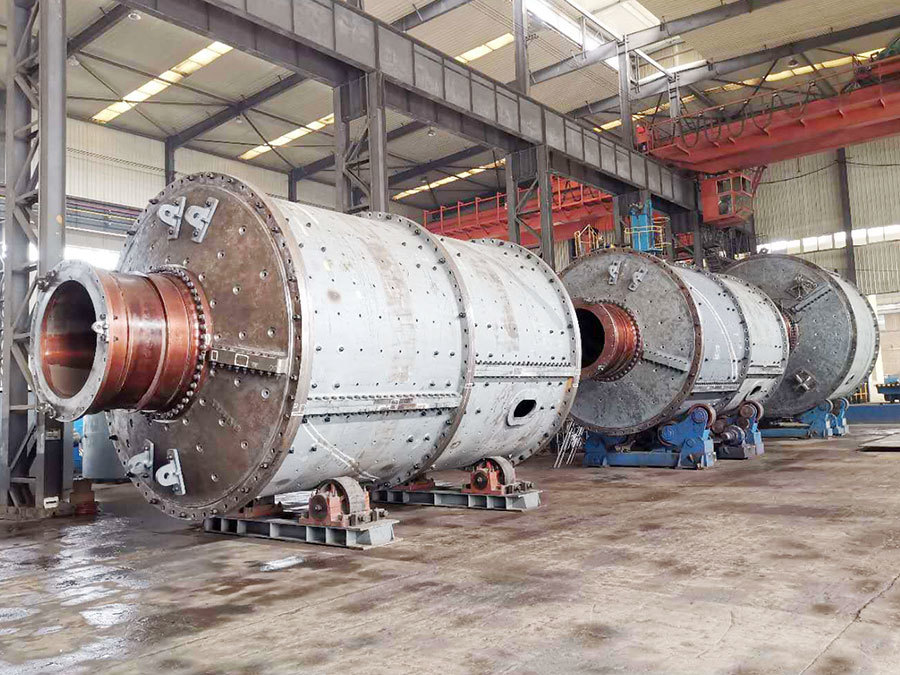
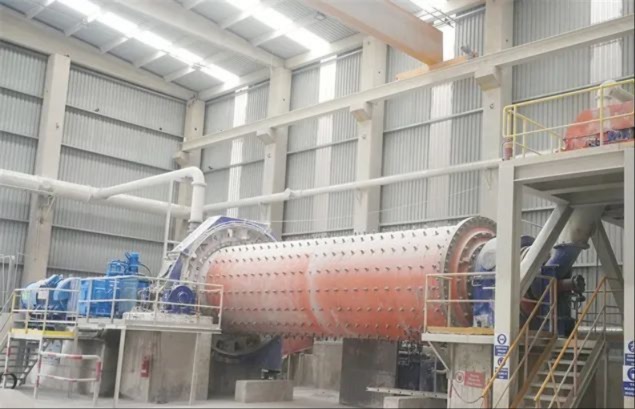
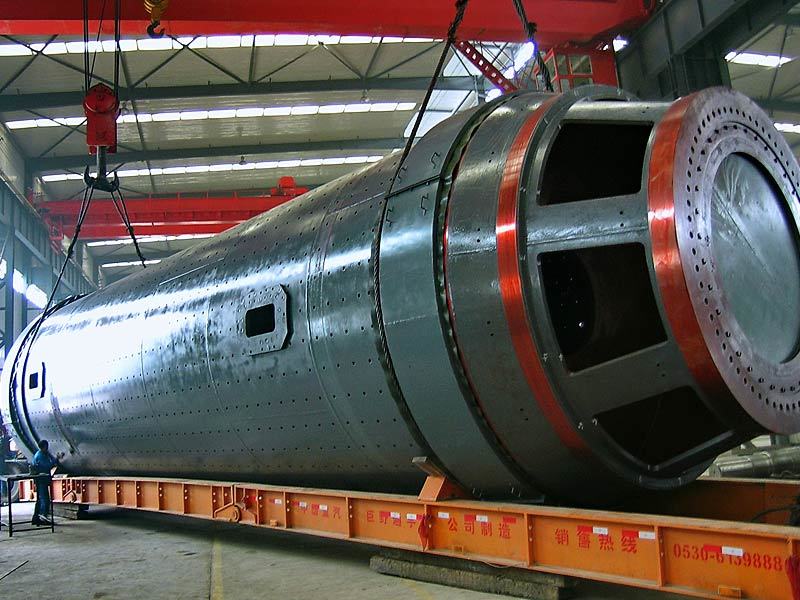
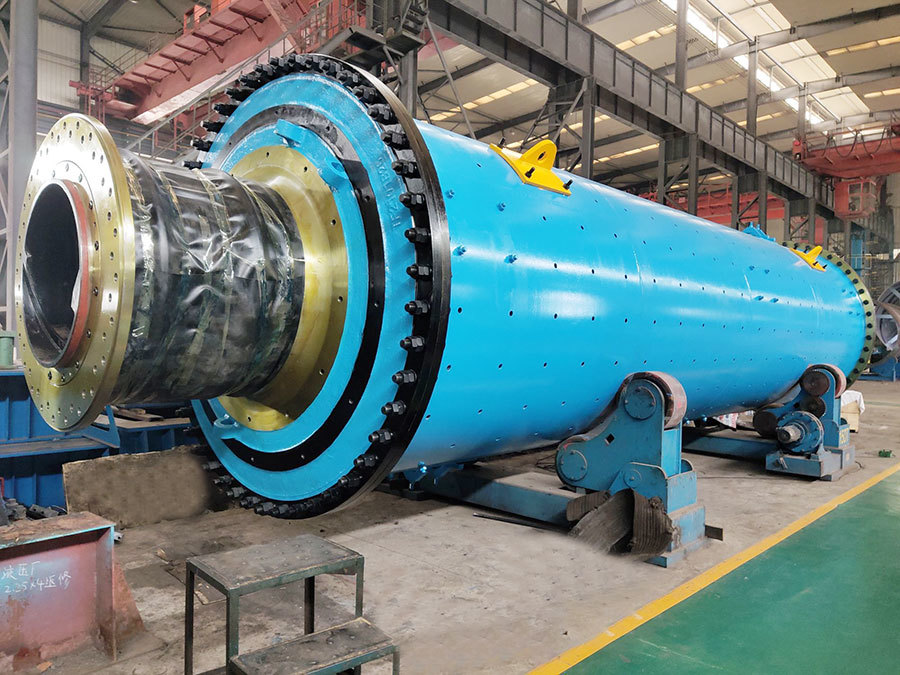
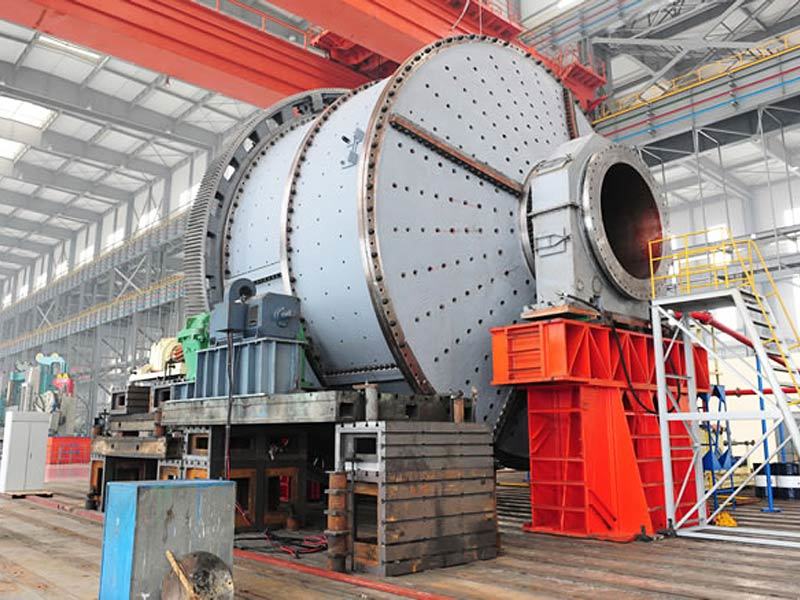
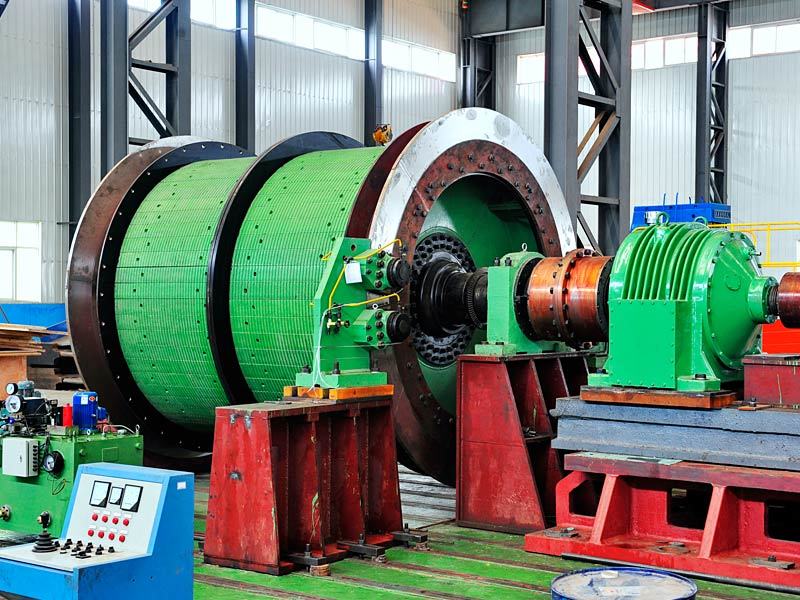
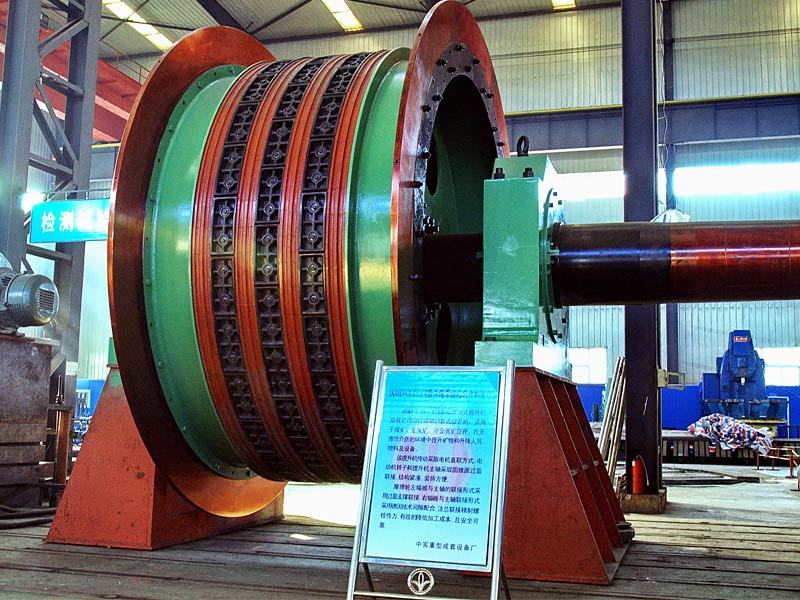
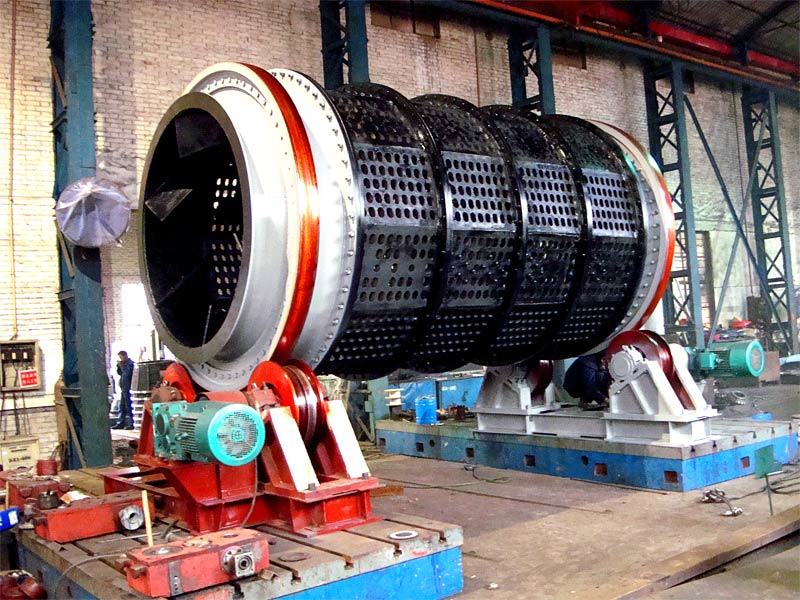
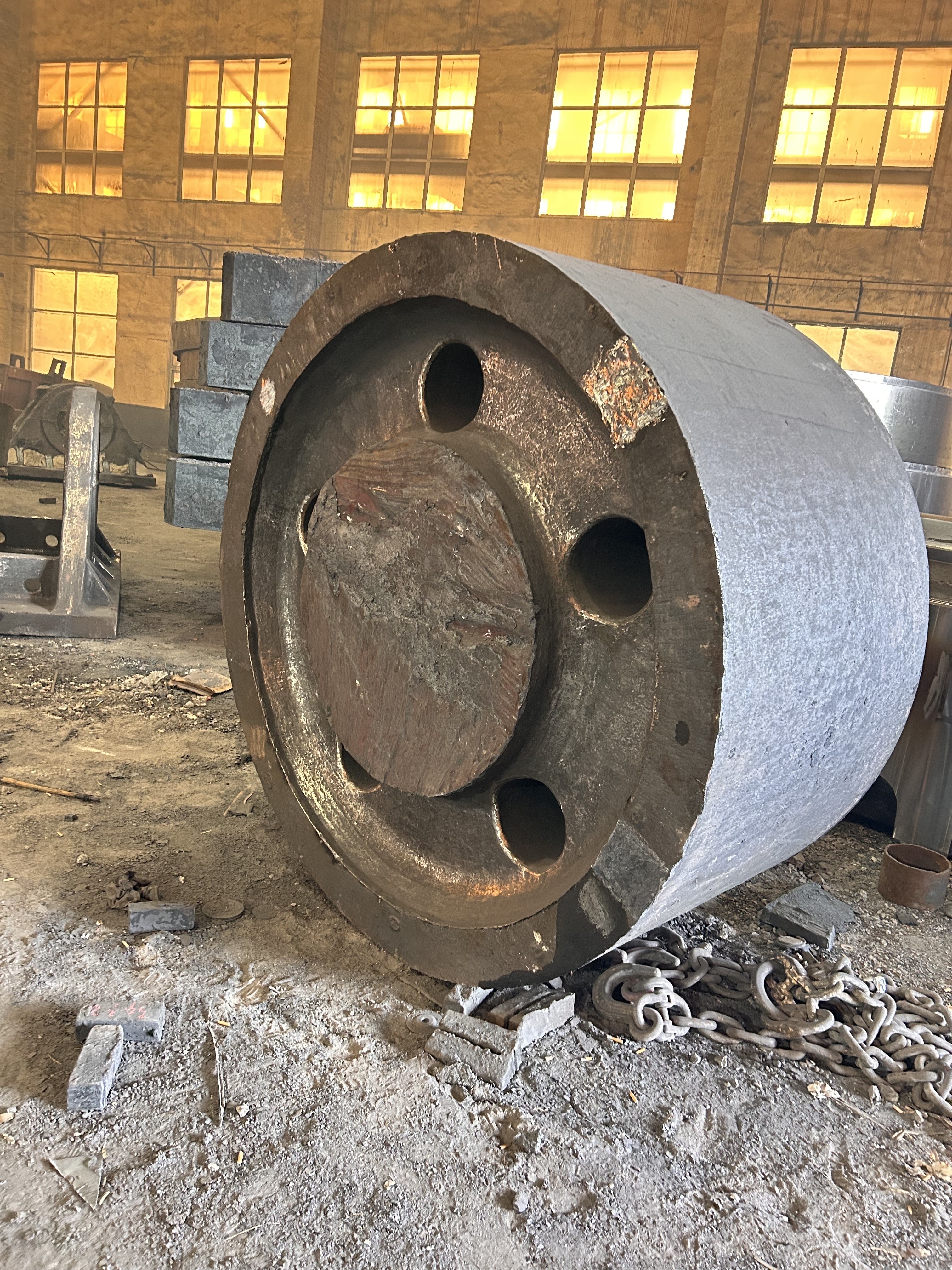
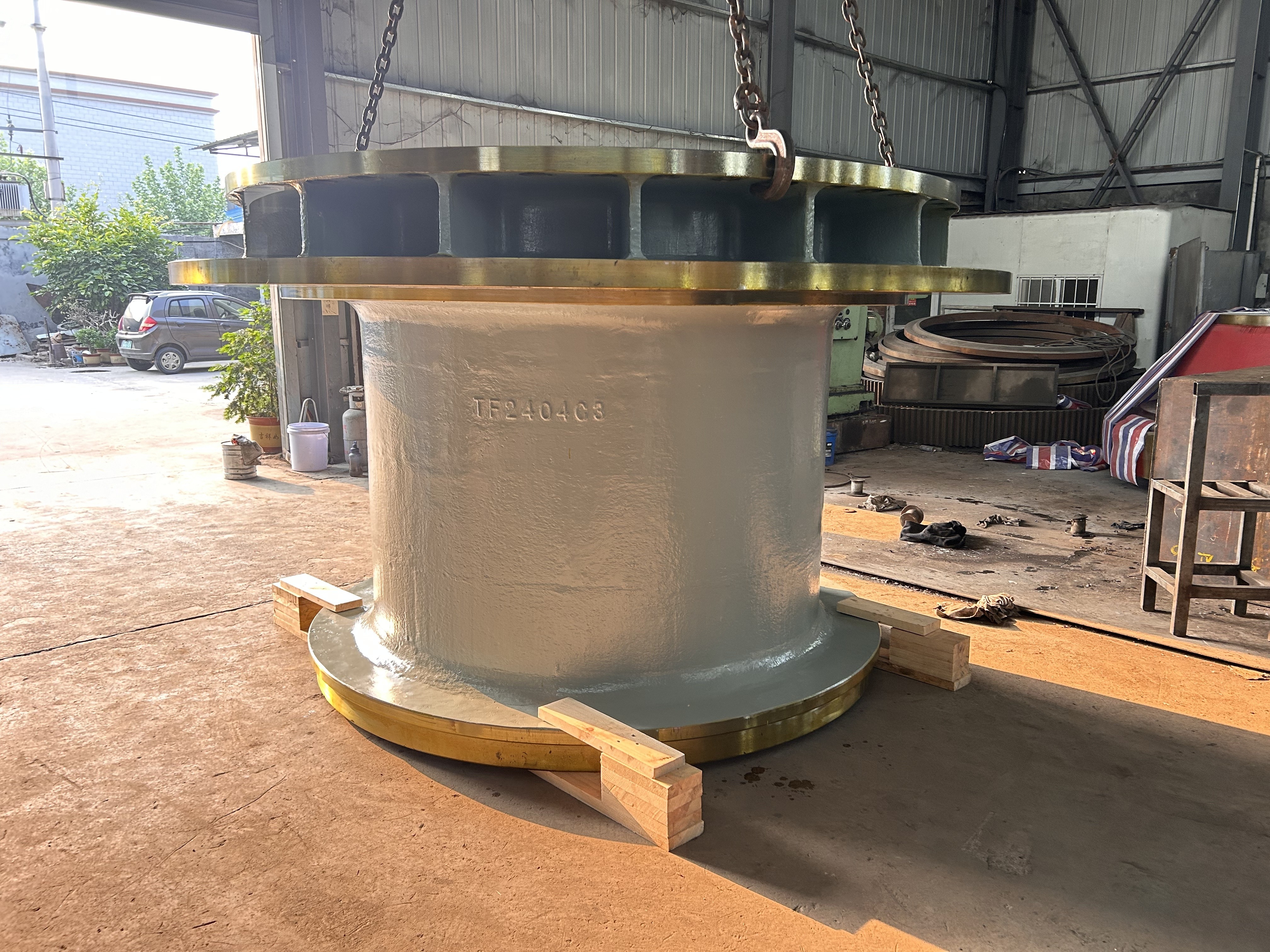
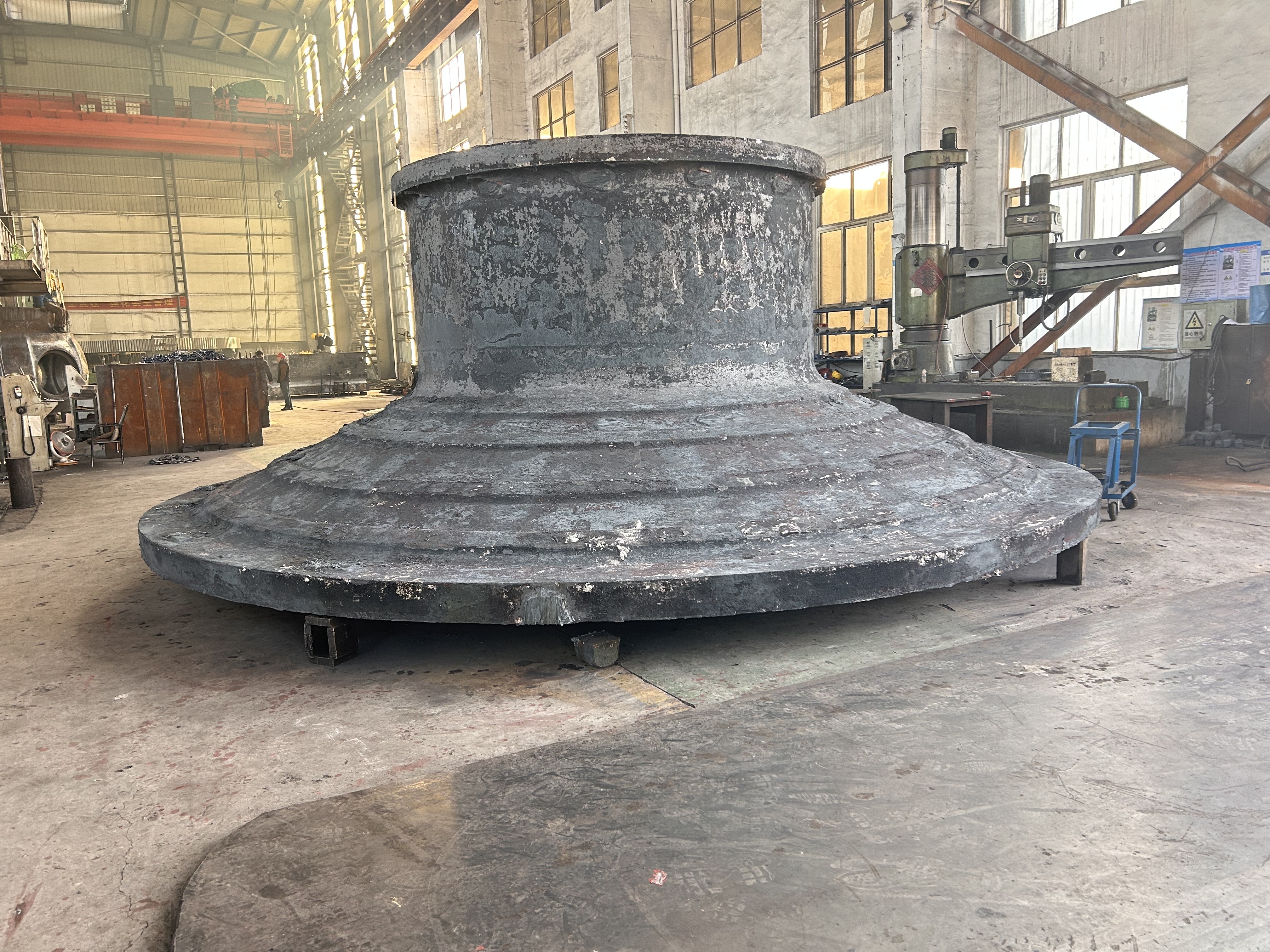
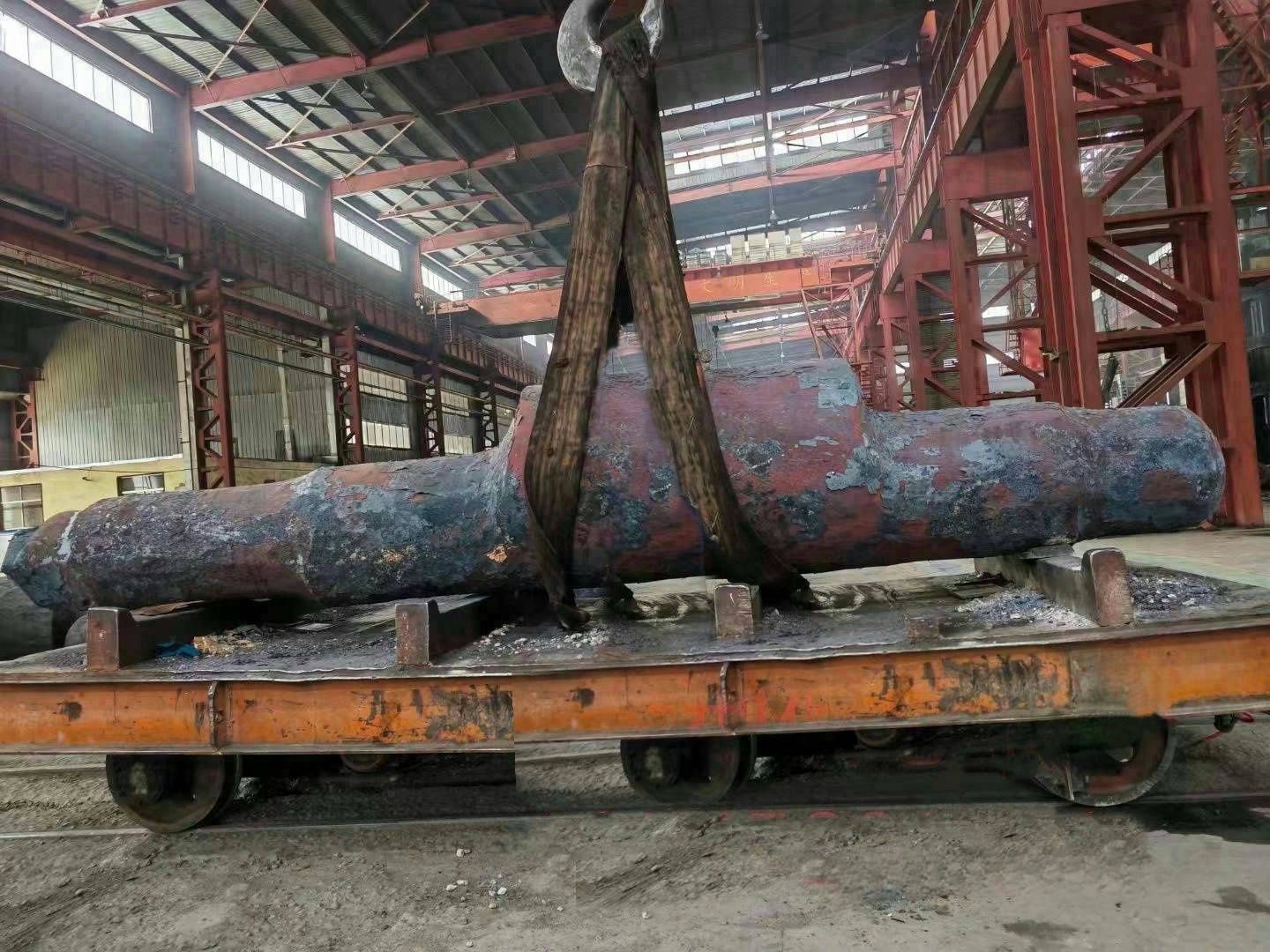
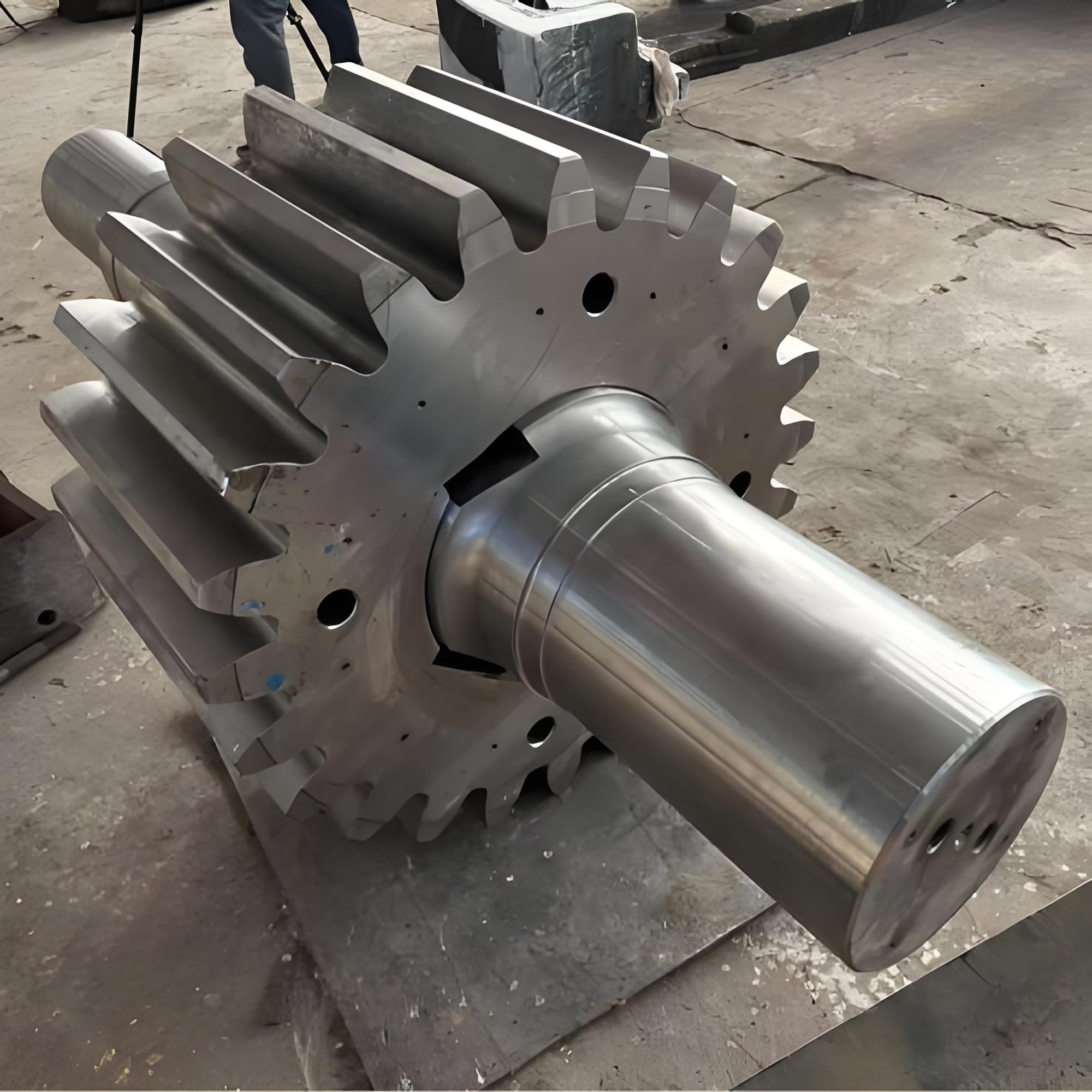
I. Introduction to Medium-Chromium Alloy Liners
The Medium Chromium Alloy Liner is a wear-resistant material developed specifically for medium-impact, medium-to-high abrasion conditions. By optimizing the chromium content (7–12%) and carefully balancing its multi-element alloy composition, it achieves an outstanding equilibrium between wear resistance, toughness, and cost-effectiveness—making it the ideal choice for lining plates in grinding equipment such as ball mills and vertical mills.
Performance Positioning
High-chromium cast iron vs. medium-chromium alloy vs. low-alloy steel
Characteristics |
High-chromium cast iron (Cr ≥ 20%) |
Medium-chromium alloy (Cr7–12%) |
Low-alloy steel (Cr ≤ 3%) |
Hardness (HRC) |
58-66 |
52-58 |
40-48 |
Impact toughness (J/cm²) |
3-8 |
10-20 |
30-60 |
Wear Resistance Index |
1.0 (Baseline) |
0.7–0.8 |
0.3–0.5 |
Corrosion resistance |
Optimal (pH 3–12) |
Mild (pH 5–10) |
Poor |
Cost per ton (Ten thousand yuan/ton) |
2.8–3.5 |
1.8–2.3 |
1.0–1.5 |
II. Performance Characteristics and Advantages of Medium-Chromium Alloy Liners
High hardness: The macroscopic hardness typically ranges from HRC 55 to 65 (in the quenched and tempered condition). The combination of a highly hard martensitic matrix and hard chromium carbides delivers exceptional resistance to abrasive wear.
Excellent wear resistance: Under abrasive wear conditions—particularly low-stress abrasive wear and moderate-stress erosive wear—the wear resistance significantly outperforms high-manganese steel (ZGMn13), typically achieving 1.5 to 3 times, or even more, its level. While the wear resistance is comparable to, or slightly lower than, that of premium high-chromium cast irons (such as Cr20 and Cr26), it offers a clear cost advantage.
Moderate toughness: It outperforms high-chromium cast iron (especially high-carbon, high-chromium cast iron) but falls short of high-manganese steel and premium alloy steels. This material can withstand moderate impact loads without easily undergoing brittle fracture or extensive spalling. It is well-suited for applications such as ball mill shell plates, grid plates, and lifting bars where the impact forces are not particularly severe.
A certain level of corrosion resistance: The addition of chromium gives it notable resistance to water and mineral slurry corrosion, surpassing that of ordinary carbon steel and low-alloy steel.
Good hardenability: Thanks to elements such as chromium, molybdenum, and nickel, the medium-chromium alloy exhibits excellent hardenability, ensuring uniform hardness across the cross-section of thick liners—such as those exceeding 100 mm—and enabling the core to develop a microstructure dominated by martensite.
III. Material Classification and Application Scenarios of Medium-Chromium Alloy Liners
Main material types
Medium-carbon, medium-chromium Type I: Suitable for crushing applications with high demands on impact toughness, this material enhances crushing efficiency by optimizing the motion state of the grinding media.
Type II medium-carbon, medium-chromium: Slightly higher carbon content results in a more uniform distribution of carbides, enhancing wear resistance and making it ideal for high-intensity wear applications.
High-carbon, medium-chromium alloy steel: containing 0.65%–0.7% carbon and 4.0%–4.5% chromium, combined with synergistic effects from elements such as Cu and Nb. It achieves a hardness of HRC50–55 and exhibits wear resistance 7.8 times greater than that of high-manganese steel²³.
Typical application areas
Mining ball mill: Protects the cylinder from direct impact by grinding media, suitable for dry-wet mixed grinding processes, and reduces equipment vibration by 1%.
Cement Industry: Utilizing alternative high-manganese steel liners to address deformation issues, reduce maintenance costs, and contribute to energy conservation and consumption reduction.
Crusher accessories: Used as a protective layer filling material, they cushion the impact of ore and reinforce the cylinder structure.
The Preparation Process and Technological Innovation of Medium-Chromium Alloy Liners
Key Production Processes
Component Design: By optimizing the formulation through multi-alloying—such as adding 0.2%–0.3% Re to high-carbon, medium-chromium liners—we achieve grain refinement and enhance the cleanliness of the molten steel. This approach also helps avoid the use of expensive elements like Mo and Ni, thereby reducing costs by 23%.
Heat treatment process: Utilizing a dual-medium quenching medium to achieve precise control of the austenitizing temperature, resulting in a composite microstructure of martensite + bainite + retained austenite, which balances hardness and toughness at level 14.
Casting and Melting: Melting in a 1550℃ medium-frequency induction furnace, followed by top-pour casting at 1450℃, ensuring uniform composition of the castings. Subsequently, the castings undergo cleaning and isothermal quenching to relieve internal stresses and optimize the microstructure.
IV. Important Notes
1. Operating Condition Matching: Avoid High Impact—In high-impact areas of large autogenous/mill semi-autogenous mills (such as the top of tall lifting bars), where toughness may be insufficient, prioritize the use of high-toughness alloy steel.
Pay attention to abrasive properties: For extremely hard, sharp abrasives (such as quartz sand), wear resistance may not be as good as that of high-chromium cast iron.
2. Heat Treatment Quality: Heat treatment is key to unlocking the full potential of medium-chromium alloys. Poor-quality heat treatment can lead to undesirable matrix structures (such as the formation of pearlite), uneven hardness, and poor toughness, significantly reducing service life.
3. Casting Quality: Internal defects (shrinkage porosity, slag inclusions) are common causes of early failure. Choose suppliers with a proven reputation and stable manufacturing processes.
4. Installation and Maintenance: Install strictly according to specifications, ensuring bolts are securely tightened. Regularly inspect the tightness and wear levels to prevent liner loosening or excessive wear that could lead to damage of the cylinder body.
Keywords
Previous: Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate






Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
Rotary kiln
-

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-

Lime Rotary Kiln
-

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
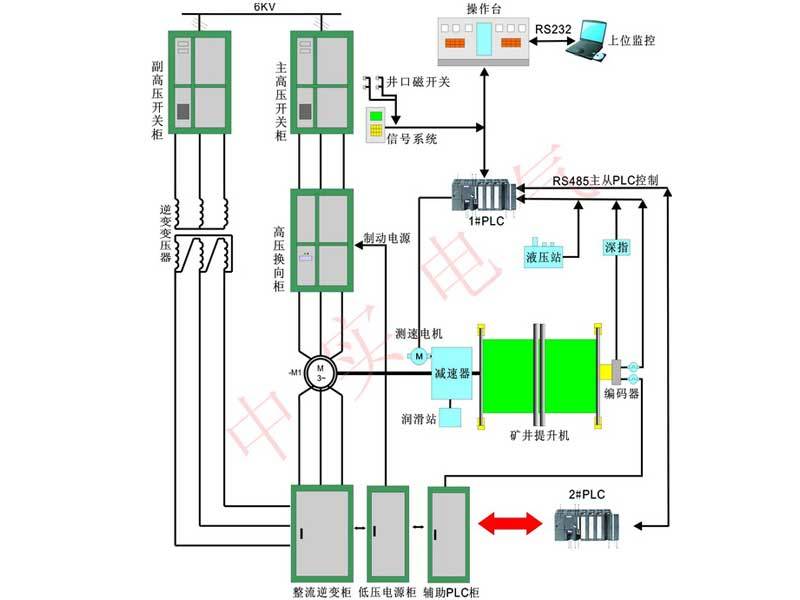
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
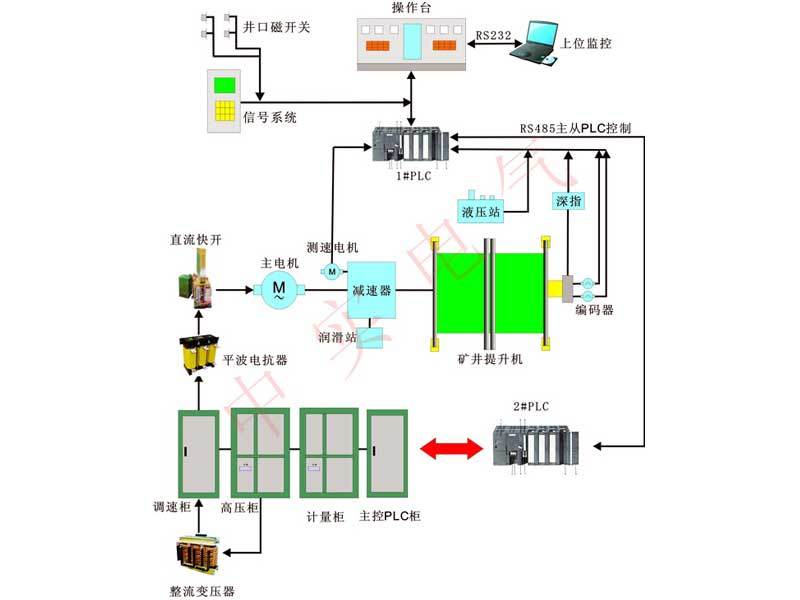
Fully digital DC control system
-
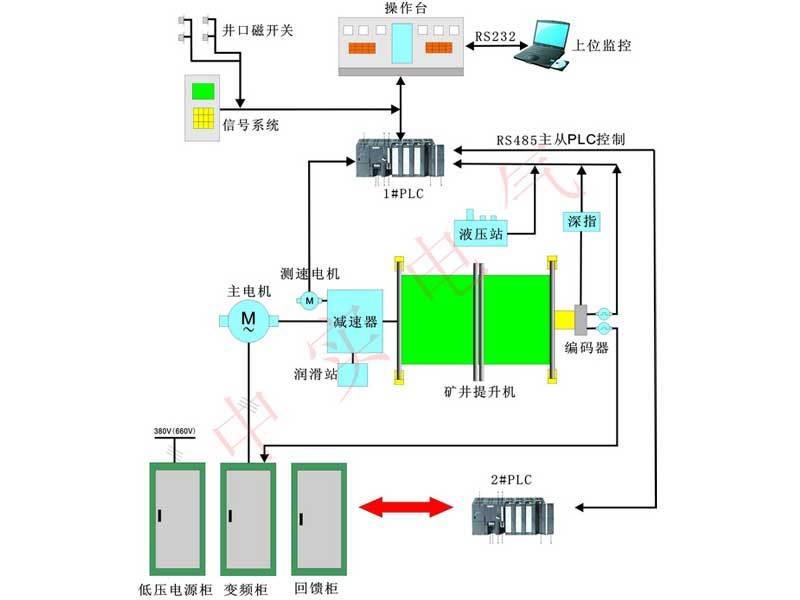
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
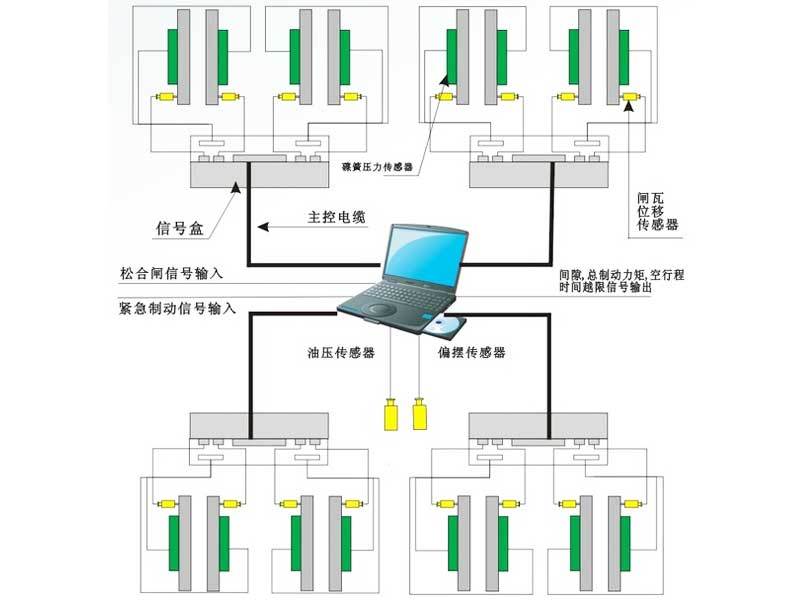
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-

Large base
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-

Bus Alloy Bushings
-

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
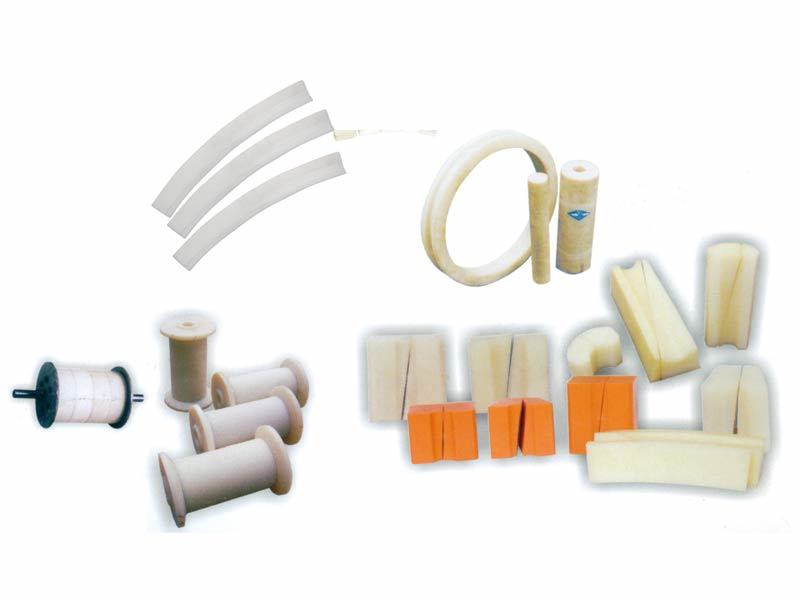

Nylon products
-
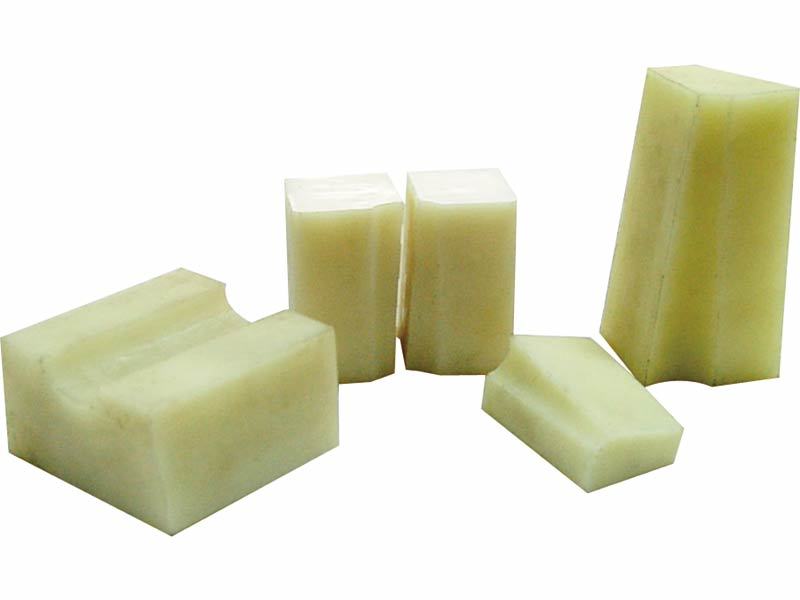

Polyurethane Products
-
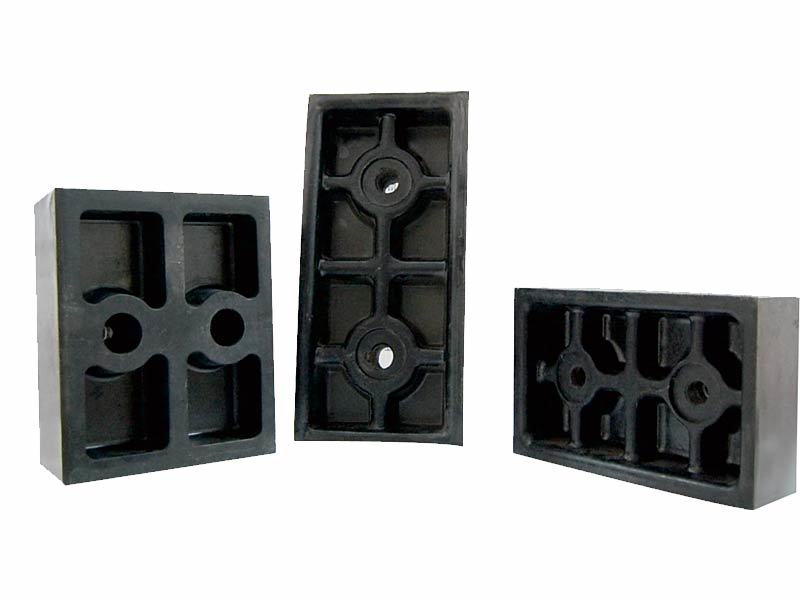

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
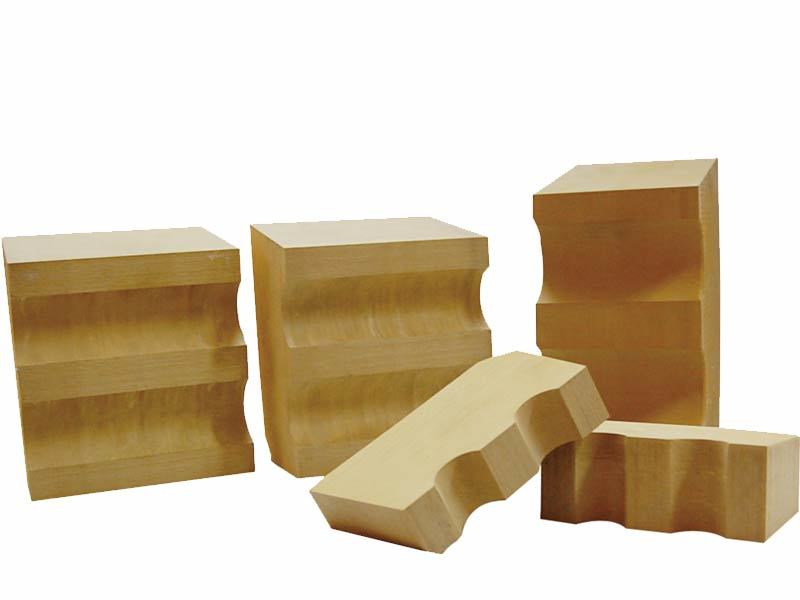

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information