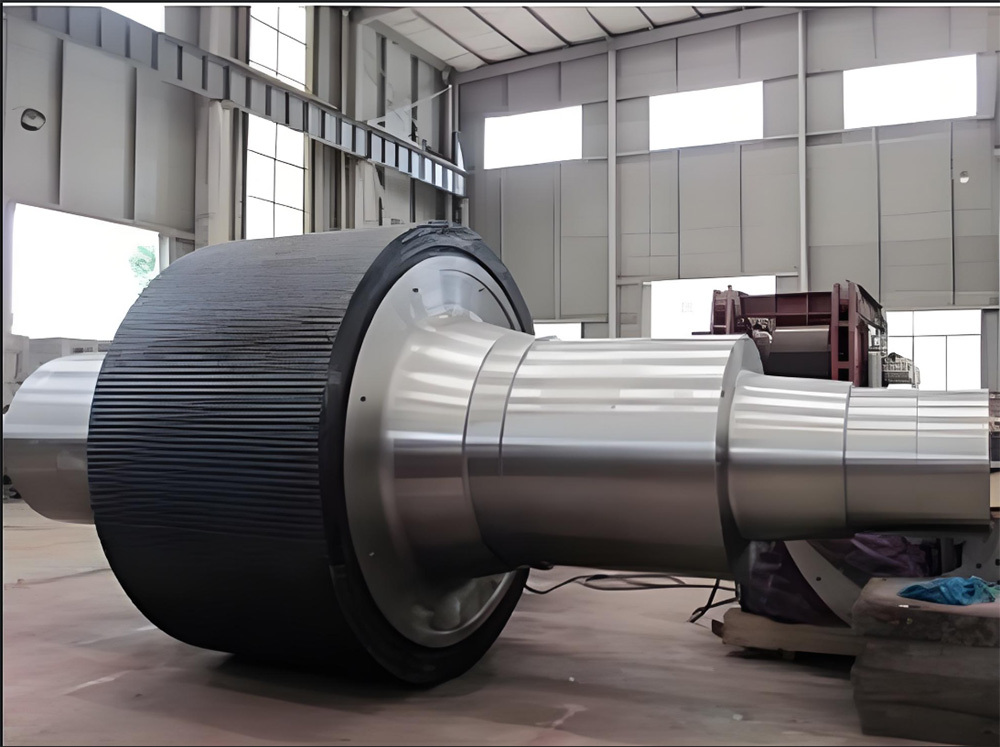
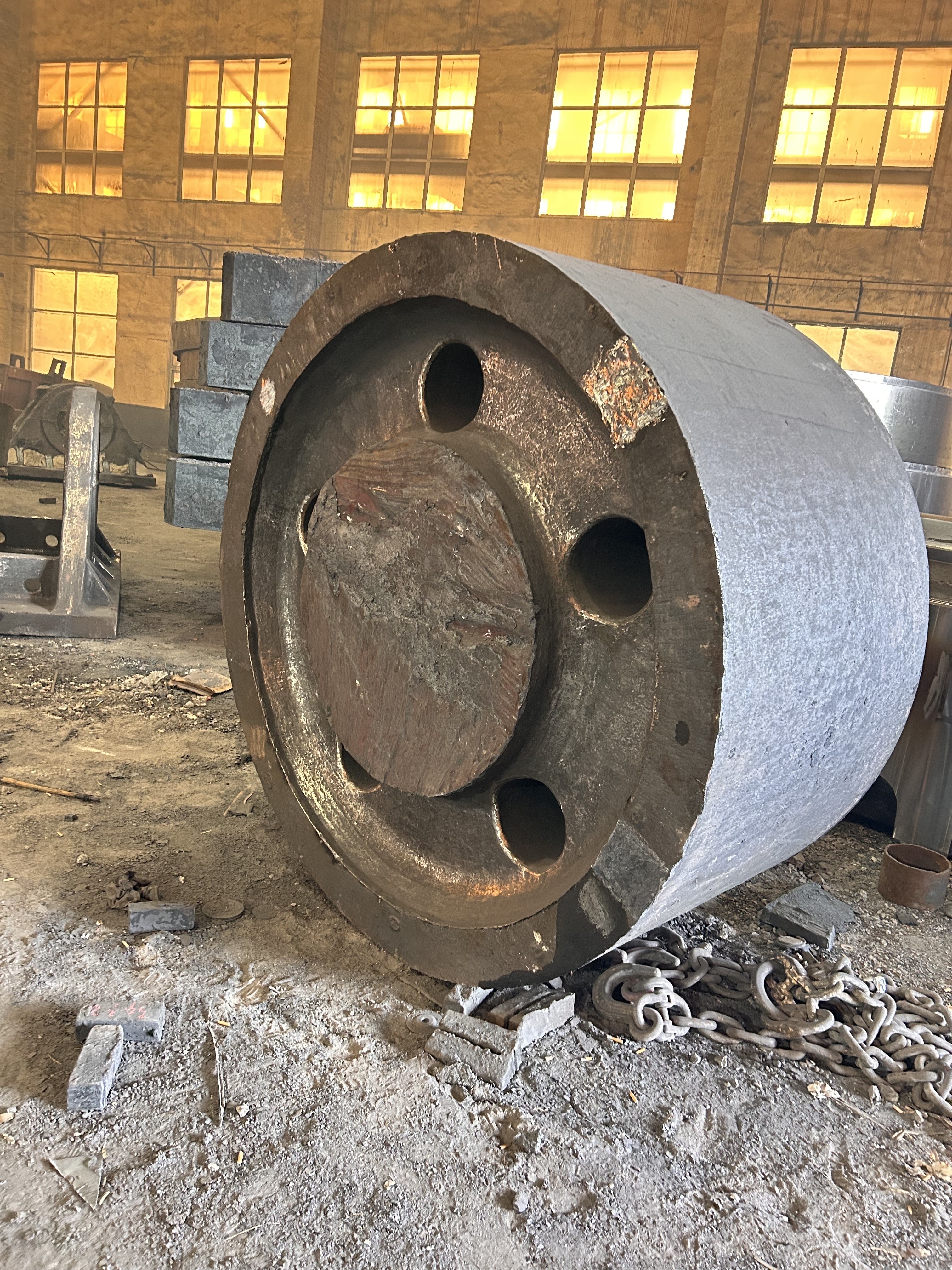
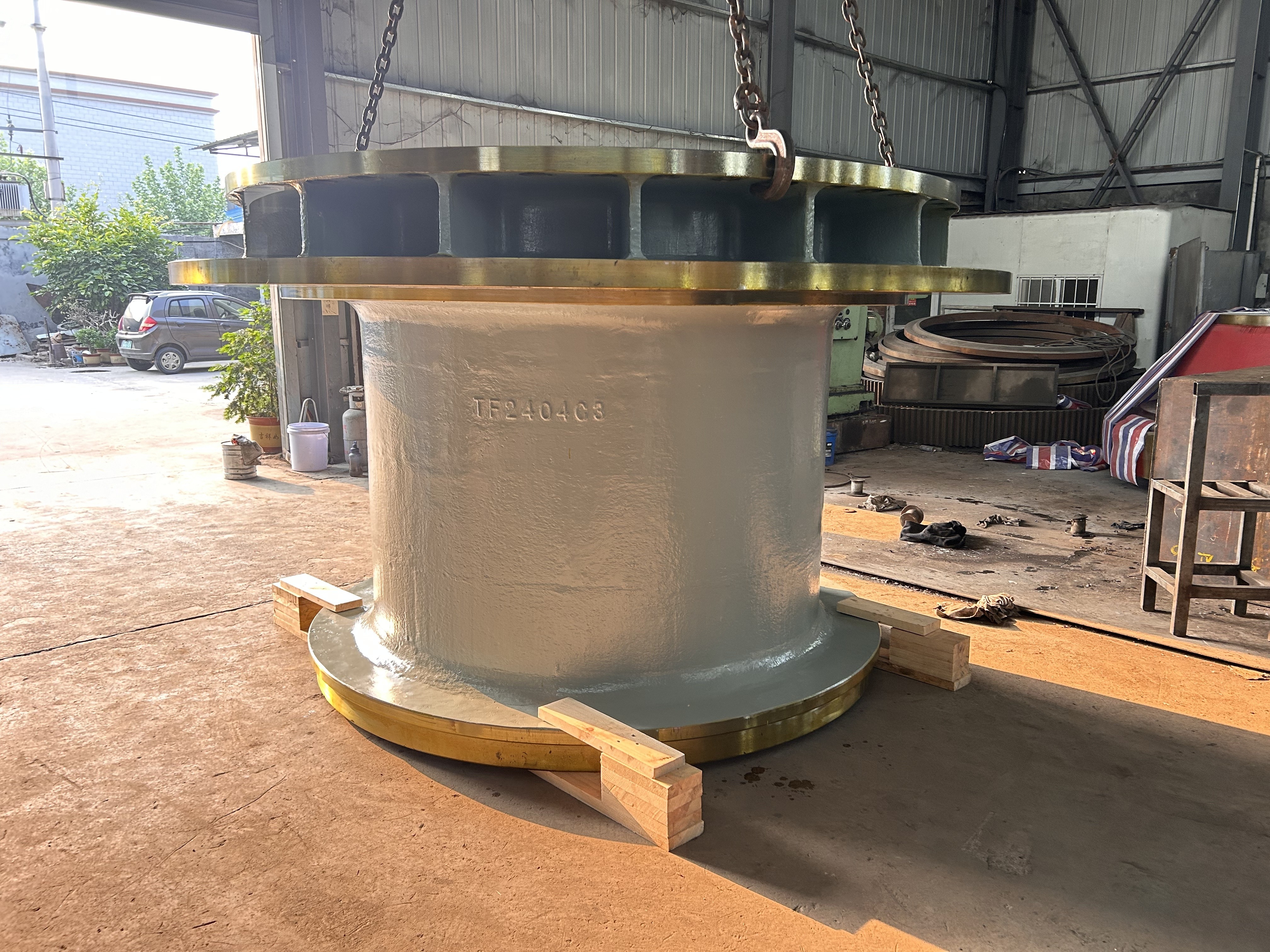
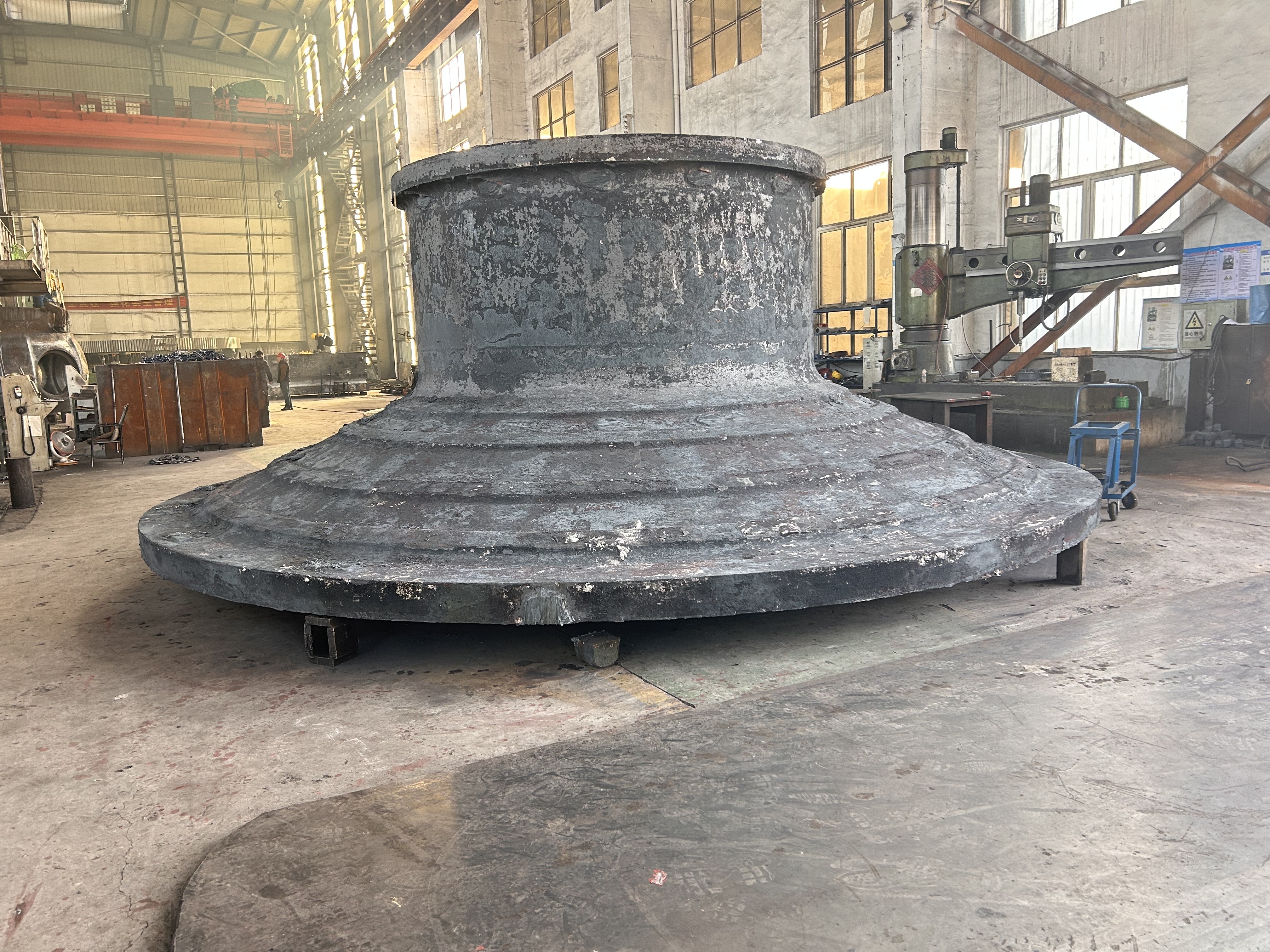
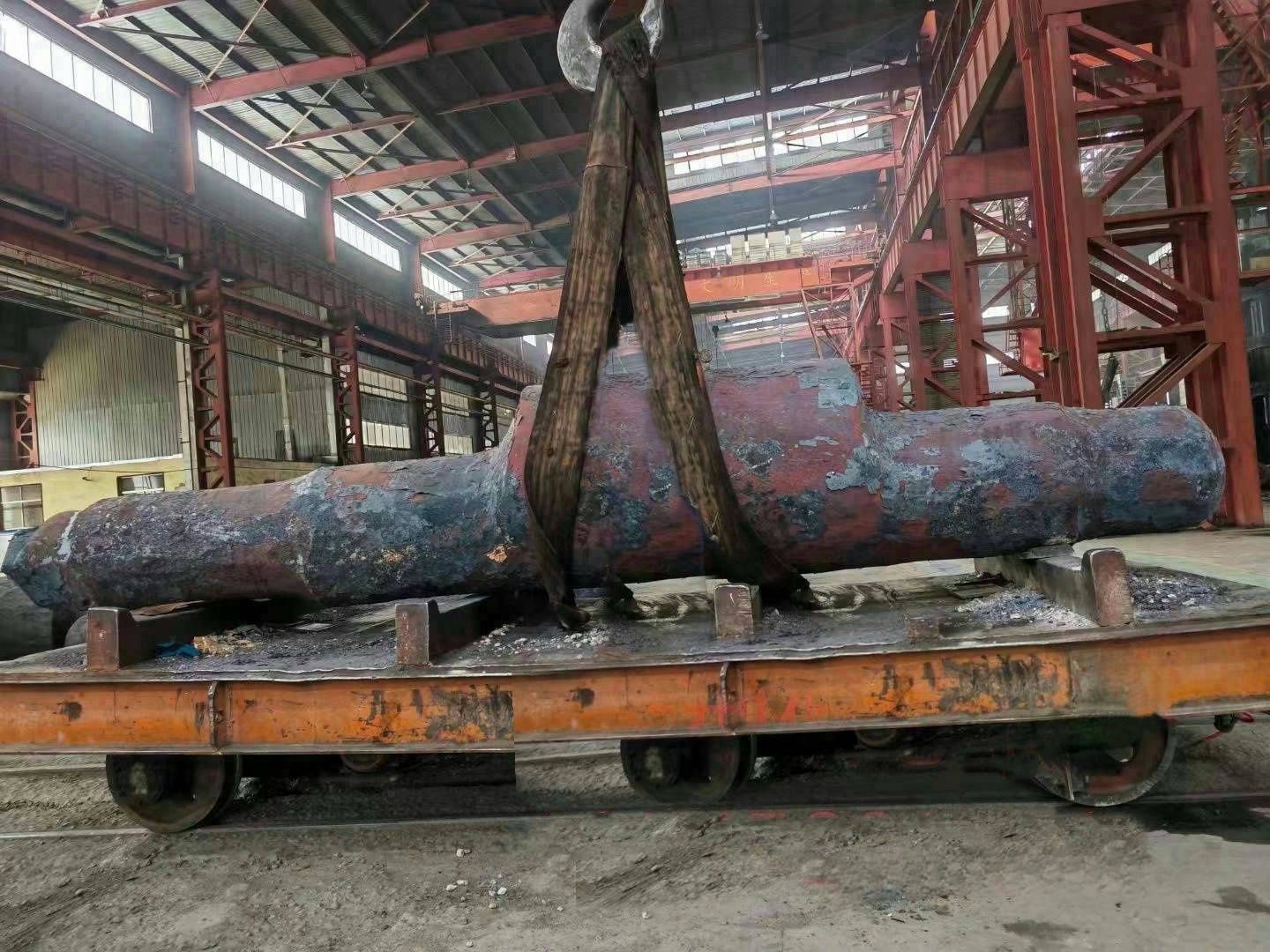
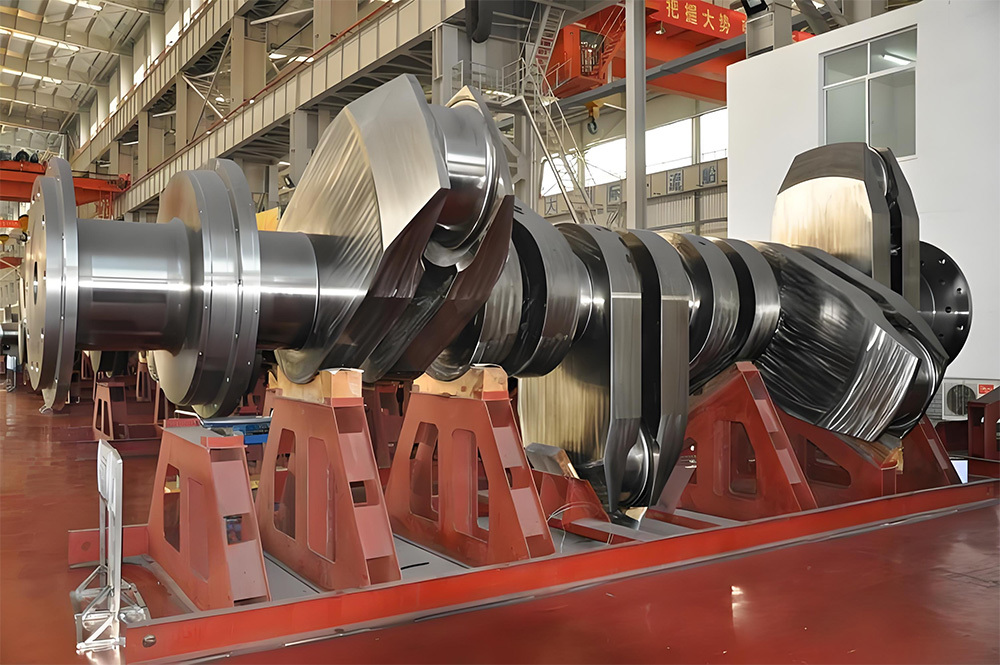
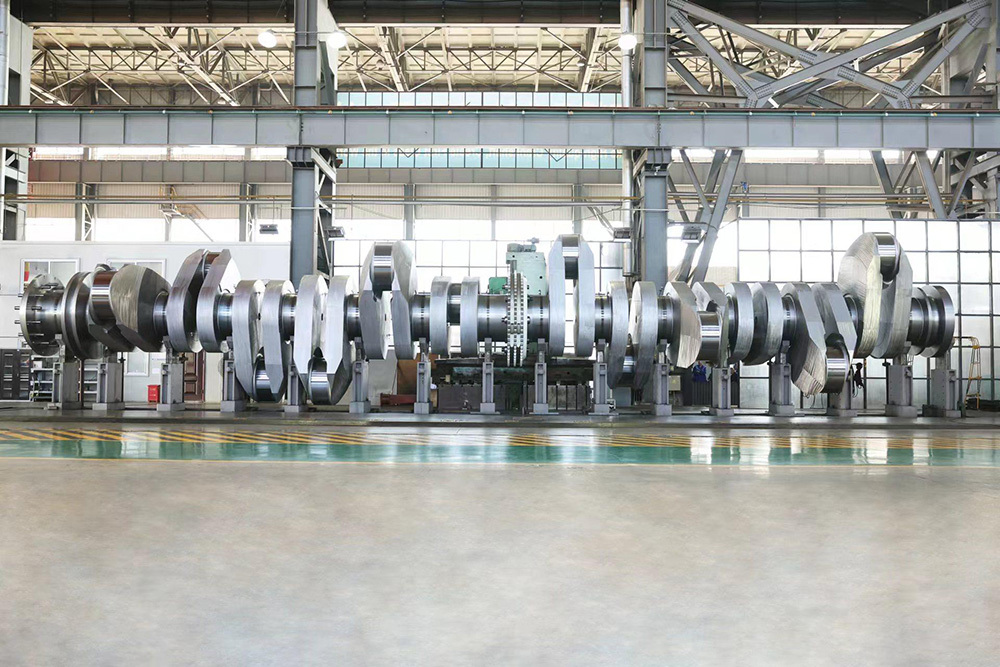
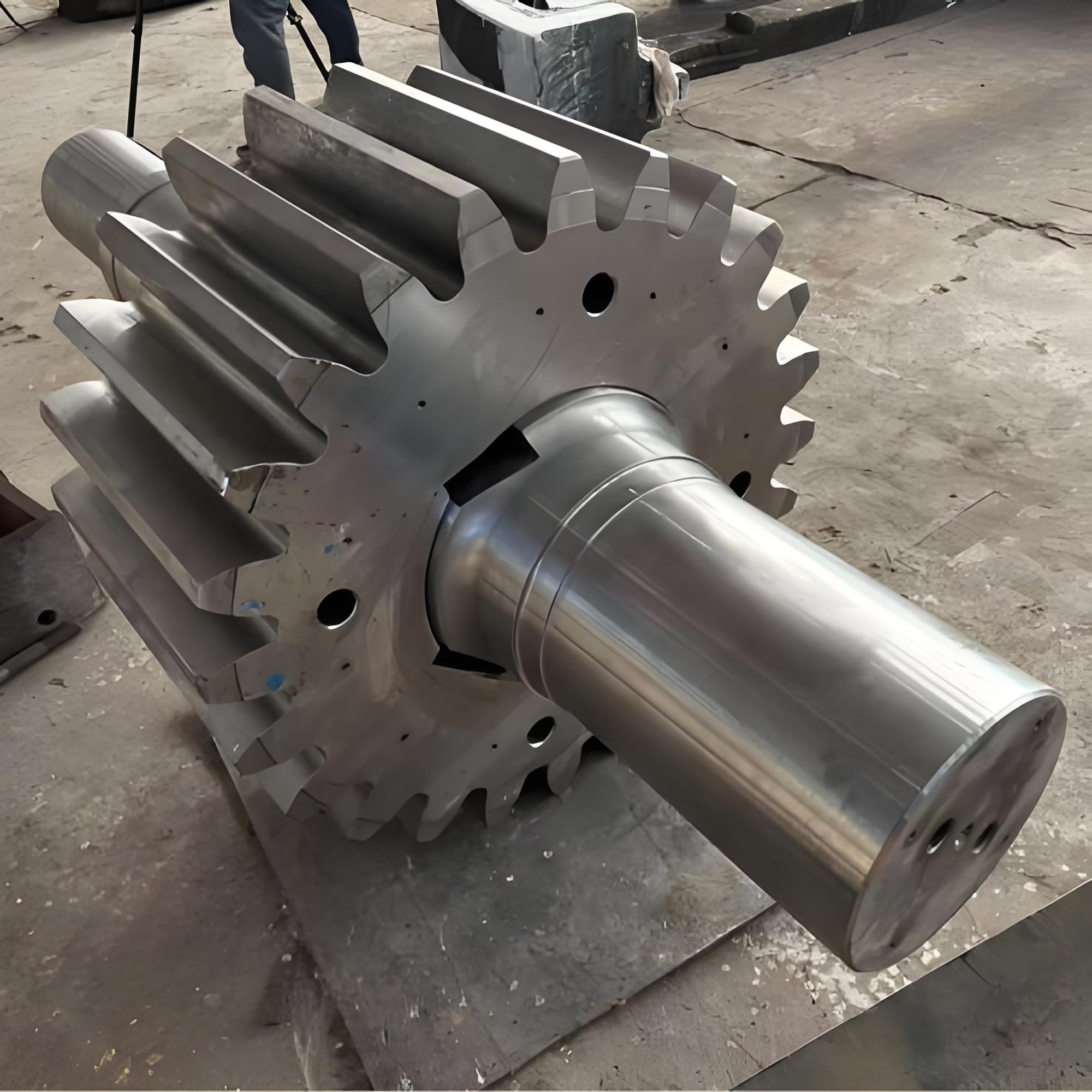
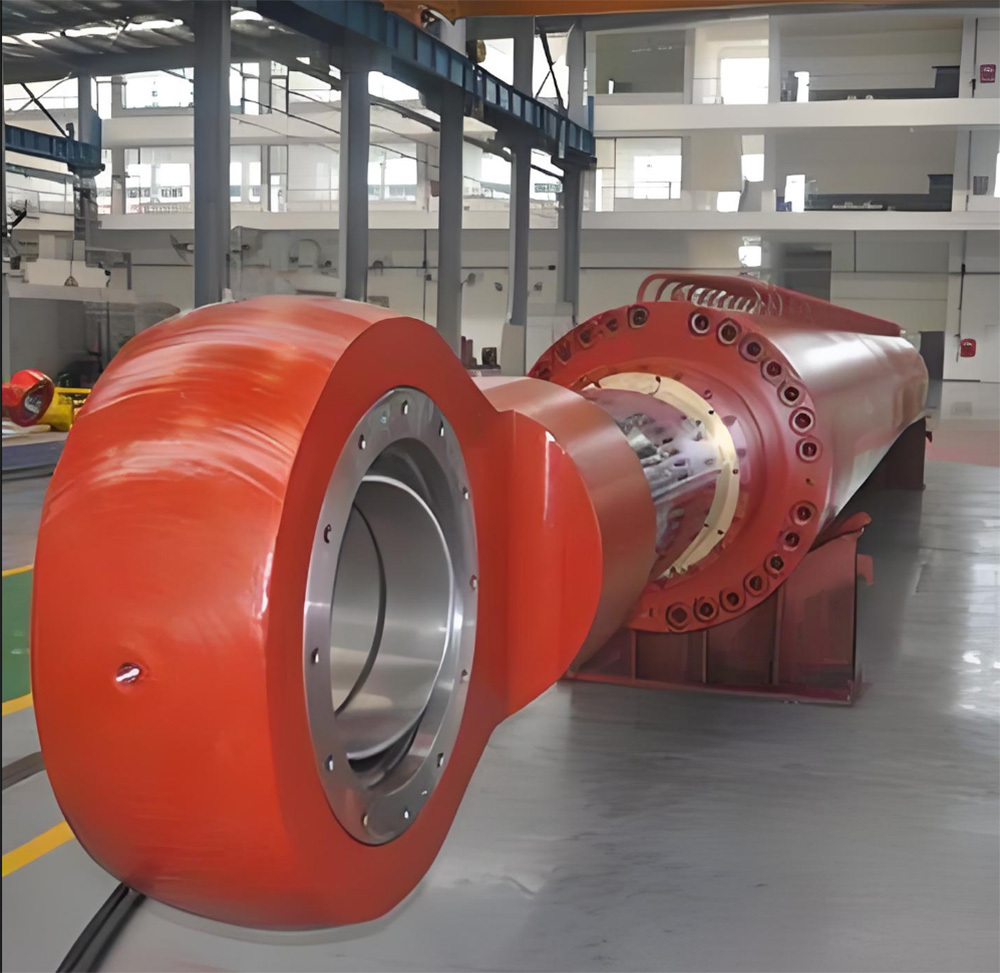
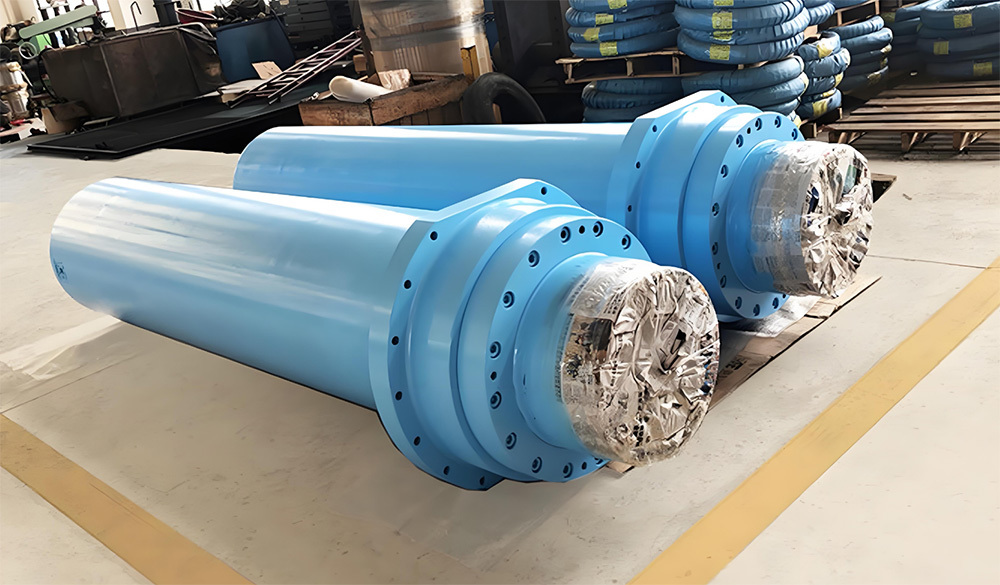
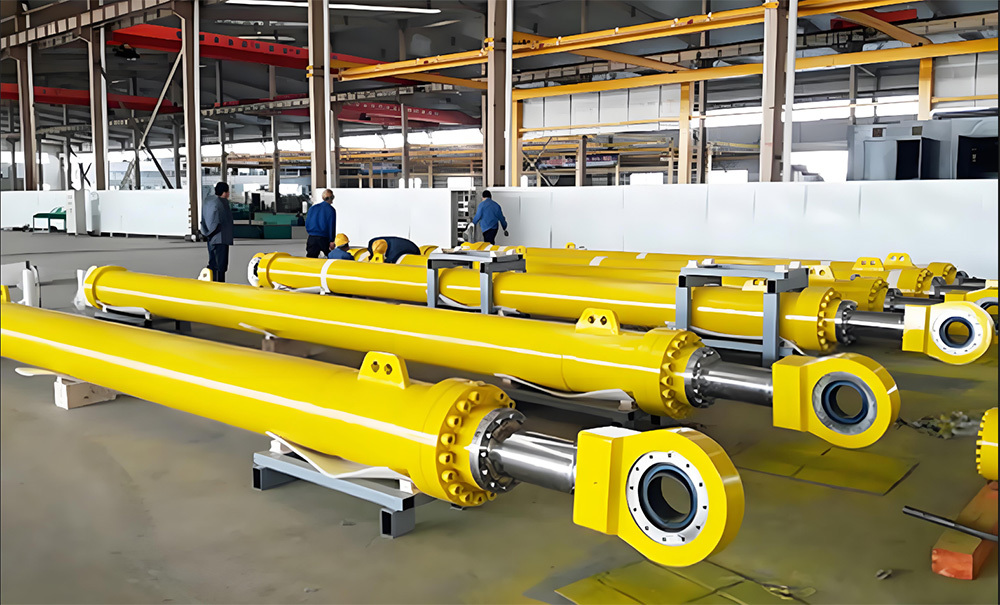
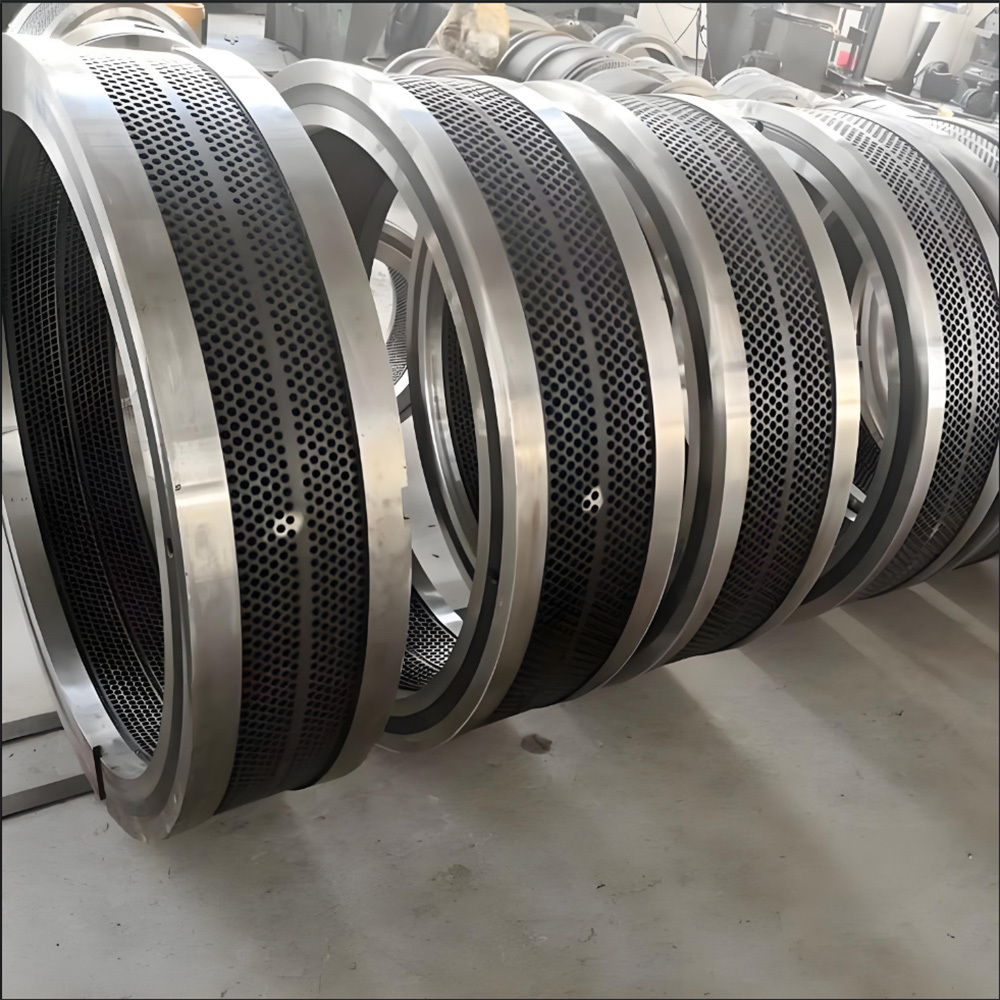
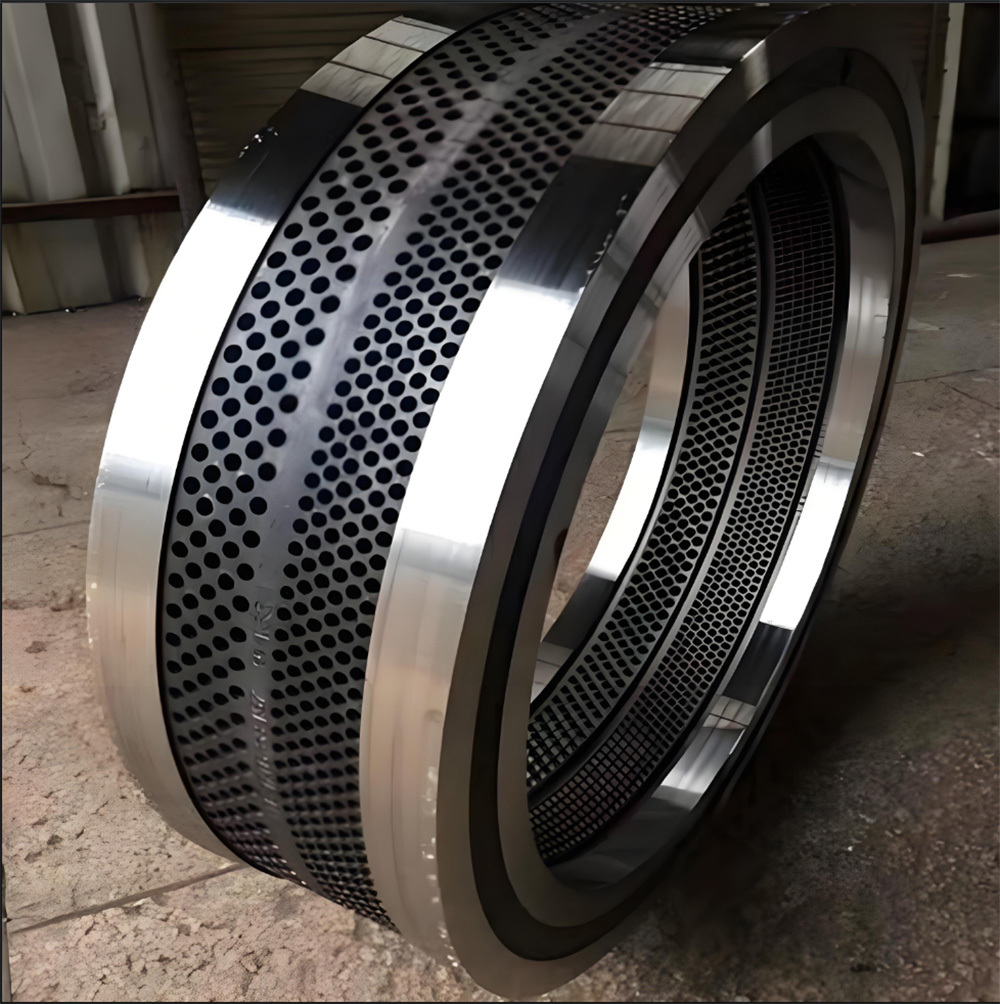
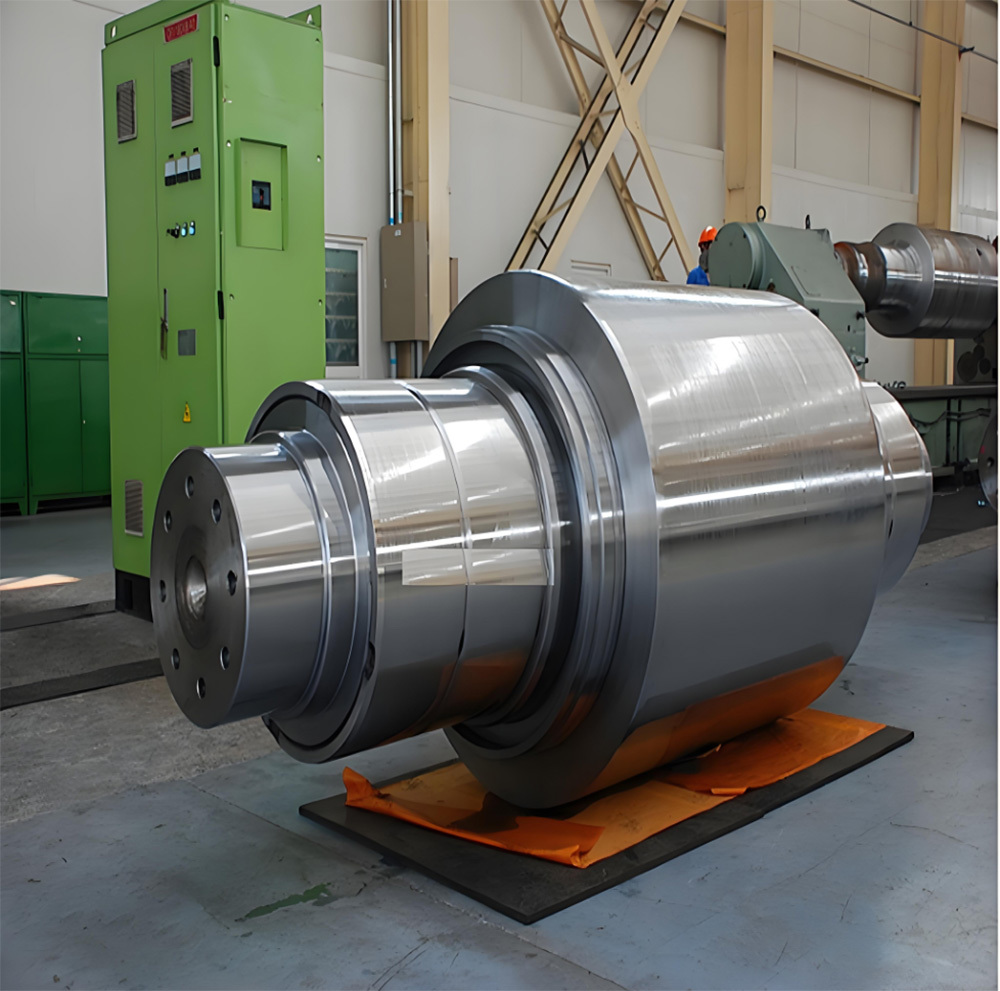
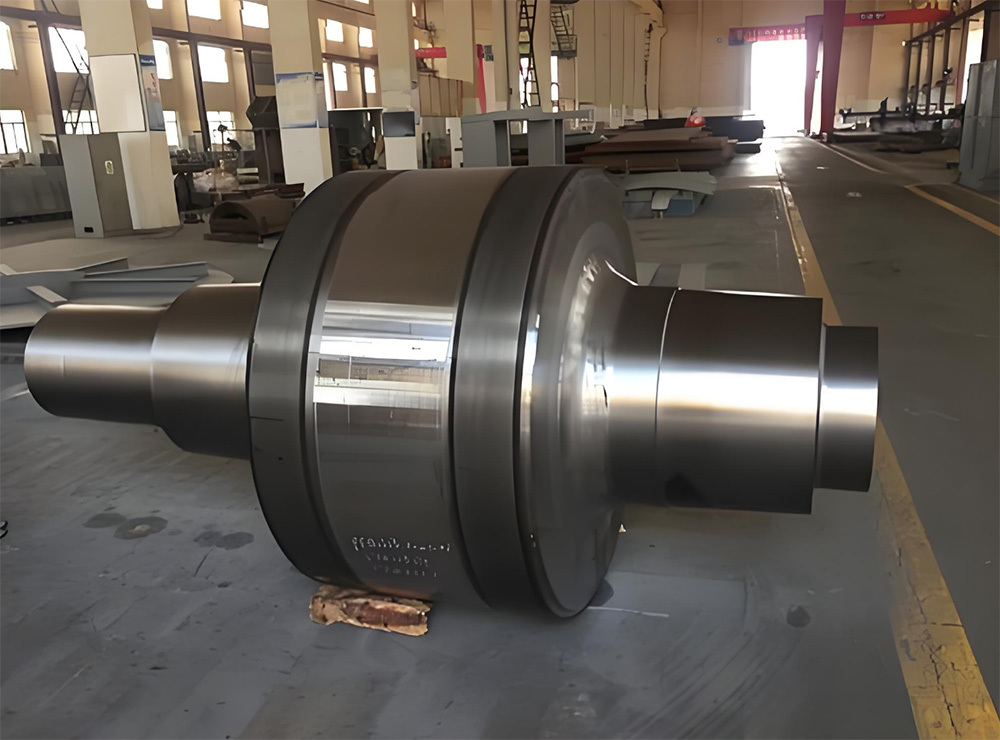
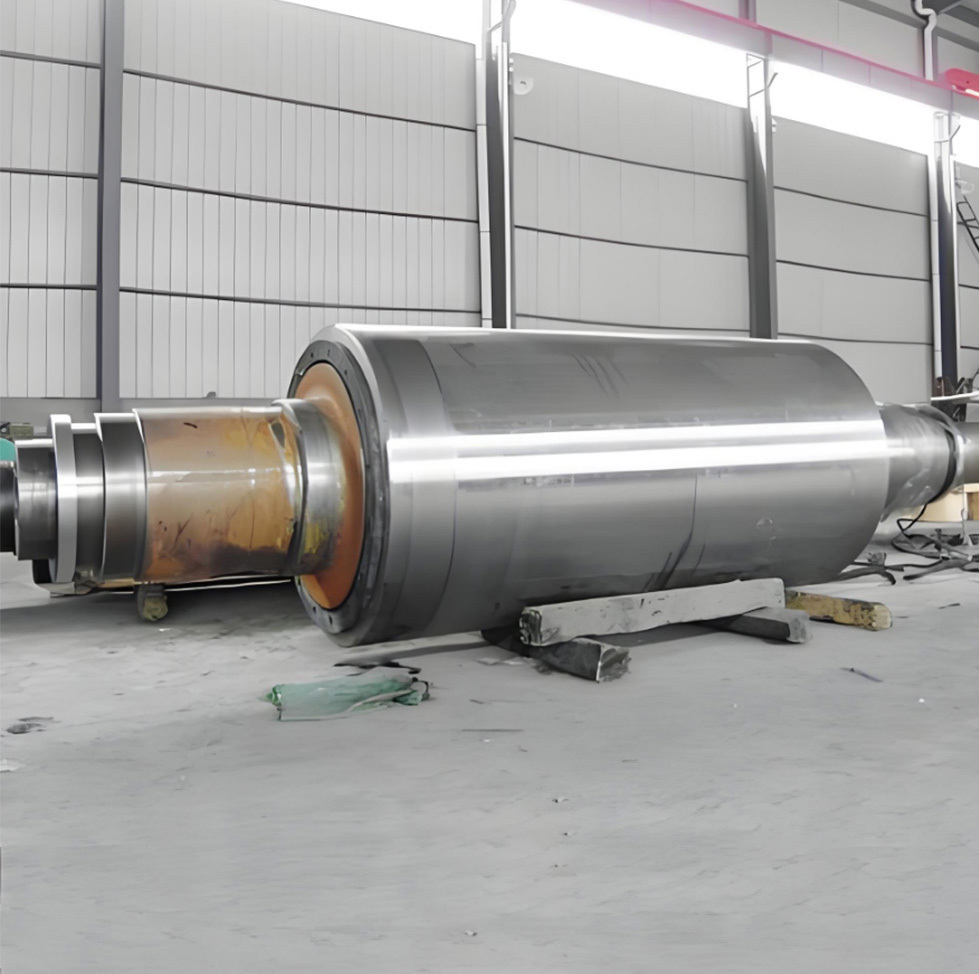
Marine crankshafts are the core components of ship power systems, used to convert the reciprocating motion of engine pistons (such as diesel engines) into rotational motion to drive propellers or other transmission devices. They are key power transmission elements in ship propulsion systems. Their reliability directly affects the ship's navigation safety, power output efficiency, and service life, requiring high strength, corrosion resistance, fatigue resistance, and the ability to withstand harsh marine environments.
Classification of Marine Crankshafts
1. By structural form:
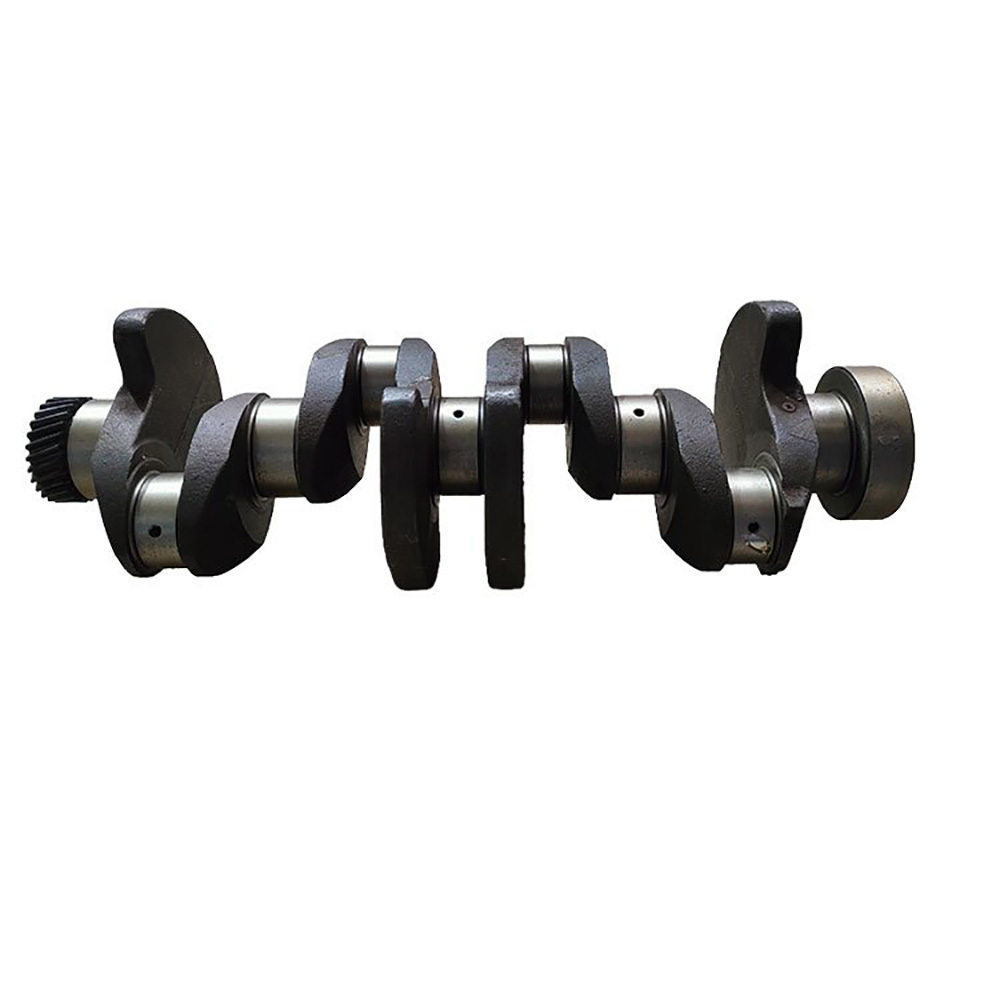
- Integral crankshaft: Suitable for medium and small ships or high-speed diesel engines, forged or cast as a whole, with a simple structure and easy maintenance.
- Composite crankshaft (semi-composite/full composite):
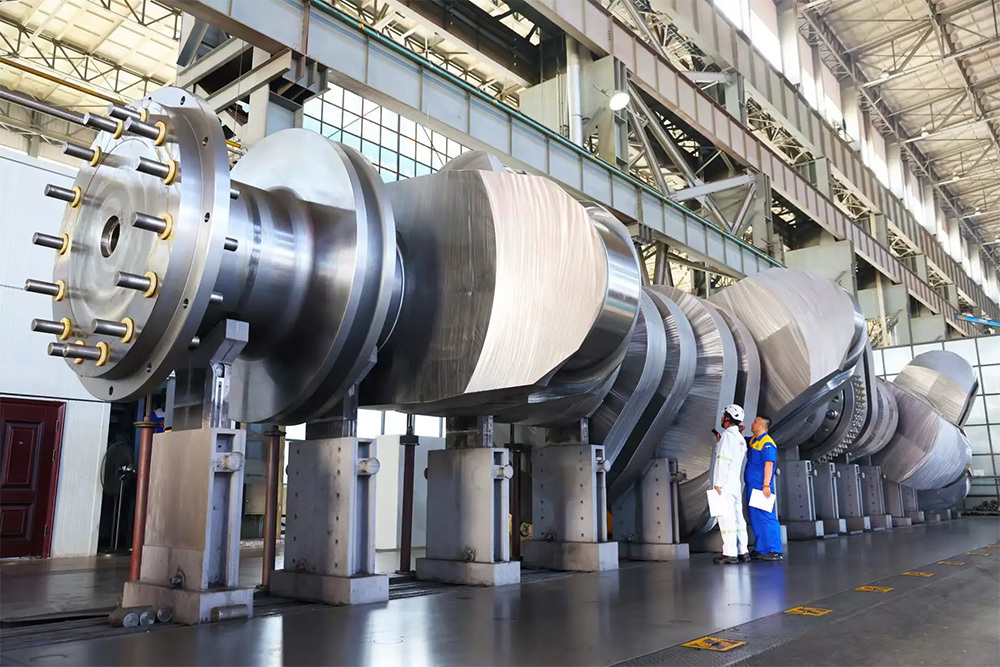
- Semi-composite: The crank throw (crank arm + crank pin) is forged as a whole and then hot-fitted with the main journal, offering high rigidity. It is suitable for large low-speed diesel engines and is the mainstream technology.
- Full composite: Each component is forged independently and then connected by welding or bolts. It offers high flexibility but slightly lower strength, commonly used in special working conditions.
2. By engine type:
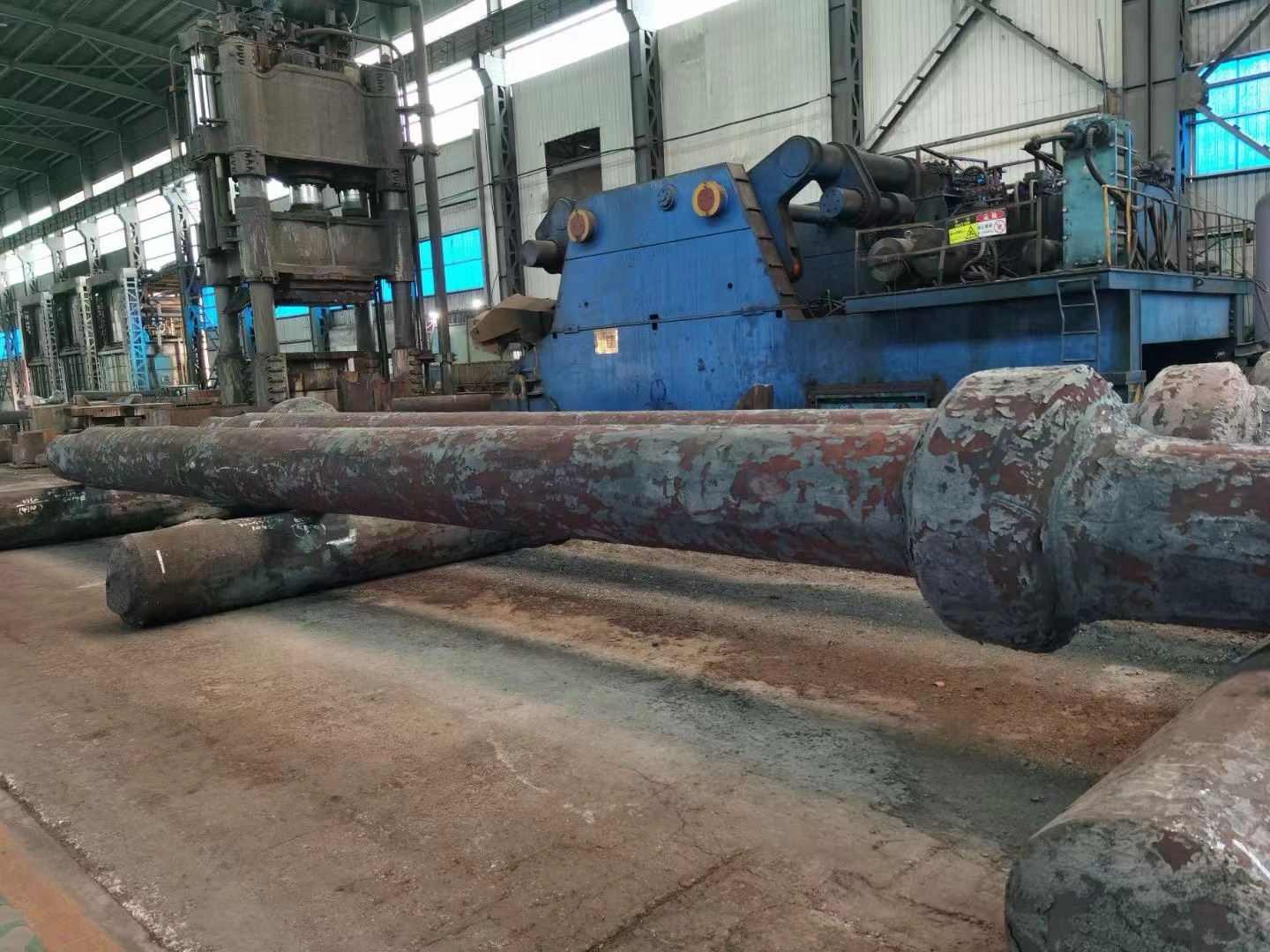
- Low-speed engine crankshaft: Low speed (<300 rpm), large size and heavy weight, such as ultra-large crankshafts for 10,000-ton ships (length can exceed 20 meters, weight hundreds of tons).
- Medium-high speed engine crankshaft: Suitable for medium and small ships or diesel generators, with higher speed and relatively smaller size.
Specifications
1. Size range:
- Diameter: Main journal diameter can exceed 2.5 meters (large low-speed engines), crank throw radius over 2 meters.
- Length: Ranges from a few meters to several tens of meters (e.g., a 488-ton ship crankshaft is 23.5 meters long).
2. Materials:
- High-strength alloy steel (such as 42CrMo, 35CrMo), forged steel or ductile cast iron (QT700-2), meeting high load and corrosion resistance requirements.
- Weight: Single crankshaft weight ranges from tens to hundreds of tons (e.g., the global W12X92 type crankshaft weighs 488 tons).
Design Parameters
1. Dimensional parameters
- Main journal diameter: Affects the crankshaft's support and load capacity, usually 0.65 to 0.75 times the cylinder diameter.
- Connecting rod journal diameter: Connects to the connecting rod and bears piston thrust, usually 0.60 to 0.65 times the cylinder diameter.
- Crank radius: Determines piston stroke and engine displacement, usually 0.25 to 0.33 times the cylinder diameter.
- Crank arm dimensions: Thickness is 0.18 to 0.25 times the cylinder diameter, width is 0.75 to 1.20 times.
2. Material selection
- Common materials: Cast iron, forged steel, alloy steel, etc., selected based on engine type and working conditions to ensure strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
3. Strength parameters
- Bending and torsional strength: The crankshaft must withstand complex bending and torsional loads, requiring sufficient strength and rigidity.
- Fatigue strength: Improved by optimizing fillet design and surface strengthening treatments to enhance fatigue resistance.
4. Balance design
- Balance weight design: To balance rotational centrifugal force and reciprocating inertia force, balance weights are set on the crankshaft. Their number, size, and position are determined by the engine's cylinder count and arrangement.
Precision Requirements
- Surface roughness: The roughness of the journal surface affects lubrication and wear resistance, with Ra values generally between 0.4 and 0.8 μm.
- Roundness and cylindricity: Geometric accuracy of the journal affects bearing fit and smooth operation, with roundness ≤ 0.005 mm and cylindricity ≤ 0.005 mm.
Applicable Scope
- Large ocean-going vessels: Container ships, oil tankers, bulk carriers, etc., equipped with low-speed high-power diesel engines.
- Inland and coastal vessels: Medium and small cargo ships, fishing boats, engineering vessels, etc., using medium-high speed diesel engine crankshafts.
- Offshore engineering equipment: Power systems for drilling platforms and floating production storage and offloading units (FPSO).
- Power generation field: Large diesel generator sets for ship power plants or land-based power stations.
Important Features
1. Ultra-high load capacity: Adapted for long-term high-load operation of ships, with a design life matching the ship's lifespan (over 20 years).
2. Corrosion resistance design: Surface coatings or special material treatments to resist seawater and fuel corrosion.
3. High reliability: Maintenance-free for life, avoiding major risks caused by offshore failures.
4. Precision manufacturing and dynamic balancing: Reduces vibration and noise, improving navigation comfort and safety.
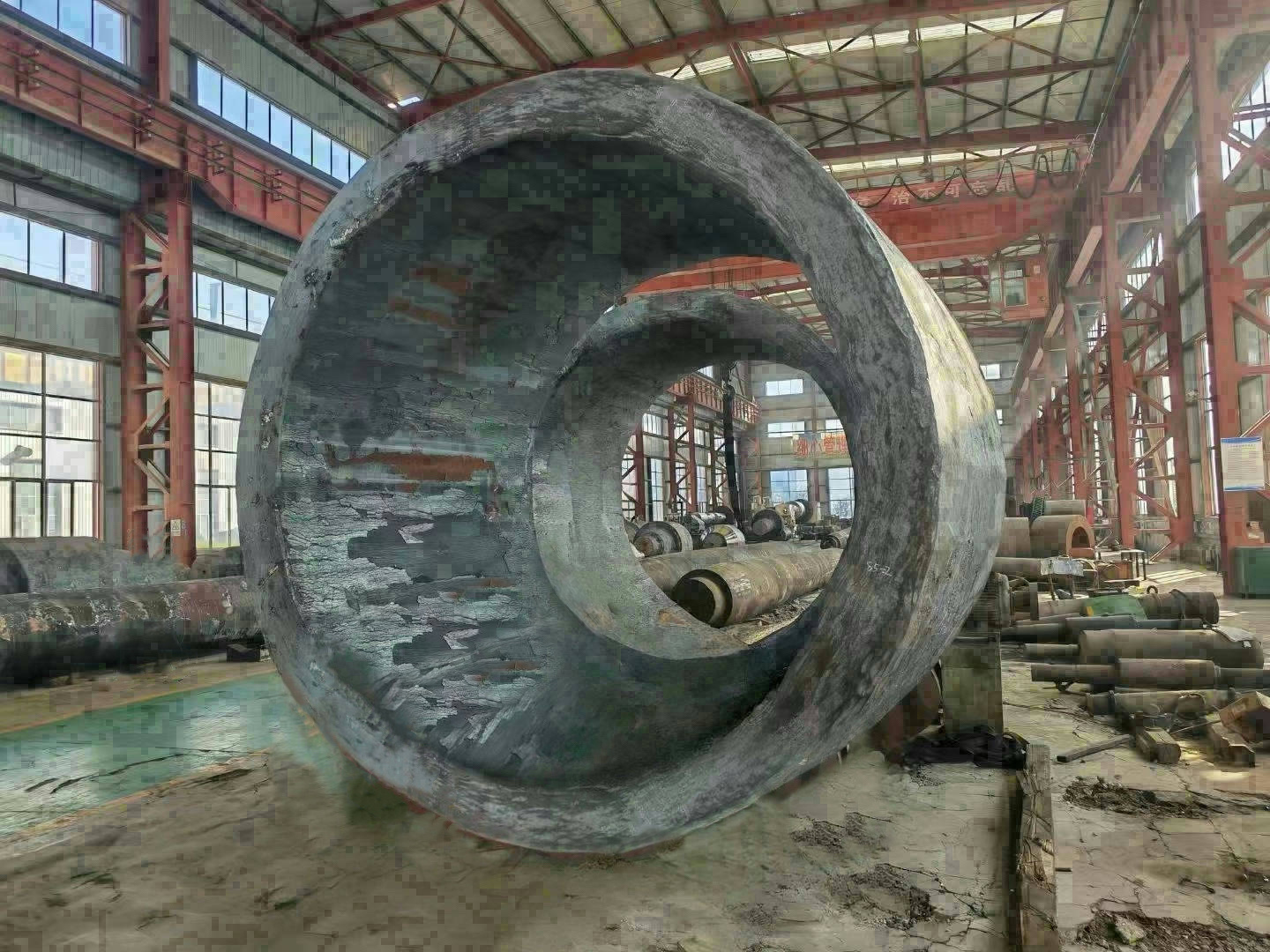
5. Modular composite design: Large crankshafts are manufactured in segments and assembled to reduce transportation and installation difficulties.
Process Introduction
1. Forging and casting:
- Large low-speed engine crankshafts: Use semi-composite process, crank throw forged as a whole plus hot-fitted main journal; or electroslag remelting to improve material uniformity.
- Medium and small crankshafts: Integral die forging or precision casting, controlling grain structure to enhance strength.
2. Machining Process:
- High-precision grinding: CNC turning and tracking grinding ensure journal accuracy.
- Deep hole machining: Precision machining of key channels such as oil holes and balance holes.
3. Strengthening Treatment:
- Fillet rolling strengthening: Increases fatigue strength by more than 30%.
- Surface quenching + nitriding: Forms a high-hardness surface layer to extend service life.
4. Inspection Technology:
- Non-destructive testing (ultrasonic, magnetic particle inspection) to detect internal defects.
- Dynamic balancing test: Ensures vibration amplitude during rotation ≤ 0.02mm.
Keywords
Previous: Crankshaft
Next: Marine crankshaft





Marine crankshaft
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-
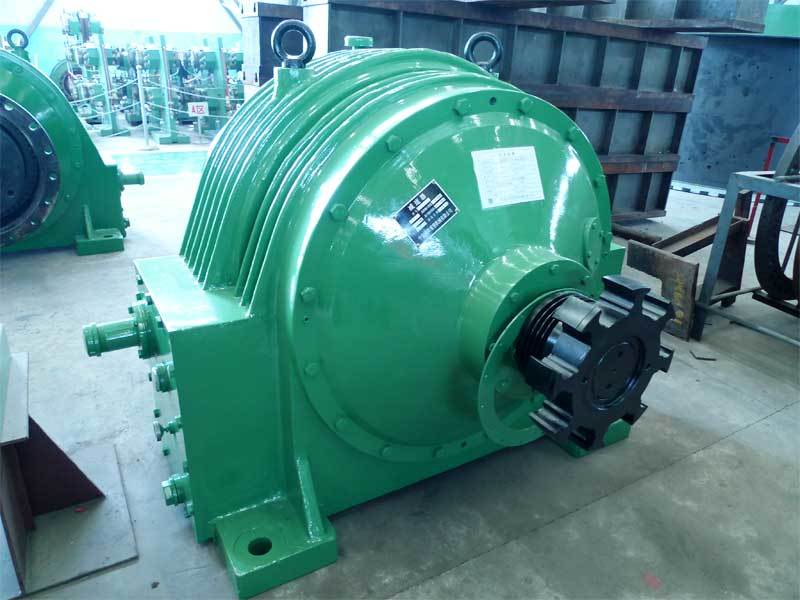

Planetary Gear Reducer
-
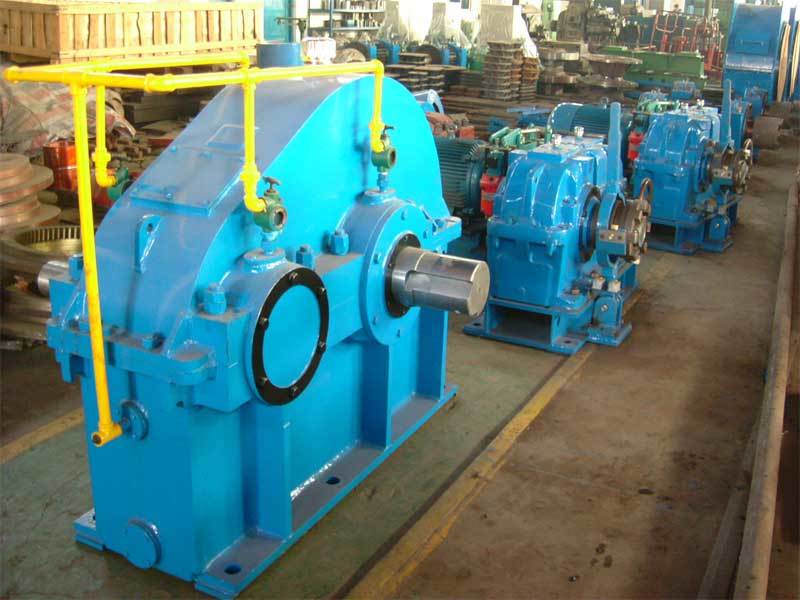

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
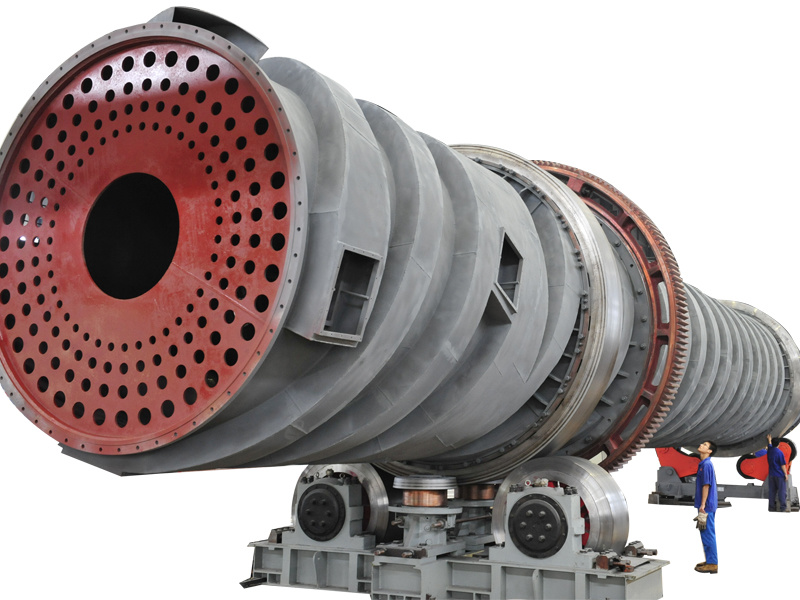
Rotary kiln
-
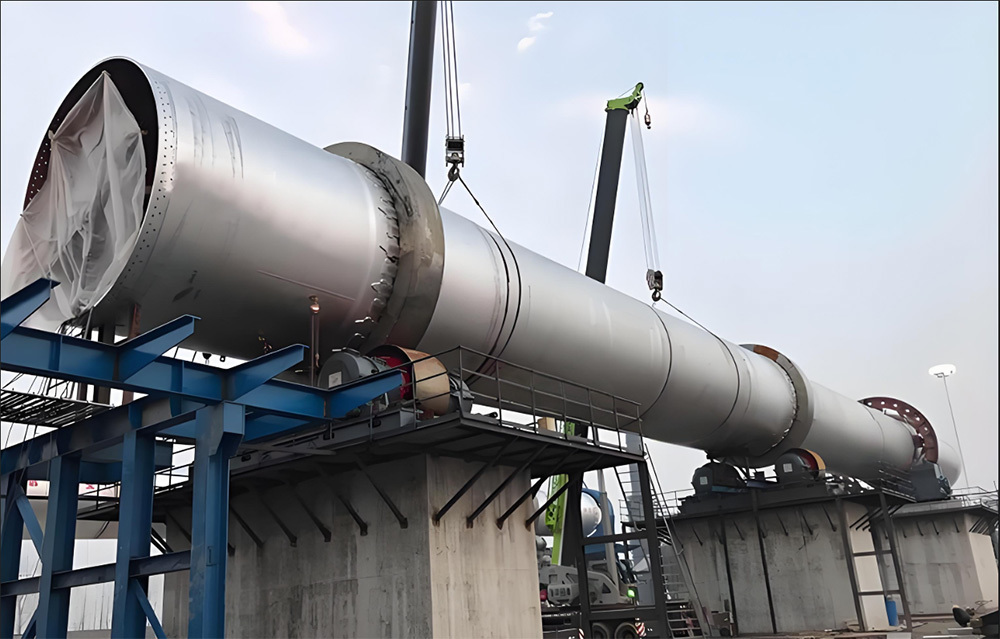

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-

Lime Rotary Kiln
-

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
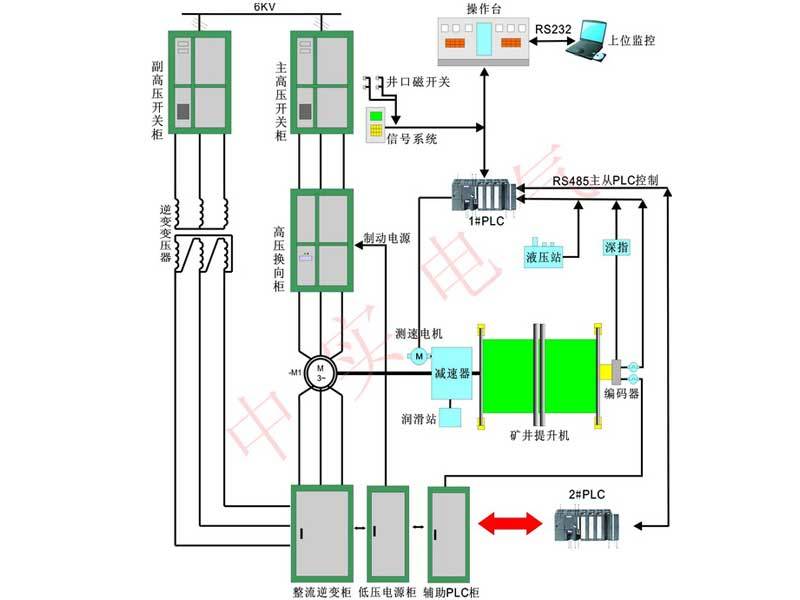
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
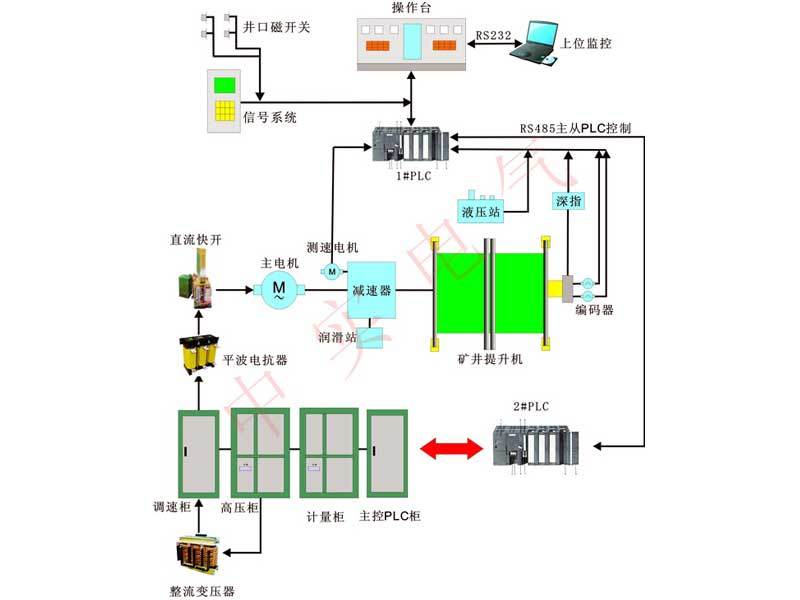
Fully digital DC control system
-
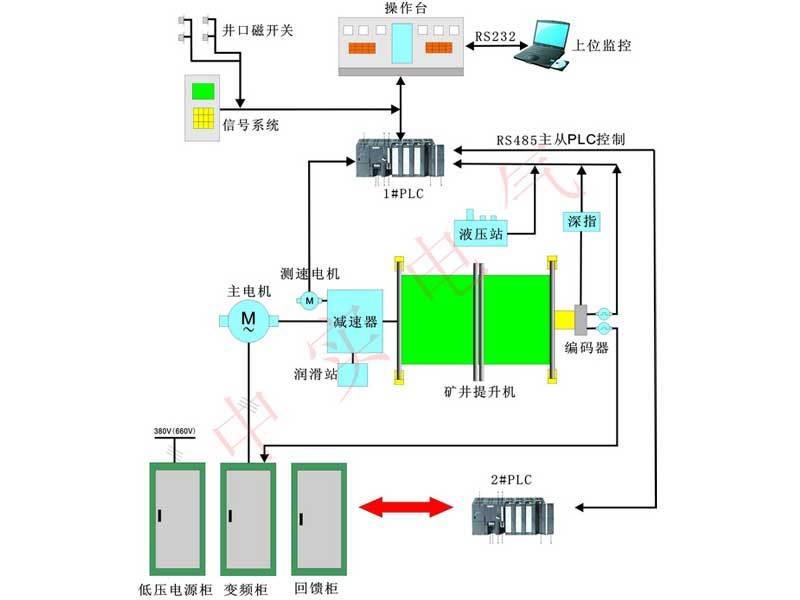
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
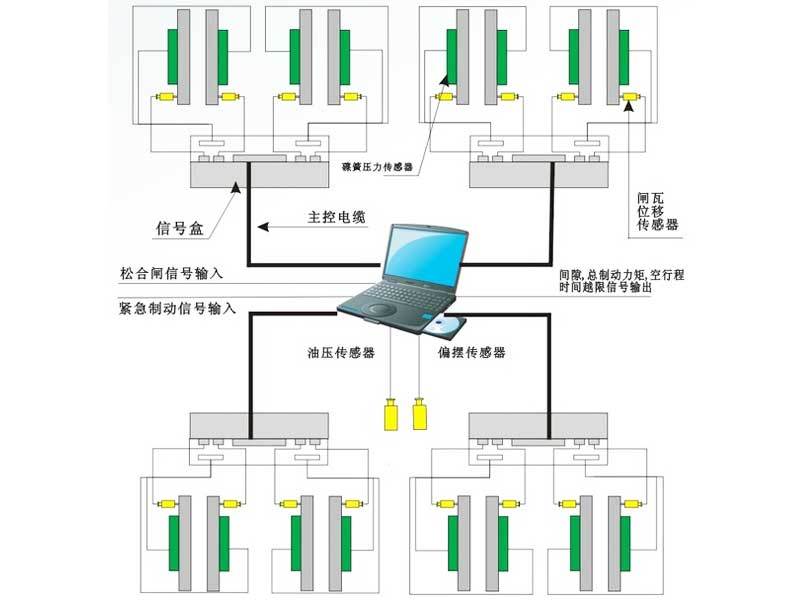
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-
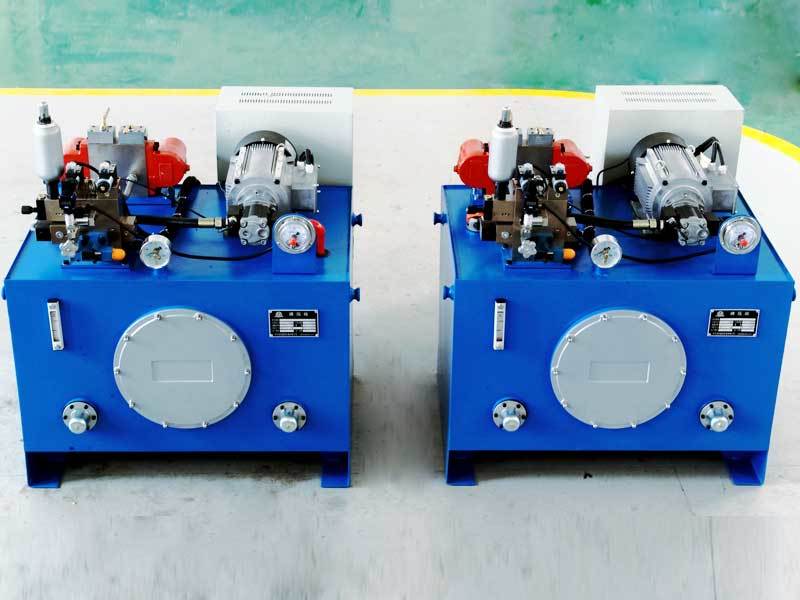

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-
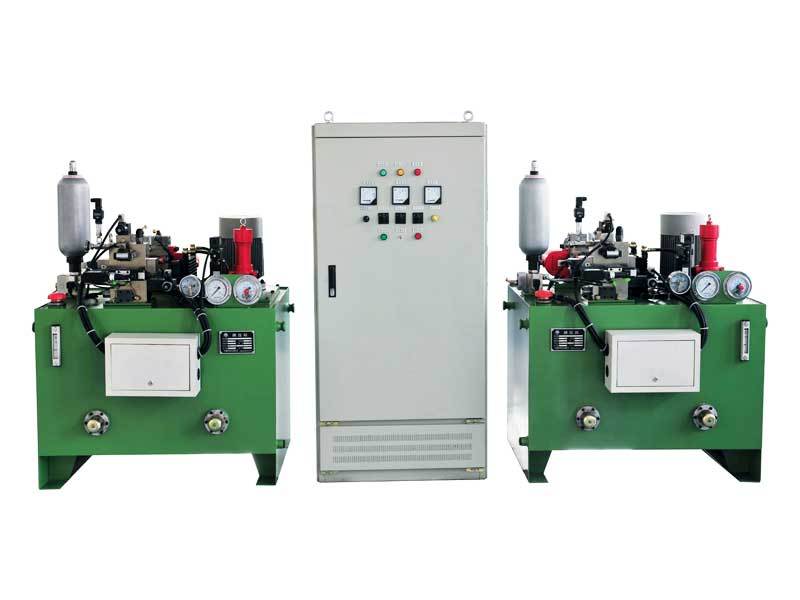

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-
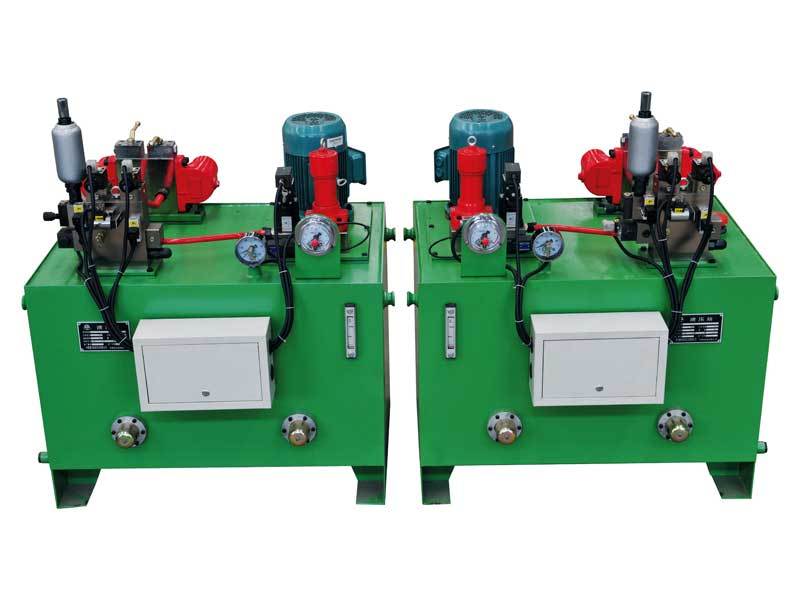

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-
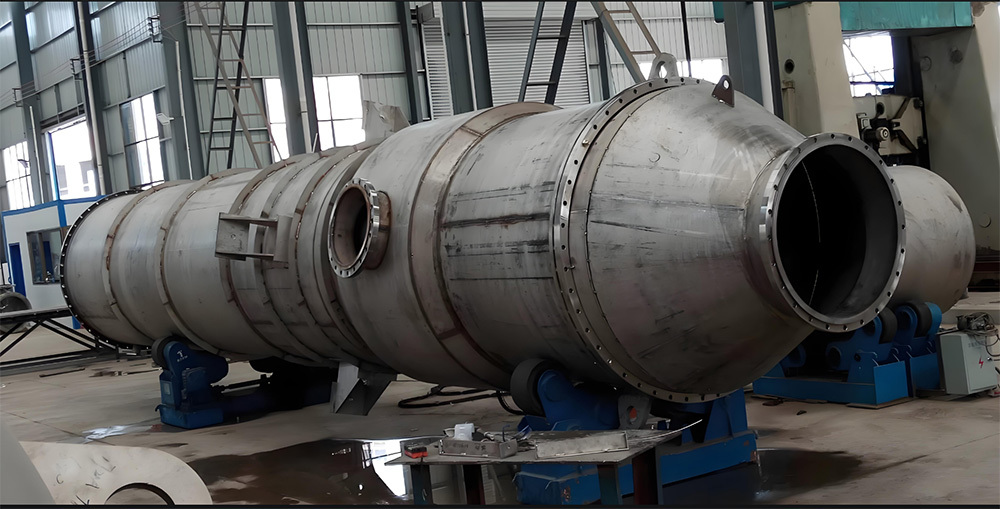

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
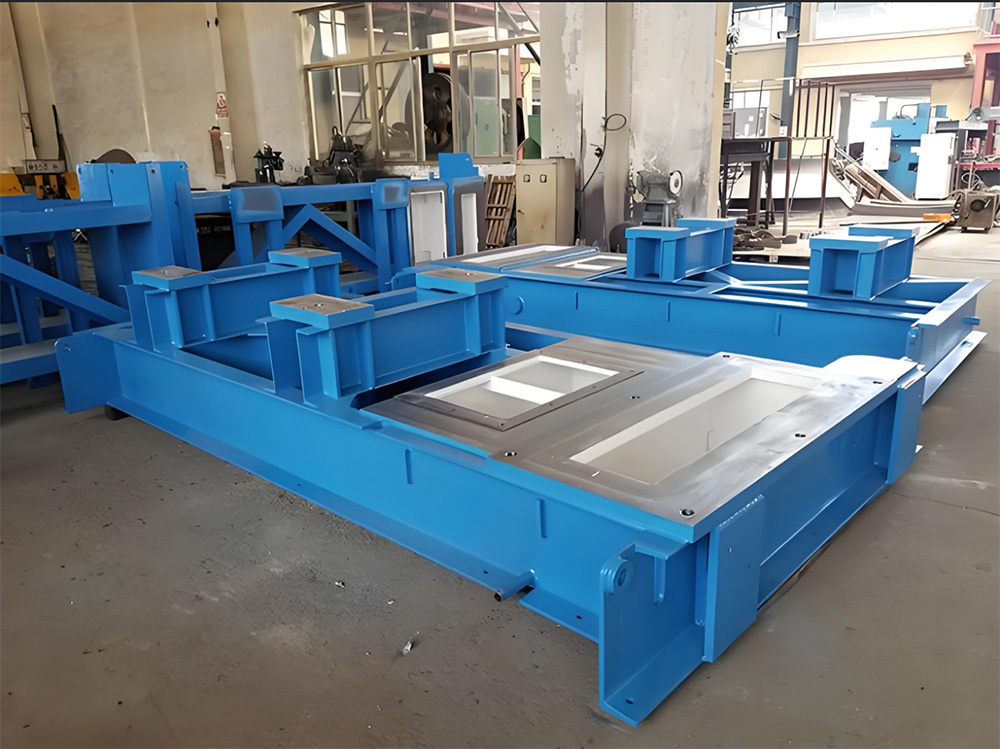

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-
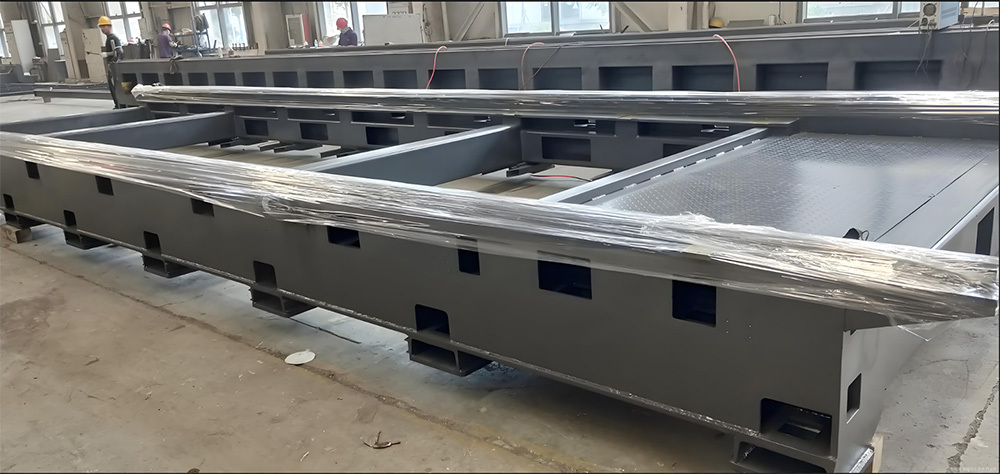

Large base
-
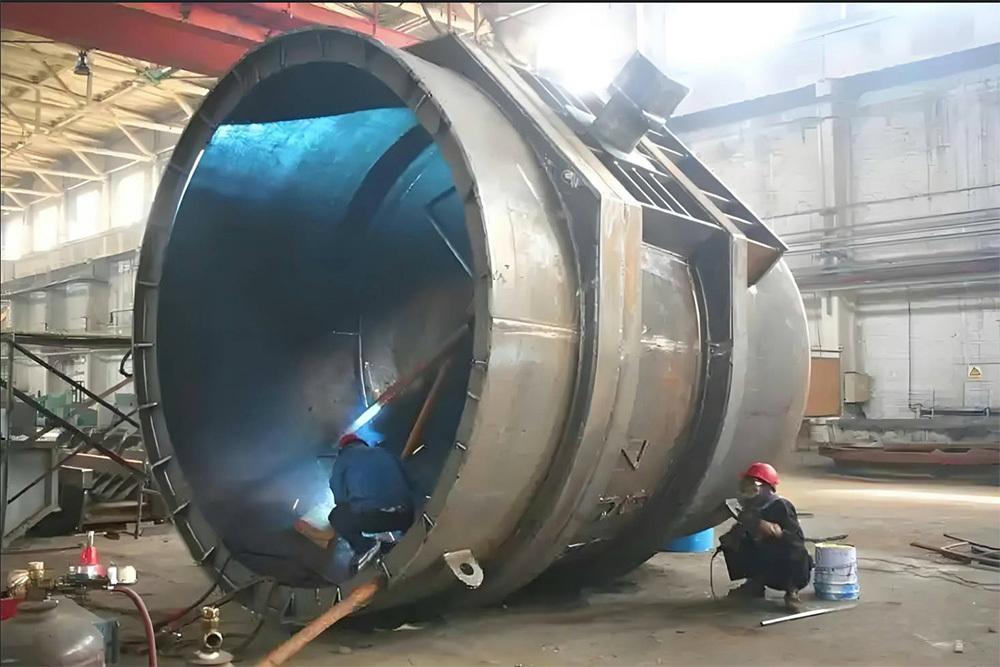

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
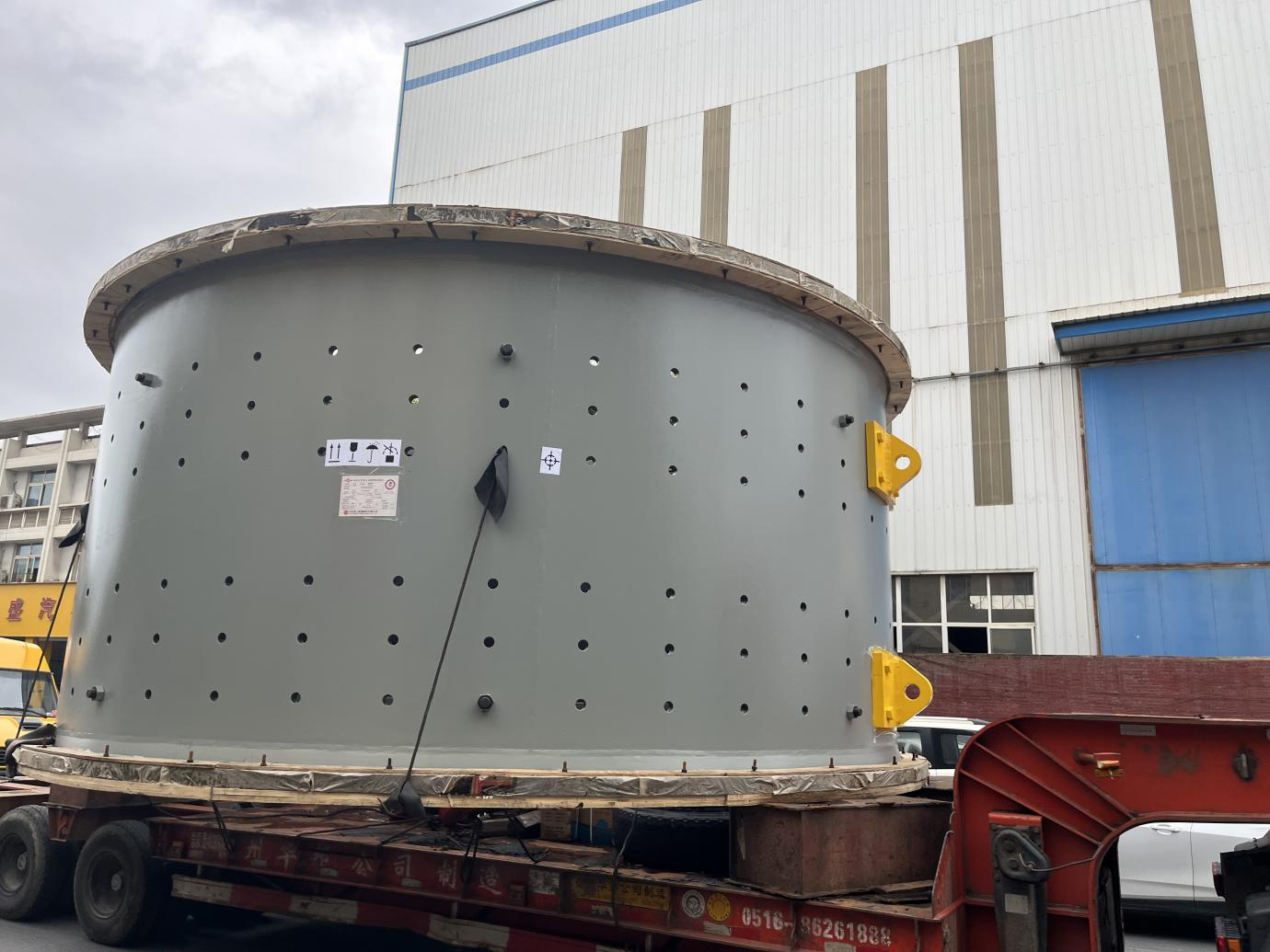

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-
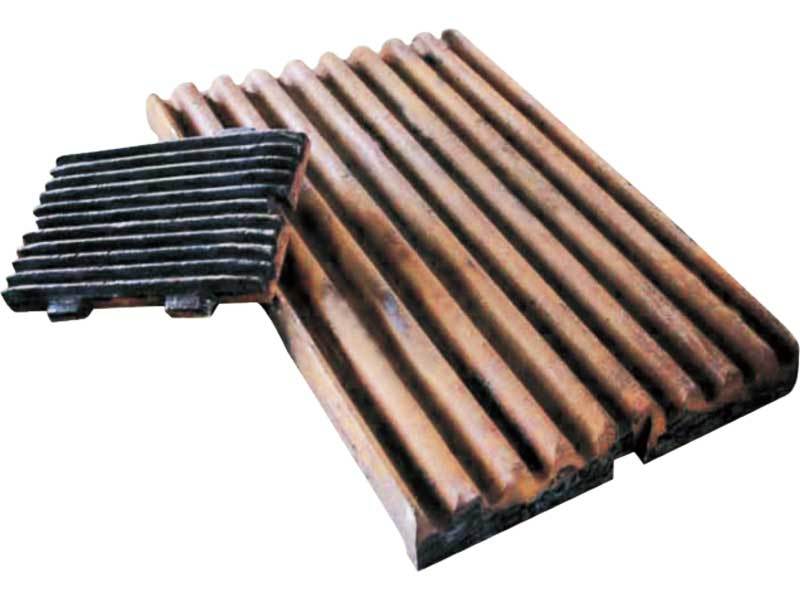

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-
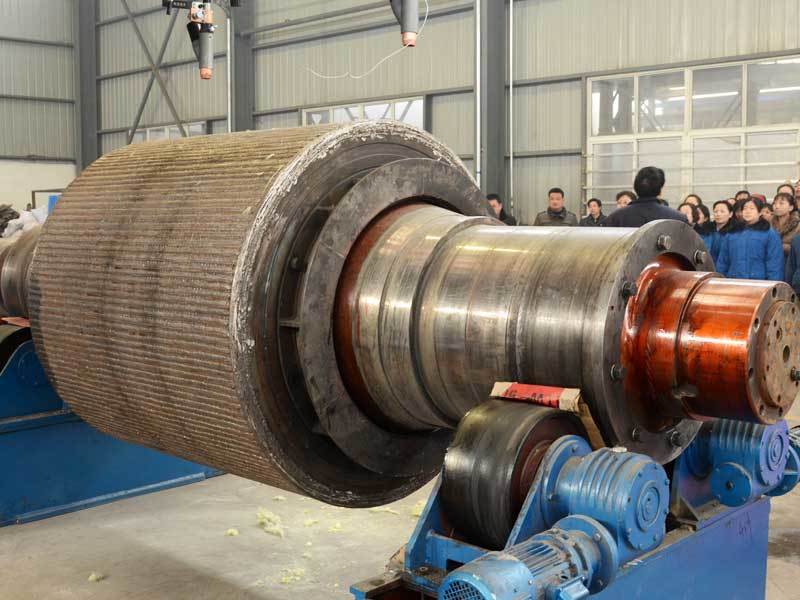

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-
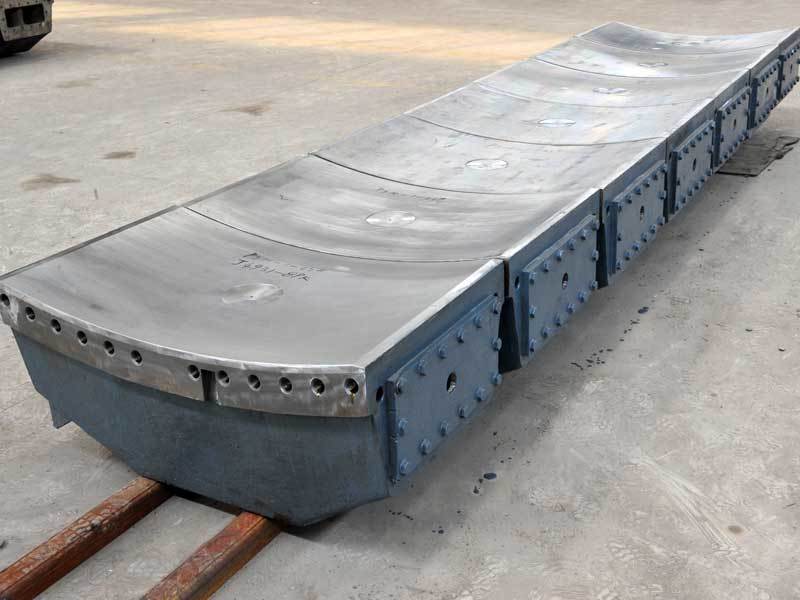

Bus Alloy Bushings
-
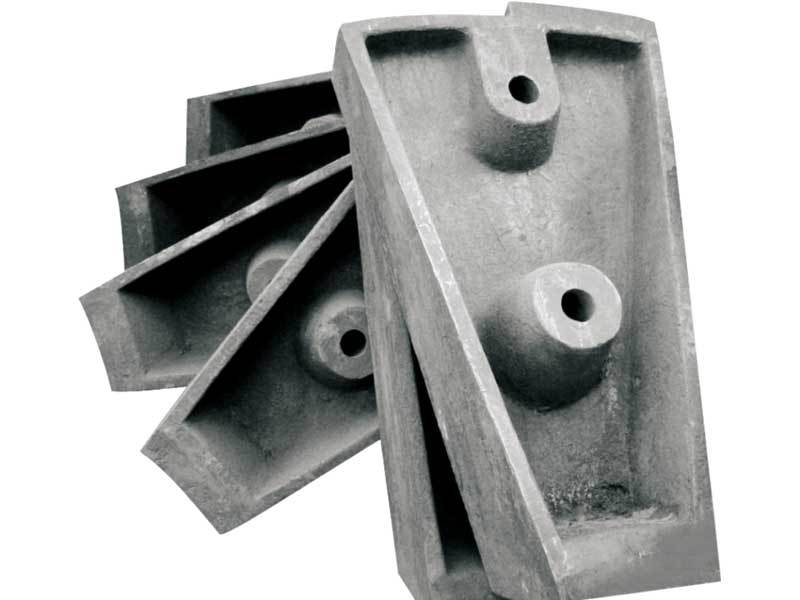

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-

Nylon products
-

Polyurethane Products
-

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-
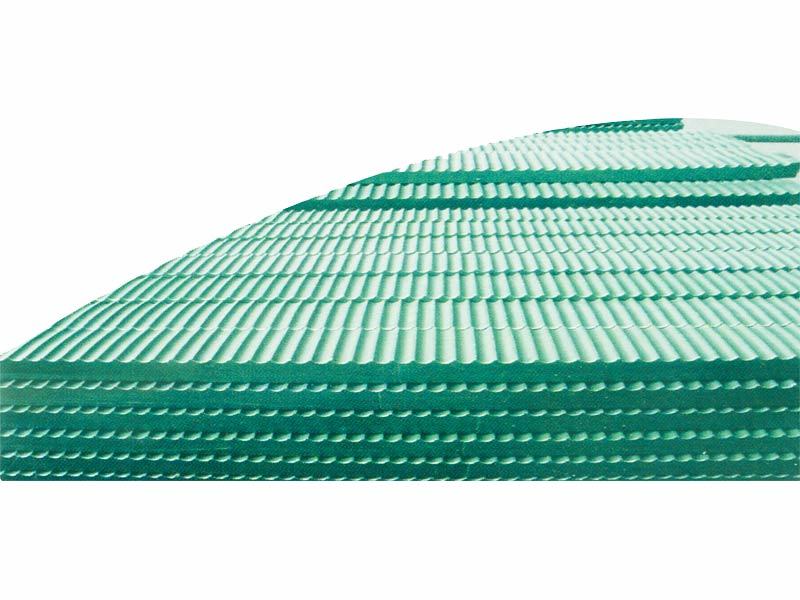

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-
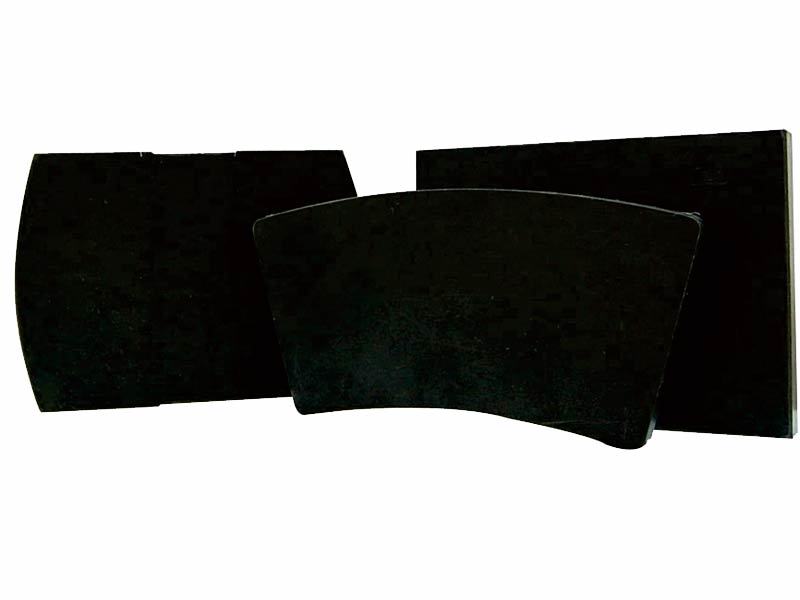

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-
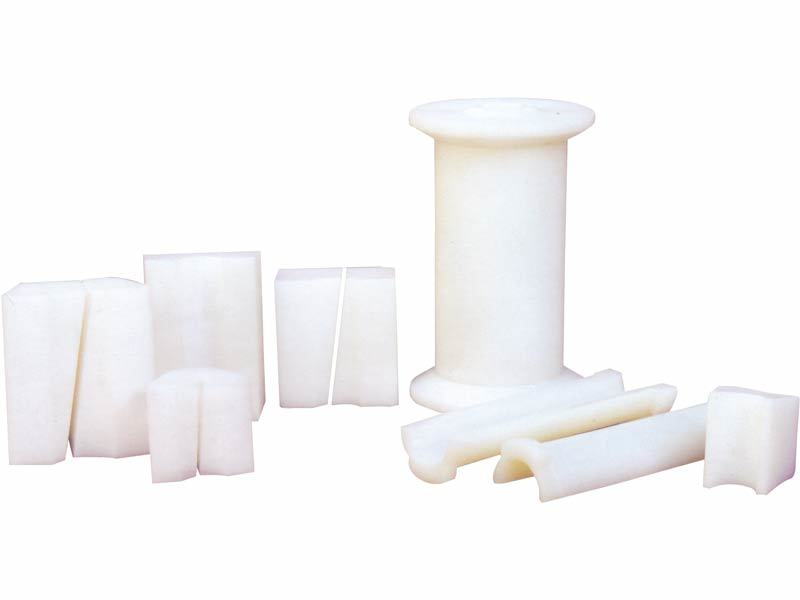

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-
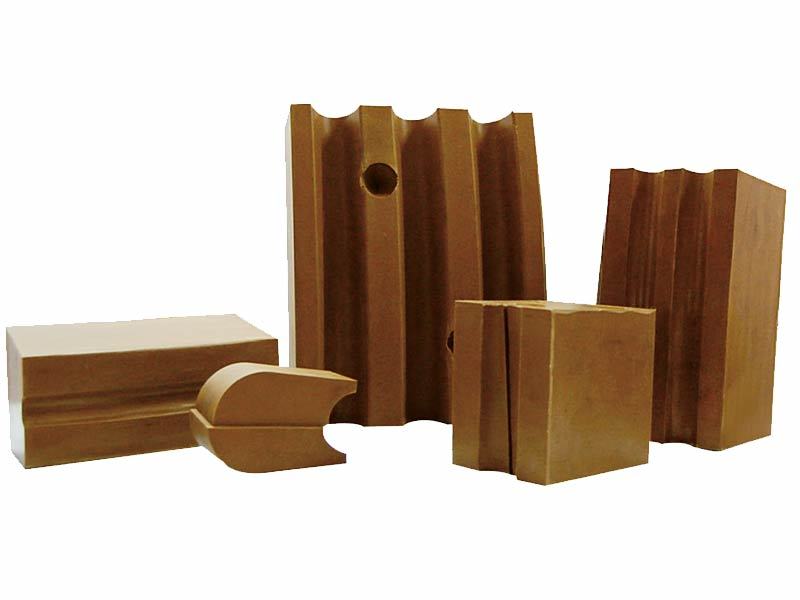

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information