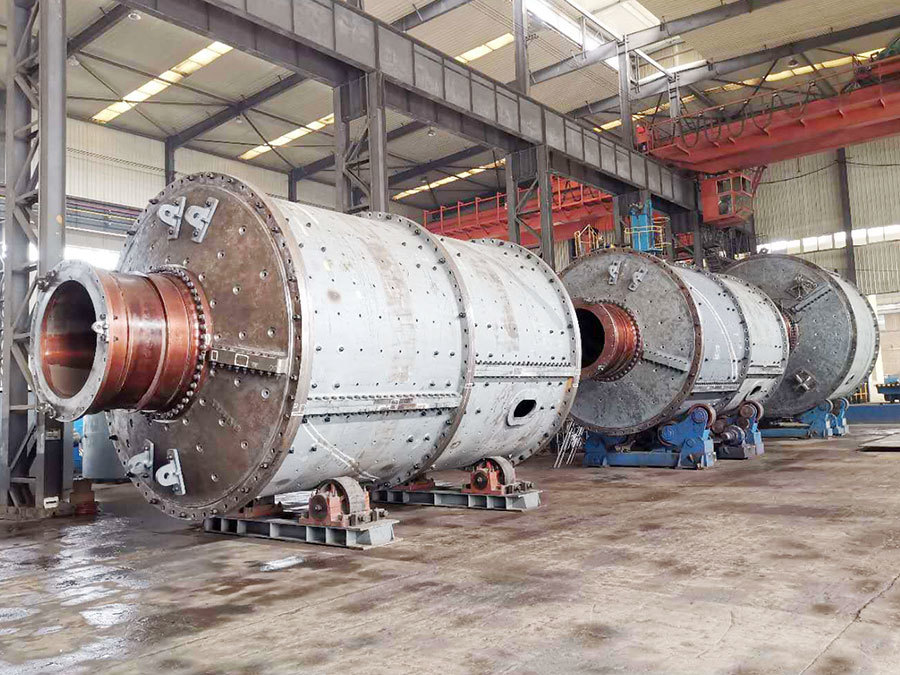
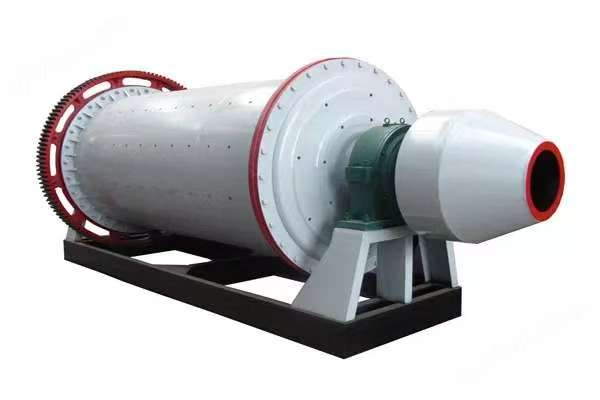
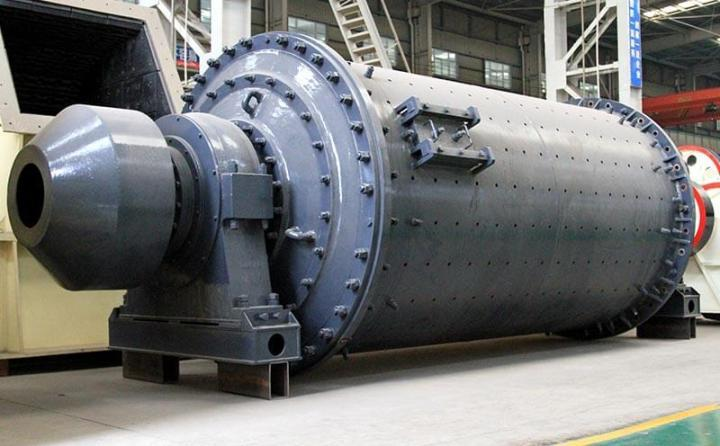
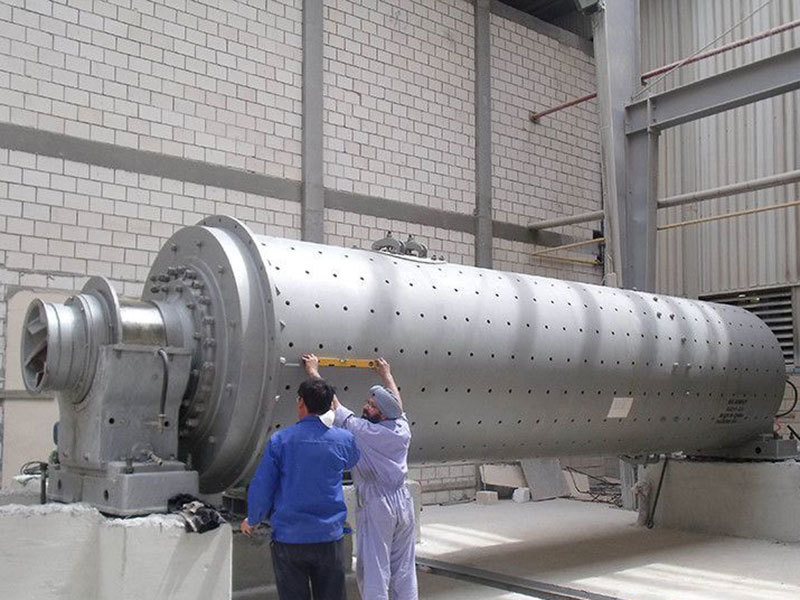
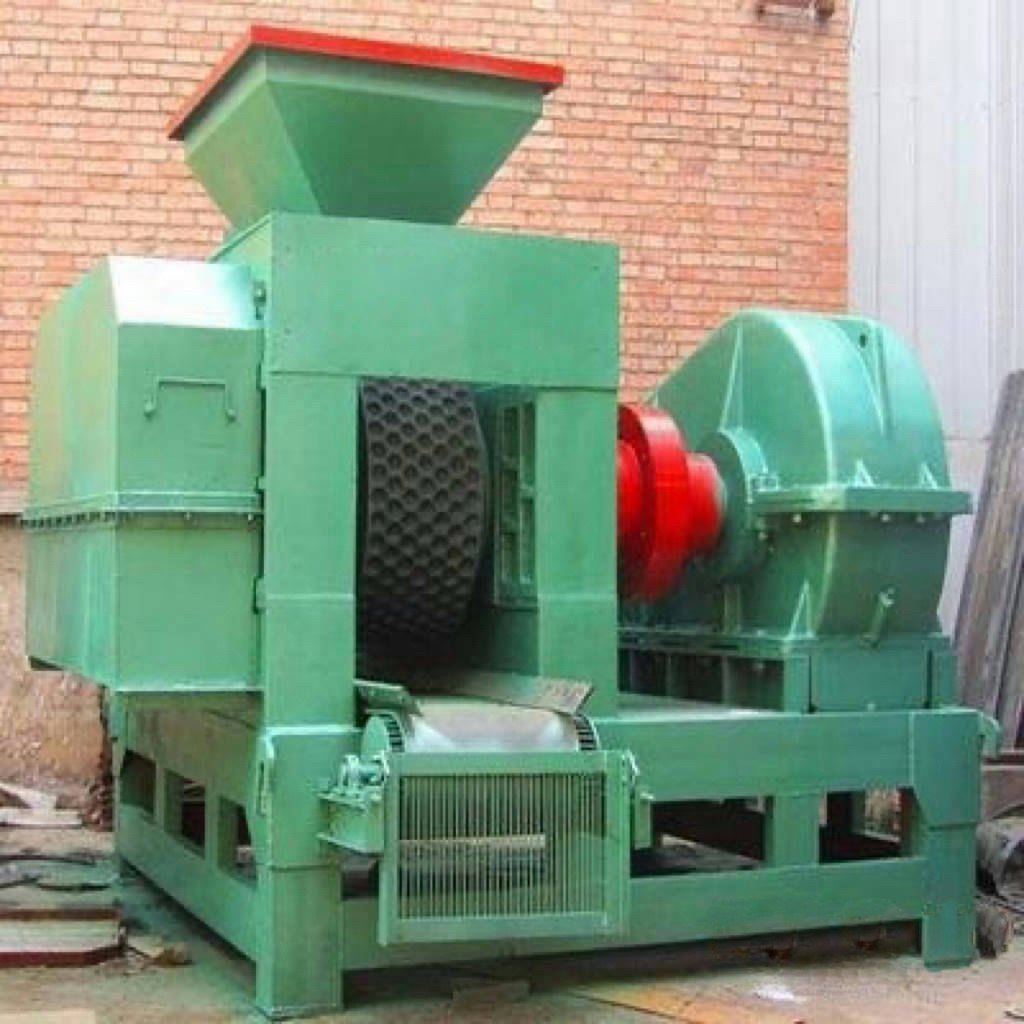
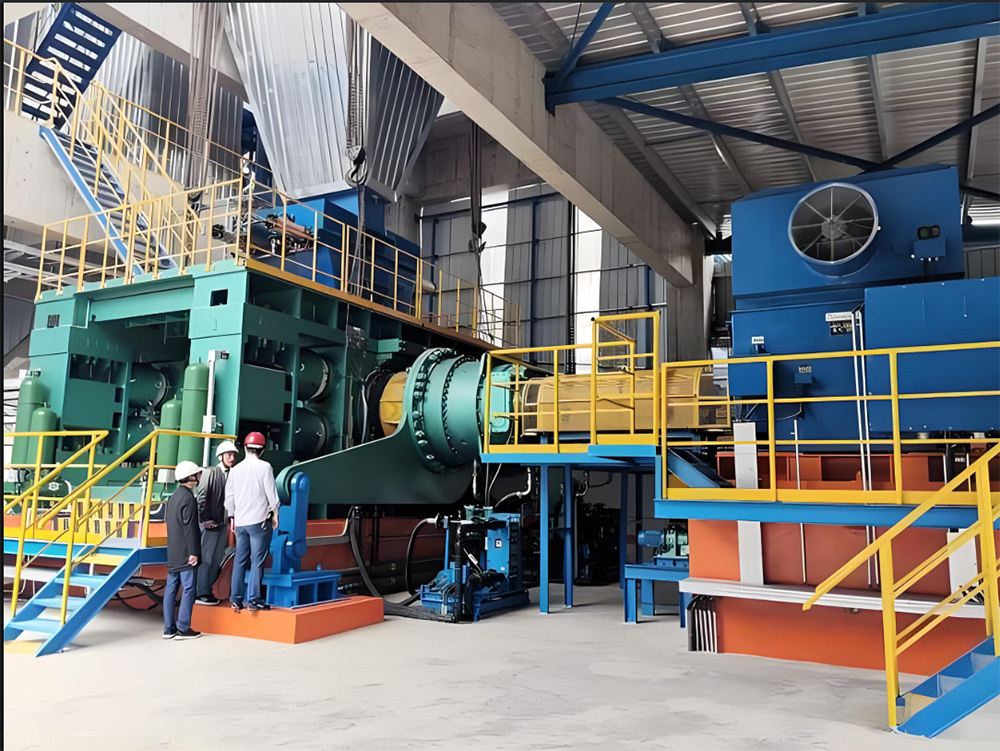
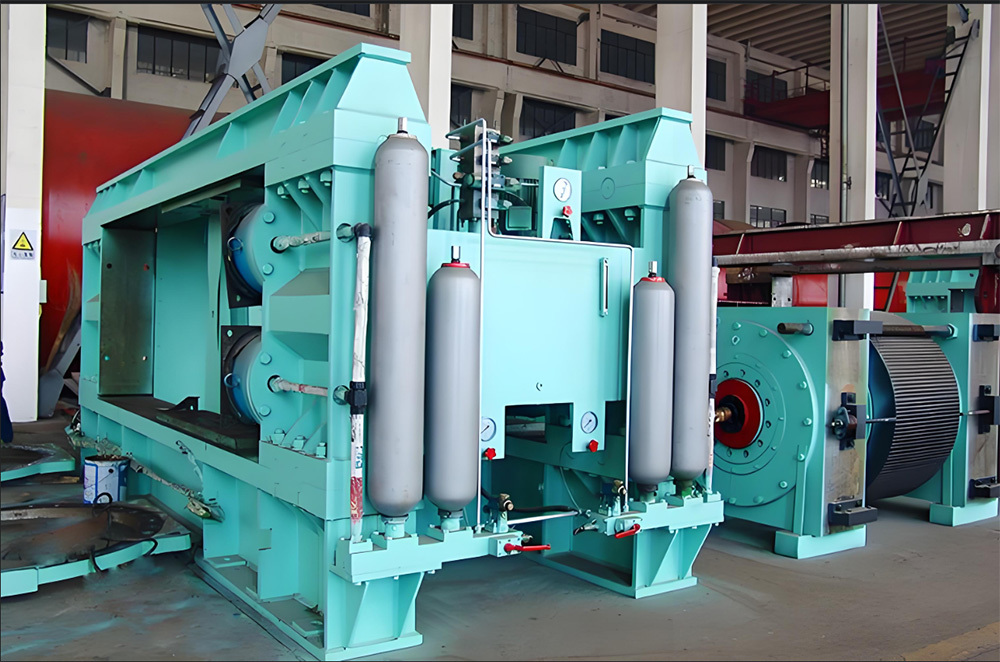
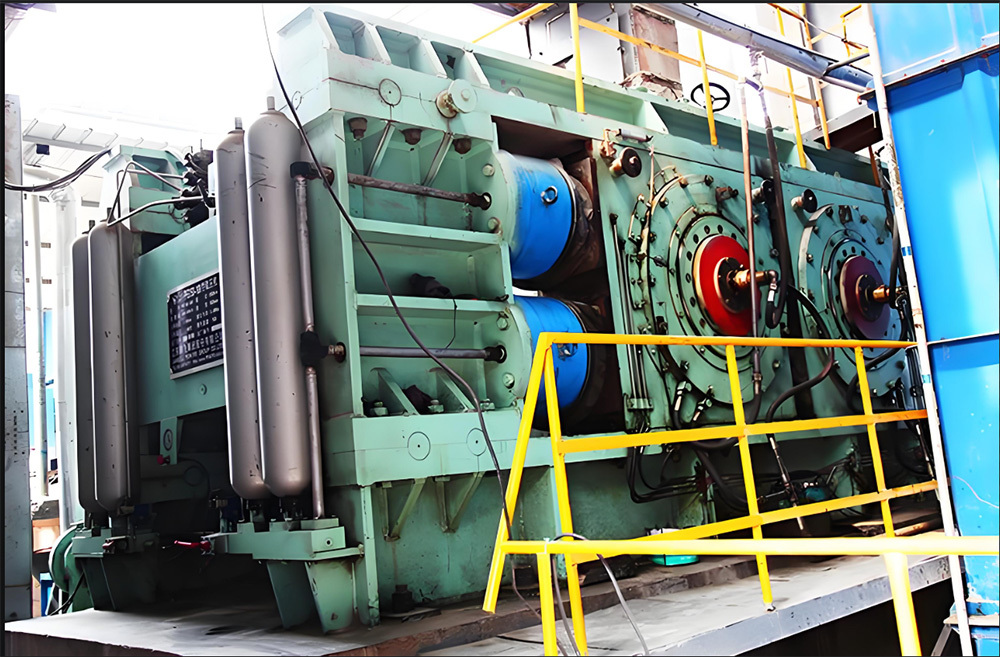
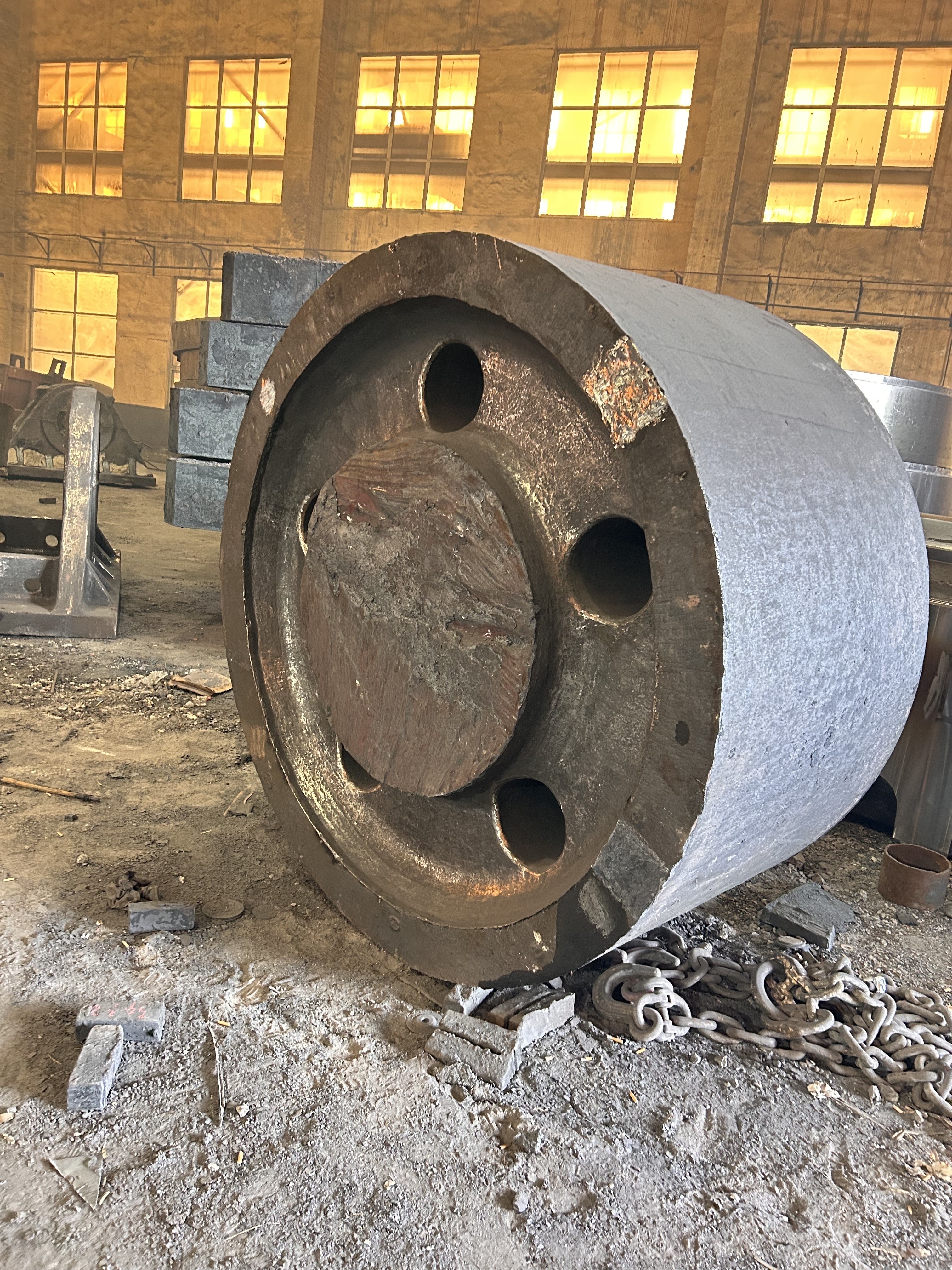
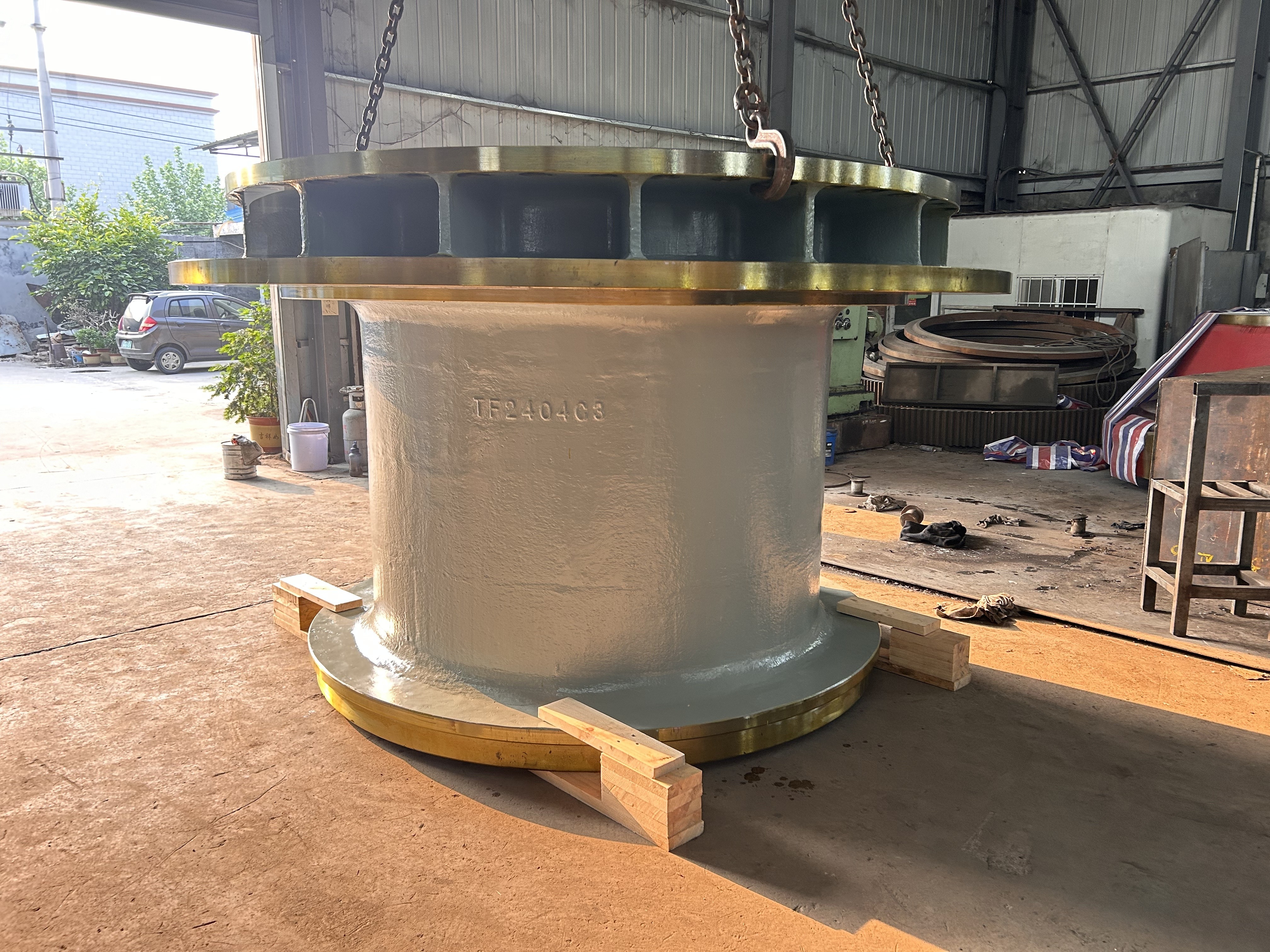
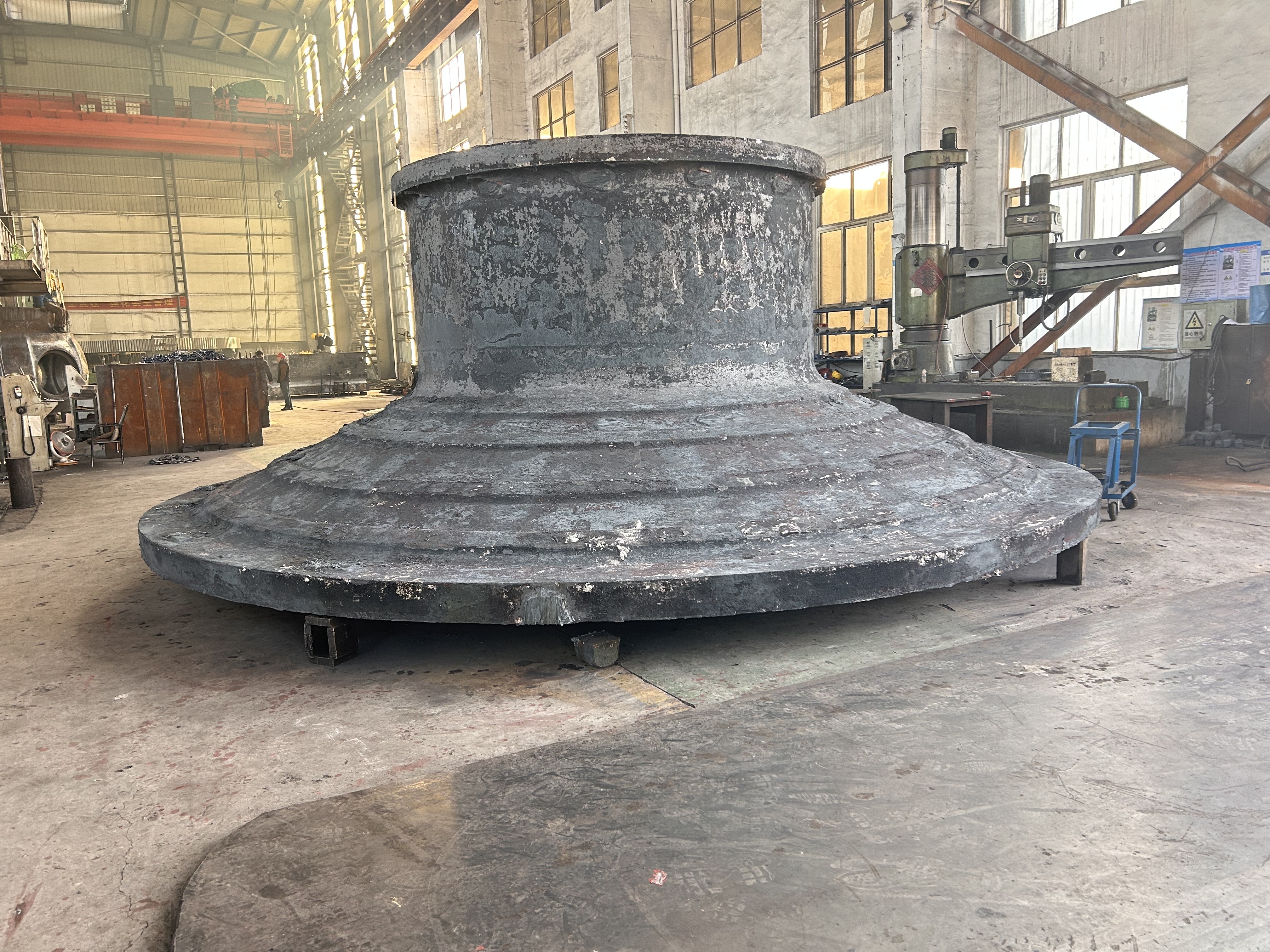
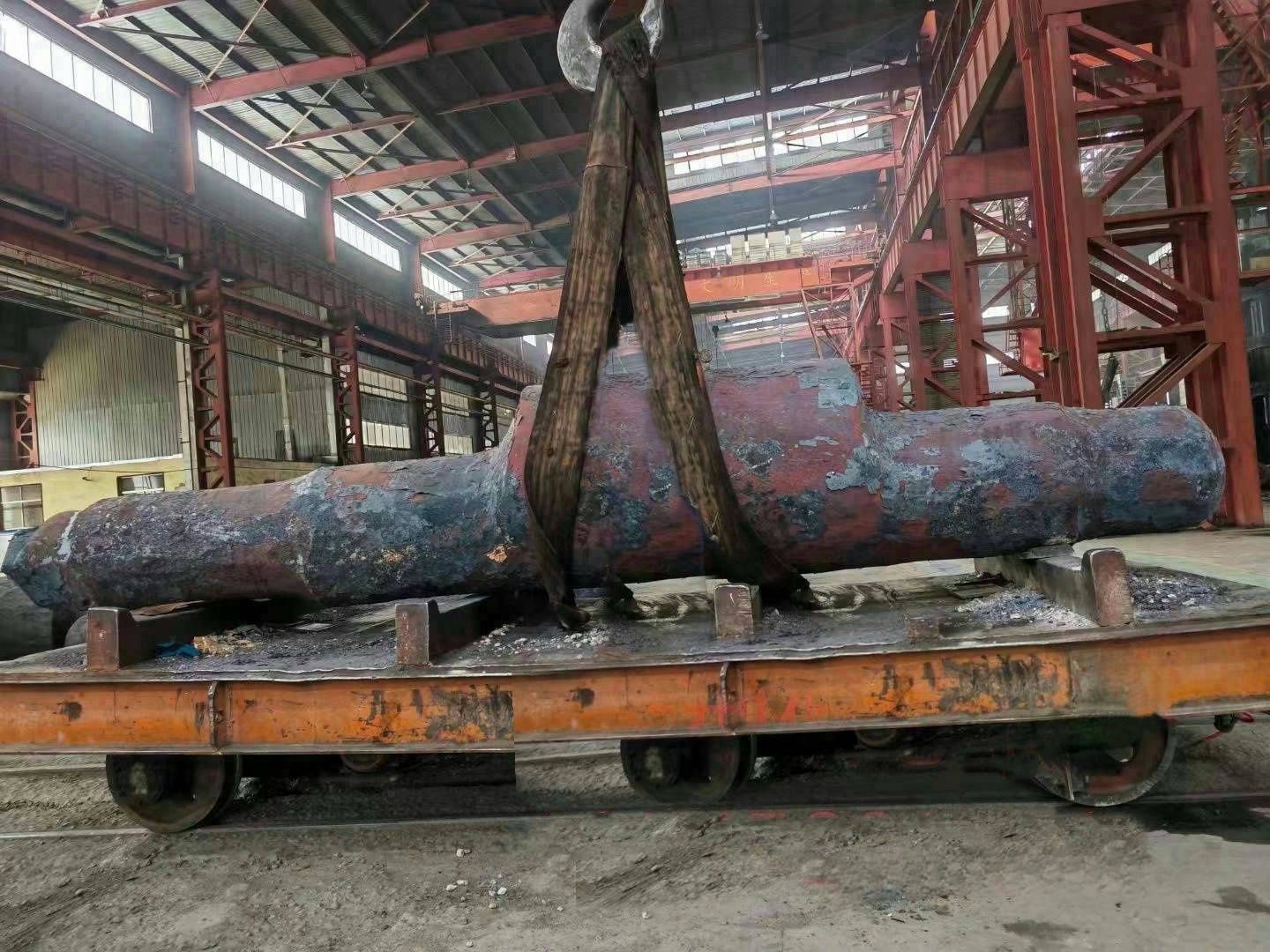
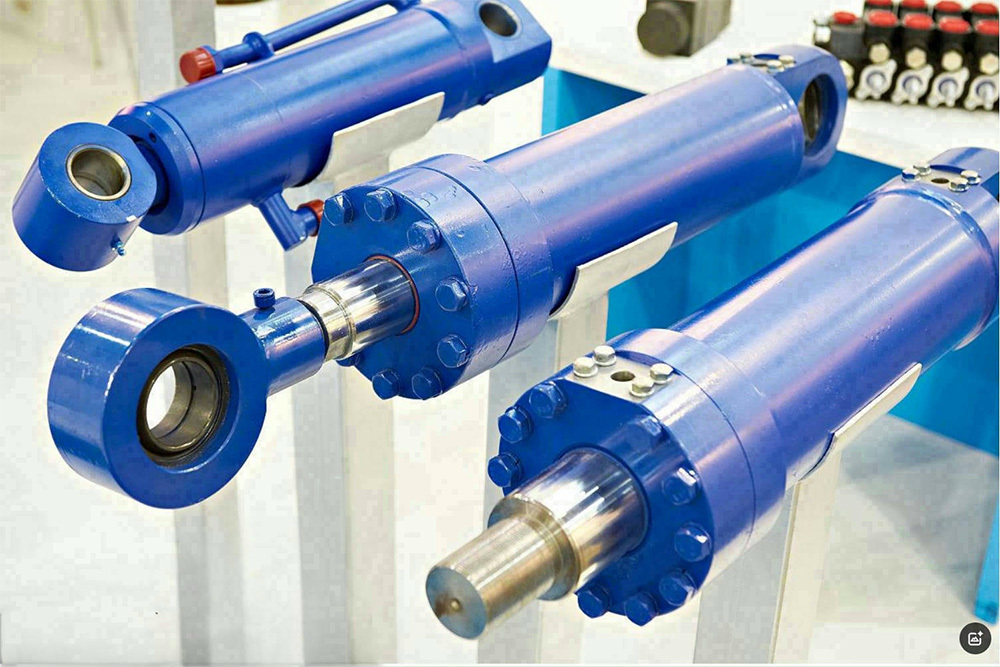
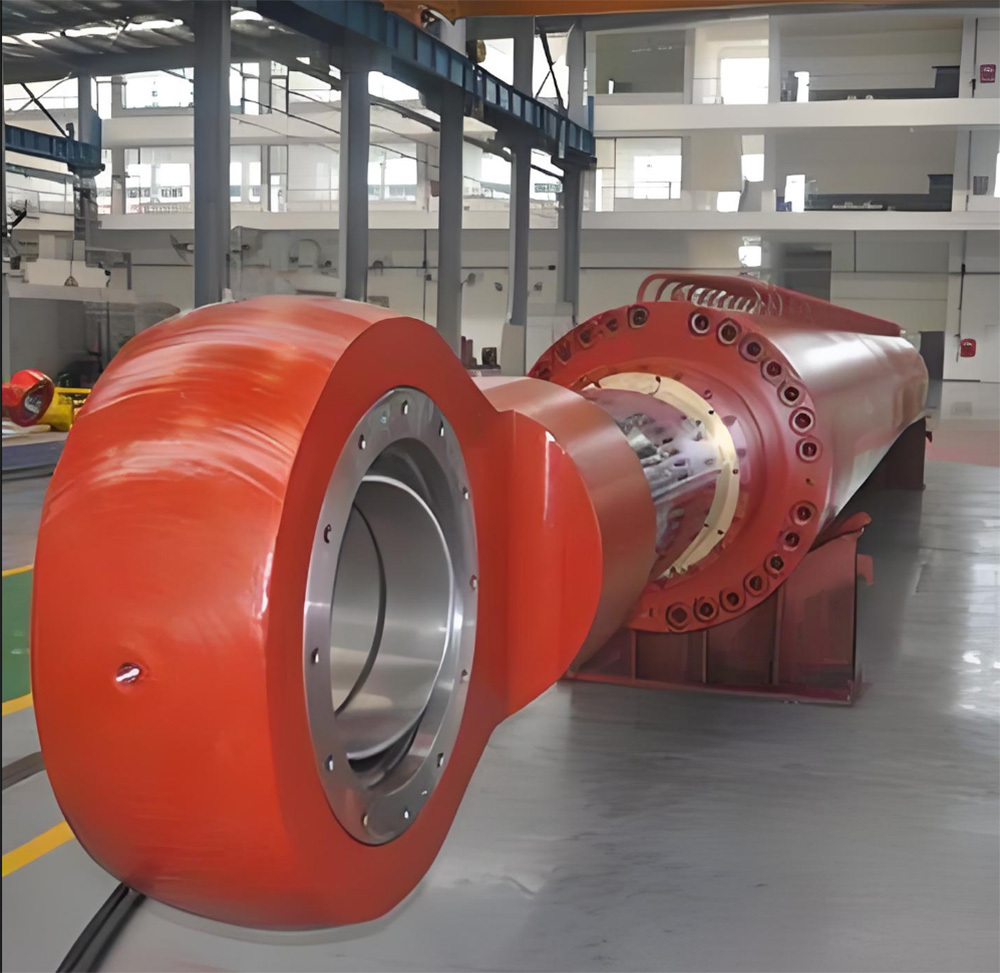
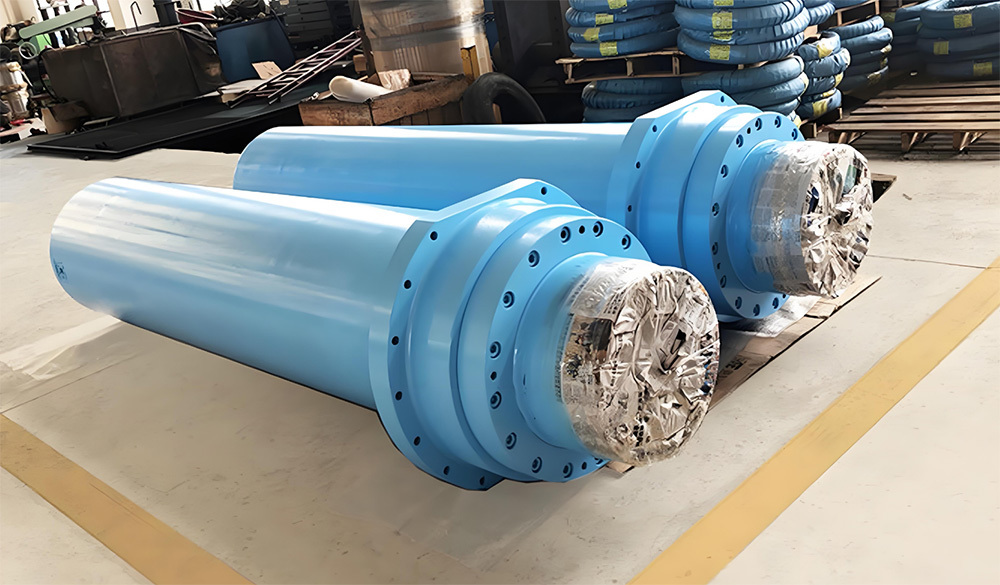
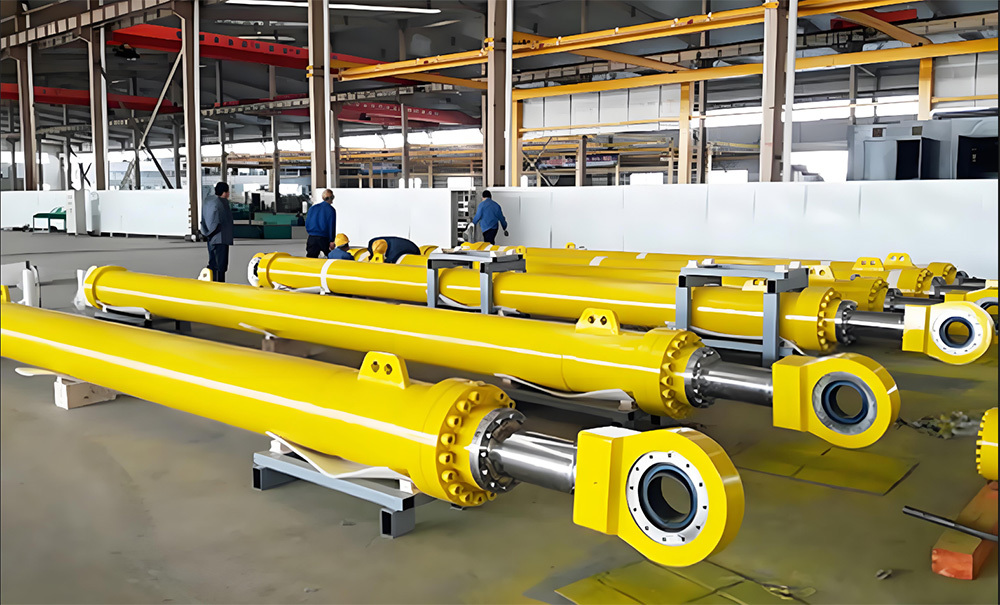
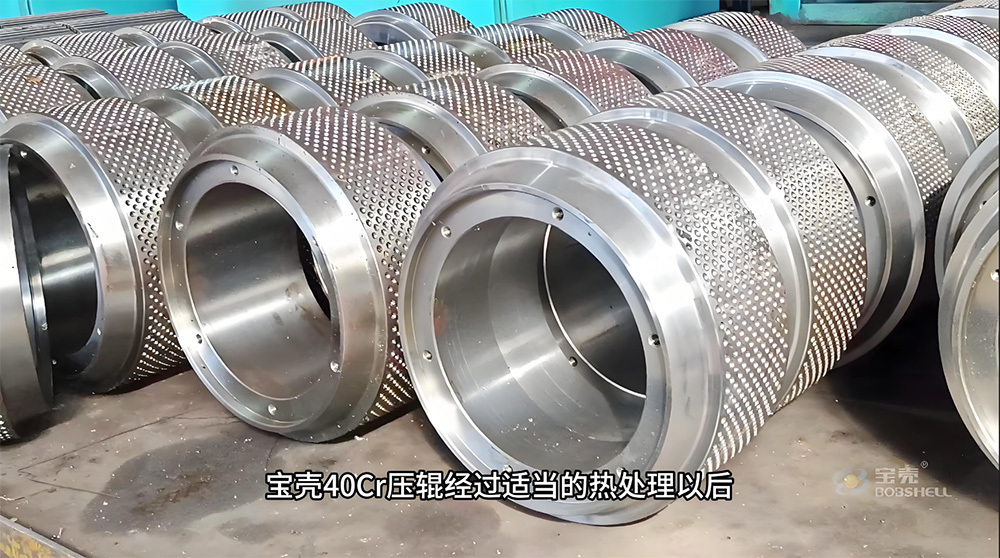
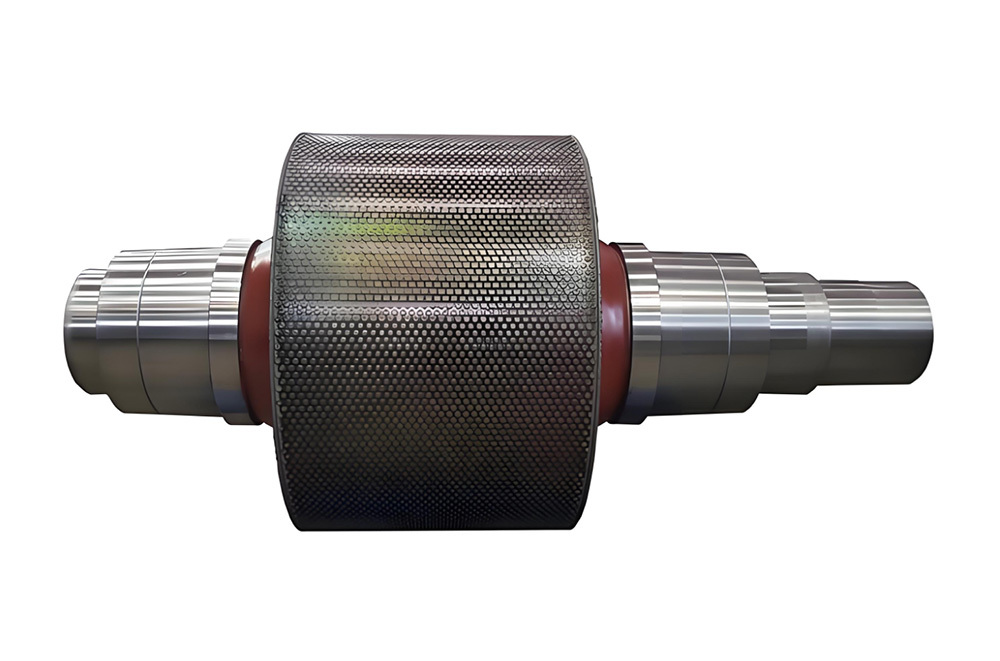
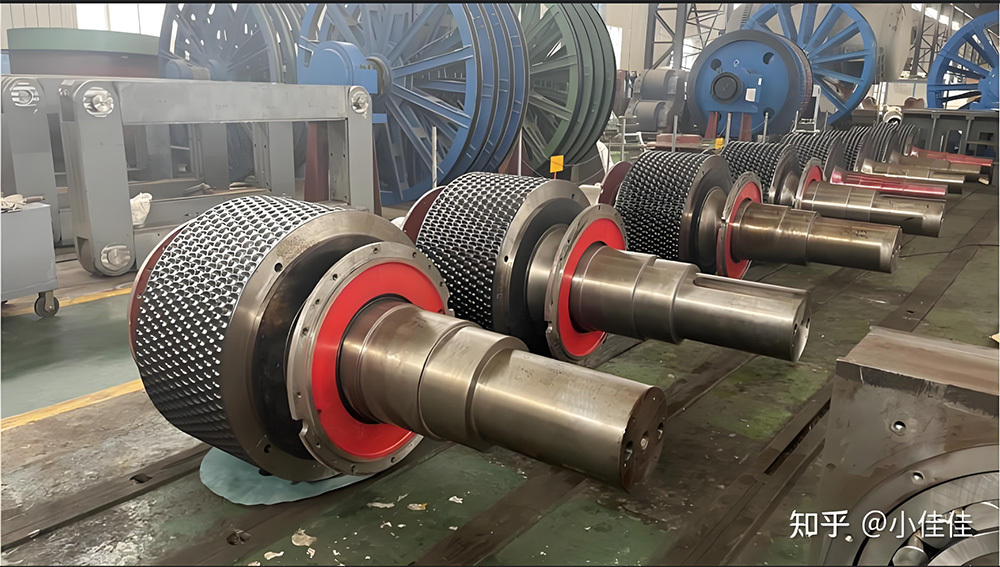
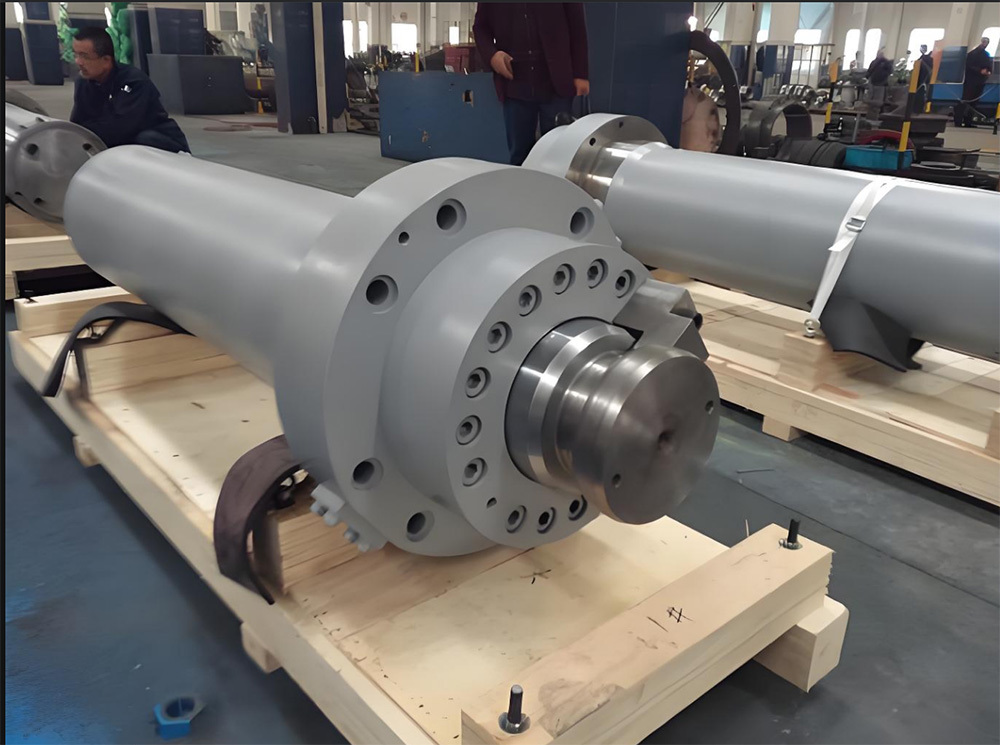
A large hydraulic cylinder is an actuator that converts hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. It uses the pressure of hydraulic oil to push the piston rod in a linear reciprocating motion, enabling power output and motion control in various types of machinery. These cylinders are widely used in fields such as engineering, metallurgy, mining, shipbuilding, and more.
Cylinder Classification
1. Classified by structural form:
- Piston-type hydraulic cylinders are classified into single-acting and double-acting types. In a single-acting cylinder, hydraulic oil pushes the piston in one direction, while the return stroke relies on an external force. In contrast, a double-acting hydraulic cylinder allows the piston to move in both directions under the action of hydraulic oil.
- Piston-type hydraulic cylinder: The piston is a single moving component, driven by hydraulic oil pressure to perform linear motion. It offers a longer stroke, making it ideal for applications requiring high thrust and extended travel—commonly used in large construction machinery and mining equipment.
- Telescopic hydraulic cylinders: Composed of multiple nested sleeves, they enable long strokes while occupying minimal space. They are commonly used in equipment such as cranes and excavators, where large strokes are required but installation space is limited.
2. Classified by installation method:
- Ear-type hydraulic cylinders: Equipped with ear structures at both ends for easy connection to other components, offering flexible installation and suitable for various mounting scenarios, such as arm-to-arm connections in construction machinery.
- Flanged hydraulic cylinders: Connected to other components via flanges for a secure attachment, making them ideal for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity, such as the transmission sections of metallurgical equipment.
- Hinge-type hydraulic cylinder: The cylinder body can swing around a hinge axis, making it suitable for applications requiring multi-angle motion, such as the steering gear systems of ships.
Design Parameters
1. Basic Parameters
- Cylinder bore diameter (D): Calculated based on the required thrust and working pressure, using the formula: , among which
For thrust,
For work-related stress.
- Piston rod diameter (d): Typically 0.3 to 0.7 times the cylinder bore diameter, meaning (
(ranging from 0.3 to 0.7), determined based on working pressure and load conditions.
Travel (S): Determined based on usage requirements, typically 10–30 times the cylinder bore diameter.
2. Structural Parameters
- Cylinder wall thickness (δ): According to the formula Calculation, where
For the test pressure (typically 1.25 to 1.5 times the working pressure),
Allowable stress for the material.
- Cylinder head thickness (h): According to the formula Calculation, where
For the cylinder bore diameter,
Allowable stress for cylinder head material.
- Minimum guide length (H): , among which
For the itinerary,
For the cylinder bore diameter.
3. Performance Parameters
- Work pressure (P): Determined according to system requirements, typically ranging from 16 to 35 MPa.
- Flow rate (Q): , among which
For speed,
For piston area.
- Speed (v): , among which
For traffic,
For piston area.
Process Introduction
1. Material Selection: High-strength steels such as 45# steel and 27SiMn are typically used to ensure the hydraulic cylinder's strength and wear resistance.
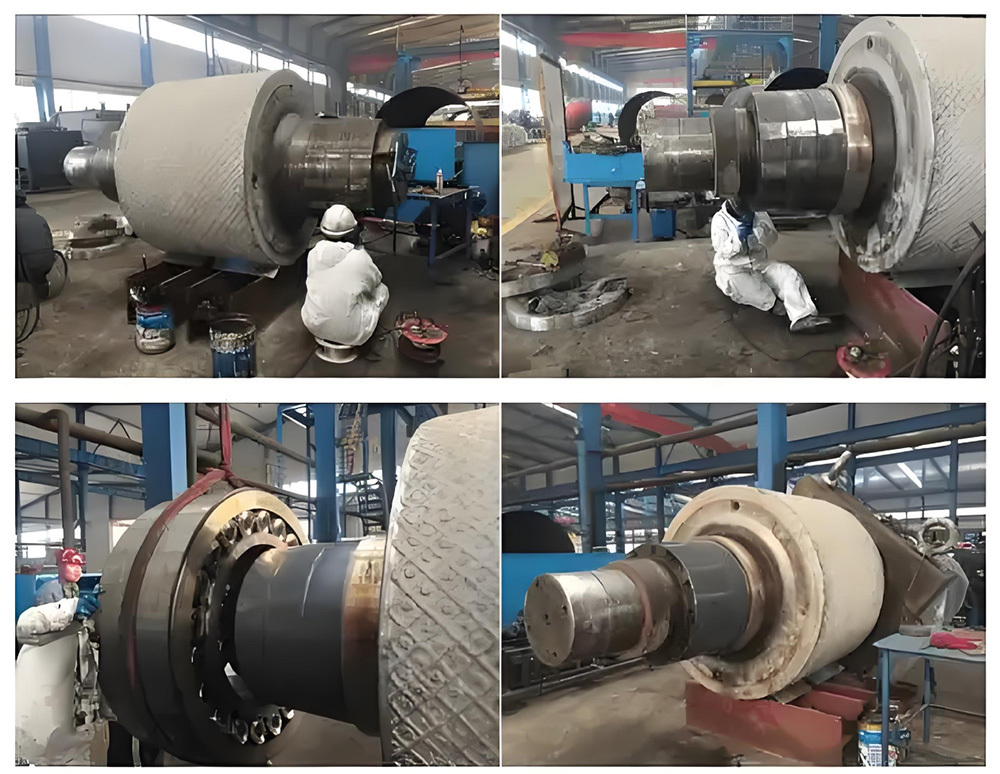
2. Manufacturing processes: These include forging, turning, grinding, boring, honing, and other techniques to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of cylinder barrels and piston rods. Key components such as pistons and seals undergo precision machining and rigorous inspection.
3. Heat Treatment Process: Perform tempering, quenching, and other heat treatments on the cylinder barrel and piston rod to enhance the material’s hardness, strength, and wear resistance.
4. Surface Treatment: Perform surface treatments such as hard chrome plating and oxidation to enhance wear resistance and corrosion protection, thereby extending service life.
5. Assembly and Debugging: Assemble strictly according to process requirements, ensuring precise fit and smooth operation of all components. After assembly, conduct rigorous debugging and testing to verify that the hydraulic cylinder’s performance indicators meet the specified standards.
Scope of Application
1. Engineering Applications: Used to drive components such as boom arms and bucket rods in construction machinery like excavators, loaders, and bulldozers, enabling actions like digging, loading, and pushing earth.
2. Metallurgical Industry: In equipment such as rolling mills and presses, it provides robust power to carry out processes like metal material rolling and pressing.
3. Mining machinery: In equipment such as coal mining machines and tunneling machines, it drives critical components like the cutting unit and traveling mechanism, supporting efficient mining operations.
4. Marine sector: Used to drive equipment such as ship steering gears, cargo cranes, and hatch covers, ensuring the safe navigation and operations of vessels.
Keywords
Previous: Large hydraulic cylinder
Next: Small hydraulic cylinder

Large hydraulic cylinder
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-
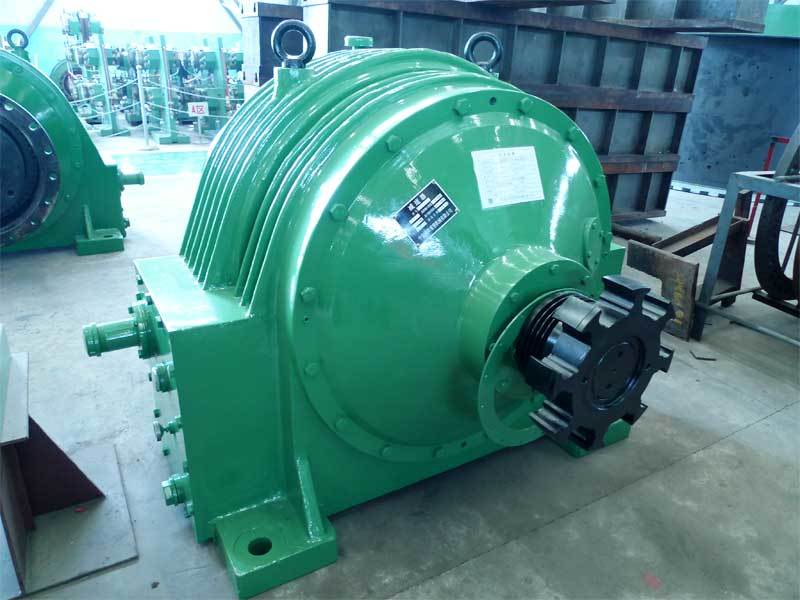

Planetary Gear Reducer
-
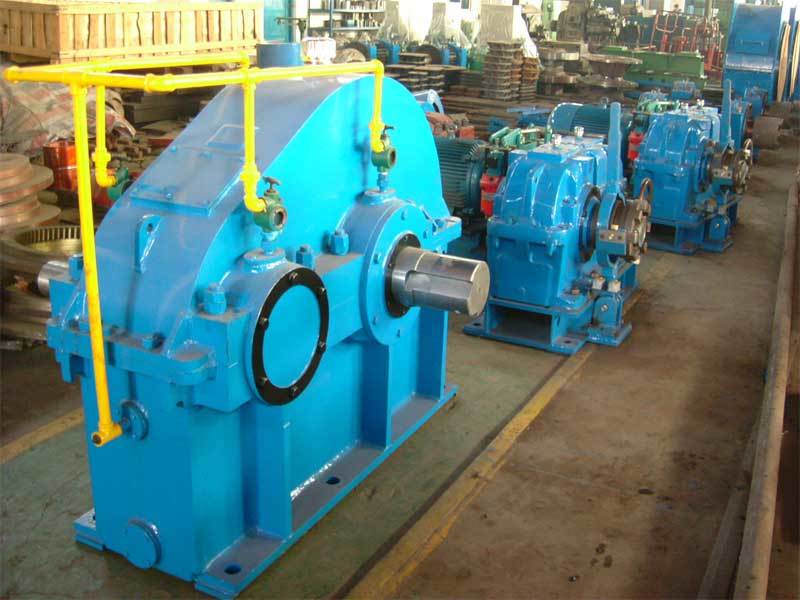

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
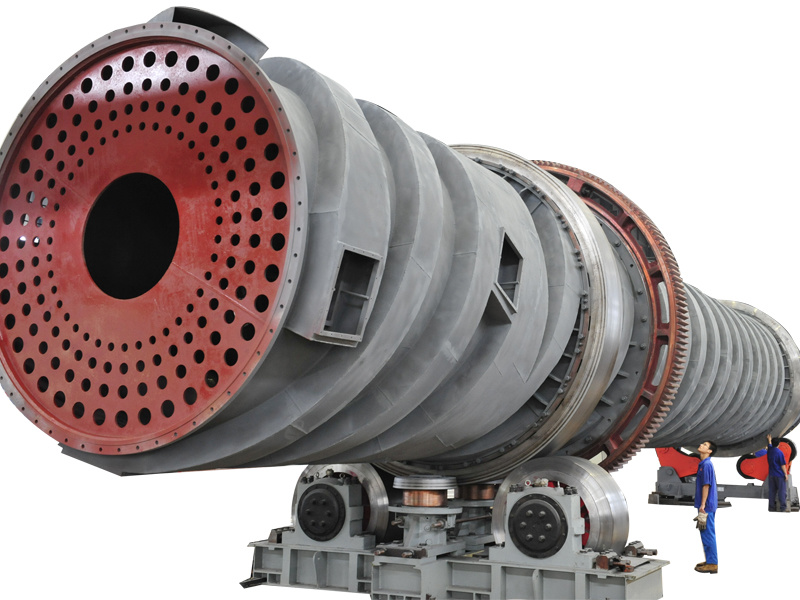
Rotary kiln
-
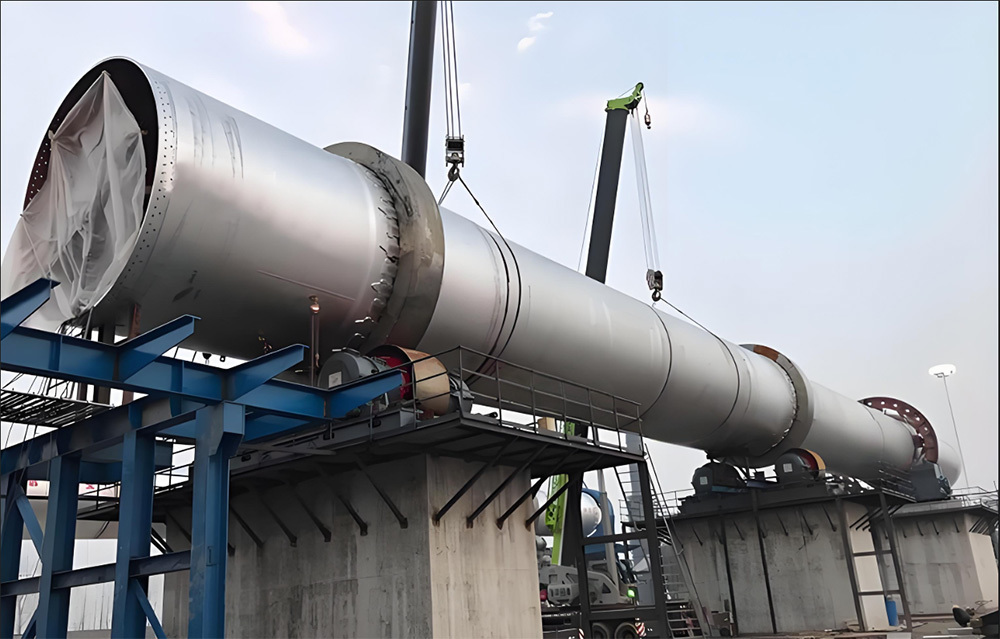

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-
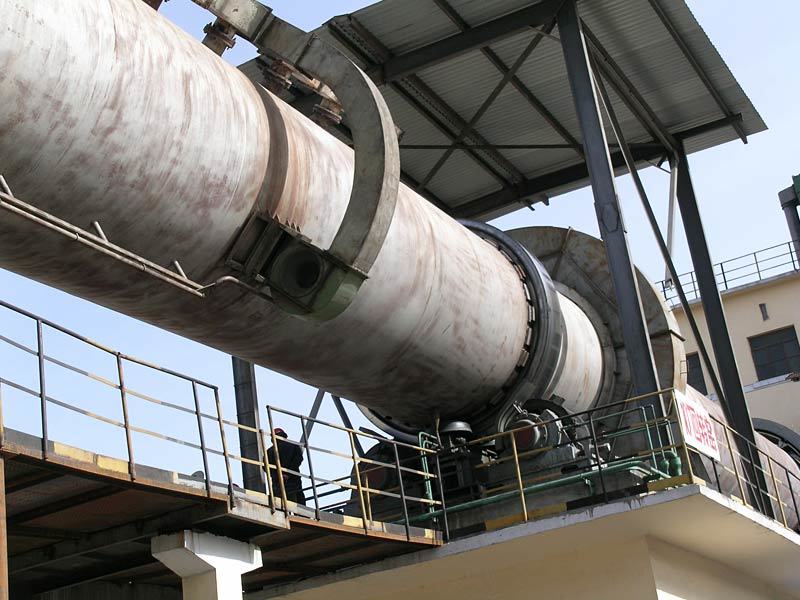

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-
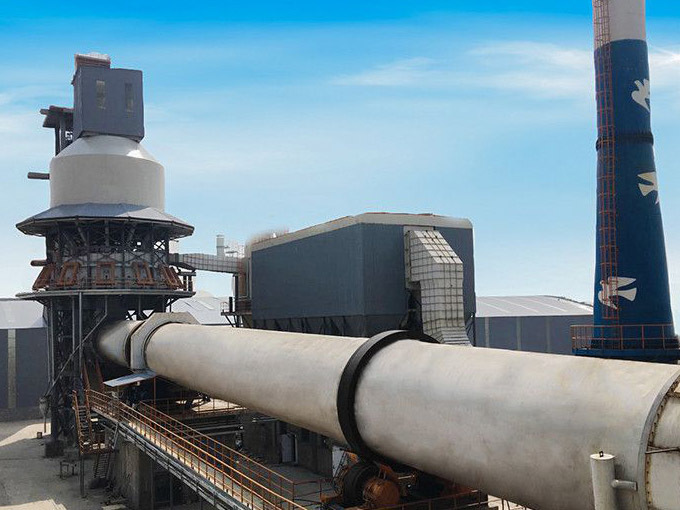

Lime Rotary Kiln
-
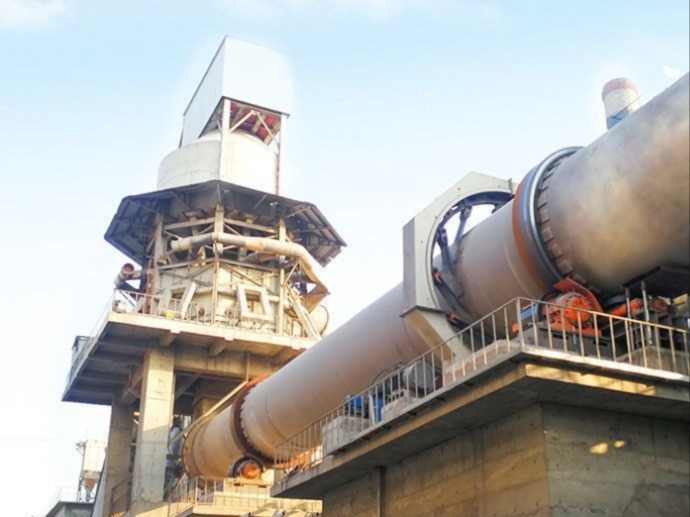

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-
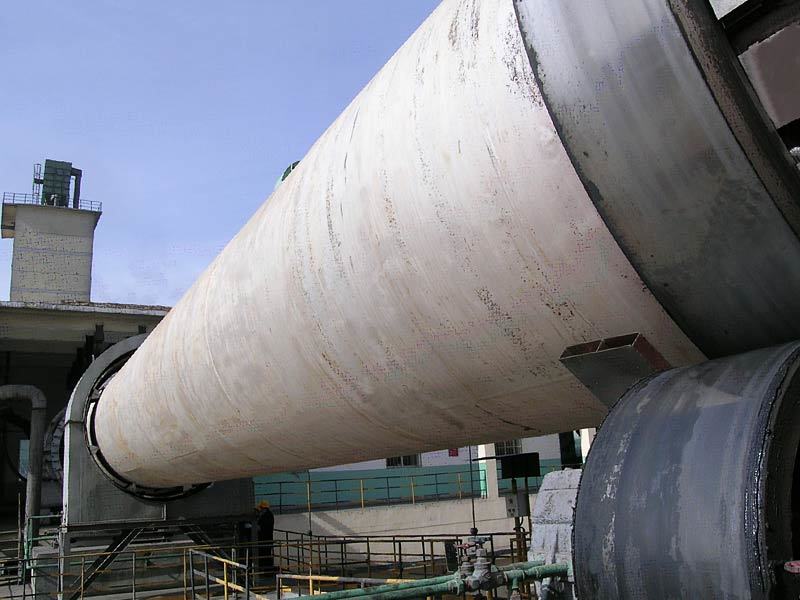

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
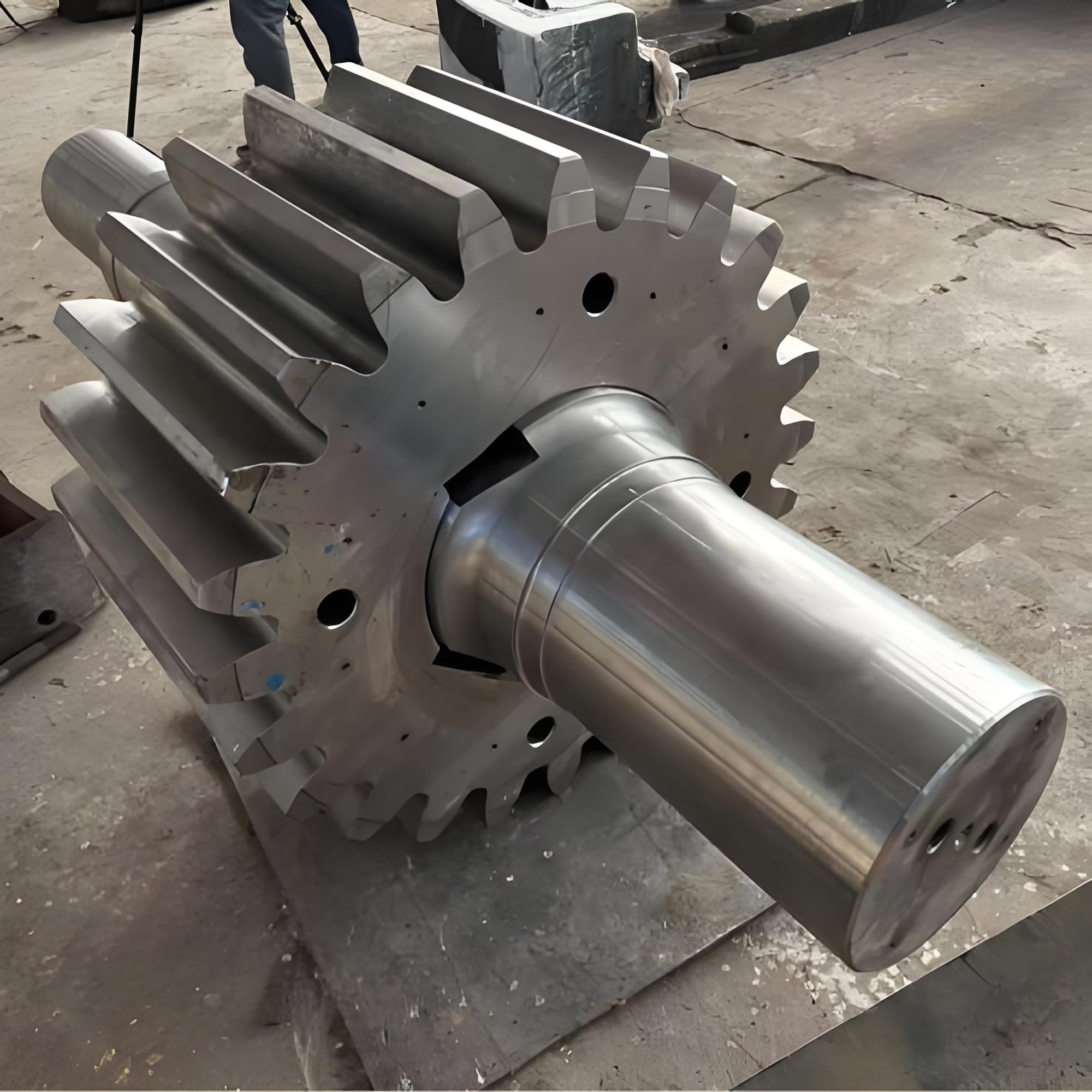
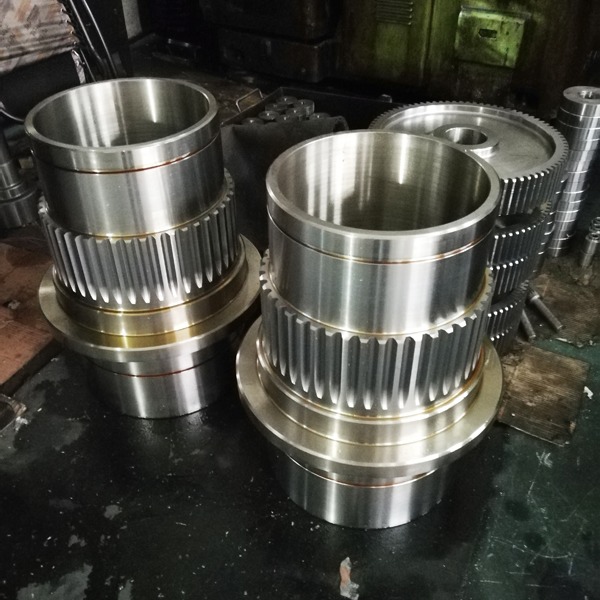
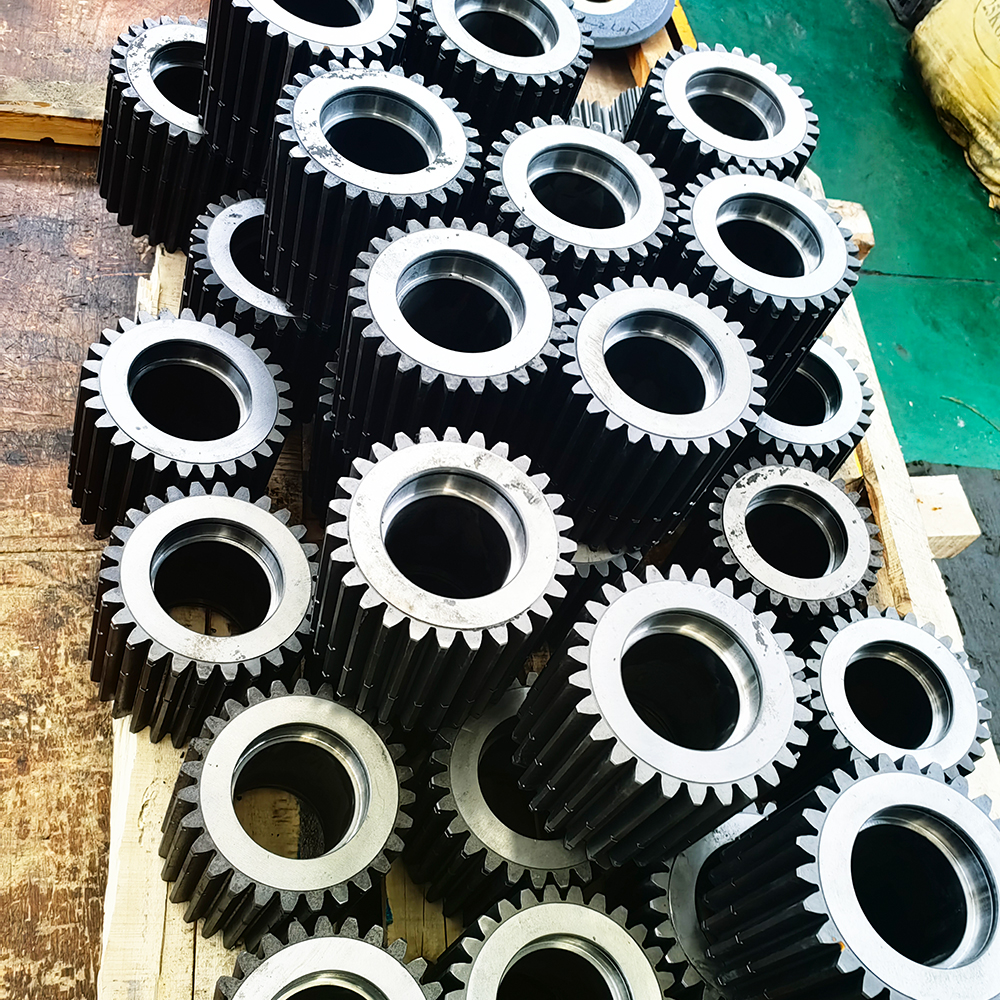
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-
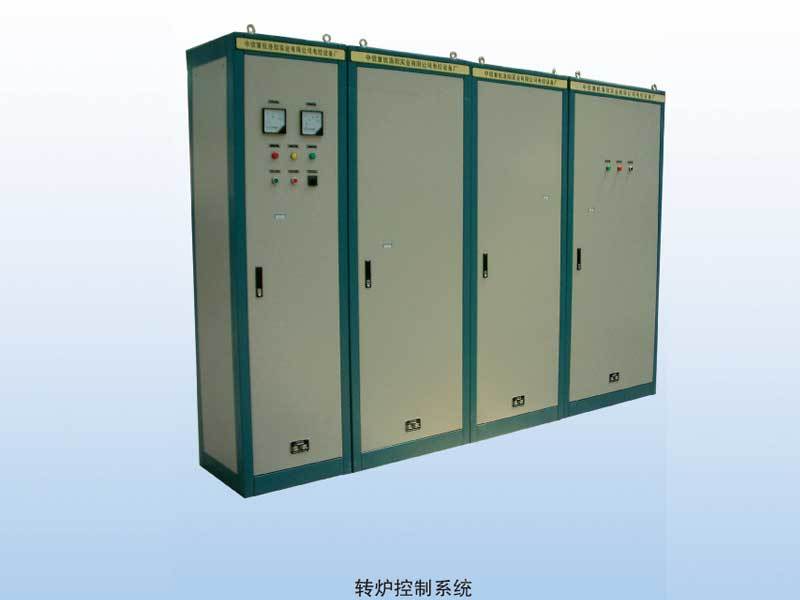

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-
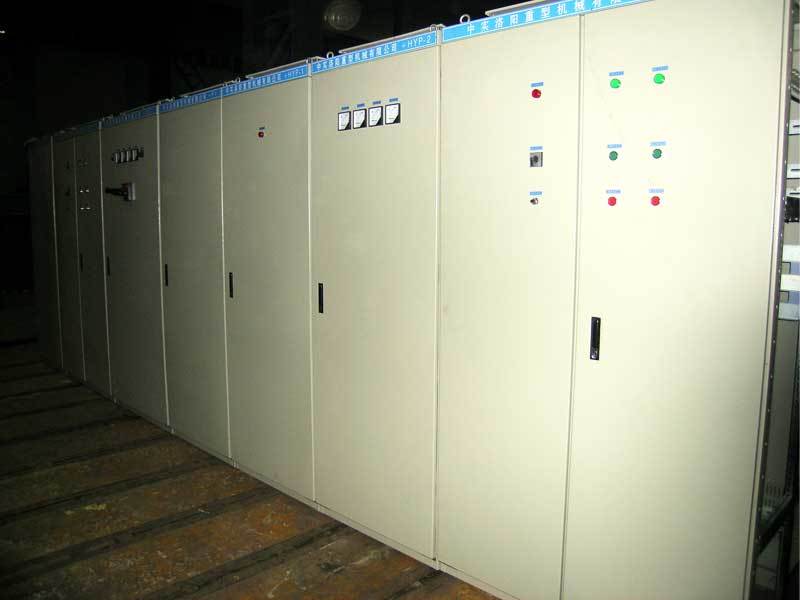

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-
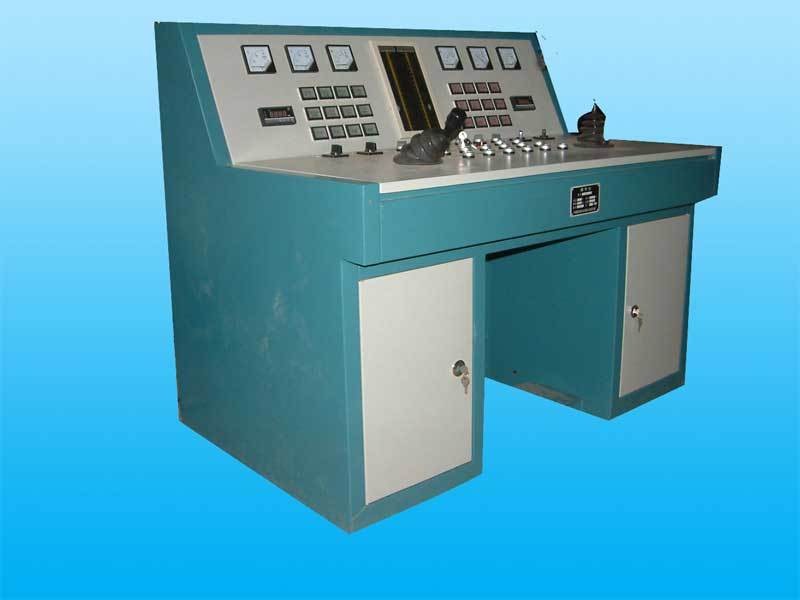

Local System Upgrade
-
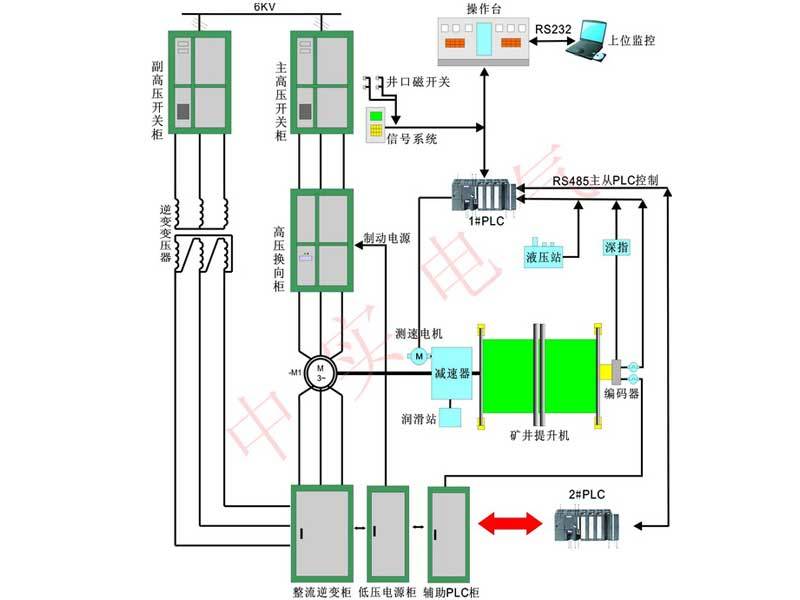
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
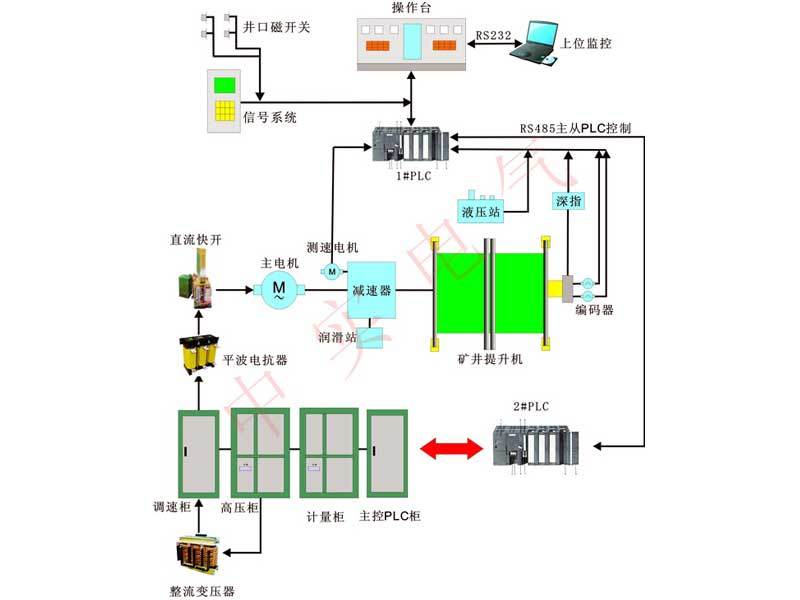
Fully digital DC control system
-
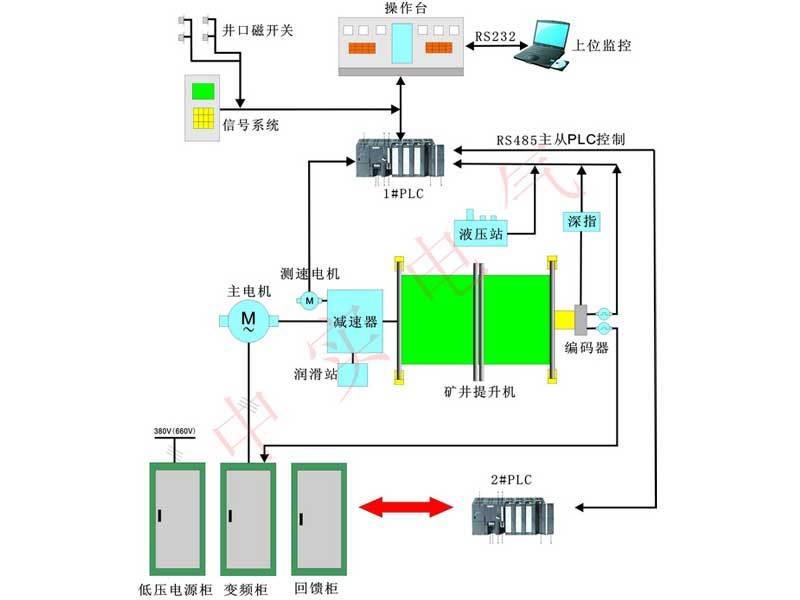
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
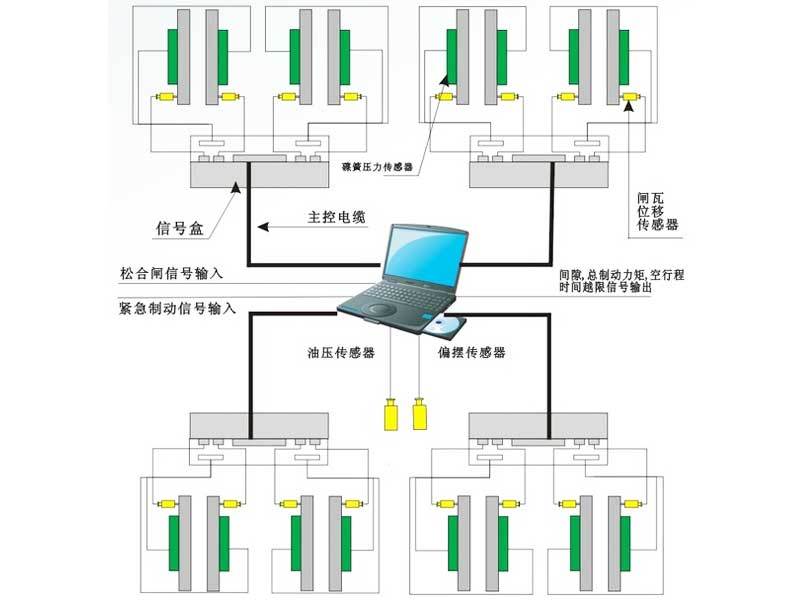
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-
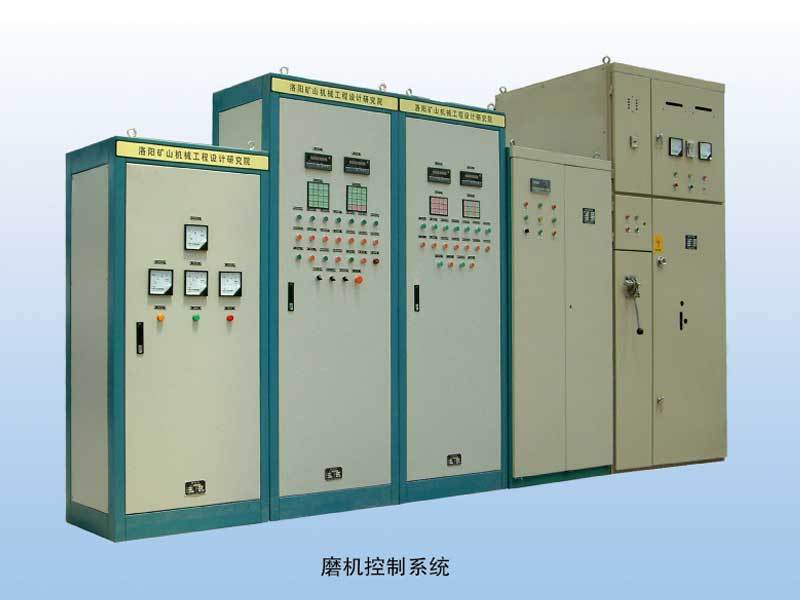

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-
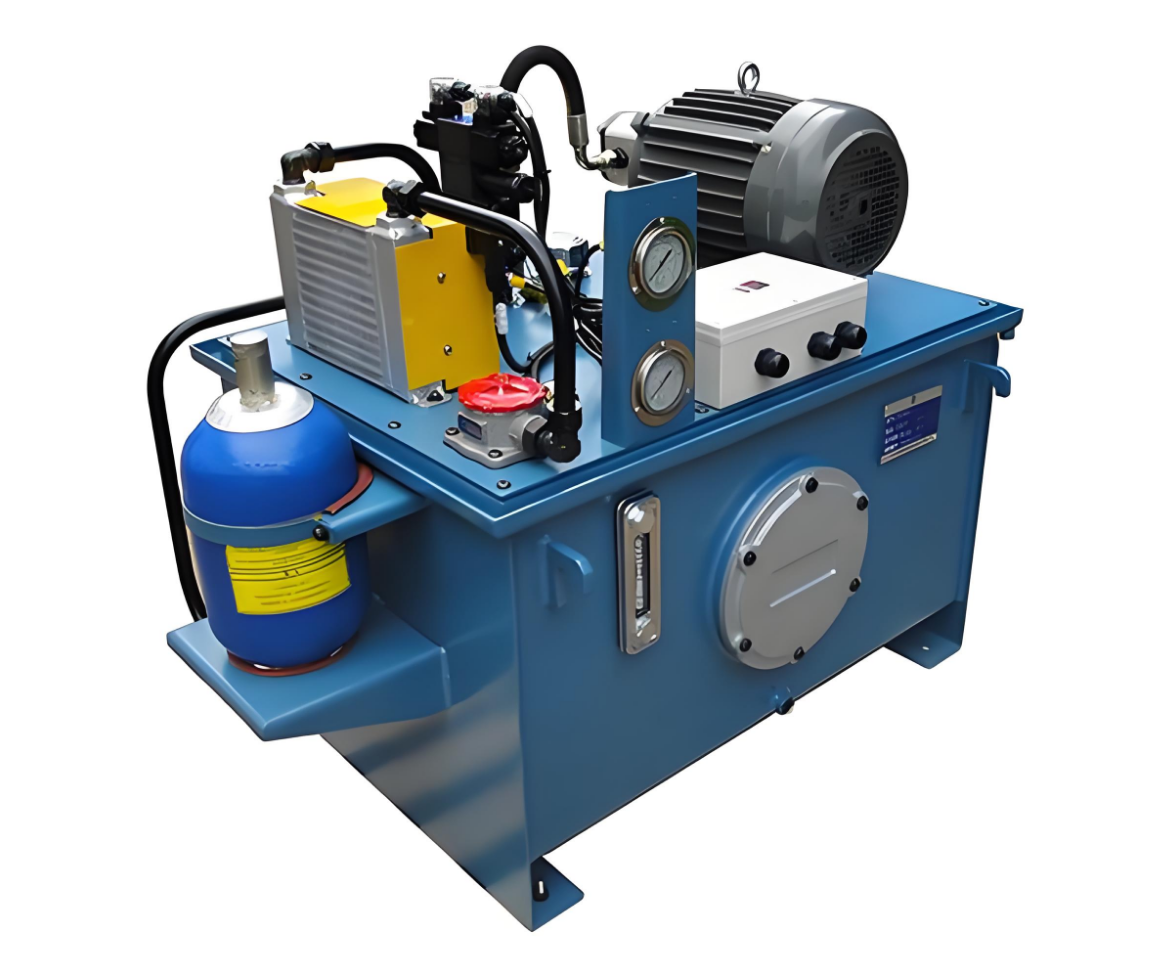

Hydraulic System
-
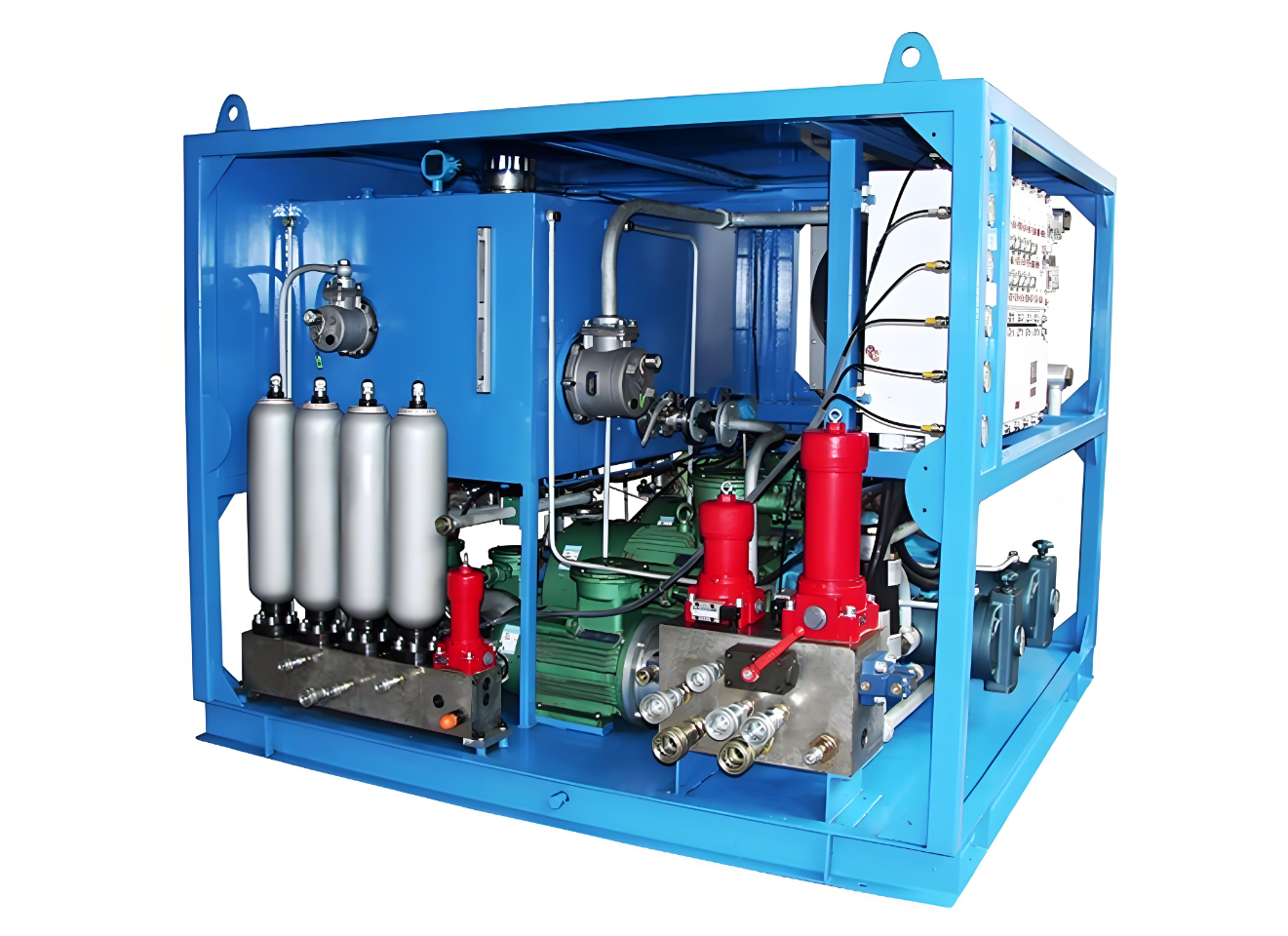

Hydraulic System
-
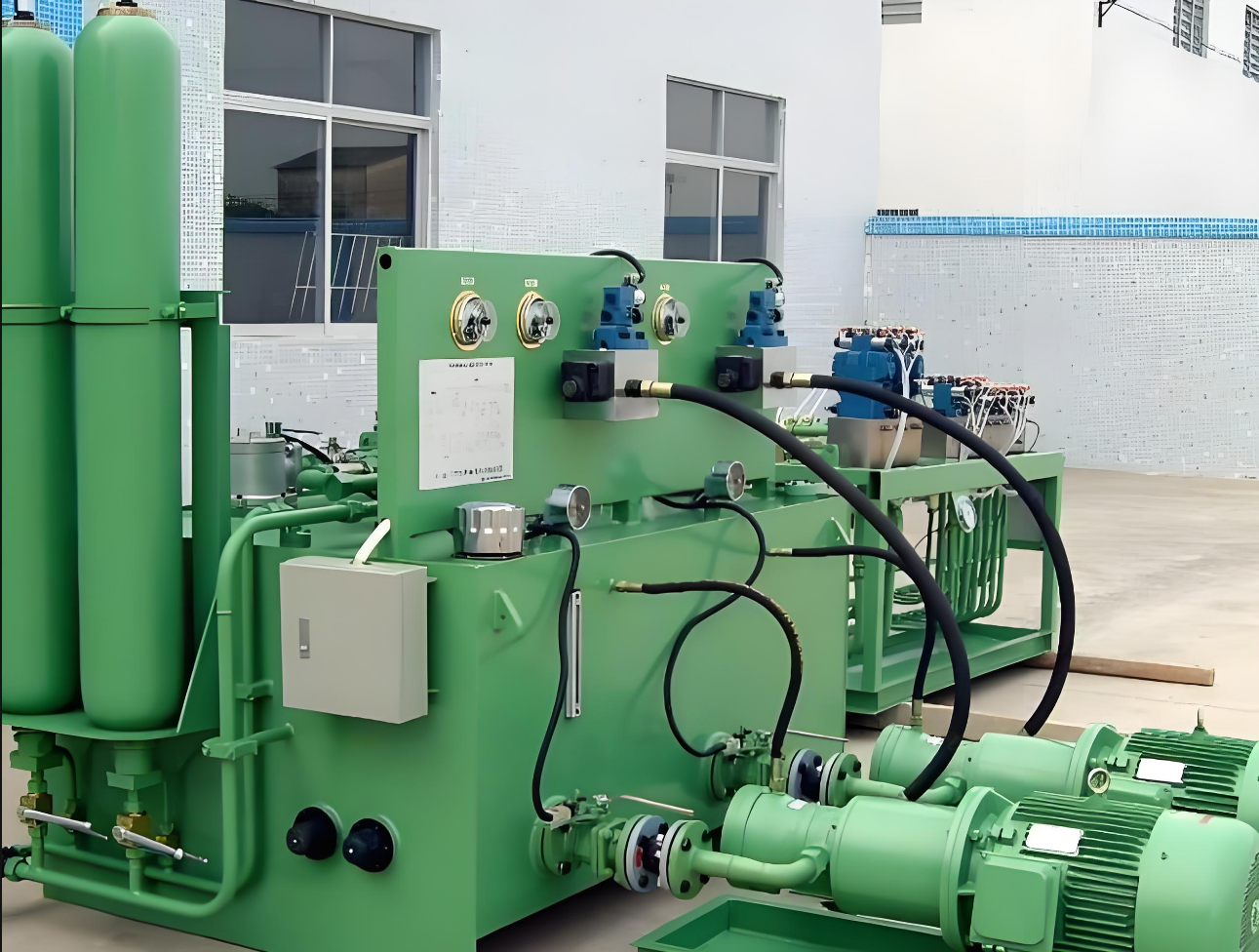

Hydraulic System
-
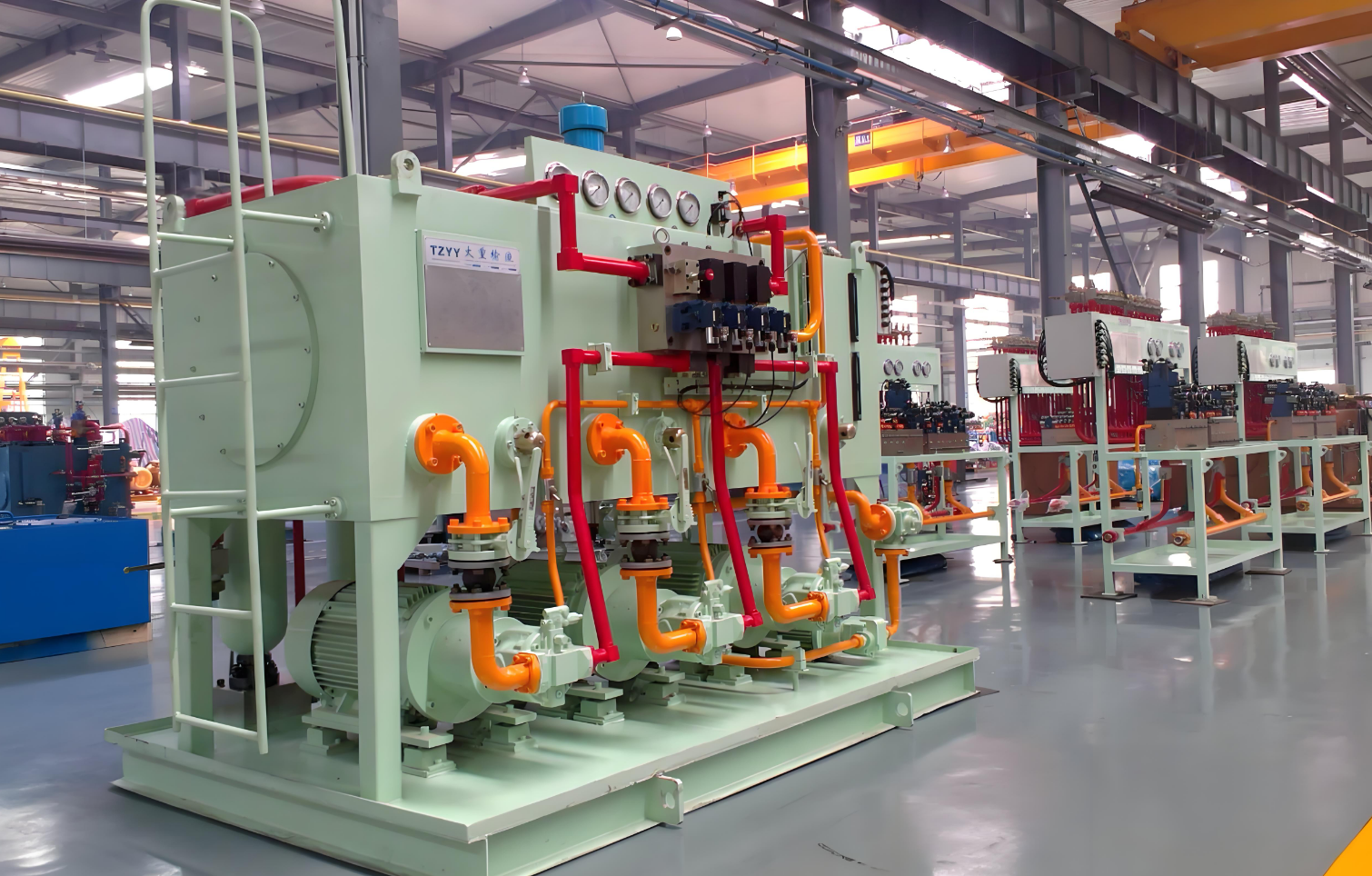

Hydraulic System
-
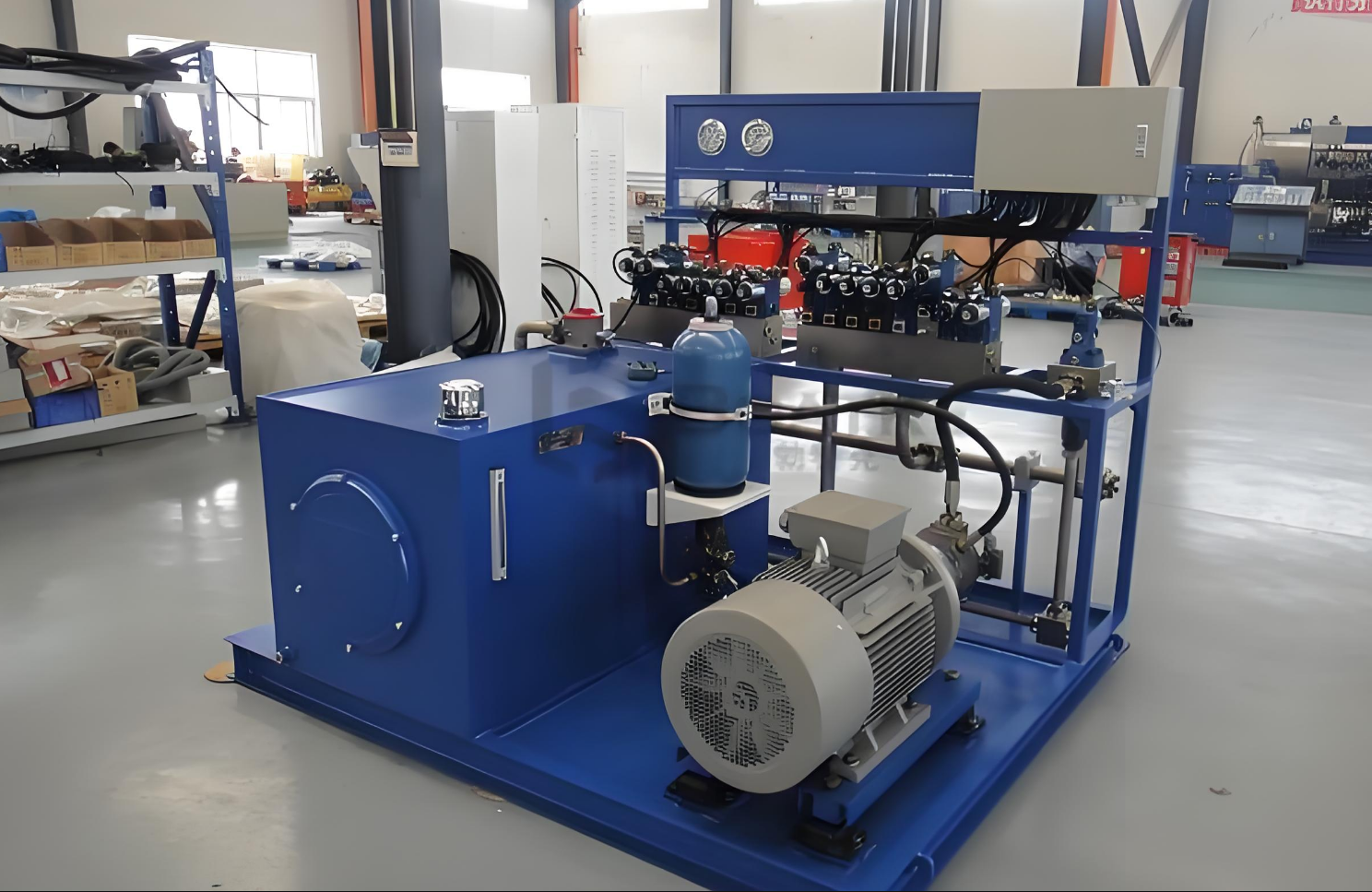

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-
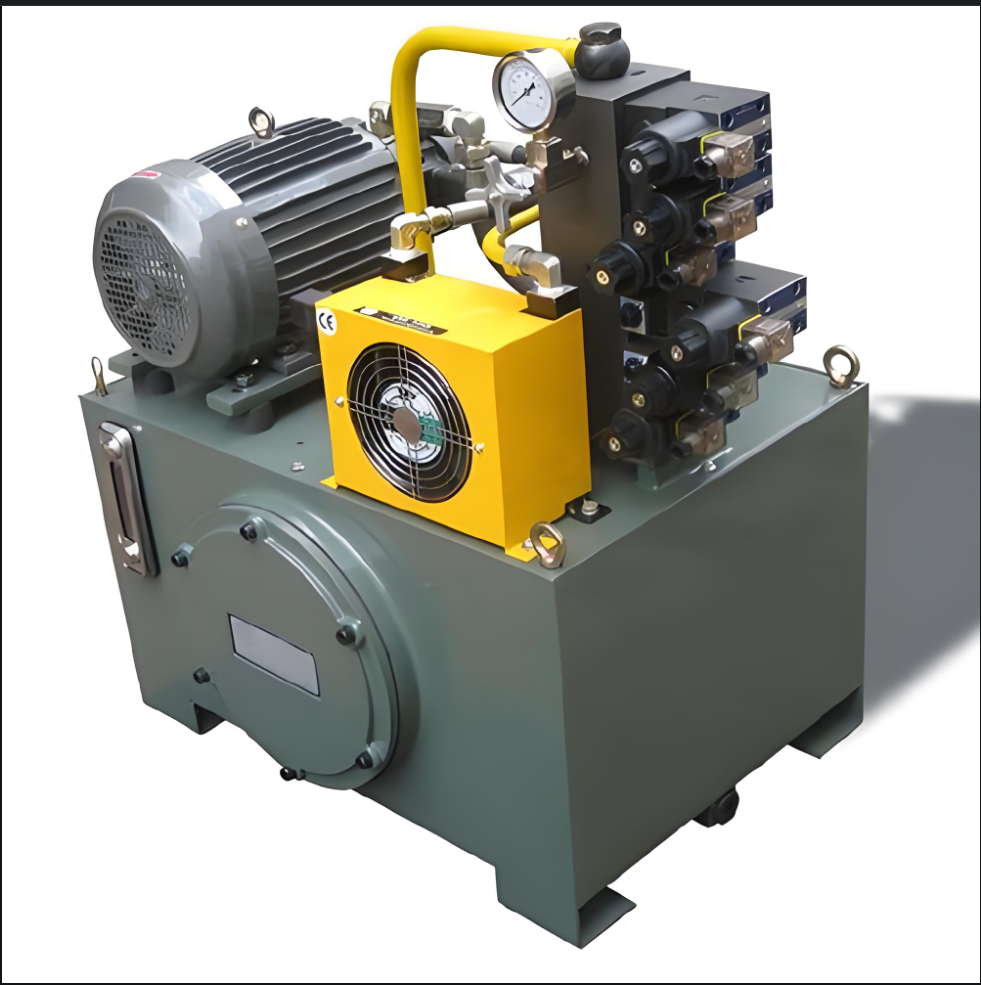

Hydraulic system
-
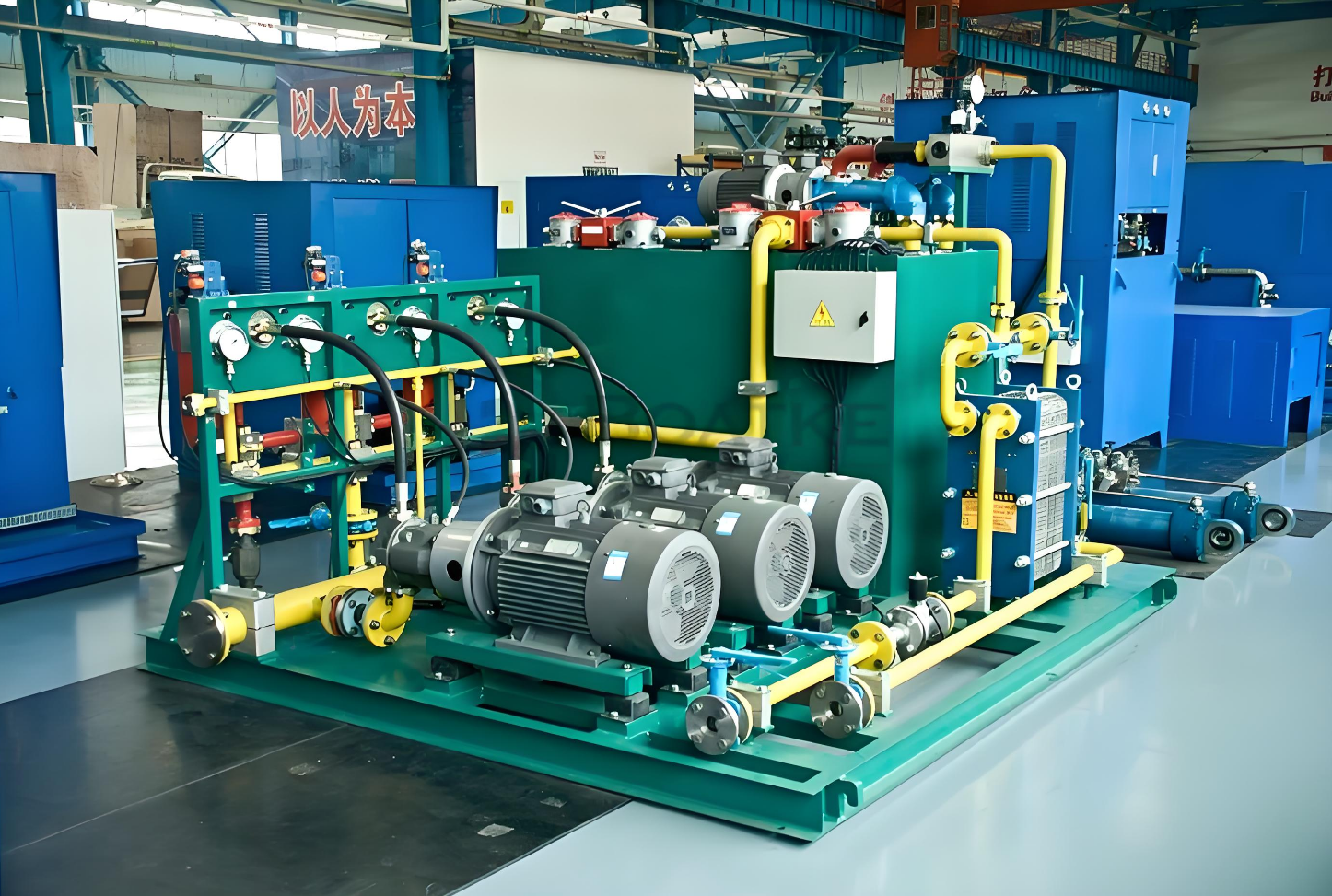

Hydraulic System
-
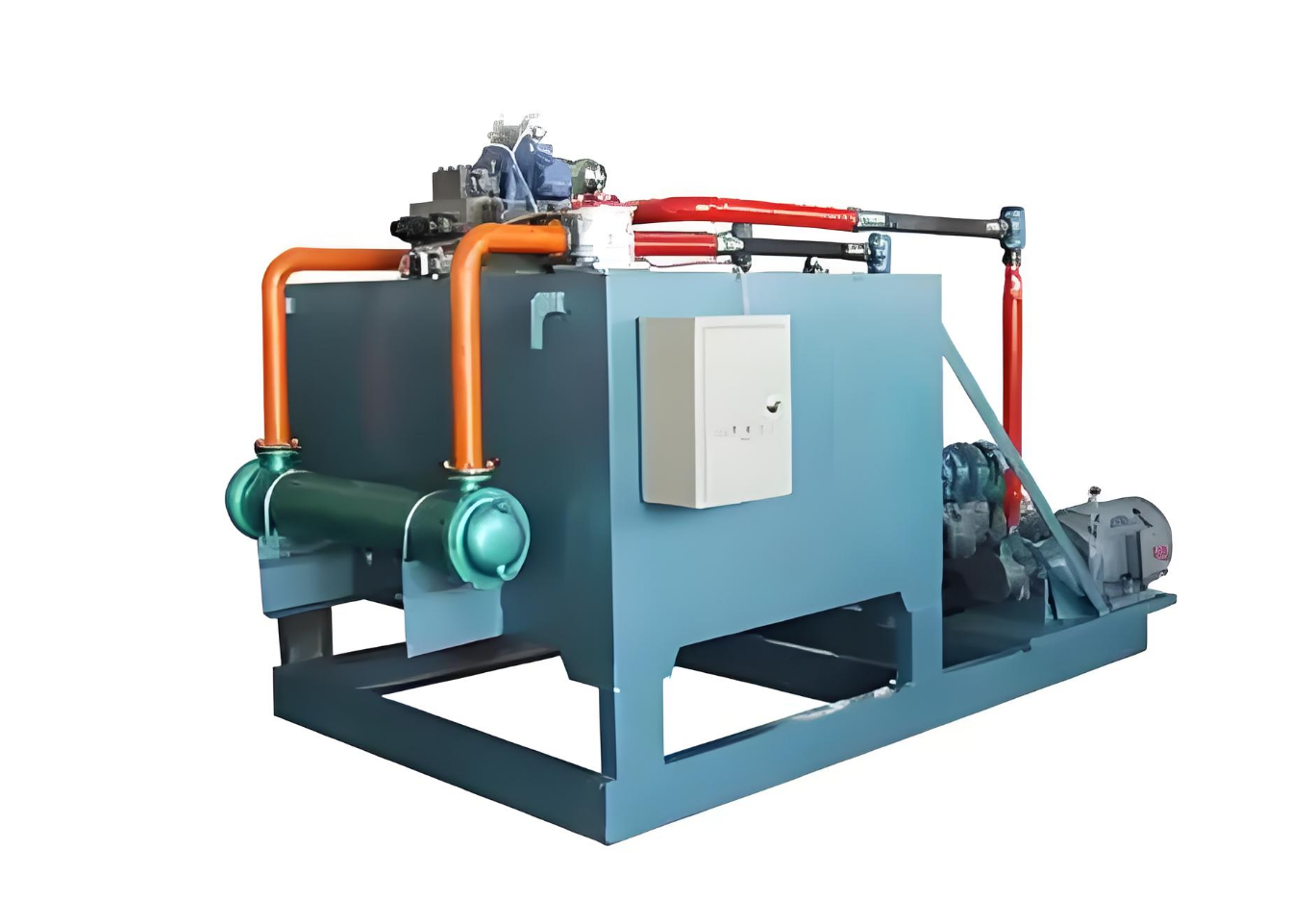

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-
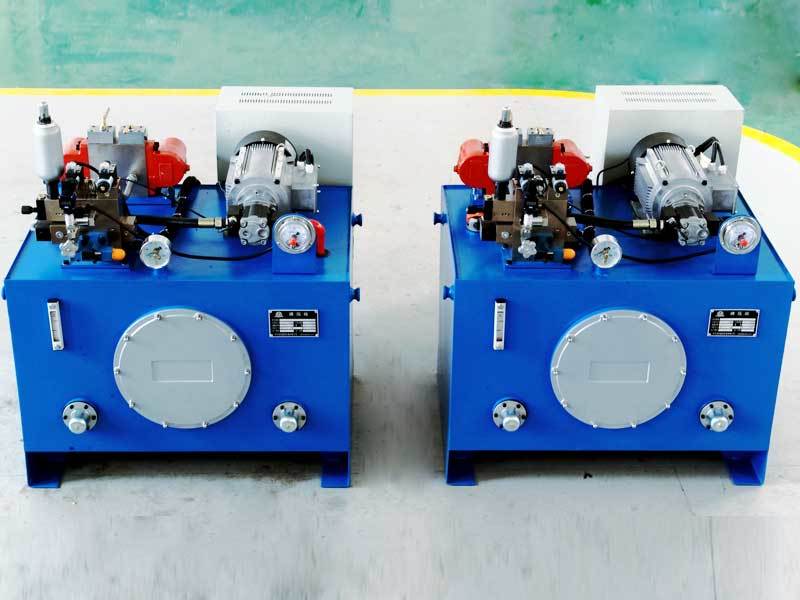

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-
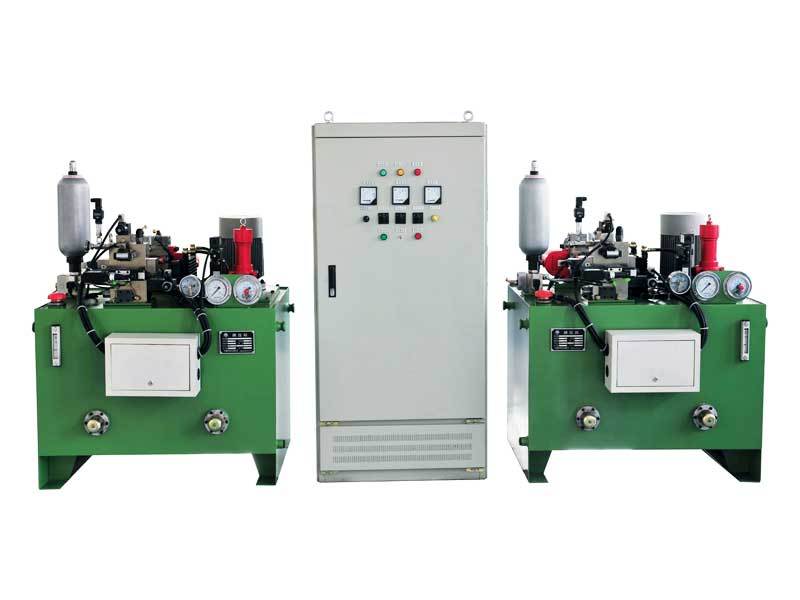

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-
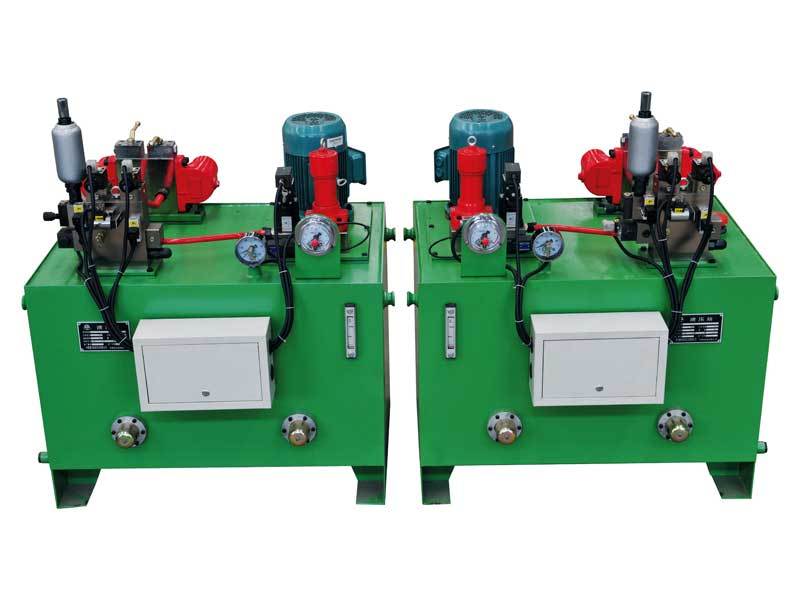

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-
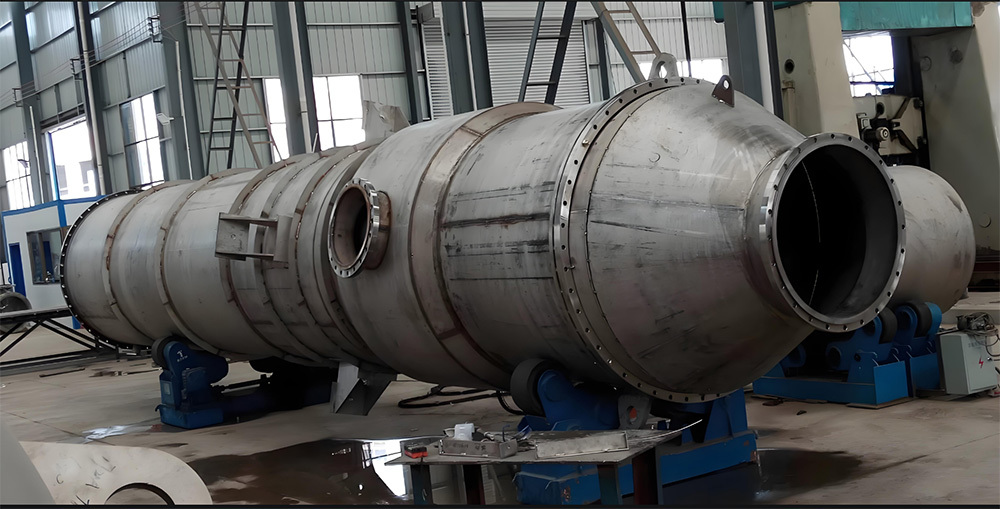

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
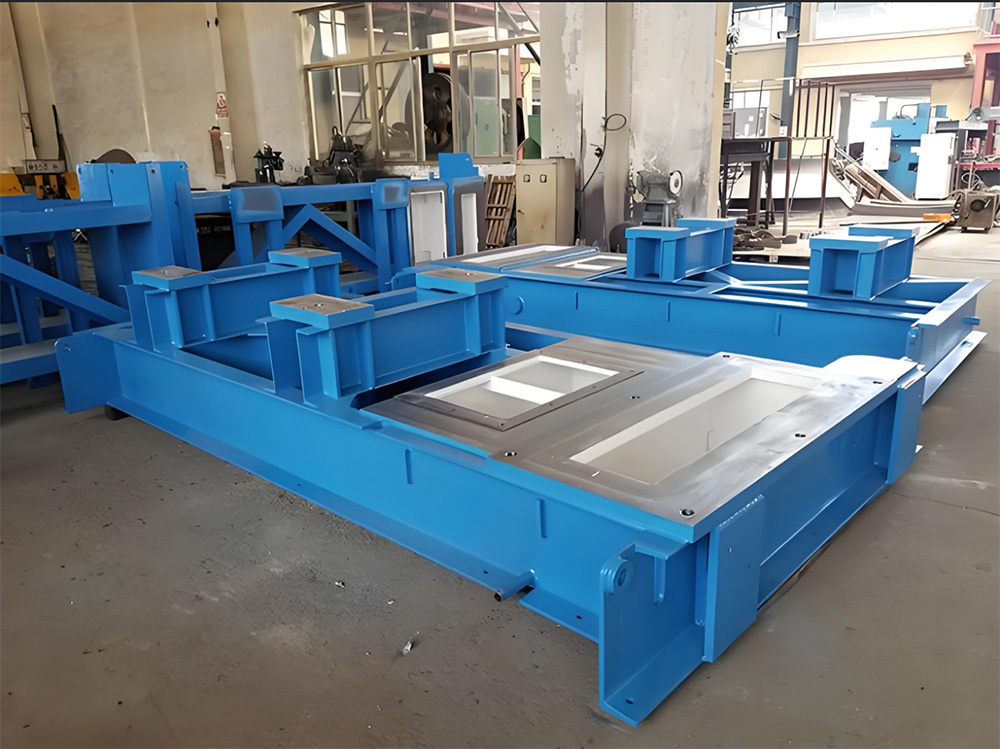

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-
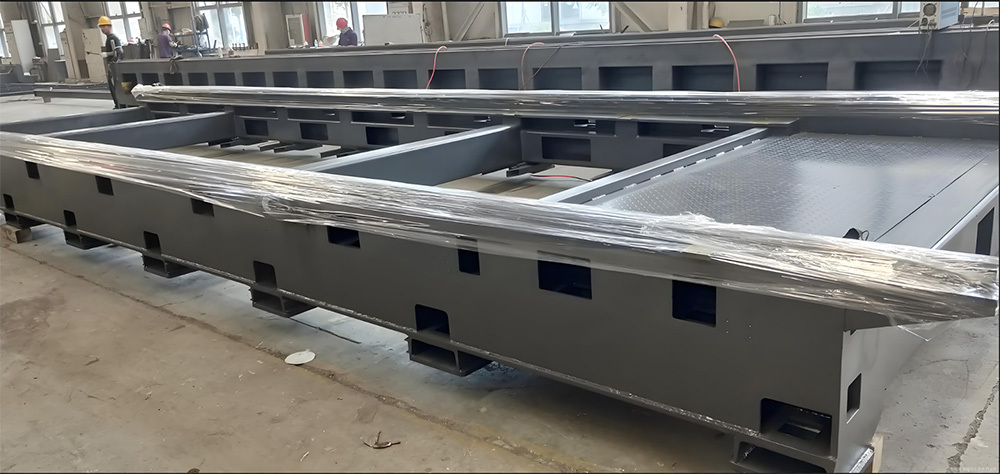

Large base
-
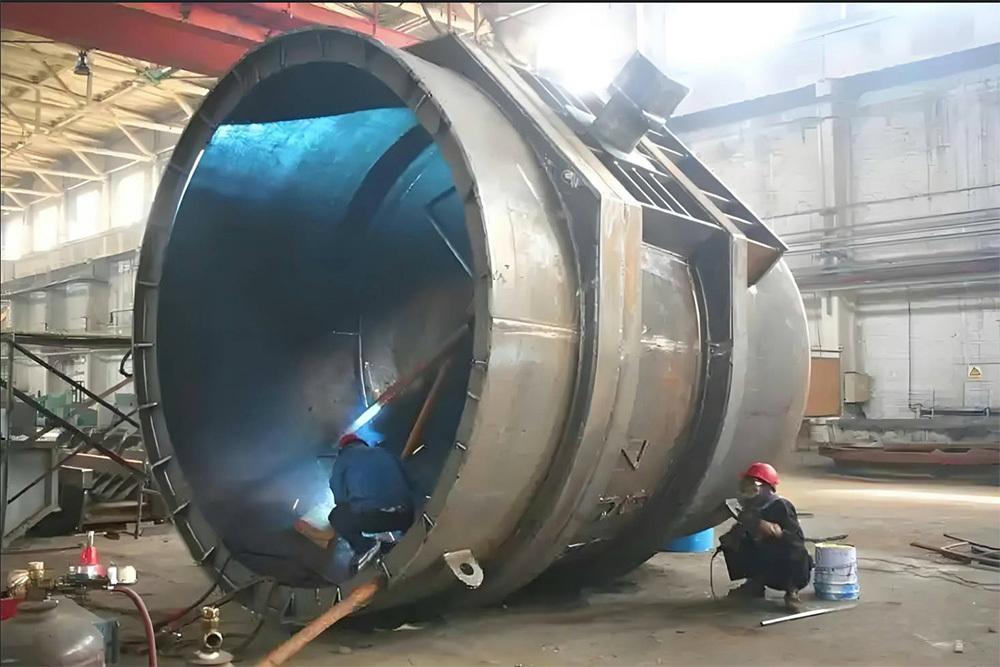

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
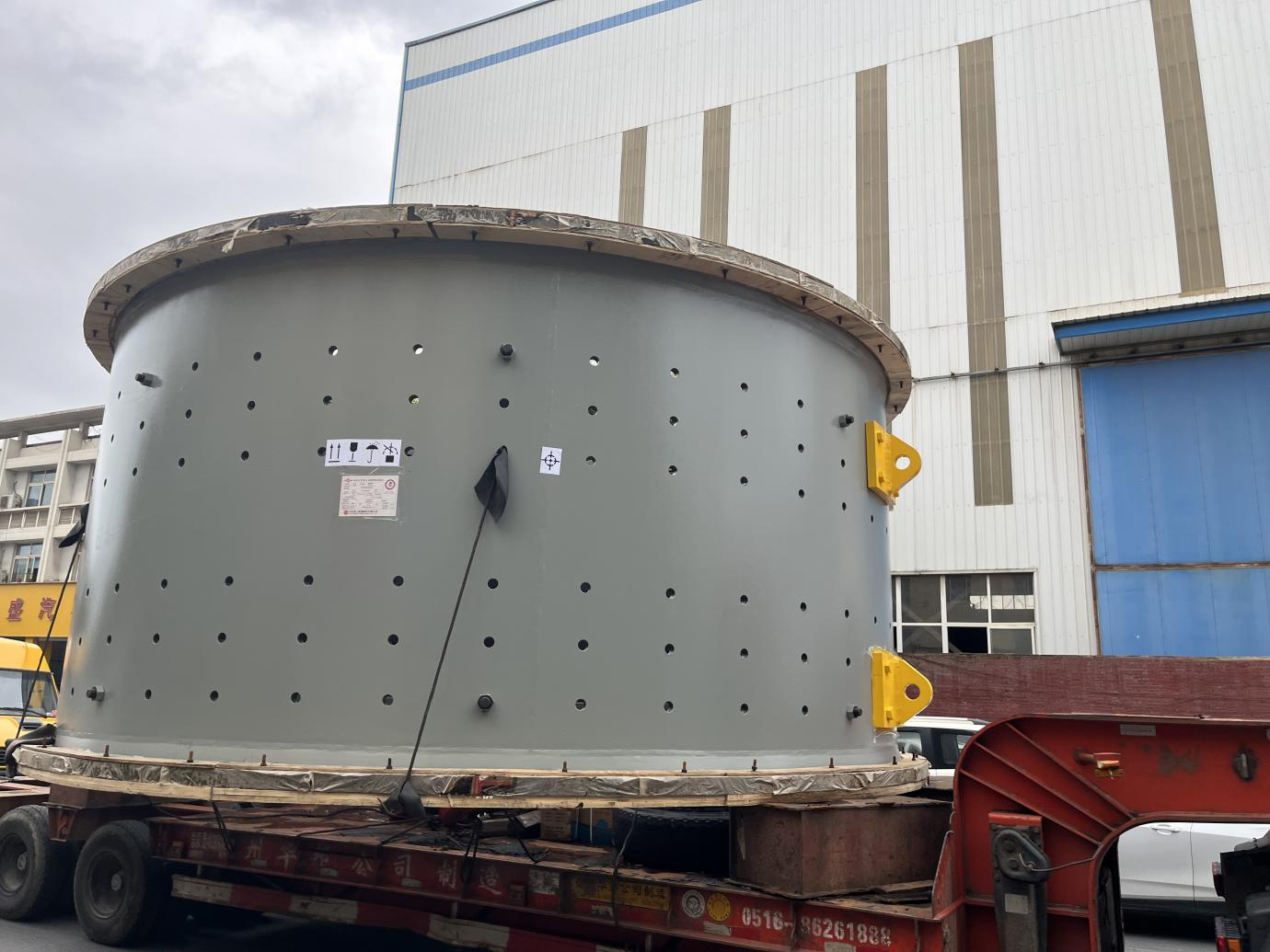

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-

Bus Alloy Bushings
-

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
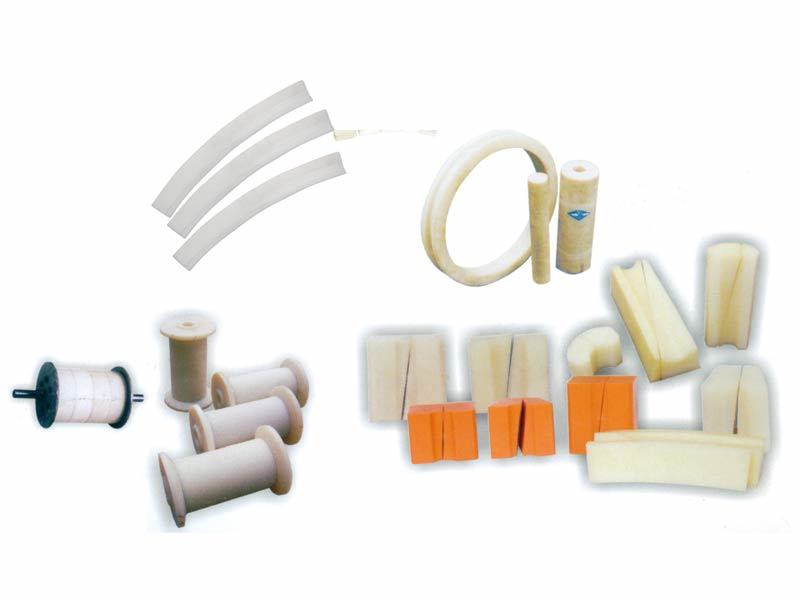

Nylon products
-
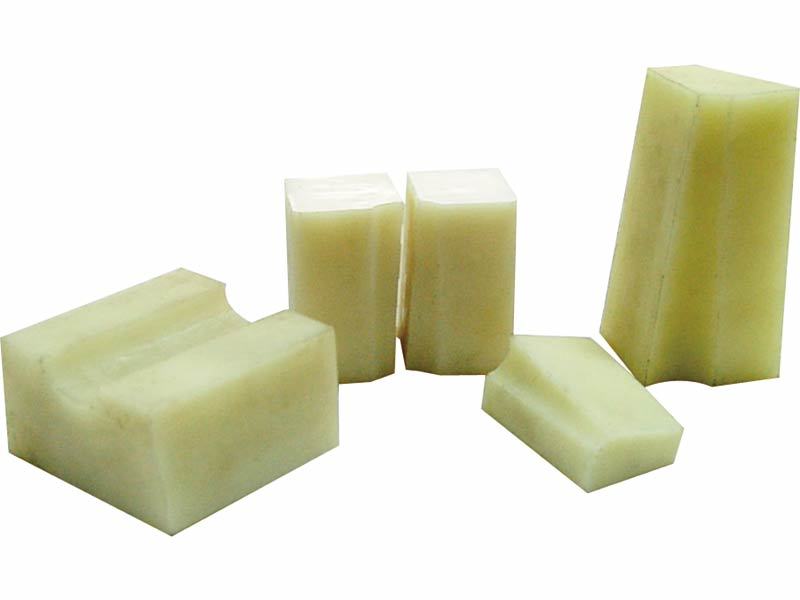

Polyurethane Products
-
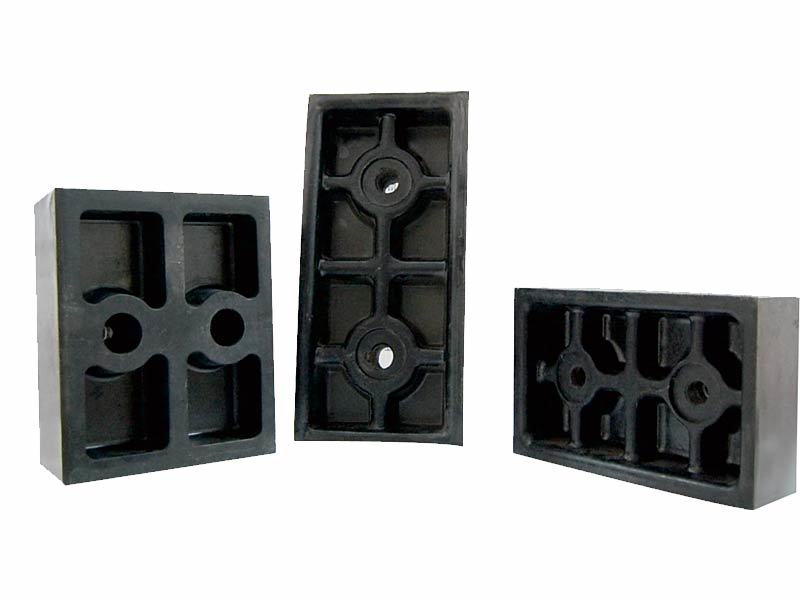

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
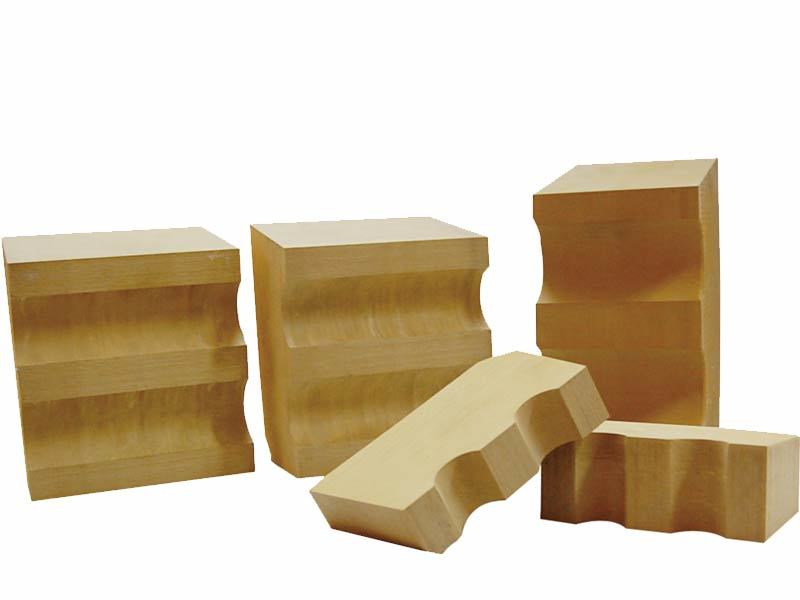

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information