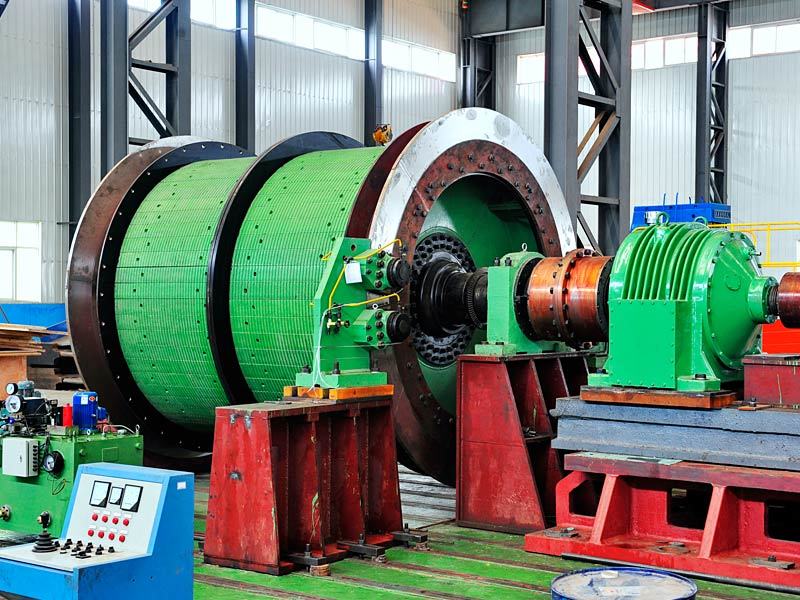
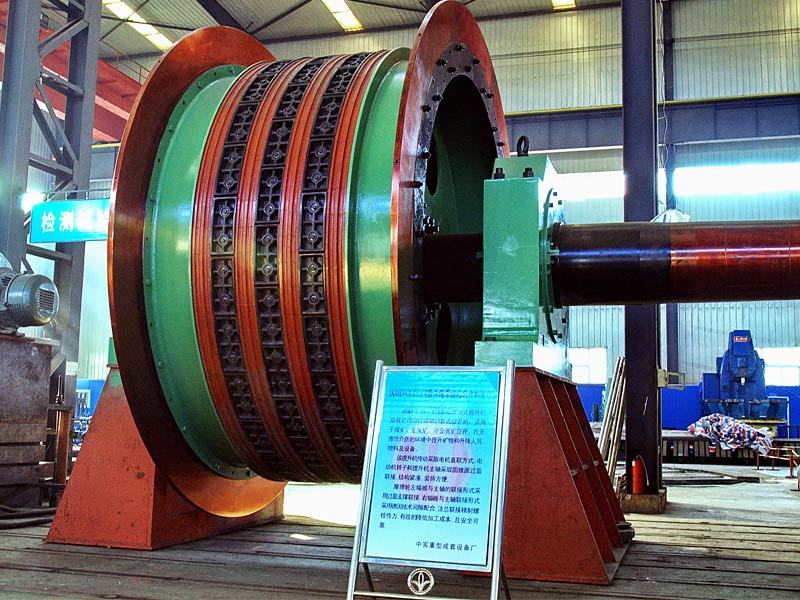
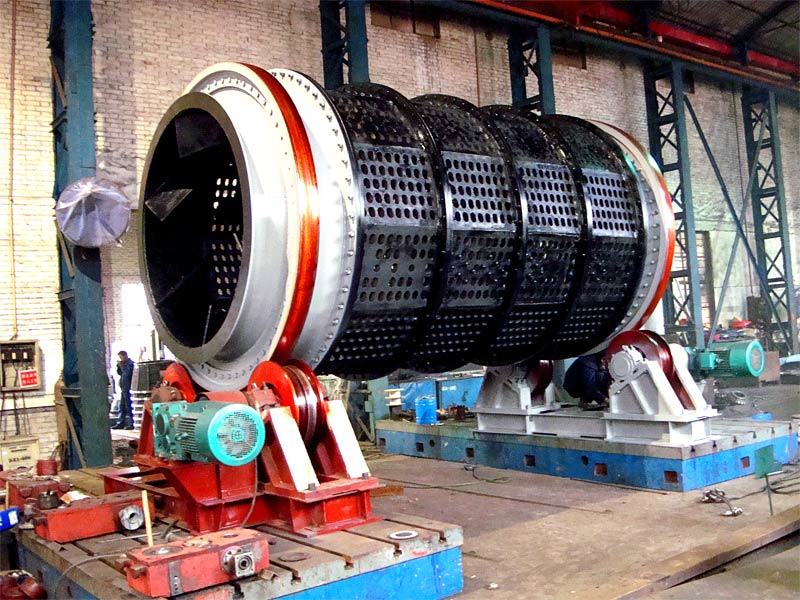
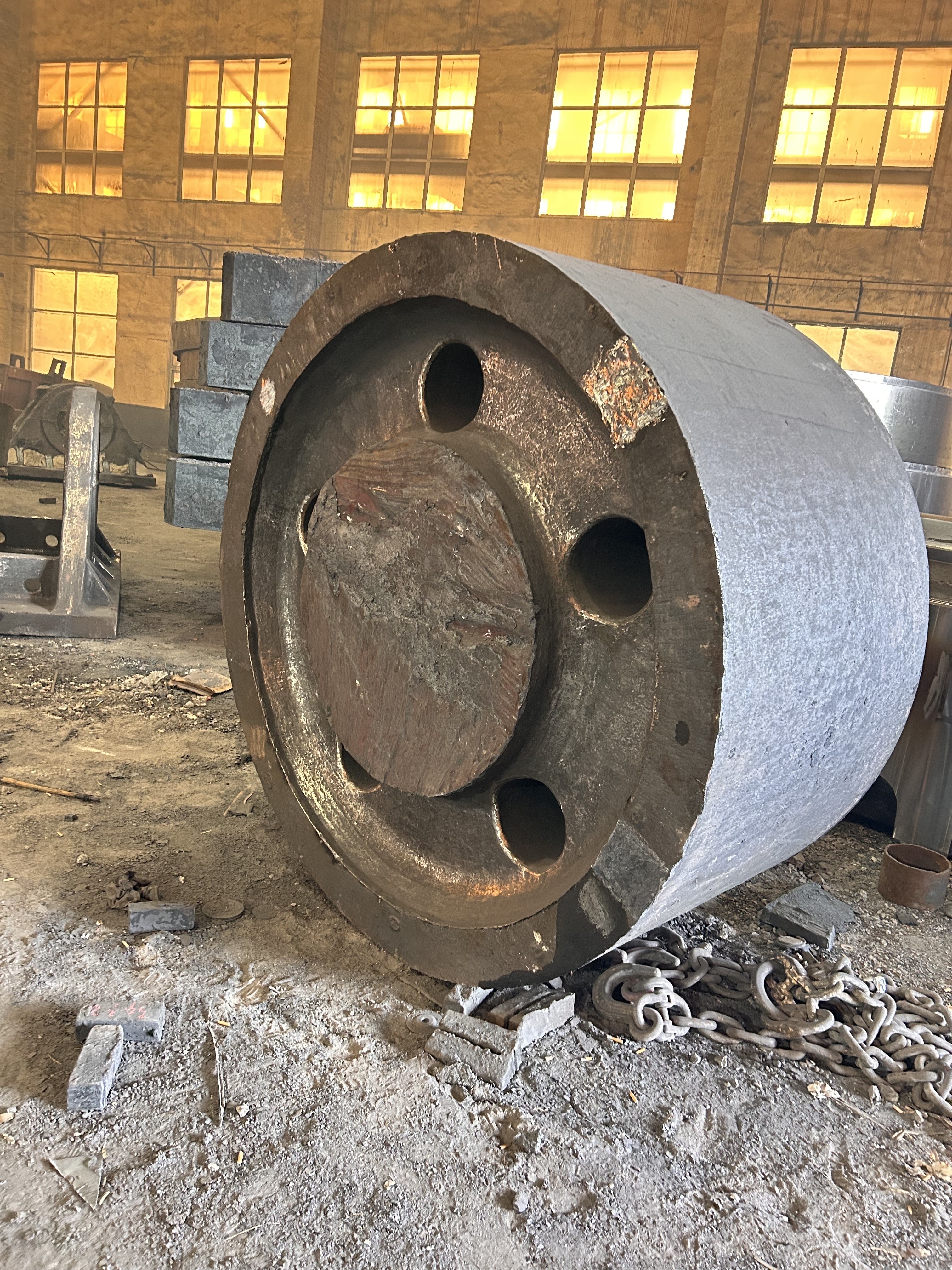
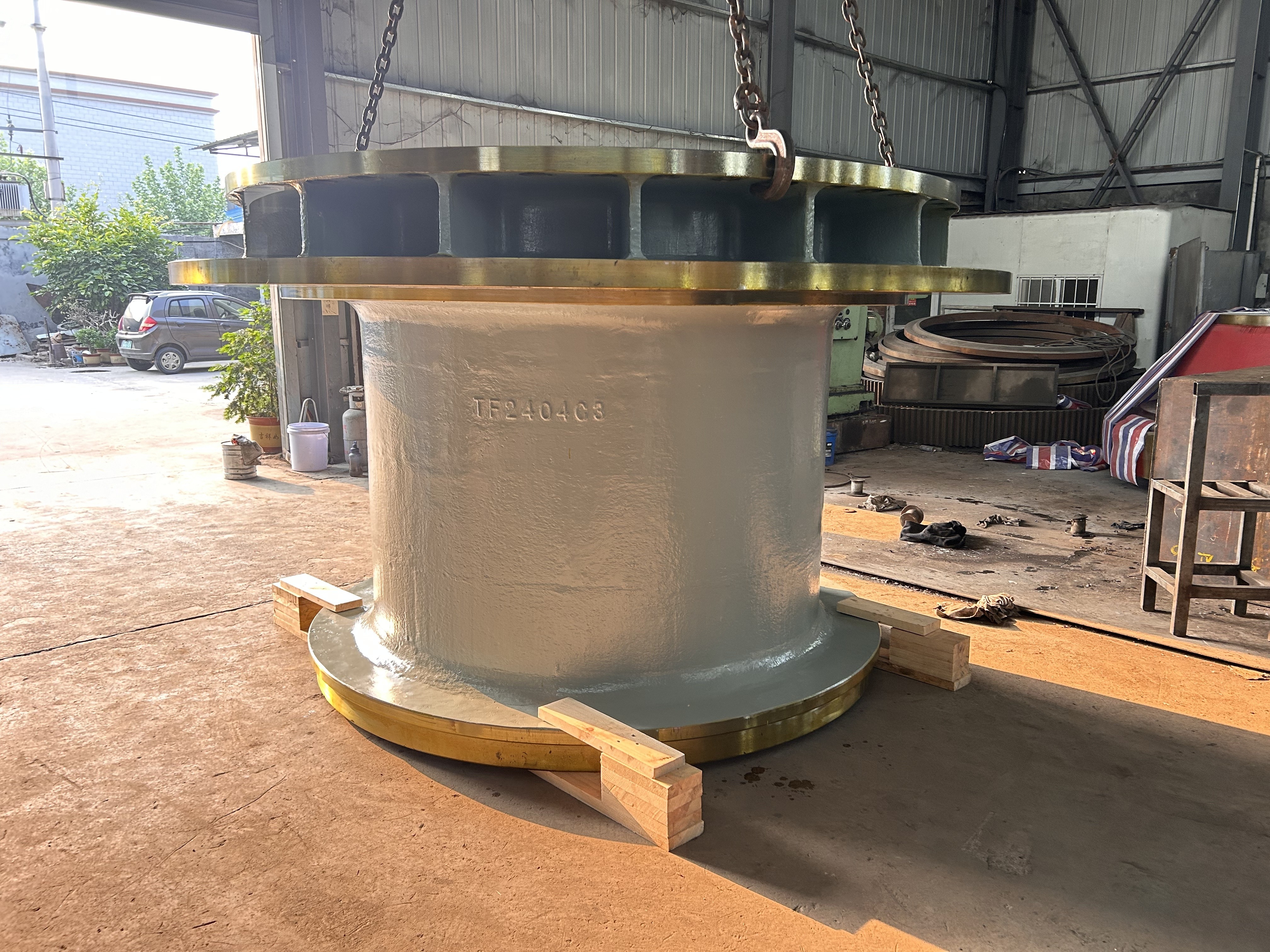
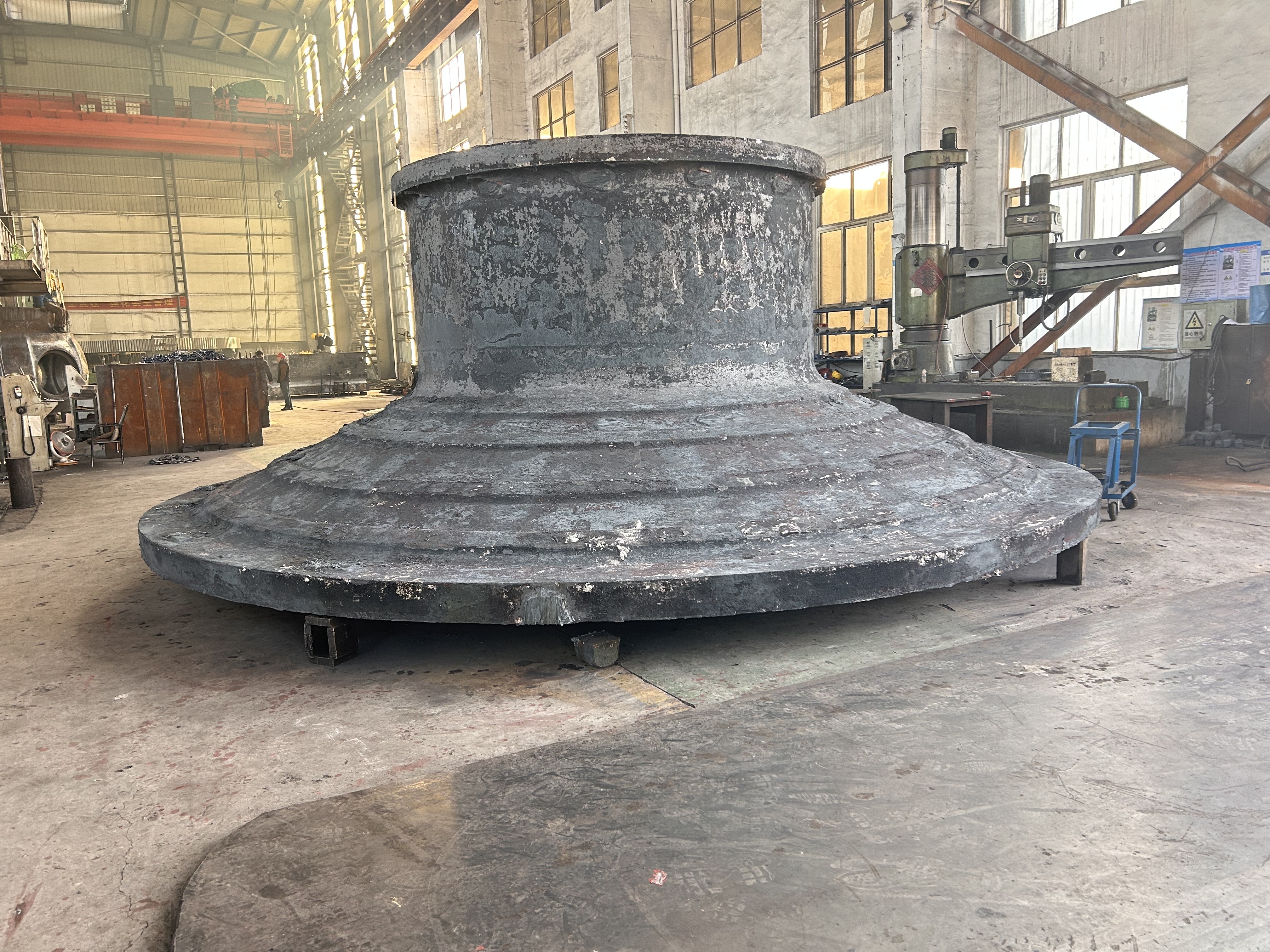
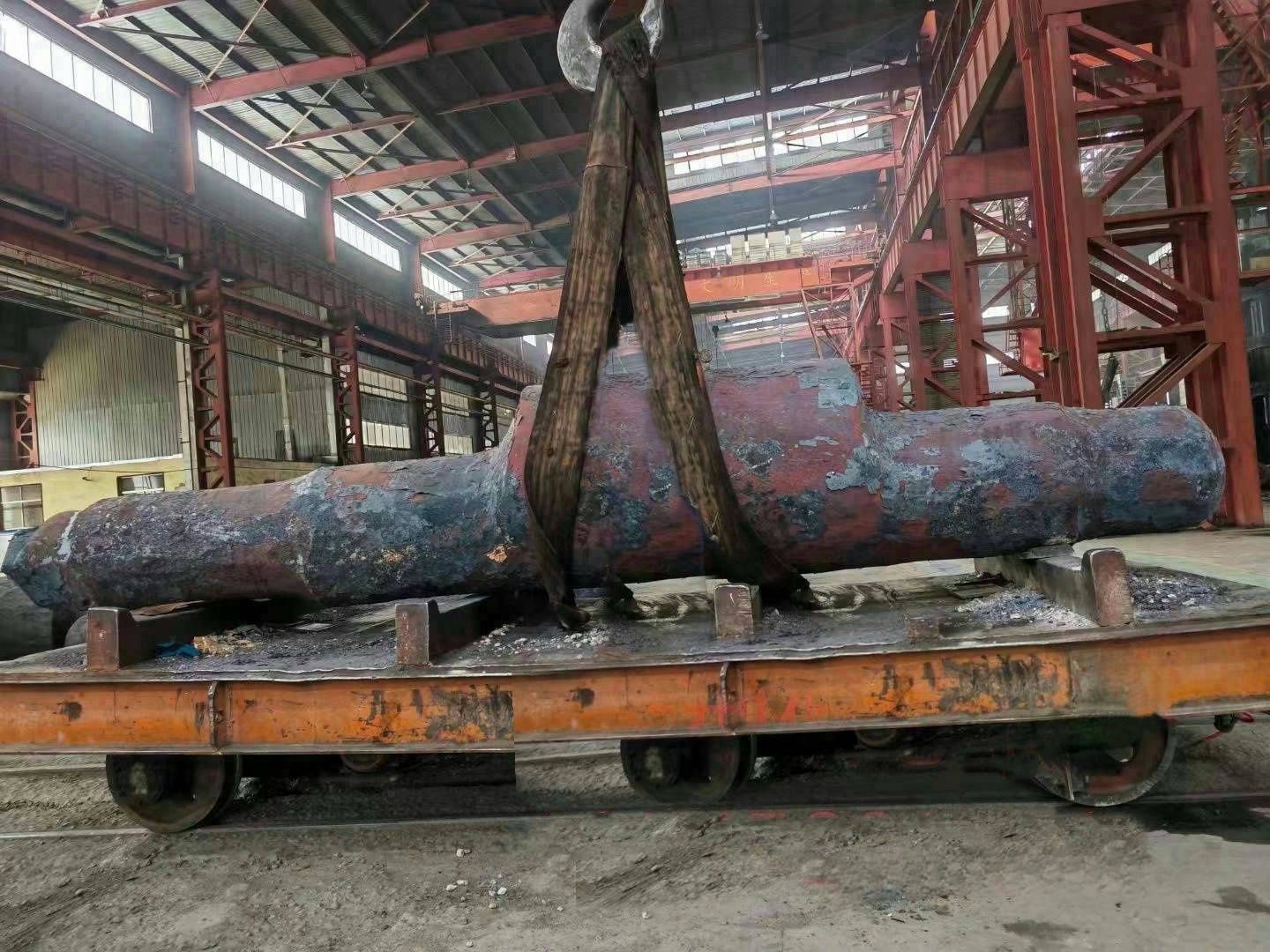
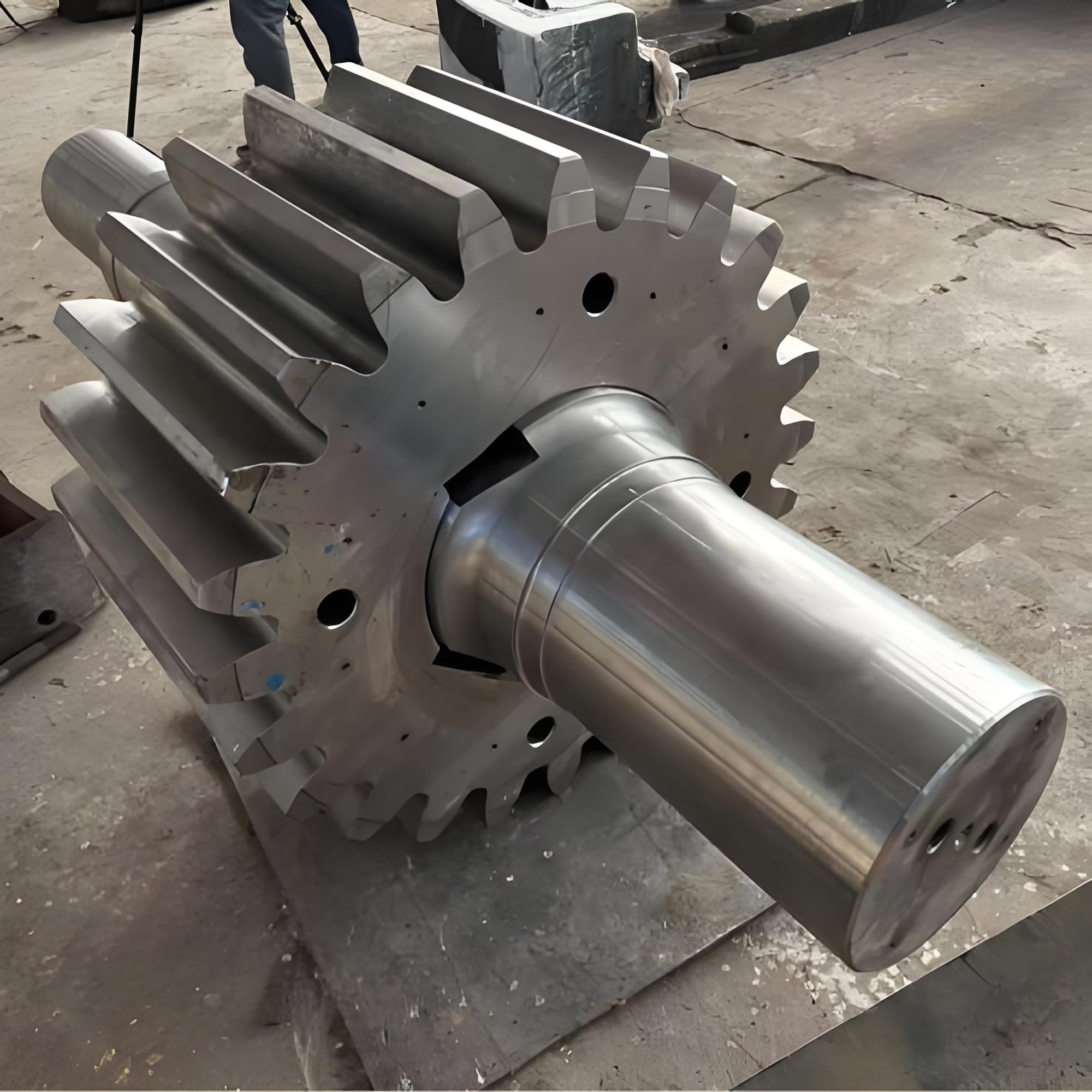
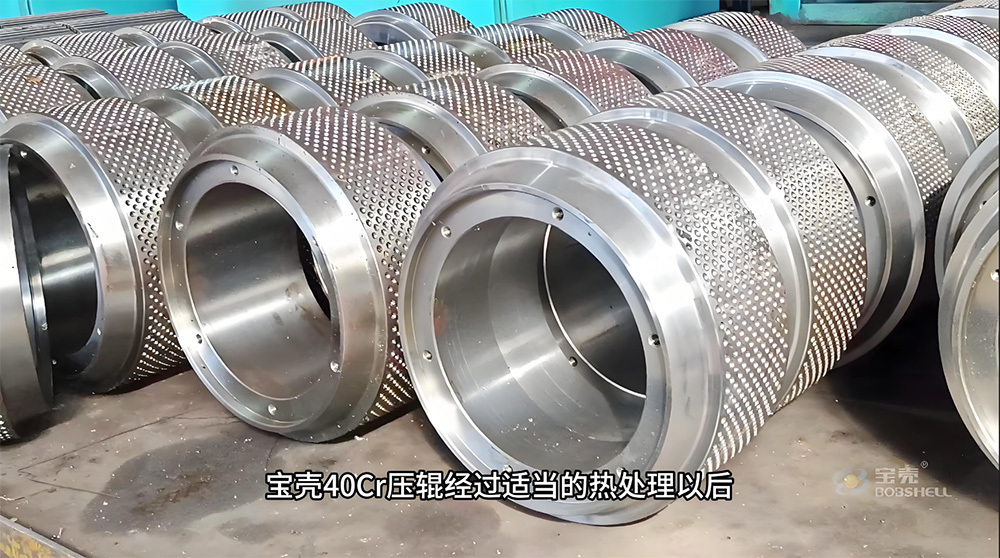
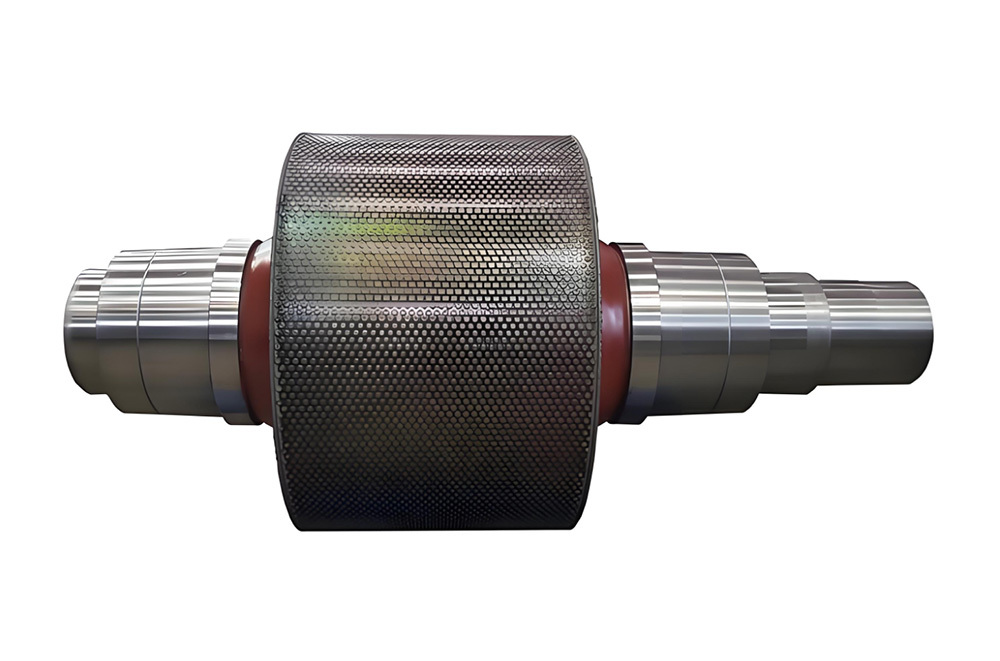
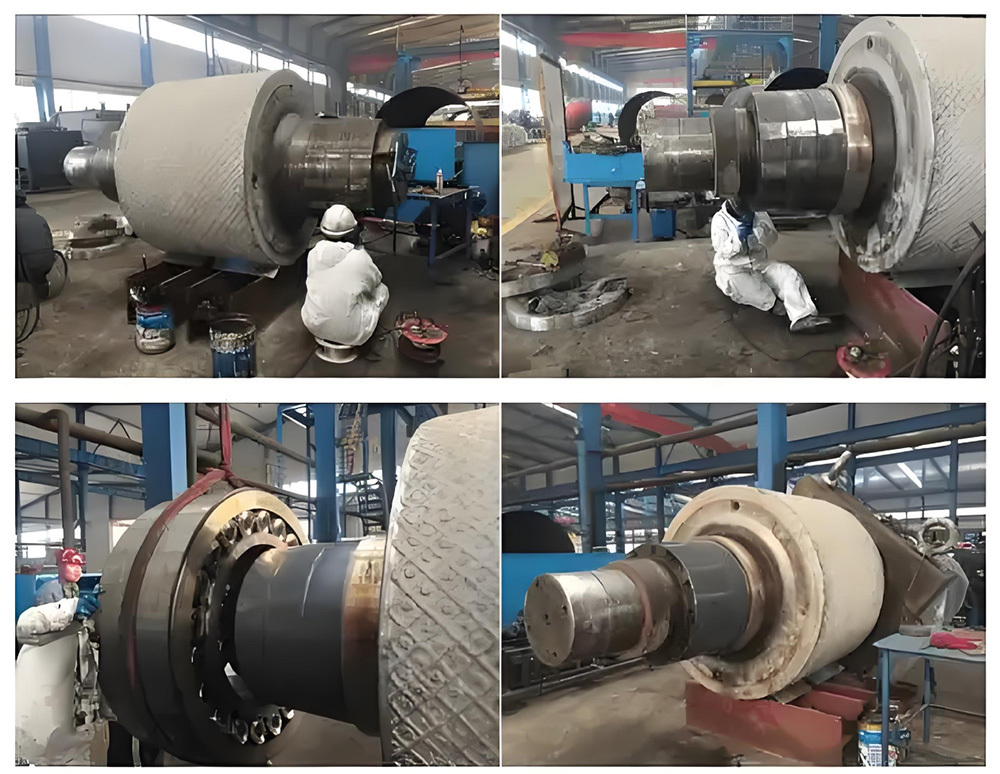
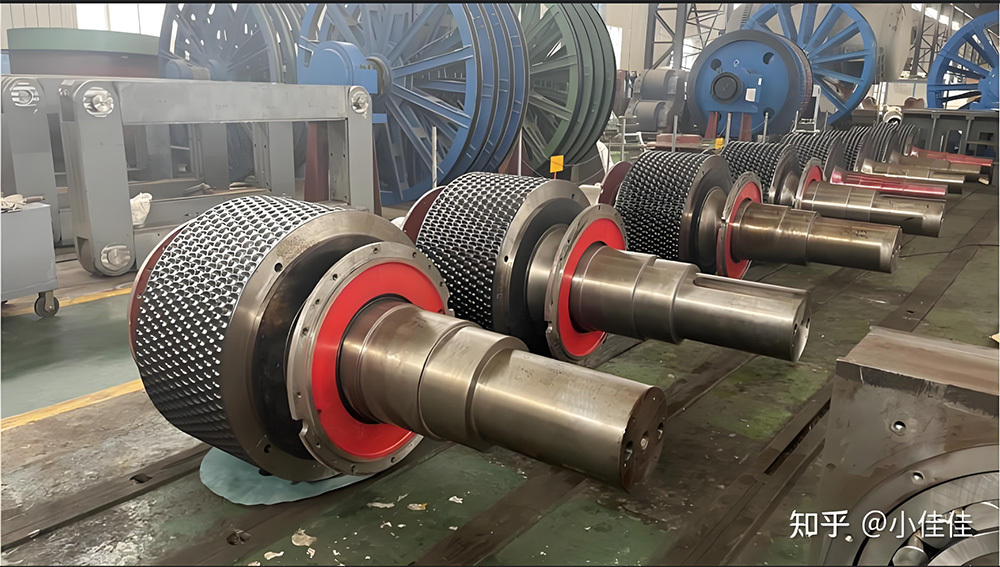
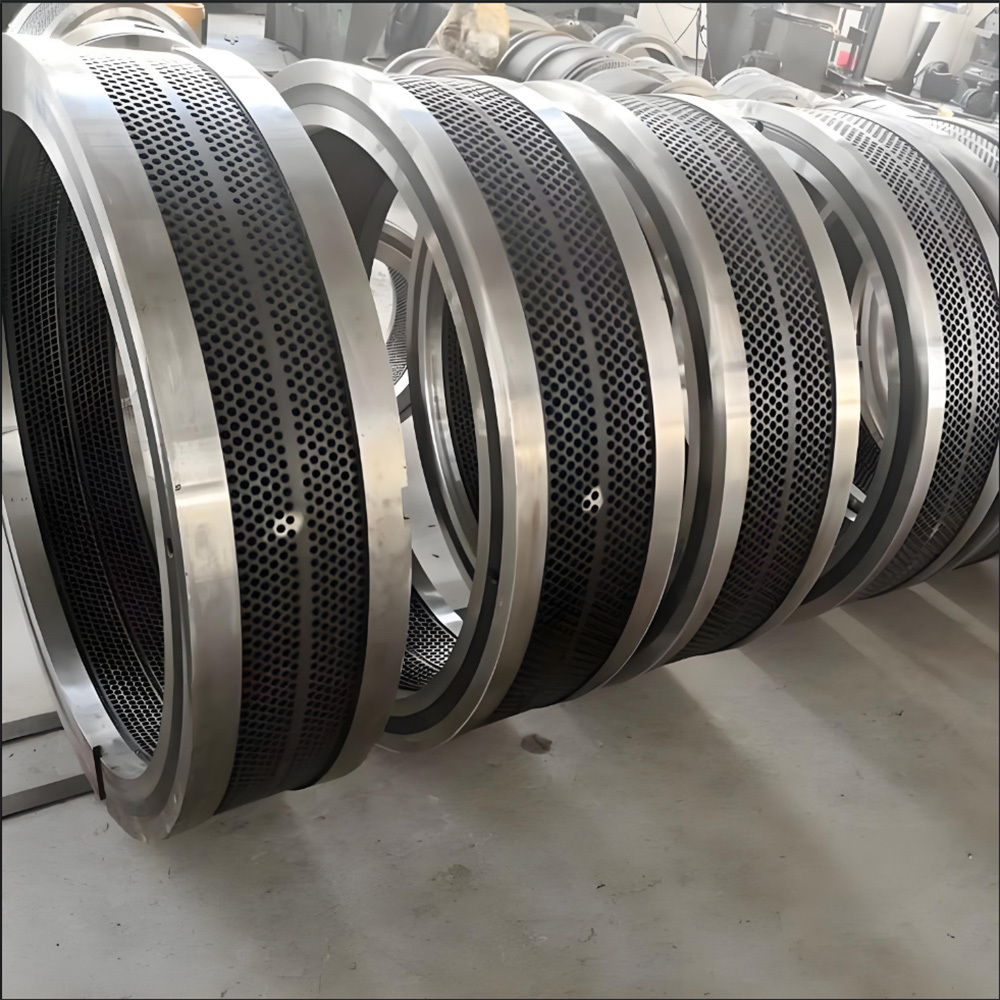
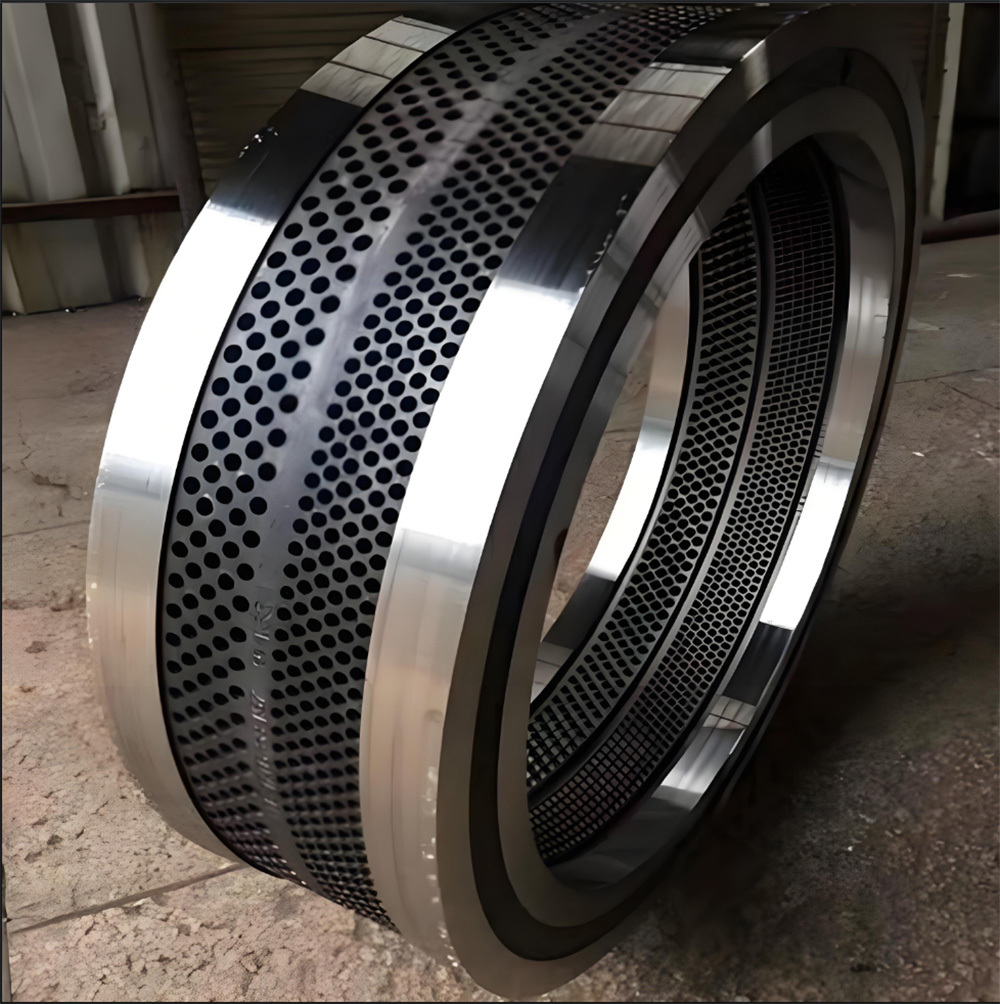
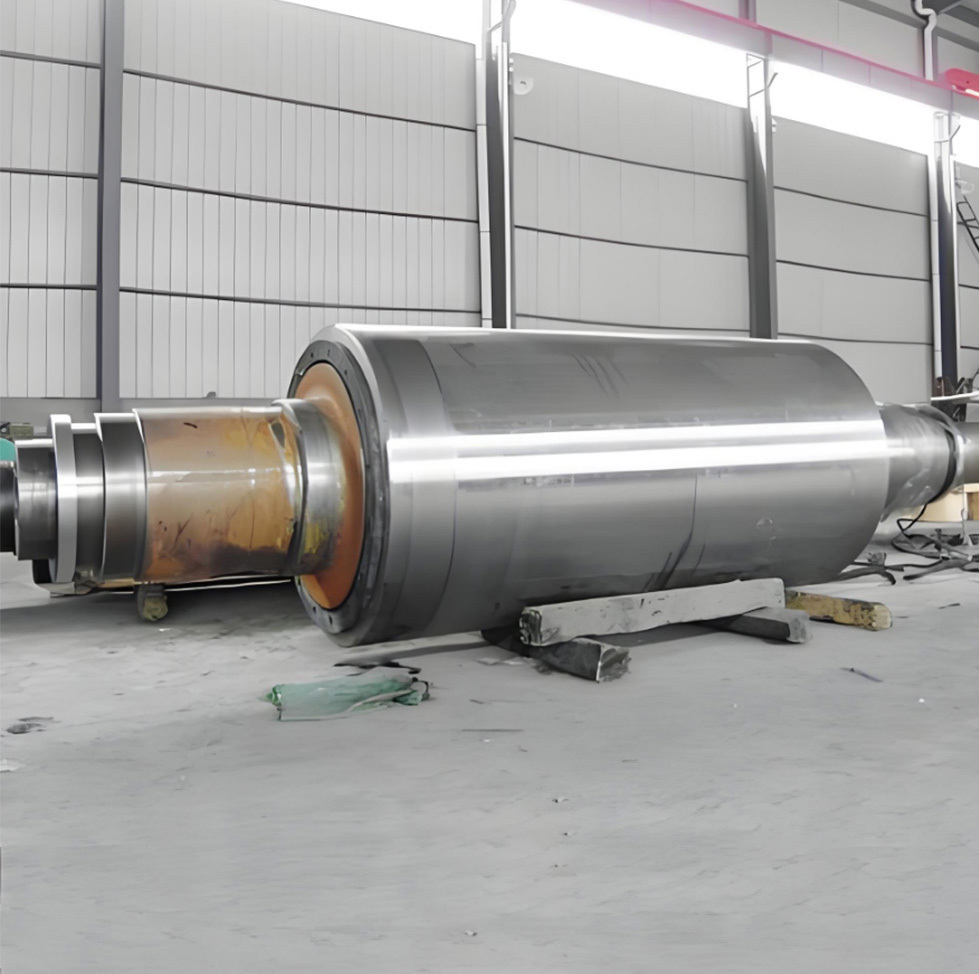
I. Introduction to a New Type of High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Technology
The new high-pressure roller wear-resistant surfacing technology is a series of advanced techniques developed on the basis of traditional surfacing methods. It addresses the heightened demands for wear resistance, spalling resistance, and service life imposed by the demanding operating conditions of high-pressure roller mills—specifically under conditions characterized by high pressure, intense abrasion, impact, and corrosion. At its core, this technology aims to significantly enhance the performance and longevity of the roller surface's wear-resistant layer, thereby minimizing downtime for maintenance and reducing overall operational costs.
II. Core Materials and Performance Characteristics
High-pressure roller wear-resistant surfacing technology significantly enhances the abrasion resistance of high-pressure rollers by applying wear-resistant materials onto their surfaces, thereby extending the service life of the equipment. At the heart of this technology lies the careful selection of suitable surfacing materials—currently, the mainstream options include wear-resistant welding electrodes and surfacing welding wires—which boast the following key performance characteristics:
High hardness and wear resistance: For instance, the D047 wear-resistant welding rod is specifically designed for extrusion rolls in rolling mills, with a deposited layer hardness reaching over HRC58. Meanwhile, tungsten carbide alloy welding rods (such as D708) enhance wear resistance through the reinforcement of hard tungsten carbide phases, making them ideal for surfacing worn components under high-temperature and high-pressure operating conditions.
High-Temperature Stability: Certain welding electrodes (such as D917) can withstand temperatures up to 860°C, making them suitable for high-temperature applications like spiral augers in mechanized charcoal plants and steel alloy equipment.
Impact and Crack Resistance: Surfacing welding wires (such as YD256 and YD266 high-manganese steel welding wires) combine impact resistance with machinability by adjusting their alloy composition—featuring high carbon and high chromium content—while remaining resistant to cracking during the welding process.
III. Classification and Application Scenarios of Wear-Resistant Surfacing Materials for High-Pressure Rollers
1. Material Classification
Based on differences in material composition and performance, high-pressure roll surfacing materials can be categorized into the following types, each suited to specific application scenarios:
Material Type |
Typical product |
Core Ingredients |
Application Areas |
Iron-based wear-resistant welding electrodes |
D047, DH-04 |
C, Cr, Mn, Si alloys |
High-wear components such as roller press squeeze rollers, chain wheel shaft assemblies for coal mine conveyors, and scraper conveyor chutes |
Tungsten Carbide Welding Rods |
D708, D917 |
WC (Tungsten Carbide) + Alloy Elements |
Chemical equipment, mining crusher hammer heads, high-temperature roll components, and other impact-resistant wear parts |
High-manganese steel welding wire |
YD256, YD266 |
Mn, Cr Alloy |
Shredder blades and high-pressure roller surface repairs require balancing wear resistance with machinability in demanding applications. |
Nickel-based alloy welding electrodes |
ENiCrFe-1 |
Ni-Cr-Fe Alloy |
Welding dissimilar materials under high-temperature corrosion environments, such as Inconel alloy joints with carbon steel/stainless steel. |
IV. Key Technical Points and Operational Guidelines for High-Pressure Roll Surfacing Technology
Principles for Material Selection
Condition matching: Select materials based on the working temperature of the high-pressure roller (ambient/high temperature) and the medium (abrasive/corrosive environment). For instance, D917 tungsten carbide welding rods are preferred for high-temperature, high-pressure applications, while DH-04 dedicated welding rods are recommended for coal mining equipment.
Base material compatibility: For carbon steel substrates, D036 edge-welding electrodes can be directly applied; for dissimilar-material welding (e.g., stainless steel to carbon steel), nickel-based electrodes (ENiCrFe-1) must be used.
Welding Process Control
Preheating and Post-Weld Heat Treatment: For high-hardness welding electrodes (such as D708), preheat the workpiece to 200–300°C before welding, and allow it to cool slowly after welding to prevent cracking. Low-hydrogen electrodes (such as D027) do not require preheating, but the interpass temperature must be controlled below or equal to 250°C. 1。
Welding methods: Oxy-acetylene surfacing is suitable for small-area repairs requiring high surface finish, with a low dilution rate (melting layer depth ≤ 0.1 mm). For large-area surfacing, shielded metal arc welding combined with flux-cored wires (such as YD507) is recommended to enhance efficiency. 3。
Quality Inspection Standards
Hardness Test: The surface hardness of the surfacing layer must meet the design requirements (e.g., HRC 58–62), and a Rockwell hardness tester can be used for on-site inspection.
Non-destructive testing: Use penetrant testing (PT) or magnetic particle testing (MT) to detect defects such as cracks and porosity in the surfacing layer, ensuring that no through-wall defects are present.
V. Applications and Advantages
This technology has been widely applied in fields such as mining, building materials, and chemical industries, with notable examples including:
Mining Machinery: High-pressure roller mill roll surface overlay welding repair—after using D047 welding electrodes for overlaying, the service life is extended by 3 to 5 times.
Cement Industry: For roller press and roll welding on vertical mills, using tungsten carbide electrodes (D708) can effectively withstand the continuous impact and abrasion caused by clinker particles.
Coal Processing: Sliding channel buildup on scraper conveyors using DH-04 welding rods boosts wear resistance against abrasive particles by more than 40%. 1。
Compared to the traditional method of replacing roller bodies, surfacing welding technology can reduce maintenance costs by 60% to 80%, while also minimizing equipment downtime, resulting in significant economic benefits.
Advantages
Significantly extends service life: Compared to traditional surfacing welding, the new technology typically boosts the wear-resistant layer lifespan of roller surfaces by 50% or even more than 100%. The WC-reinforced surfacing layer shows an especially remarkable improvement in durability.
Outstanding anti-fatigue spalling performance: Enhanced toughness and gradient design effectively inhibit crack propagation and large-scale spalling of the wear-resistant layer, enabling the roll surface to maintain its integrity for a longer period.
Higher wear resistance: The optimized hard-phase type, quantity, and distribution, combined with a highly tough matrix, work together to deliver exceptional resistance against abrasive wear.
Reducing downtime: Extended service life means longer intervals between replacements or repairs.
Efficient automated surfacing welding reduces the time required for each repair.
Good resistance to shelling reduces unexpected downtime.
Reducing overall costs: Although the initial cost of surfacing may be higher—particularly when using WC materials—the significantly extended service life and reduced downtime for maintenance and repairs lead to a substantial decrease in both the operational cost per unit time (OPEX) and the cost of handling each ton of material.
Enhancing equipment operational stability: The roller surface wears evenly and is resistant to flaking, ensuring consistent working pressure and output for the high-pressure roller mill.
Keywords
Previous: Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
Next: Bus Alloy Bushings


New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
Rotary kiln
-

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-

Lime Rotary Kiln
-

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
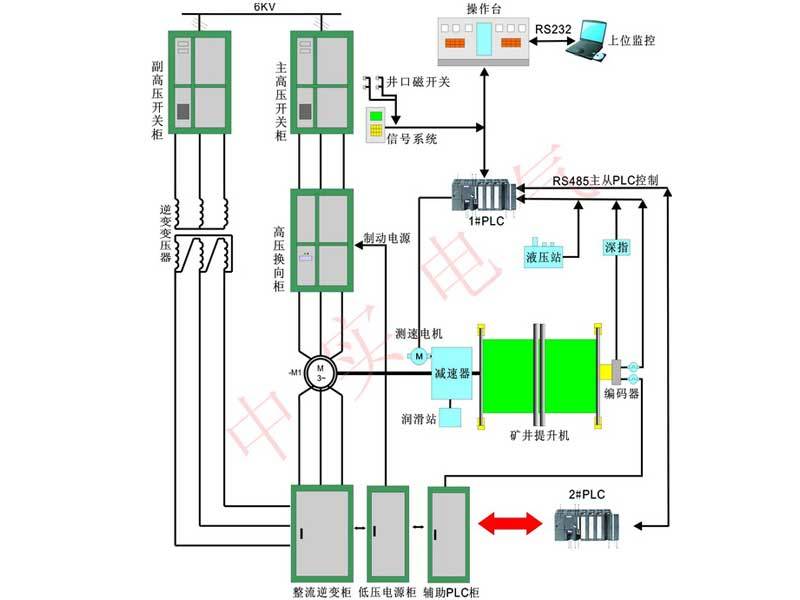
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
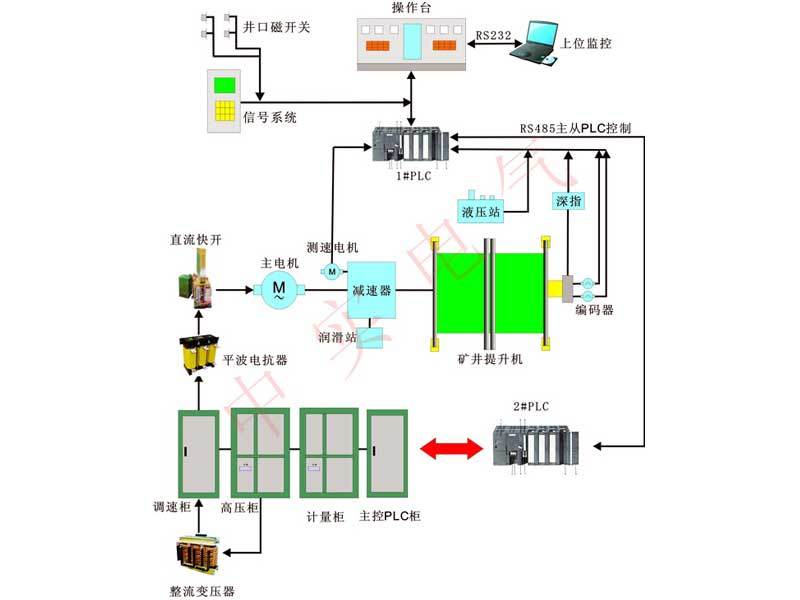
Fully digital DC control system
-
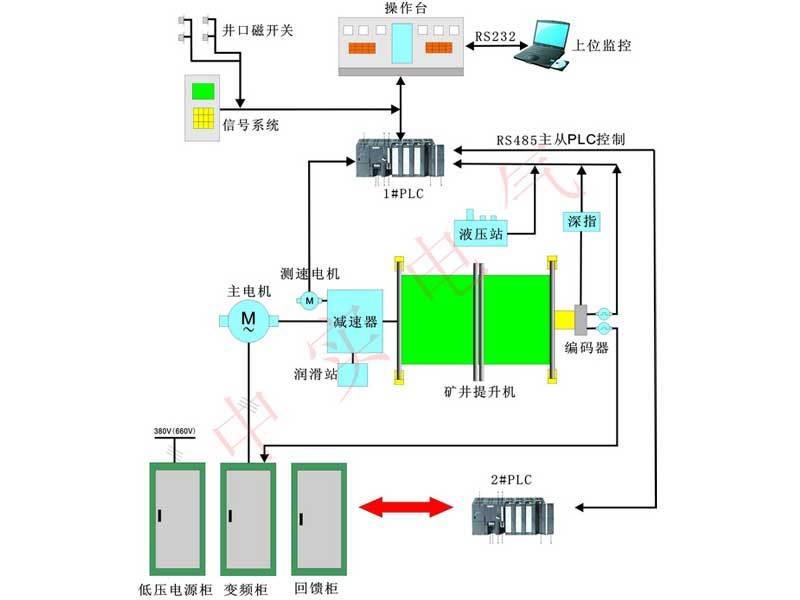
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
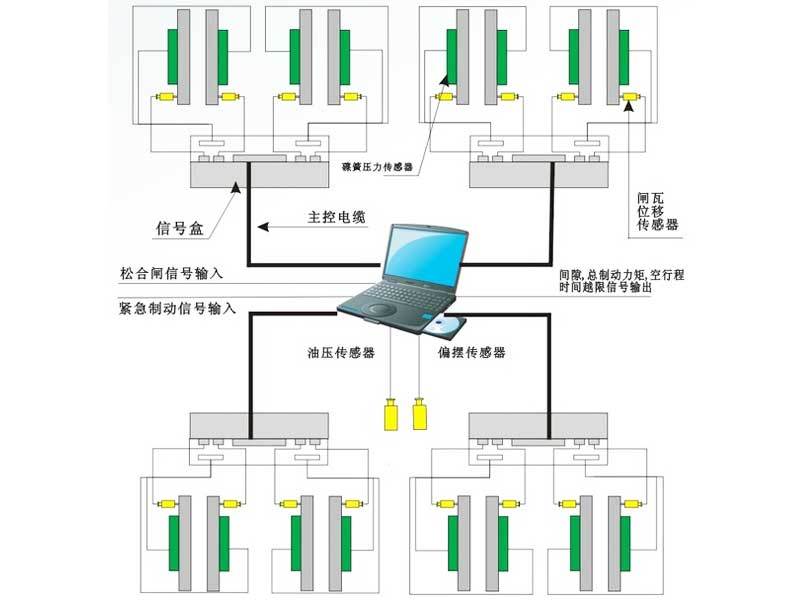
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
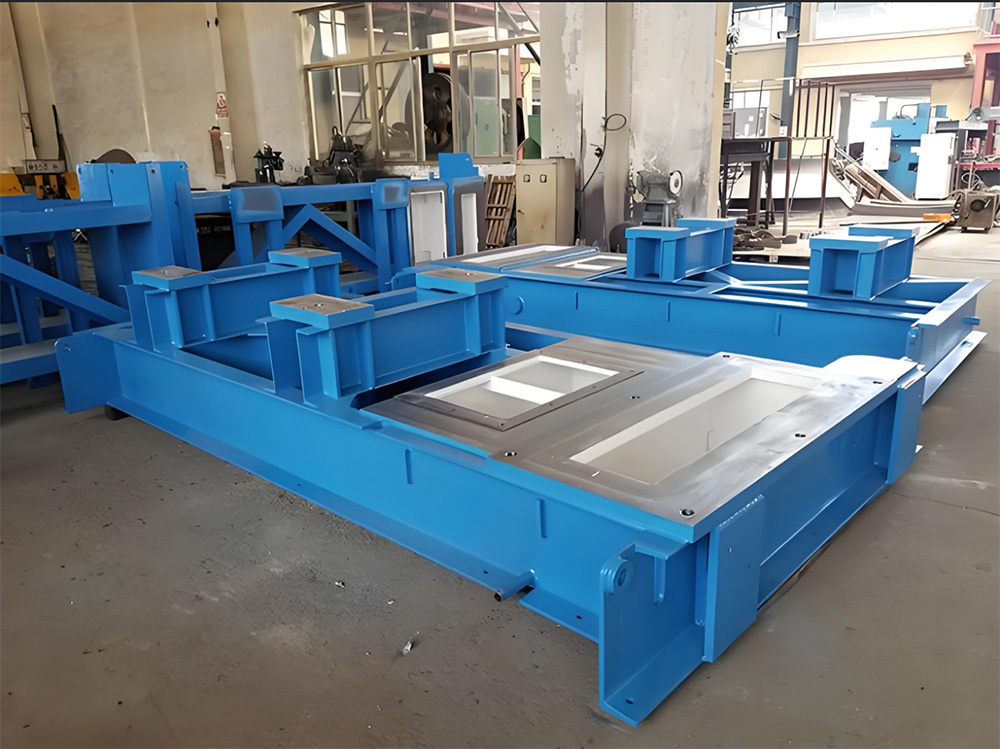

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-
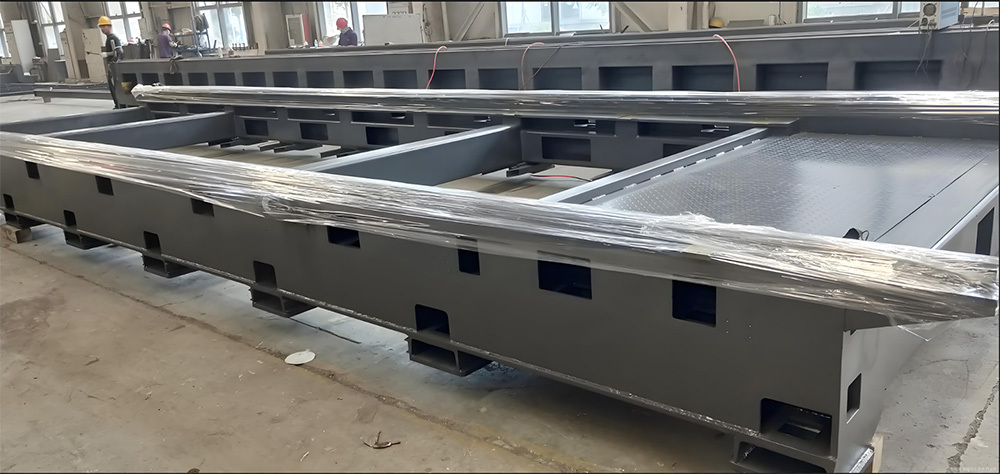

Large base
-
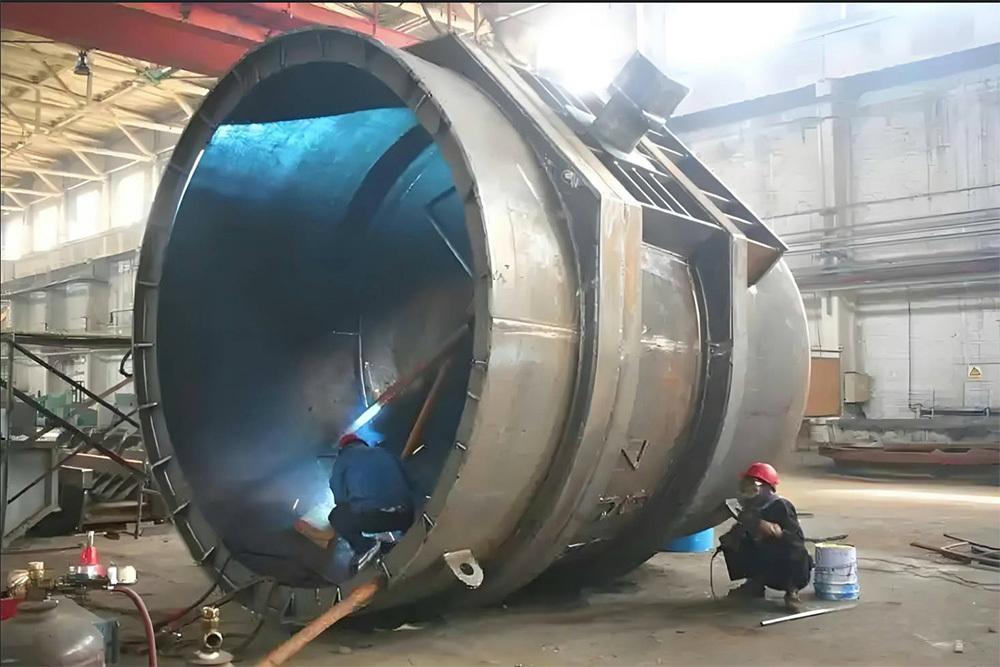

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
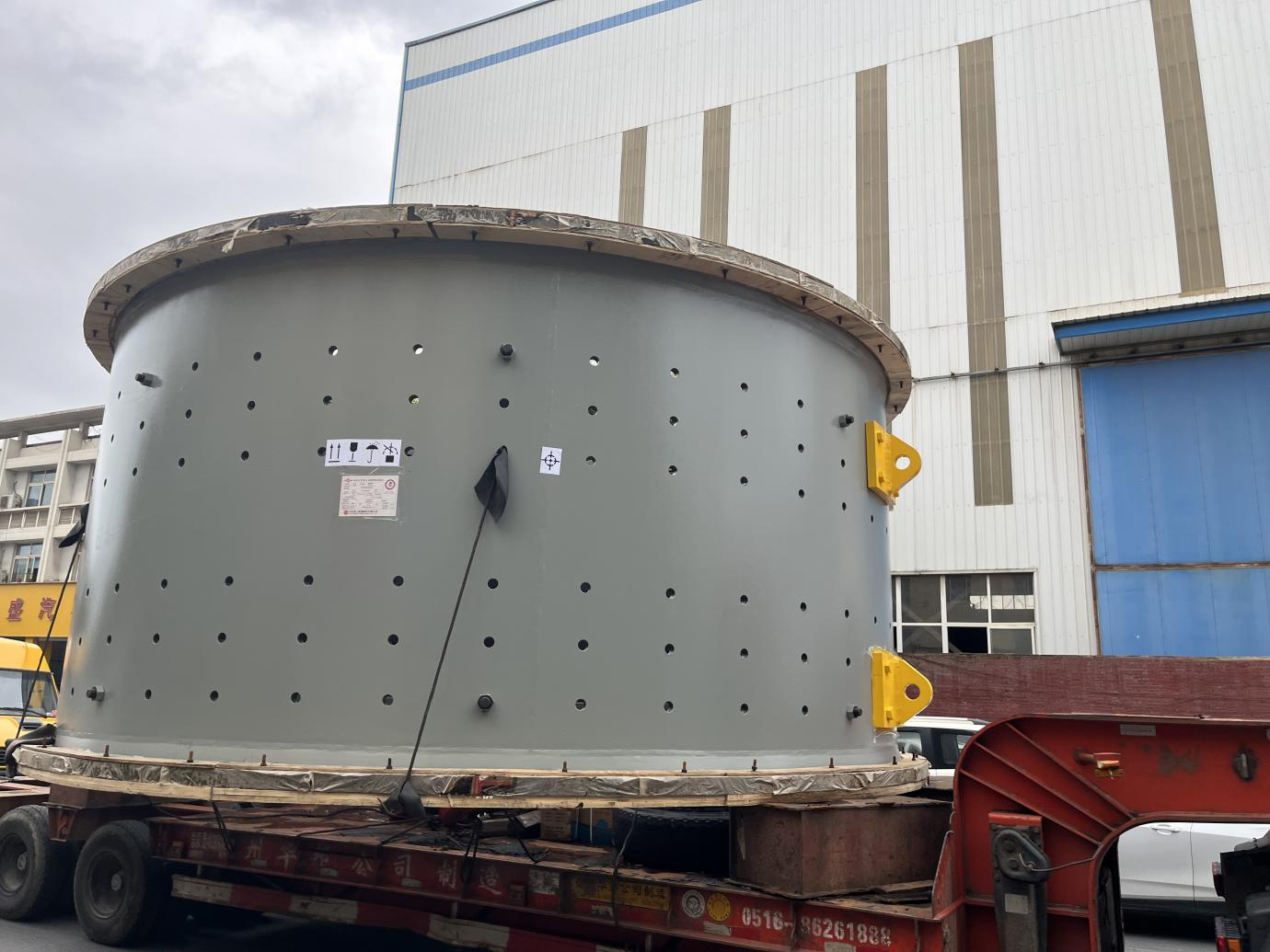

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-
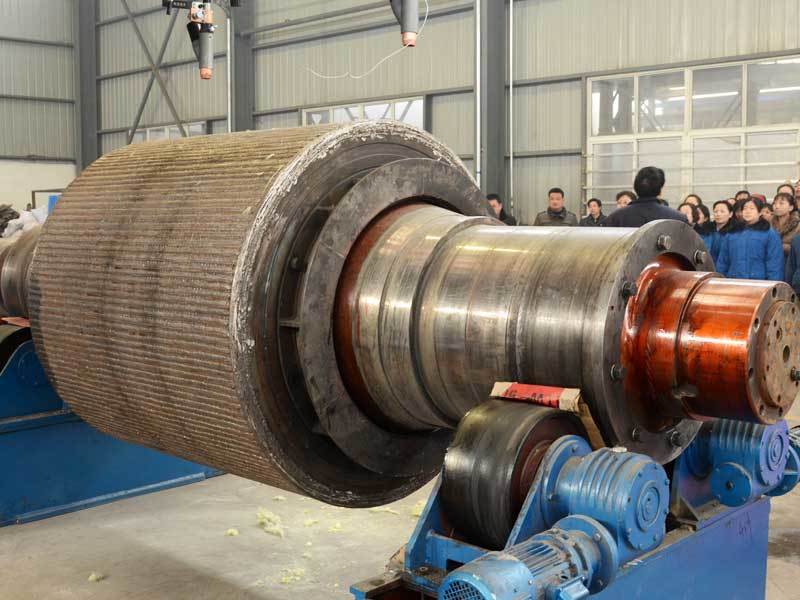

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-

Bus Alloy Bushings
-

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
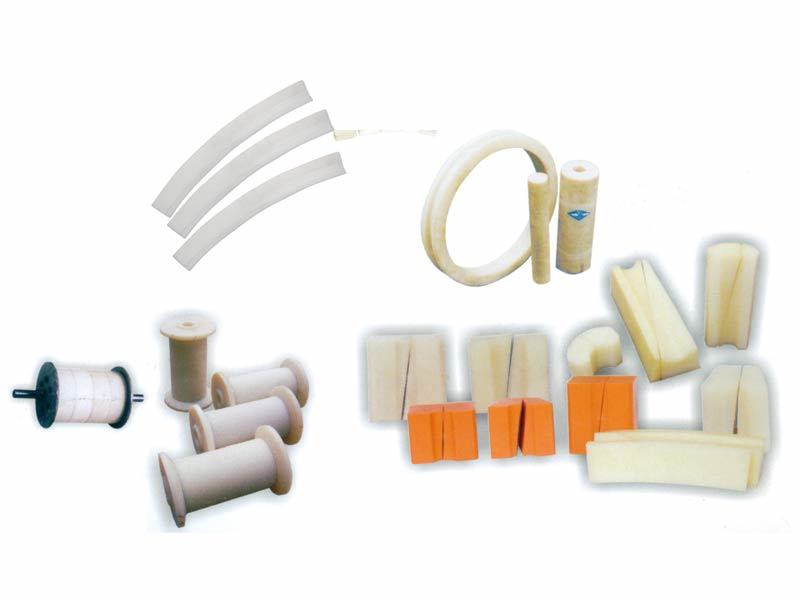

Nylon products
-
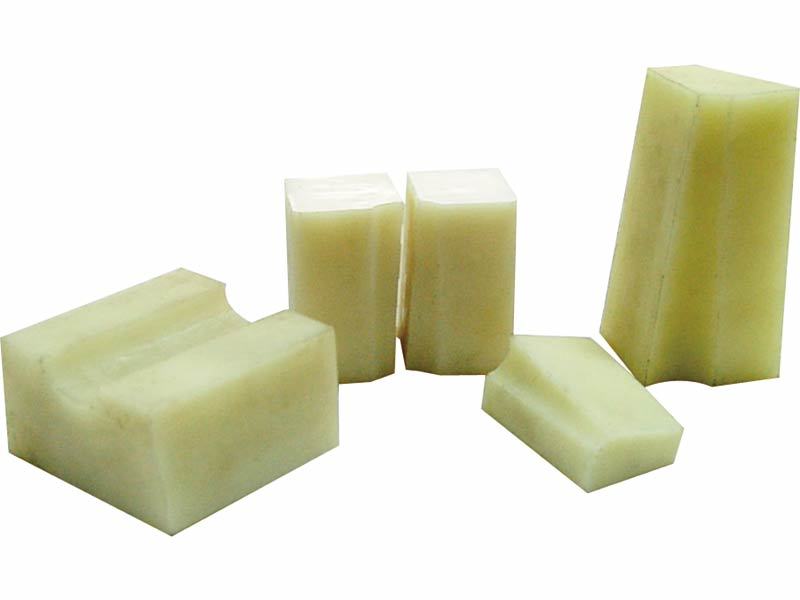

Polyurethane Products
-
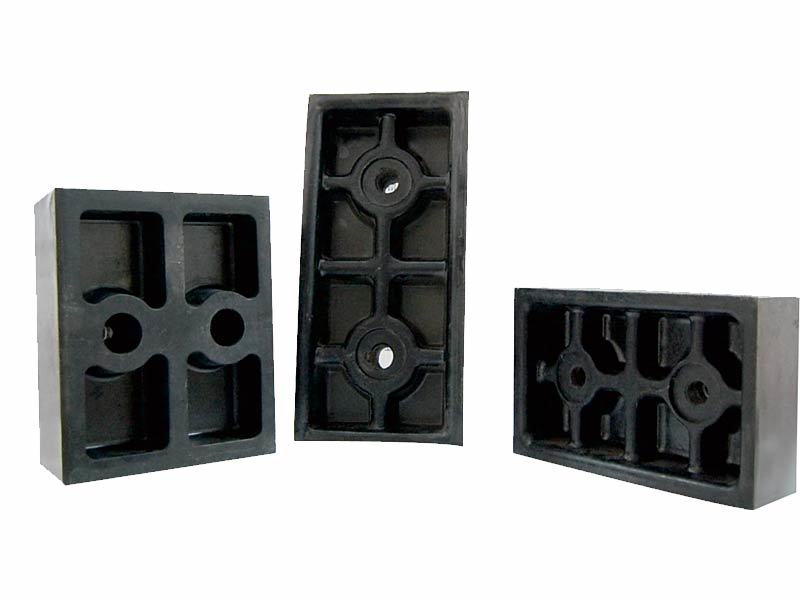

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
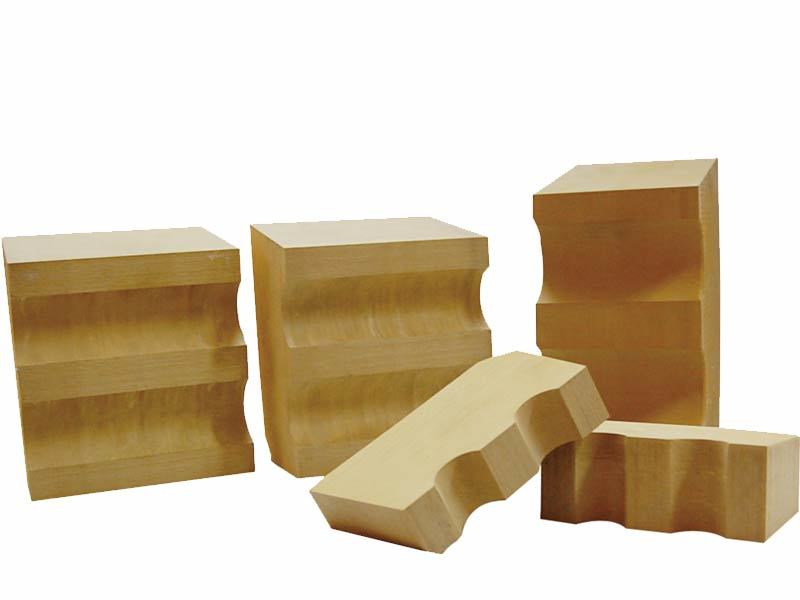

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information