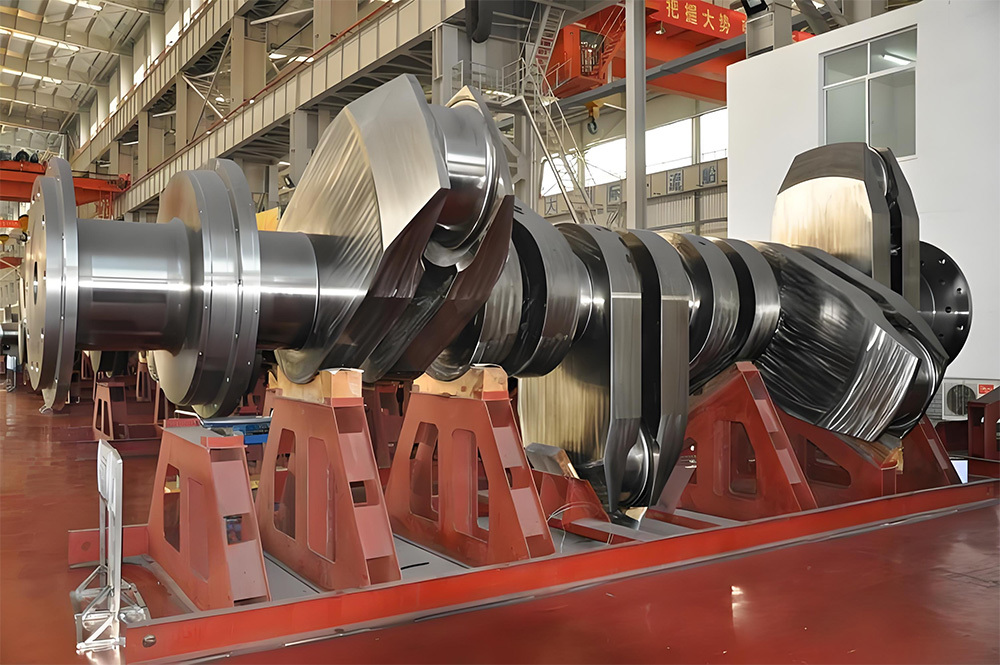
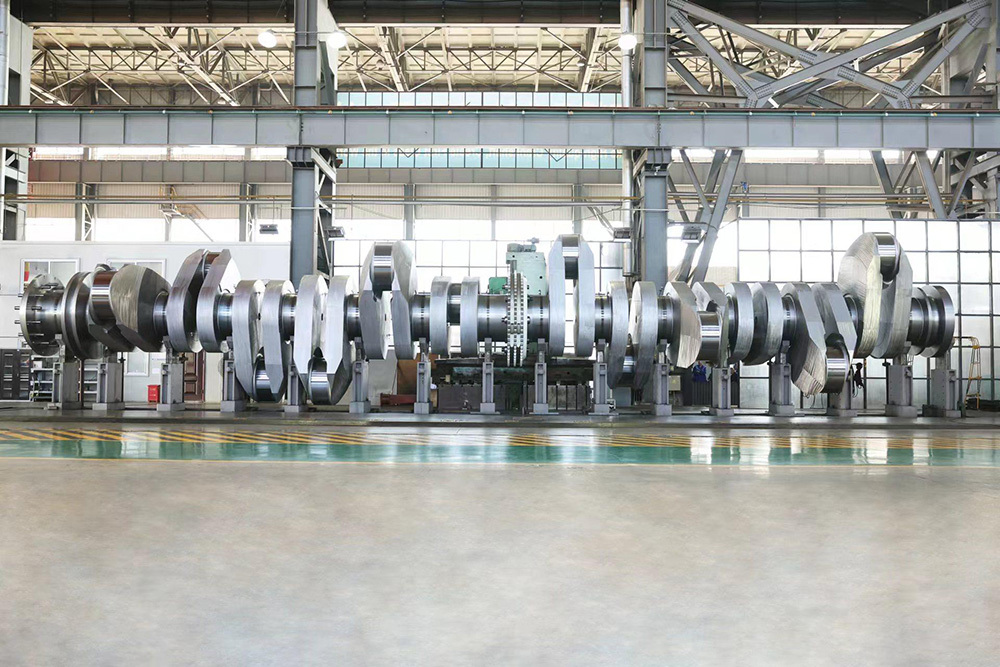
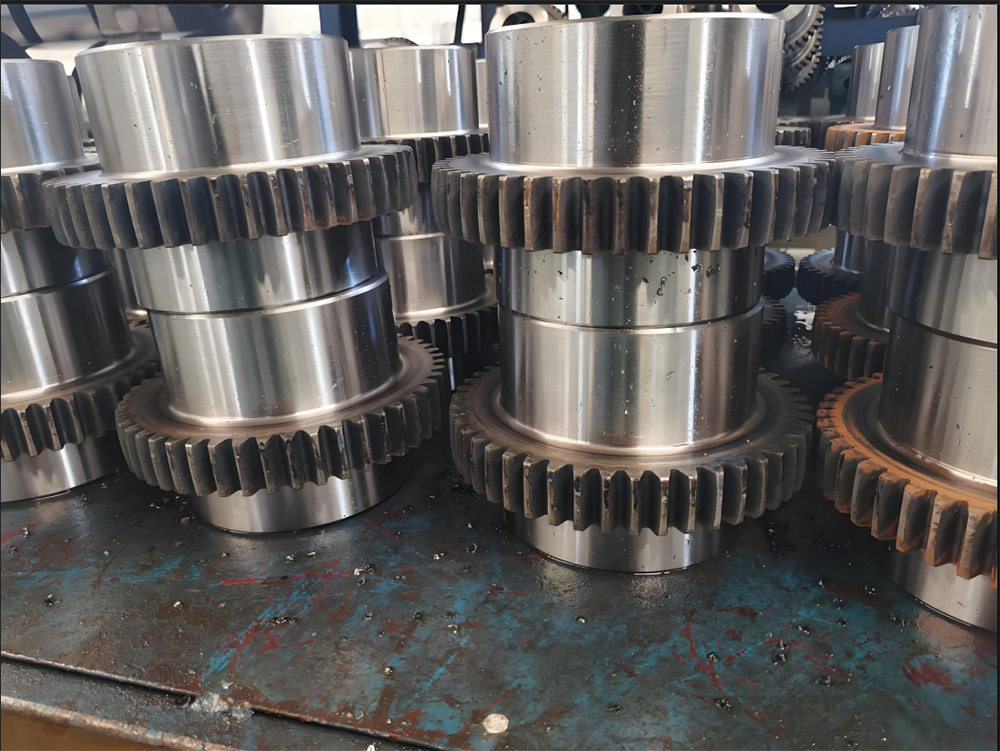
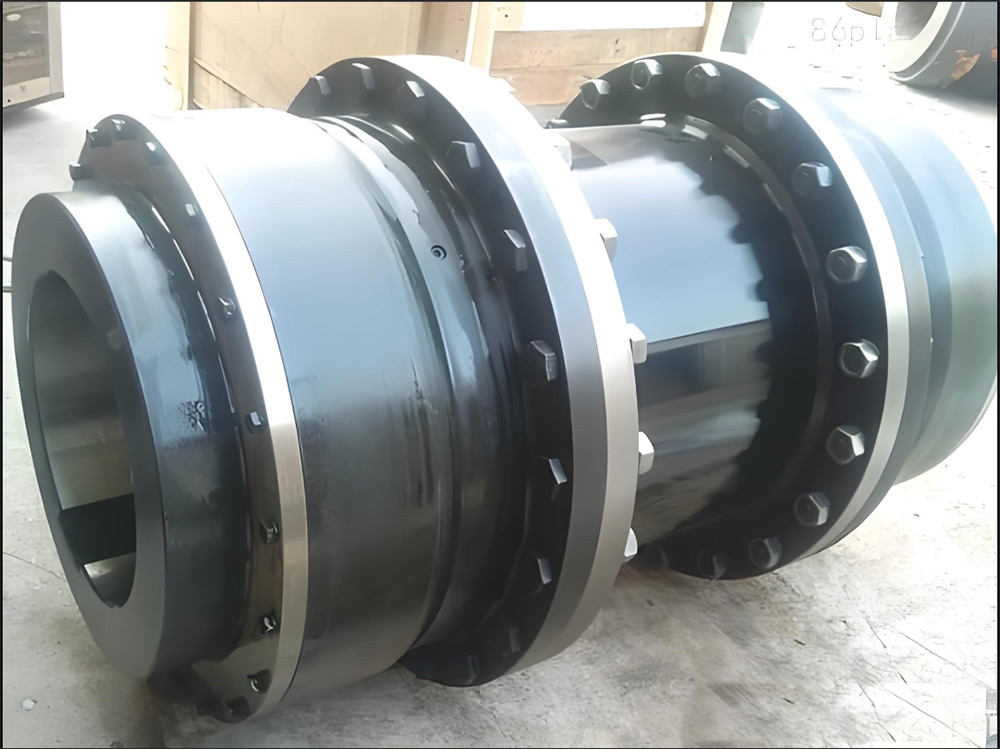
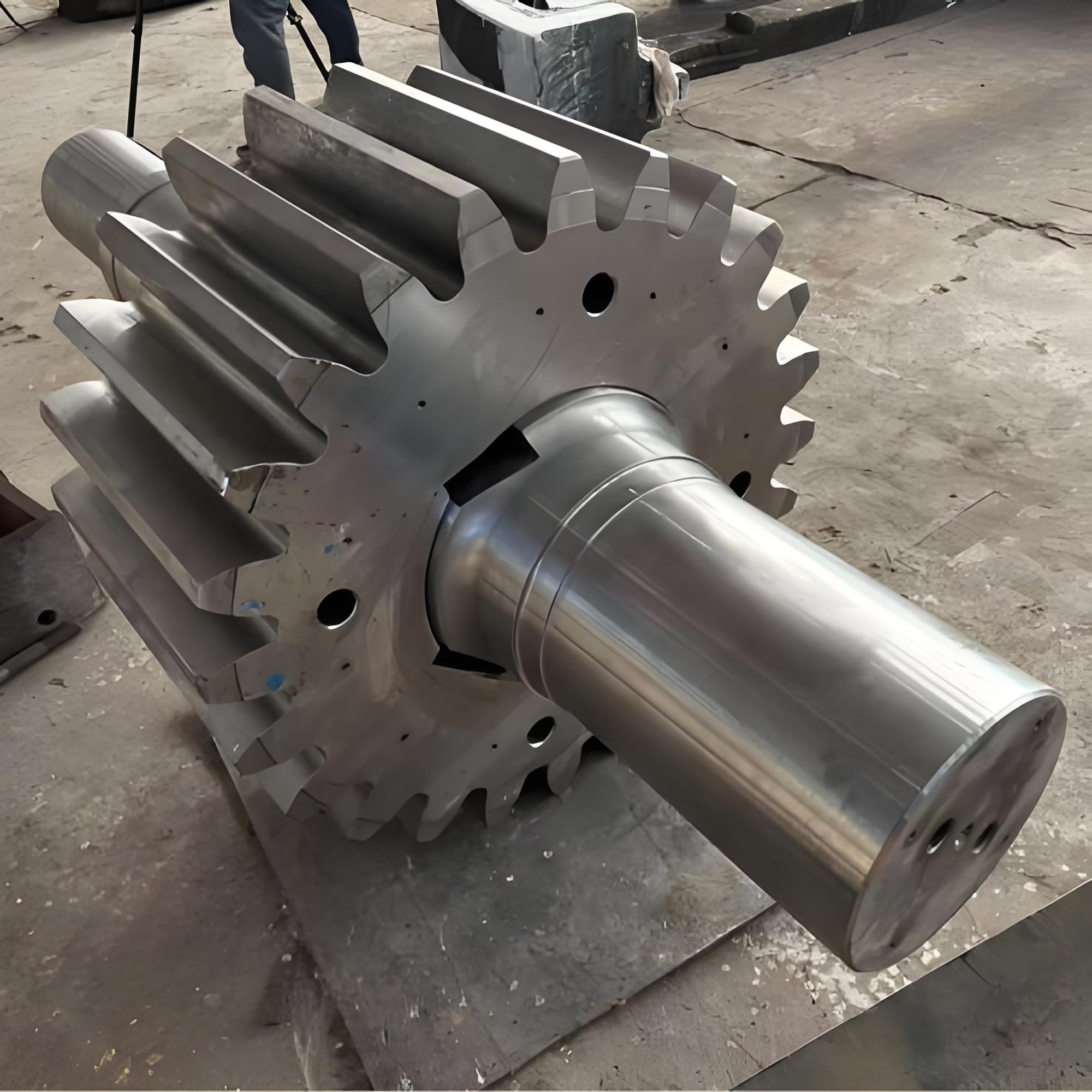
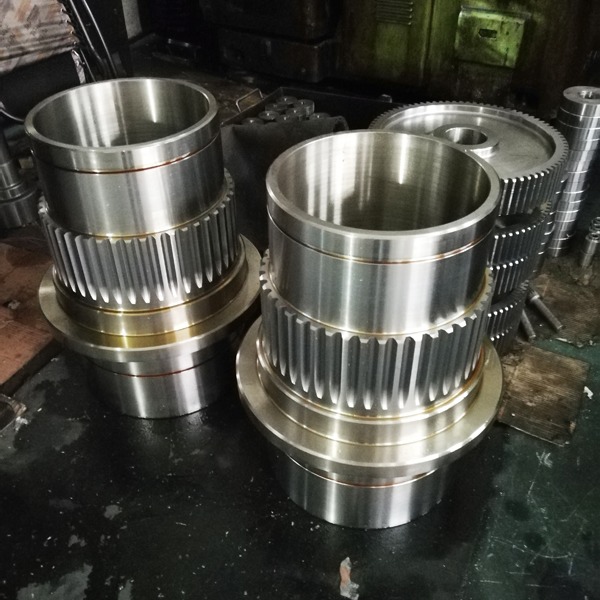
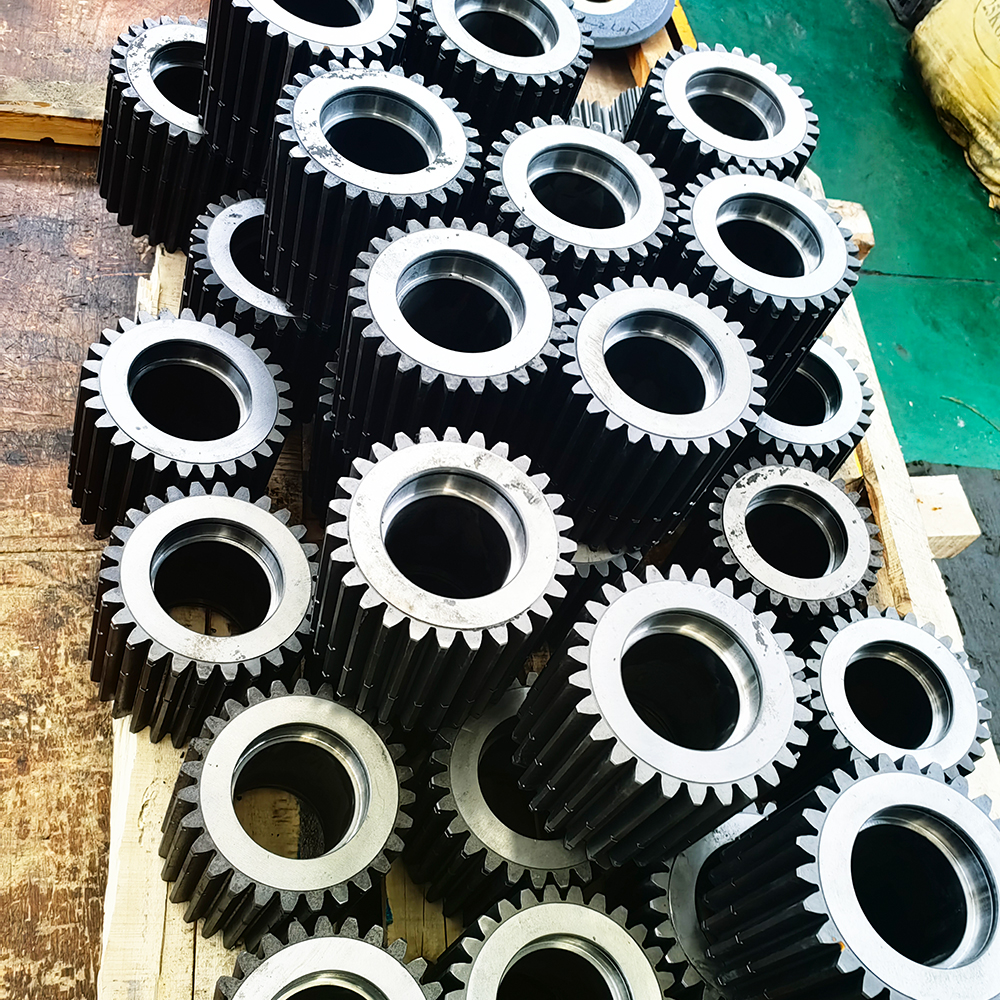
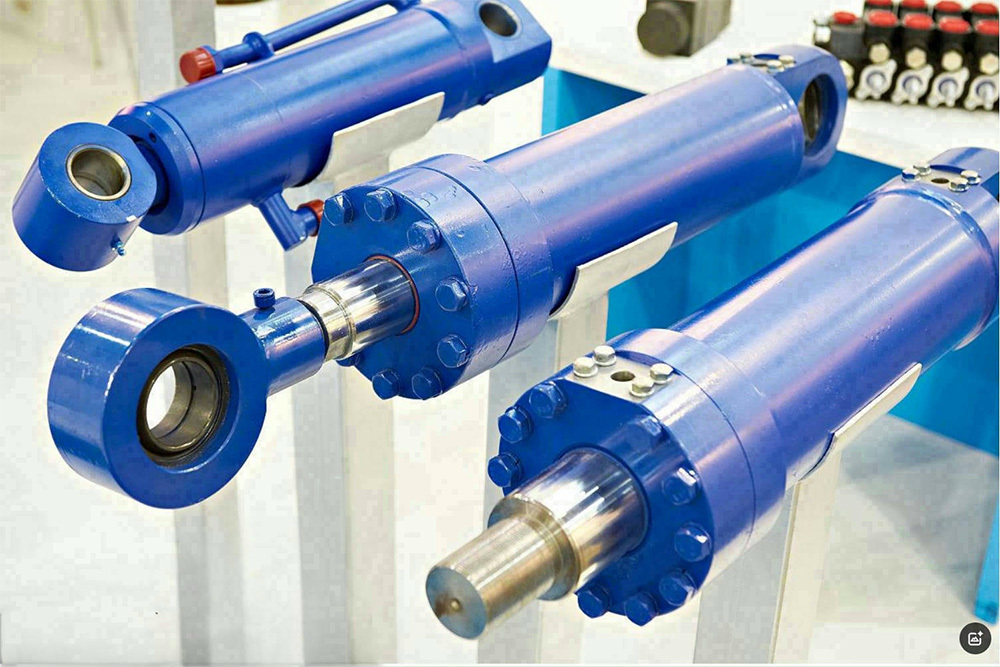
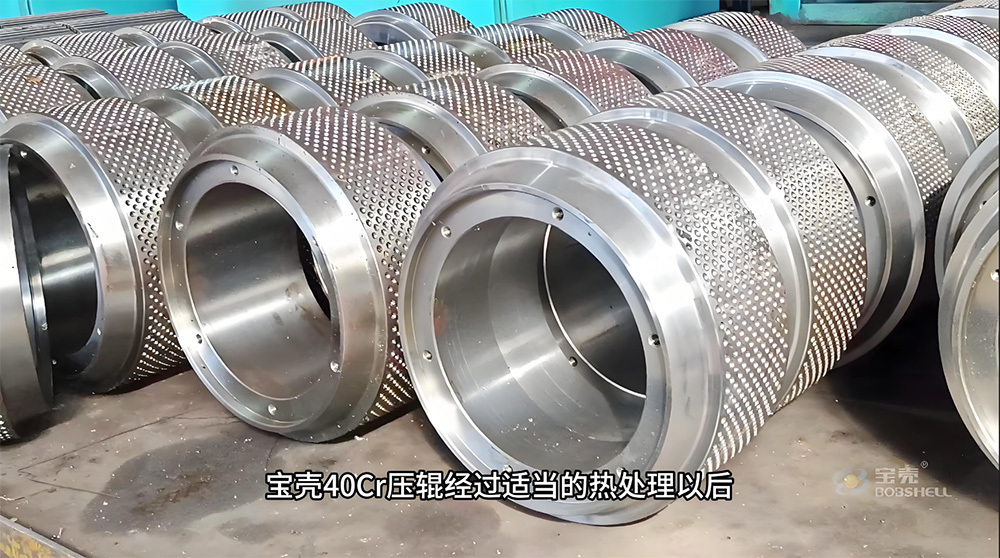
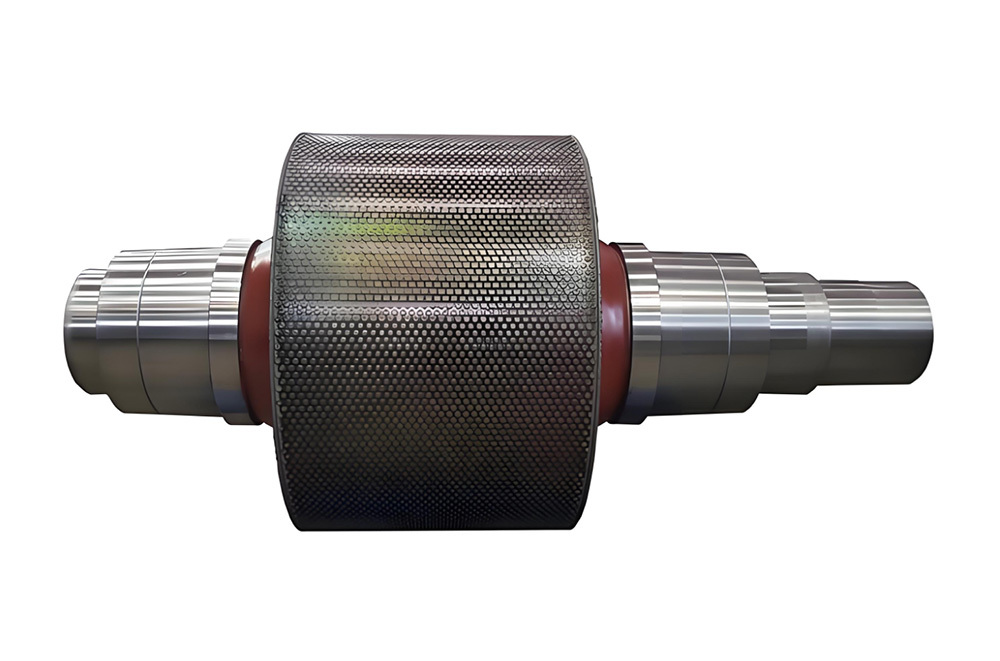
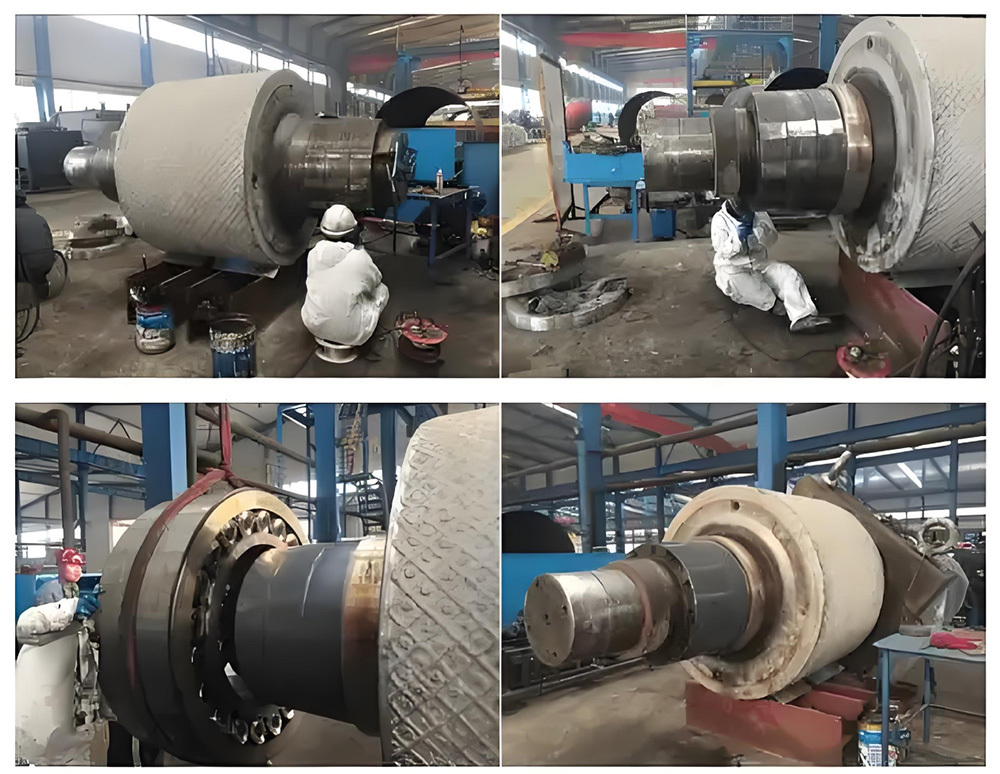
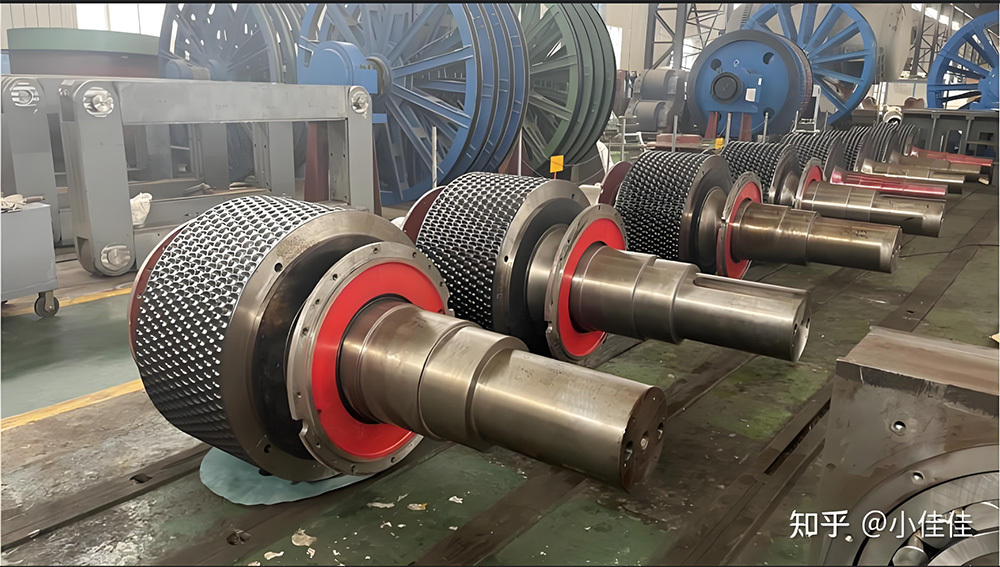
I. Introduction to High-Forged Cast Iron Parts
High-chromium cast iron is a wear-resistant alloy cast iron characterized primarily by its high chromium content (typically ≥11%). With its ultra-high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and moderate corrosion resistance, it has become the material of choice for industries such as mining, cement, and power generation—fields that face extremely demanding wear conditions.
Ingredients and Organization
Element |
Typical Content |
Core Role |
Chromium (Cr) |
11–30% |
Forming M₇C₃-type carbides (hardness HV1500-1800), which create a wear-resistant skeleton and enhance the corrosion resistance of the matrix. |
Carbon (C) |
2.0–3.5% |
When combined with chromium to form carbides, the higher the content, the greater the wear resistance (though brittleness also increases). |
Molybdenum (Mo) |
0.5–3.0% |
Refine grain size, suppress high-temperature pearlite transformation, and enhance hardenability (essential for thick-walled components). |
Copper (Cu) |
0.5–1.5% |
Replace molybdenum to reduce costs and enhance corrosion resistance (especially in acidic conditions). |
Nickel (Ni) |
0.5–1.5% |
Stabilizes austenite and enhances toughness (in synergy with molybdenum) |
Manganese/Silicon |
≤1.5% |
Deoxygenation and flow control—excess can reduce toughness. |
II. Advantages
Wear Resistance Benchmark: Under abrasive wear conditions, its service life is 3 to 5 times longer than that of high-manganese steel and more than twice as long as ordinary white cast iron. The M₇C₃ carbide boasts a hardness nearly equivalent to corundum abrasive (Al₂O₃), making it highly resistant to quartz abrasion (hardness HV1000–1200).
Corrosion and wear resistance: When the Cr content is ≥20%, the material exhibits significantly superior corrosion resistance compared to low-alloy steel in pulp with pH values ranging from 3 to 12.
High-temperature stability: Hardness remains virtually unchanged below 600°C (outperforming most wear-resistant steels)
III. Key Control Points in Manufacturing Processes
1. Casting Process
Melting: Medium-Frequency Induction Furnace + Argon Deoxidization (reduces slag inclusion)
Pouring: Use low-temperature, rapid pouring (1380–1420°C) to prevent chromium oxidation.
Chill design: Must use insulated chills combined with a heating agent to compensate for the high-chromium iron's shrinkage rate (≈2.1%).
2. Heat Treatment Core
Phase |
Process parameters |
Purpose |
Equipment Requirements |
Softening Annealing |
950℃ × 4h → Furnace cool to 700℃ |
Eliminate casting stress—preparing for machining |
Controllable Atmosphere Furnace |
Quenching |
980-1050℃ × 2-4h → Air cooling/Oil cooling |
The matrix transforms into martensite, achieving high hardness. |
Precise temperature control (±10℃) |
Tempering |
200–450°C × 4–8 hours |
Eliminate quenching stress and adjust toughness. |
Avoid the 450-550℃ brittle zone |
Warning: Thick-walled components (>100mm) must undergo stepwise heating (300°C/h); otherwise, cracking is inevitable!
IV. Typical Application Scenarios and Failure Analysis
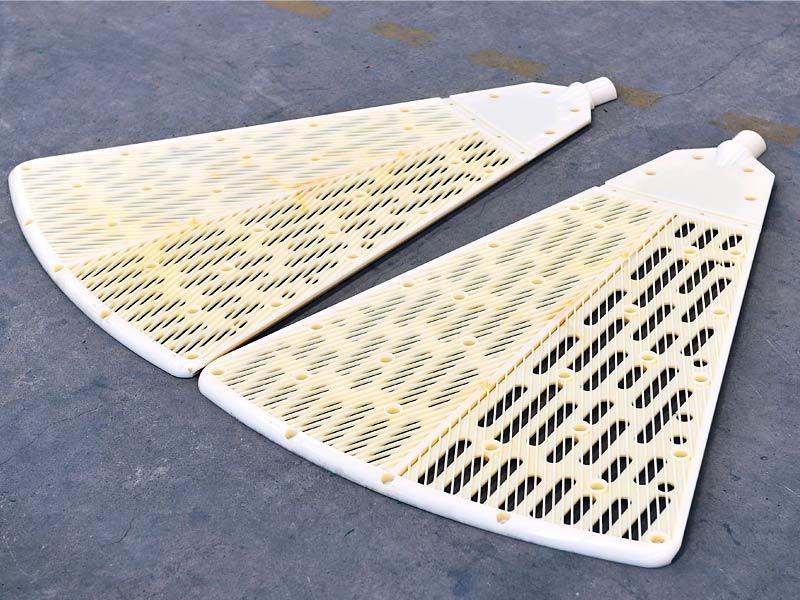
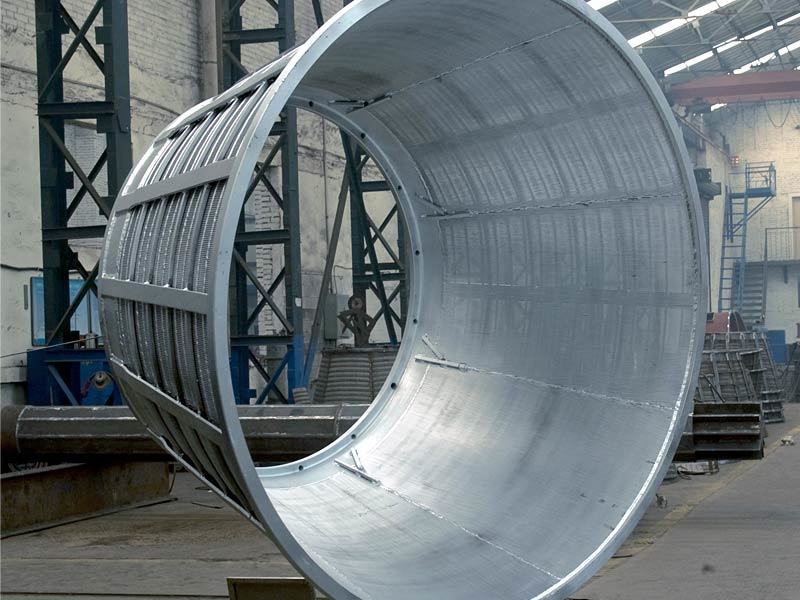
Major application areas: High-chromium cast iron components are widely used in mining, cement production, power generation, road construction machinery, and refractory materials. Since the 1980s, they have also been increasingly employed in manufacturing the chambers of shot blasting machines, as well as in producing shot blaster blades and lining plates—effectively preventing high-speed, densely packed shot streams from penetrating the steel shell. Meanwhile, these materials find extensive applications in fields such as construction, power generation, and mining as well.
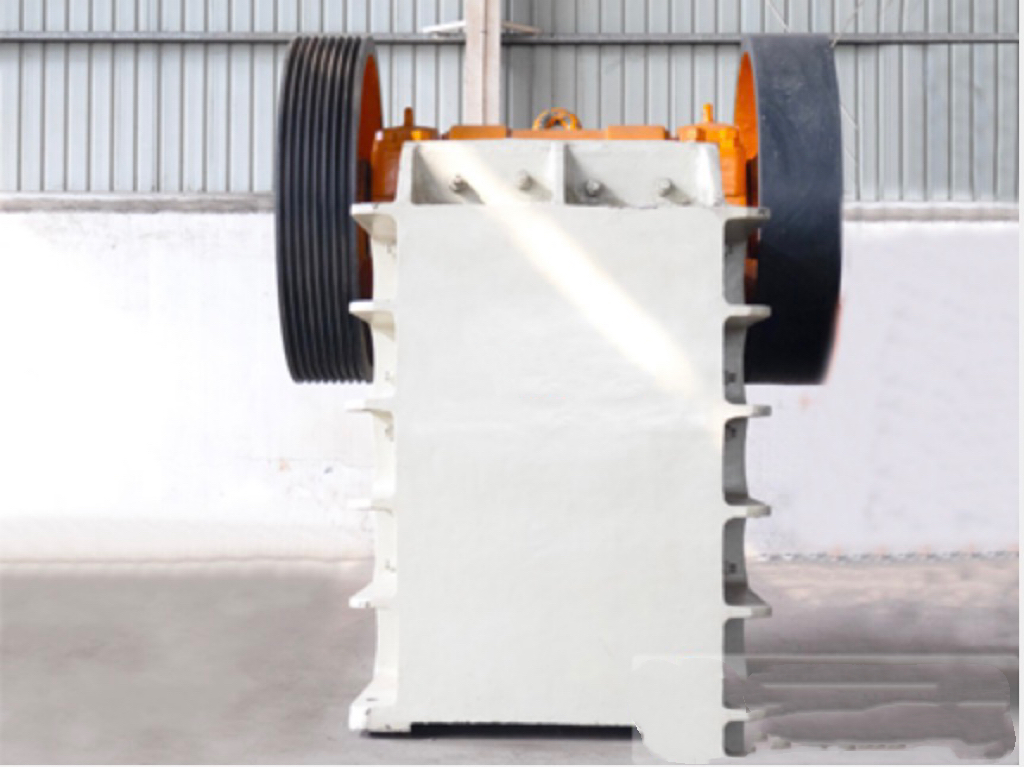
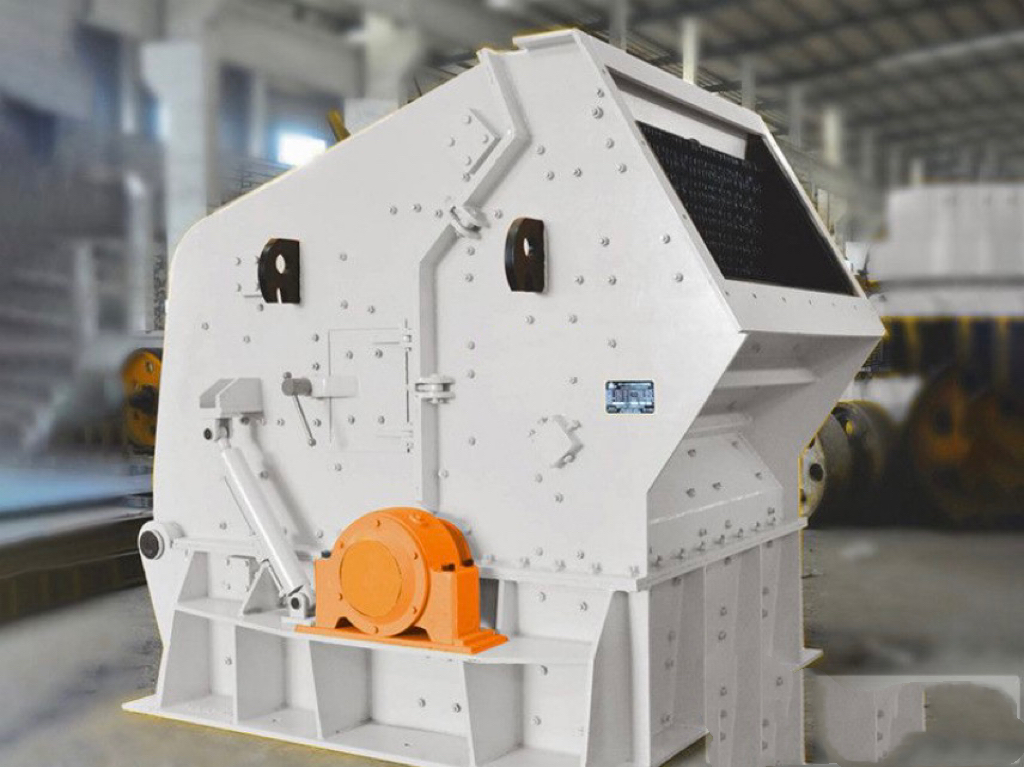
Typical application example: As a highly wear-resistant material, it has been effectively used in mechanical and metallurgical equipment such as crushers, grinders, and material-handling systems. It is particularly widely applied to components subjected to abrasive and impact wear, including crusher rollers, hopper liners, blast-furnace charging chutes,料斗 (hoppers), coal-conveying trough linings, roller casings for coal mills, rolling rolls, and flow-path components of slurry pumps. For instance, the high-chromium grooved liners installed at Henan Xiangshan Group (formerly Henan Yanshi Cement Plant) in early 1988 have operated successfully for 12 years, significantly reducing the plant’s costs and minimizing the frequency of liner replacements.
Keywords
Previous: High-manganese steel product series



High-precision cast iron parts
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-
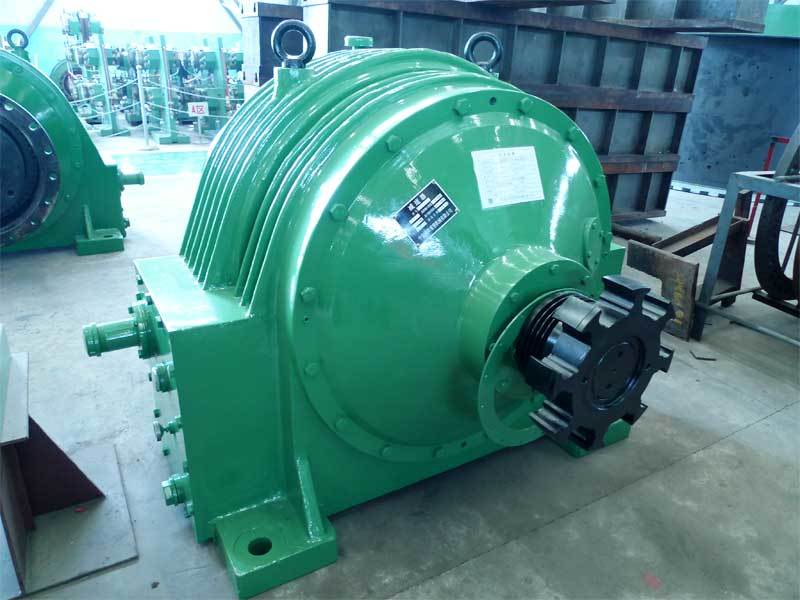

Planetary Gear Reducer
-
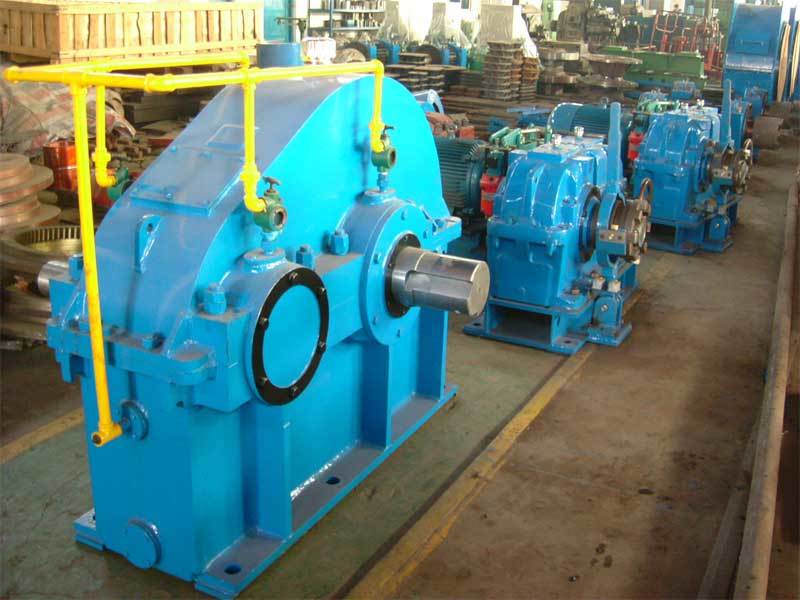

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
Rotary kiln
-
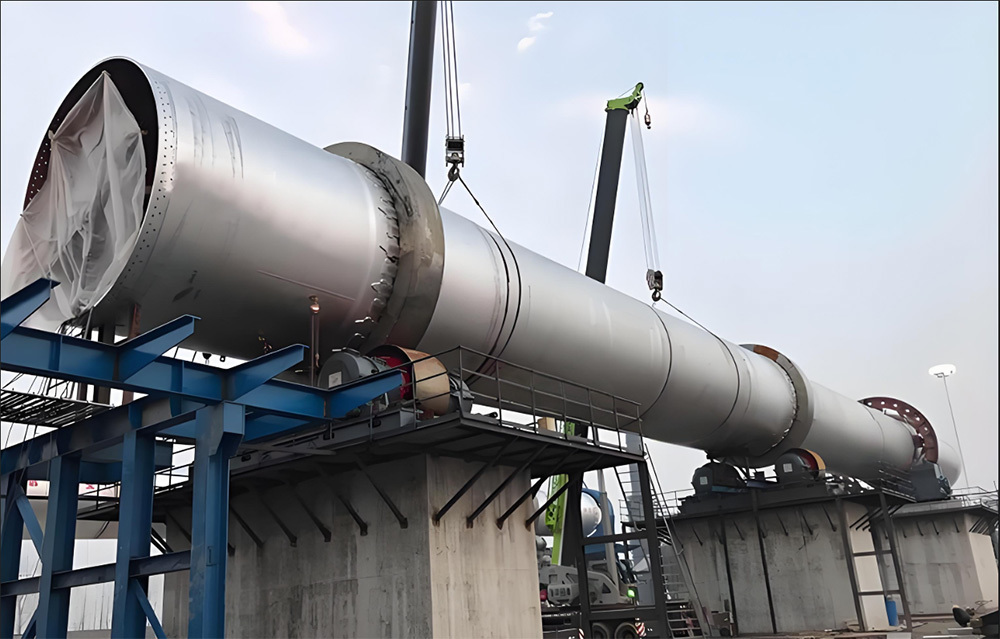

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-
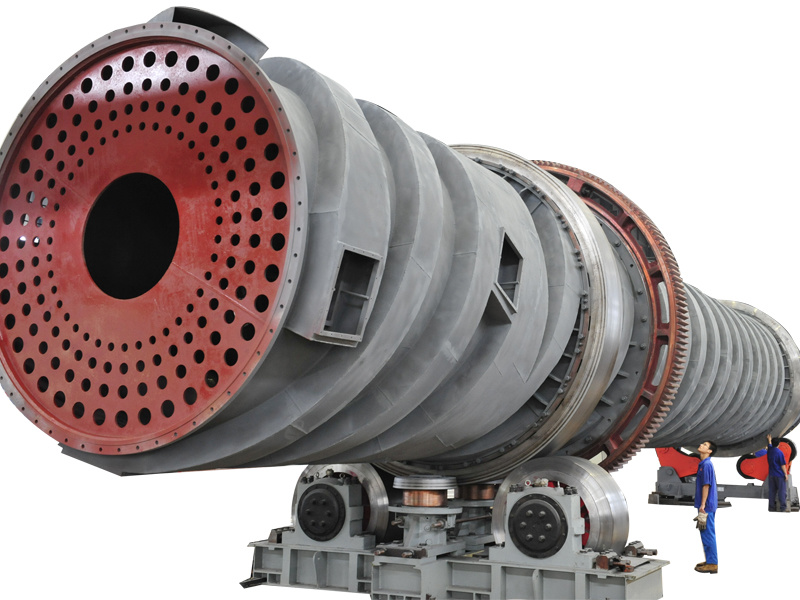

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-

Lime Rotary Kiln
-

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-
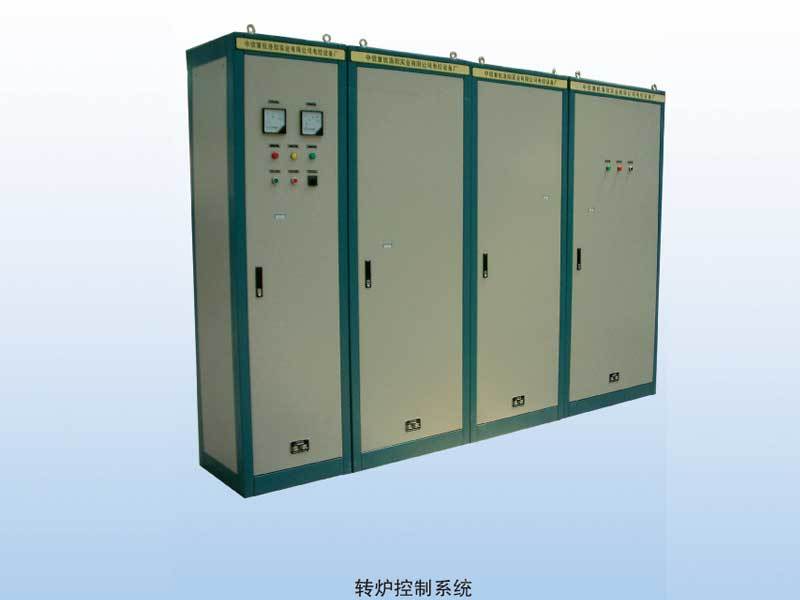

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-
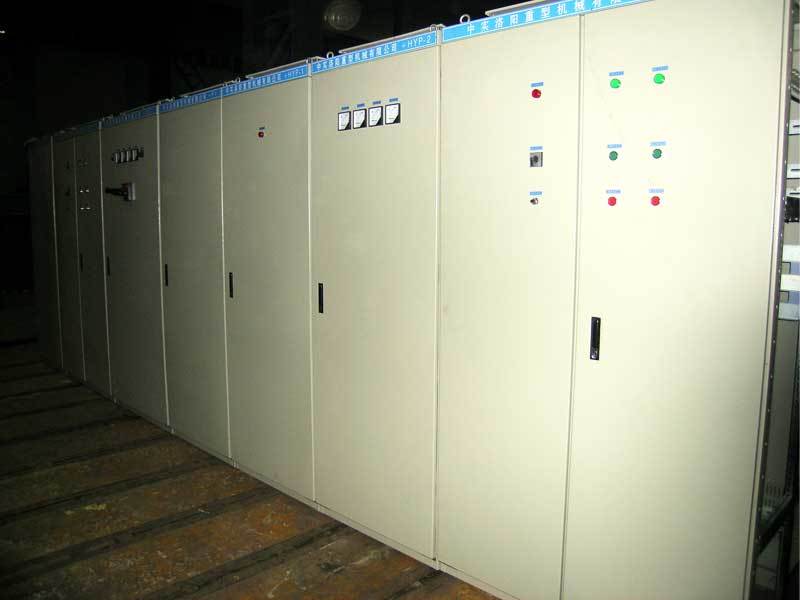

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-
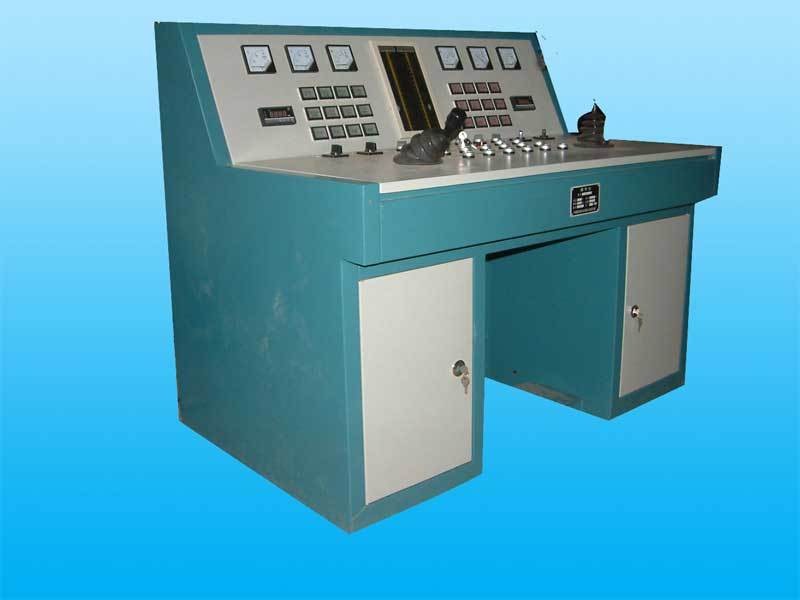

Local System Upgrade
-
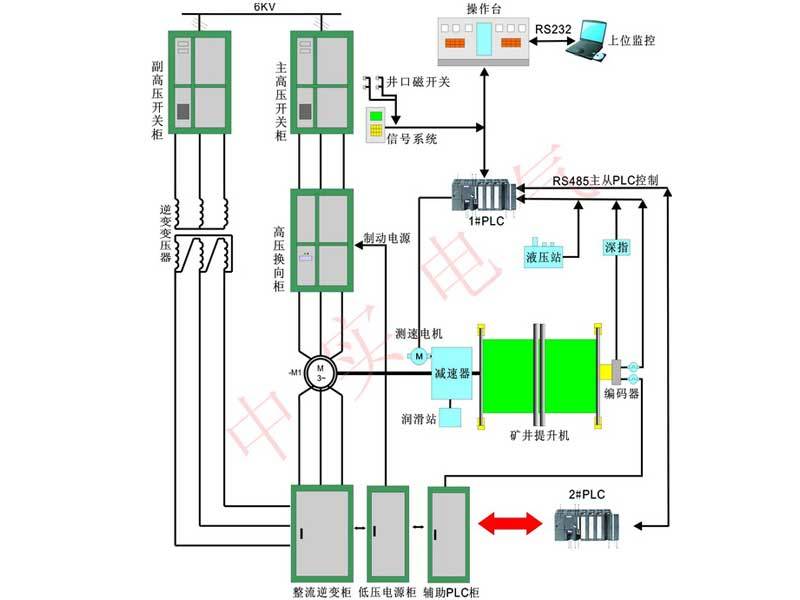
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
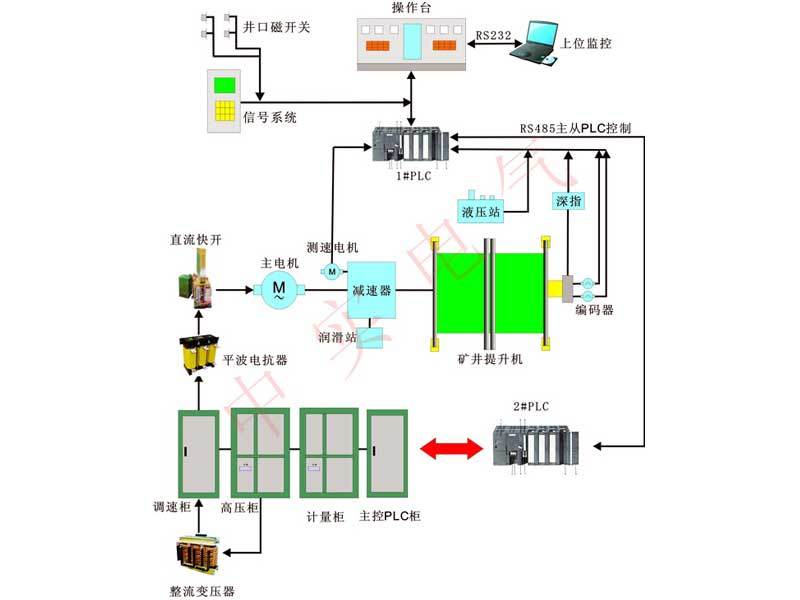
Fully digital DC control system
-
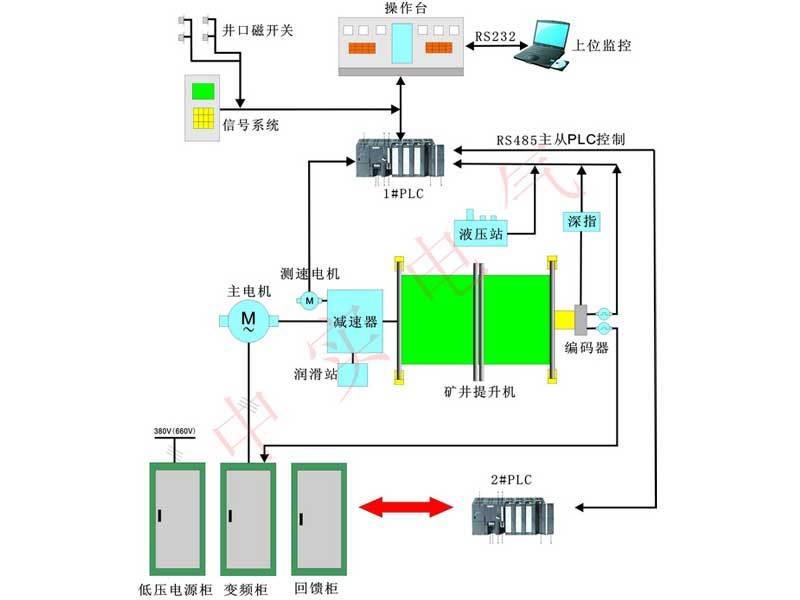
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
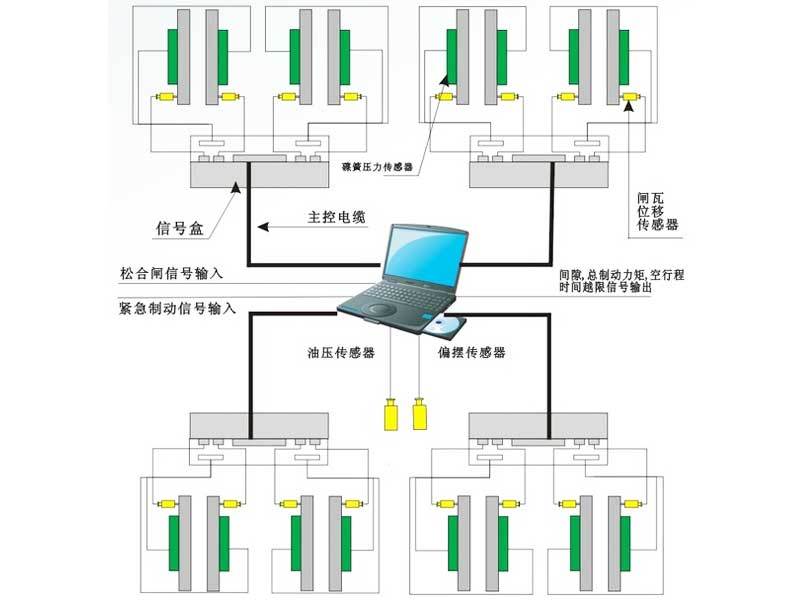
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-
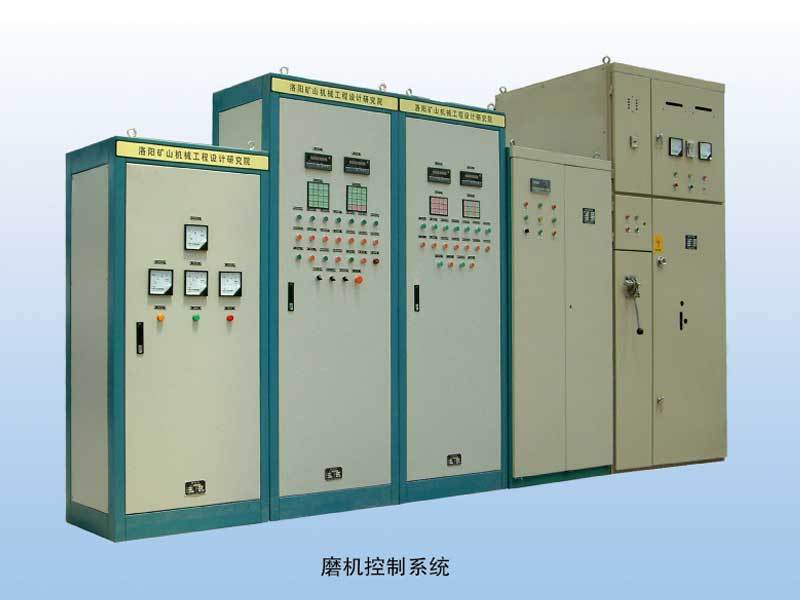

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
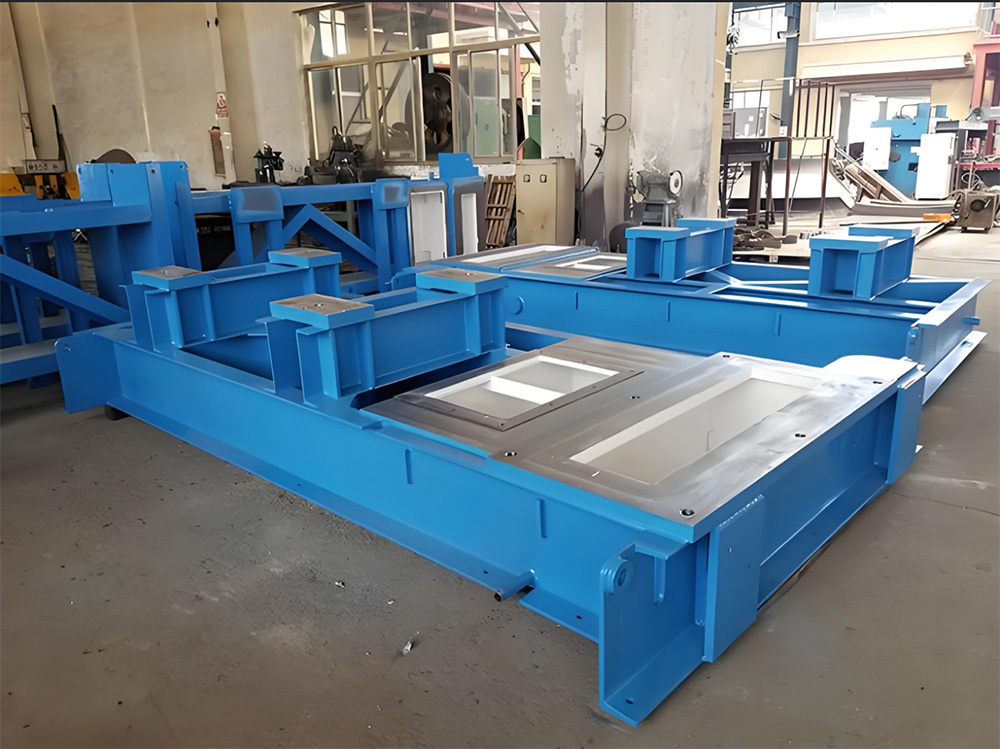

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-
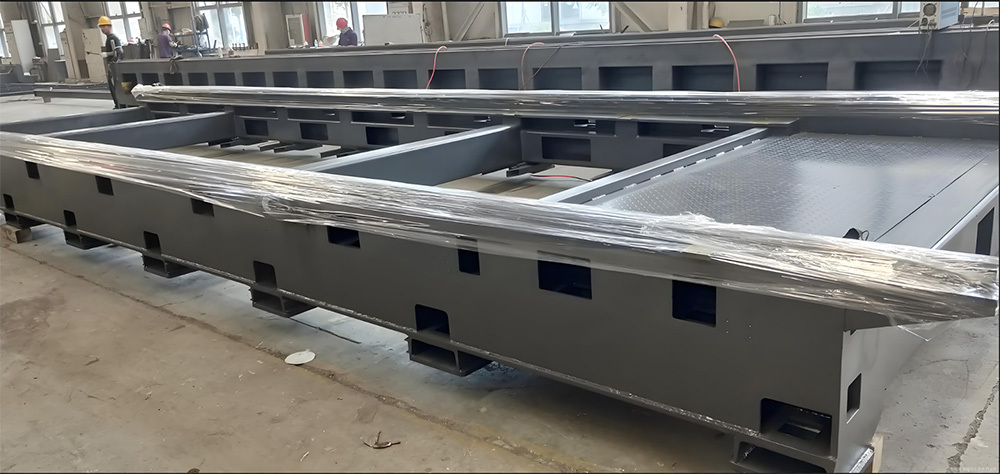

Large base
-
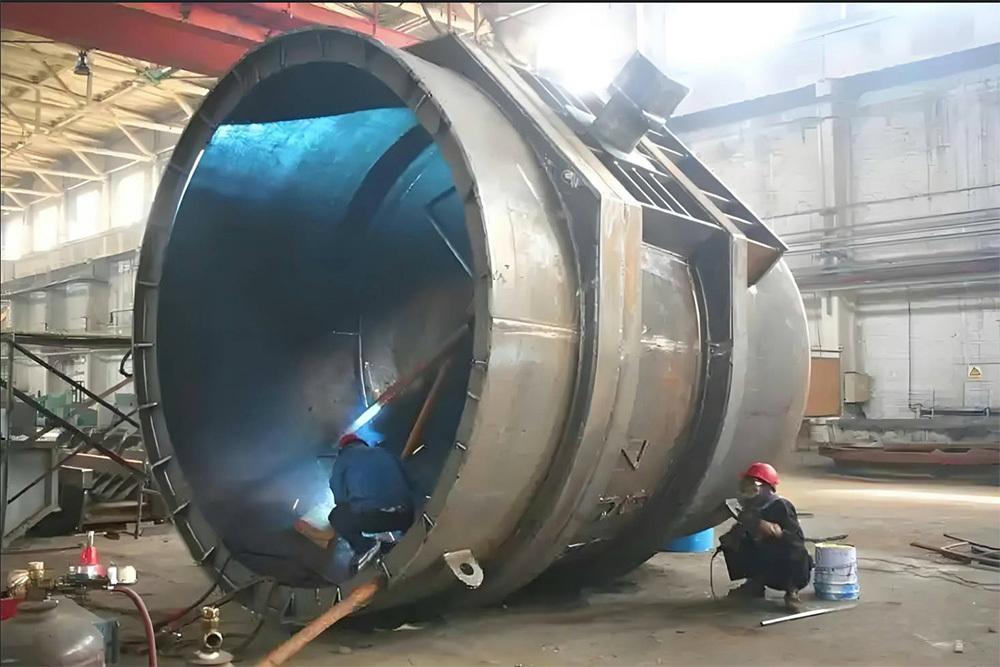

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
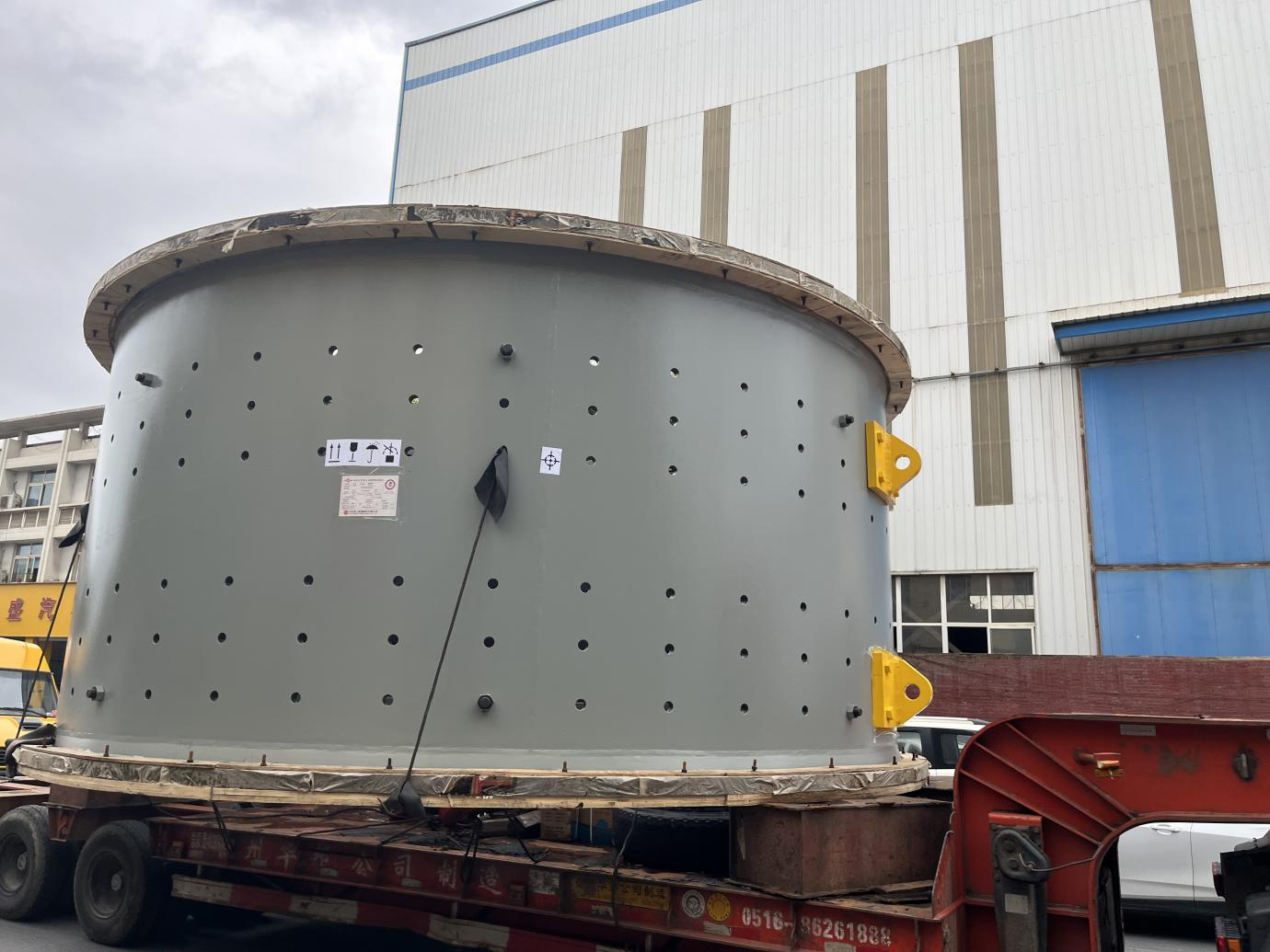

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-
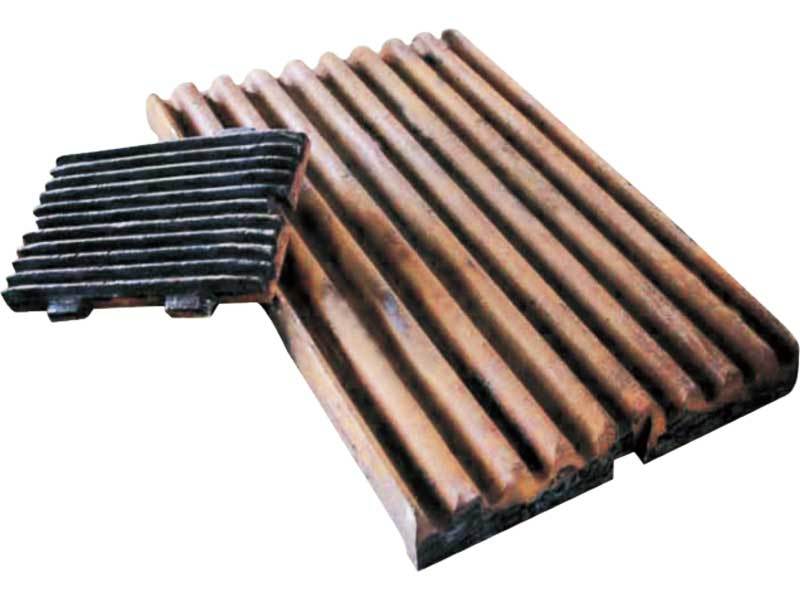

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-
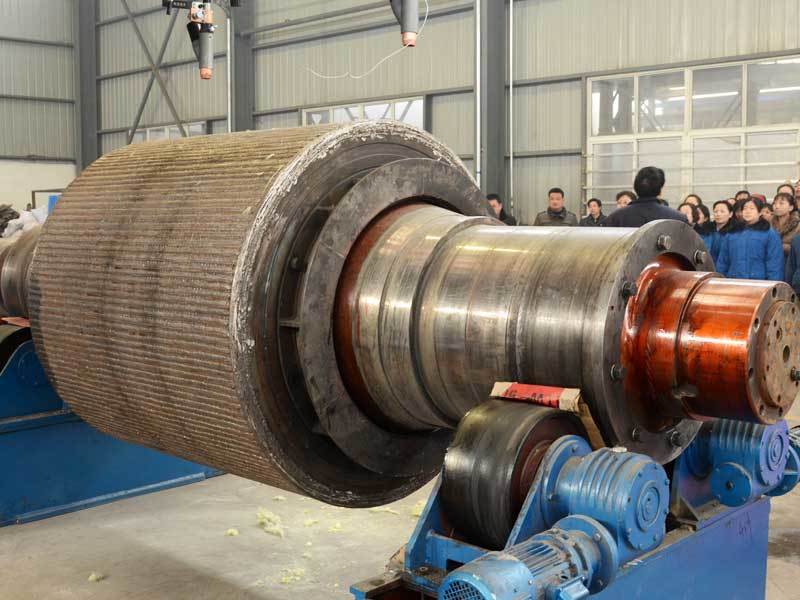

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-

Bus Alloy Bushings
-
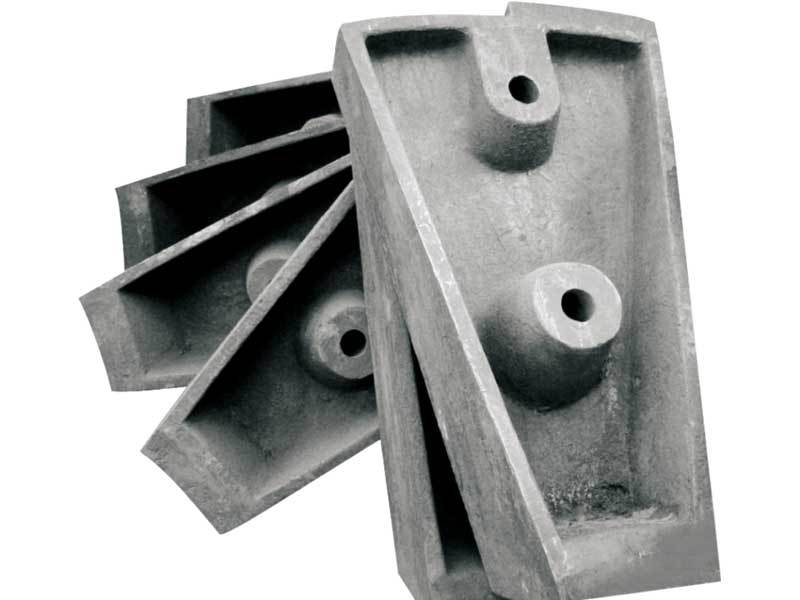

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
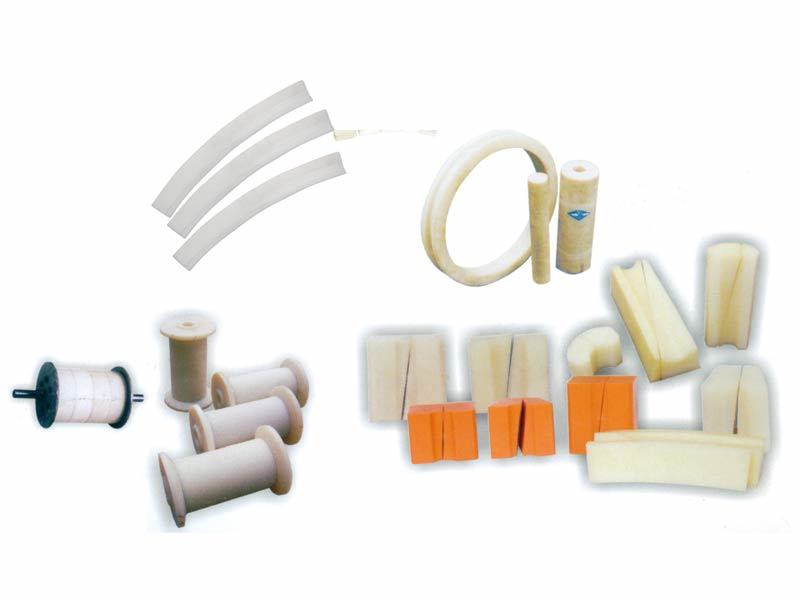

Nylon products
-
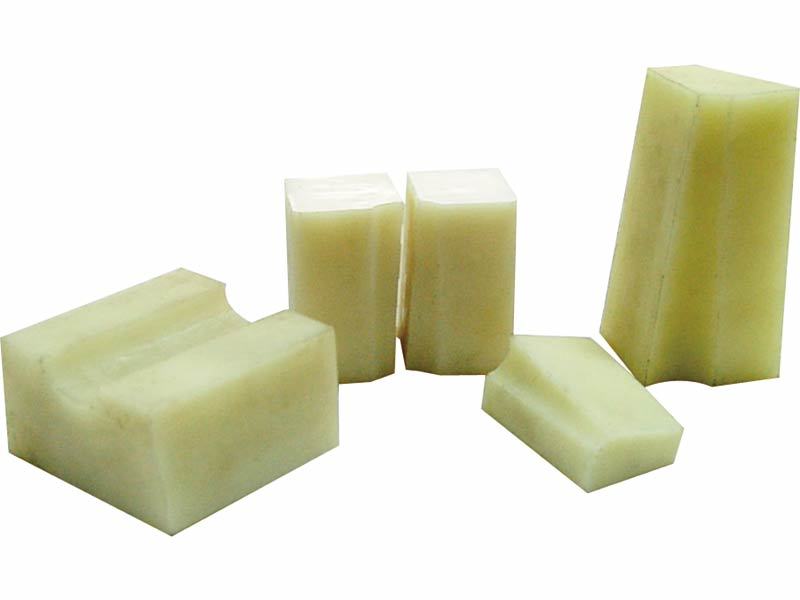

Polyurethane Products
-
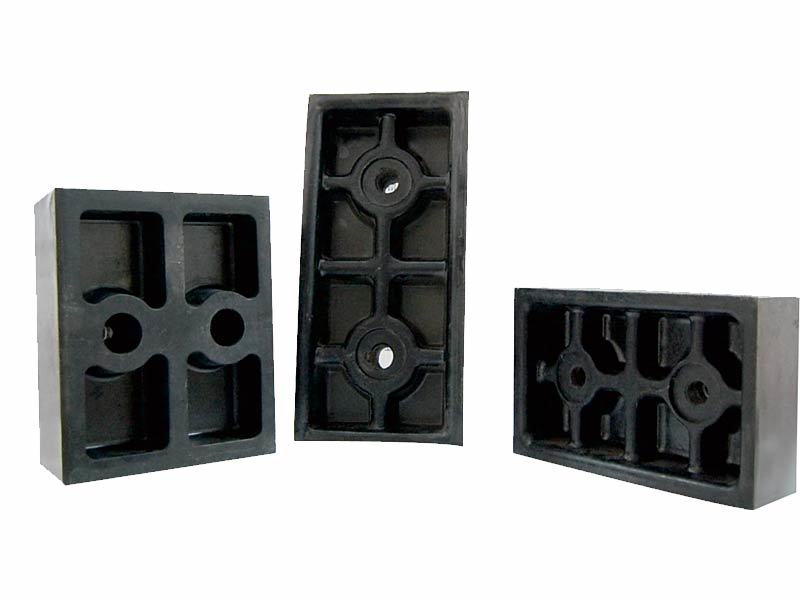

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
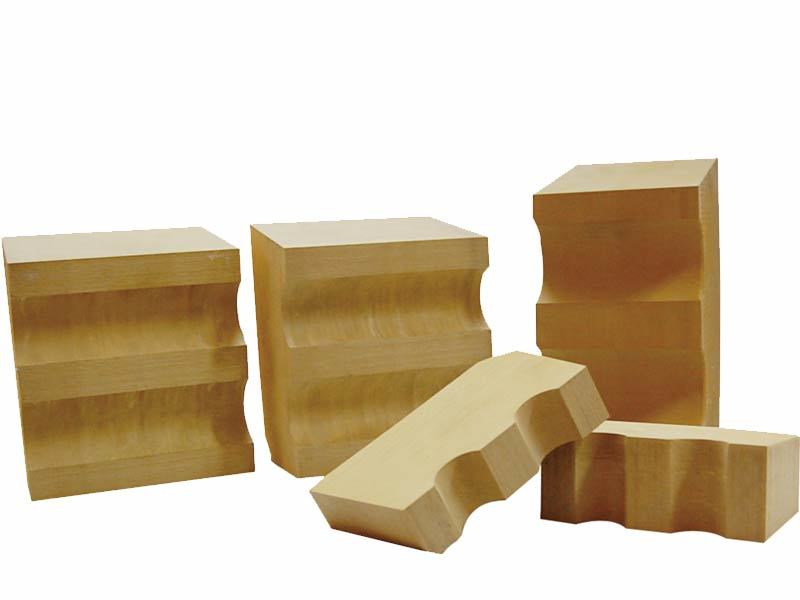

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information