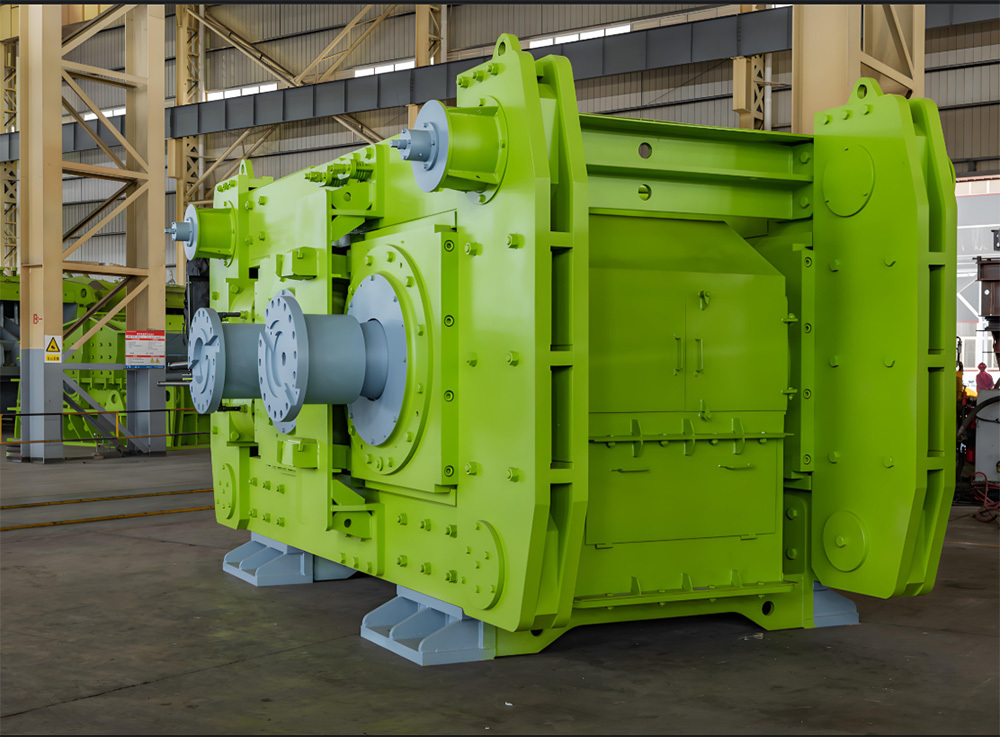
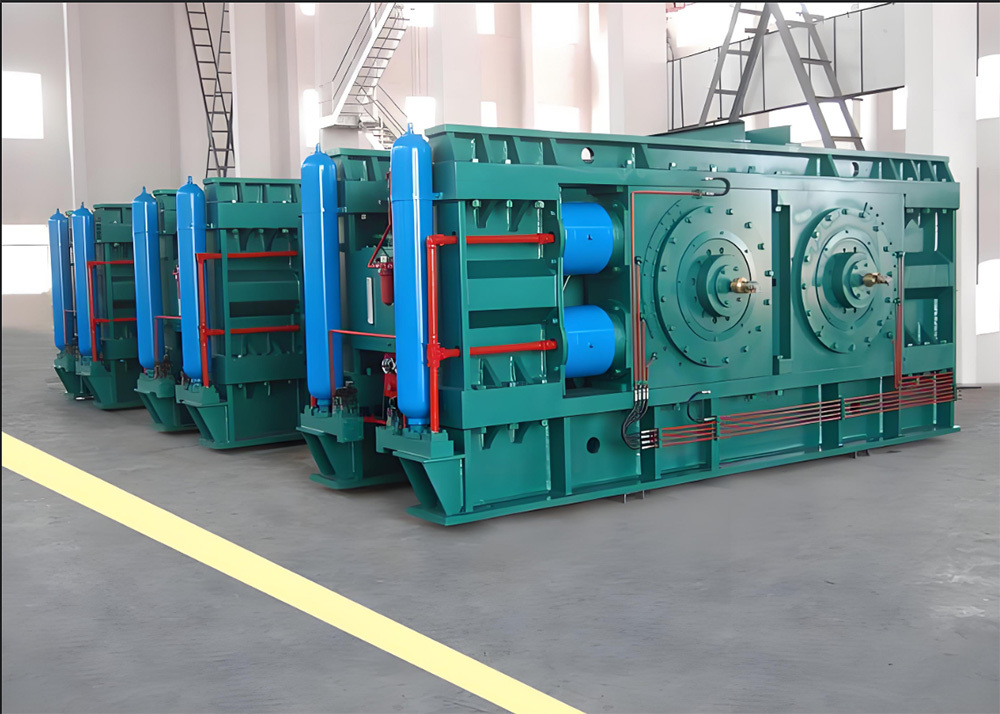
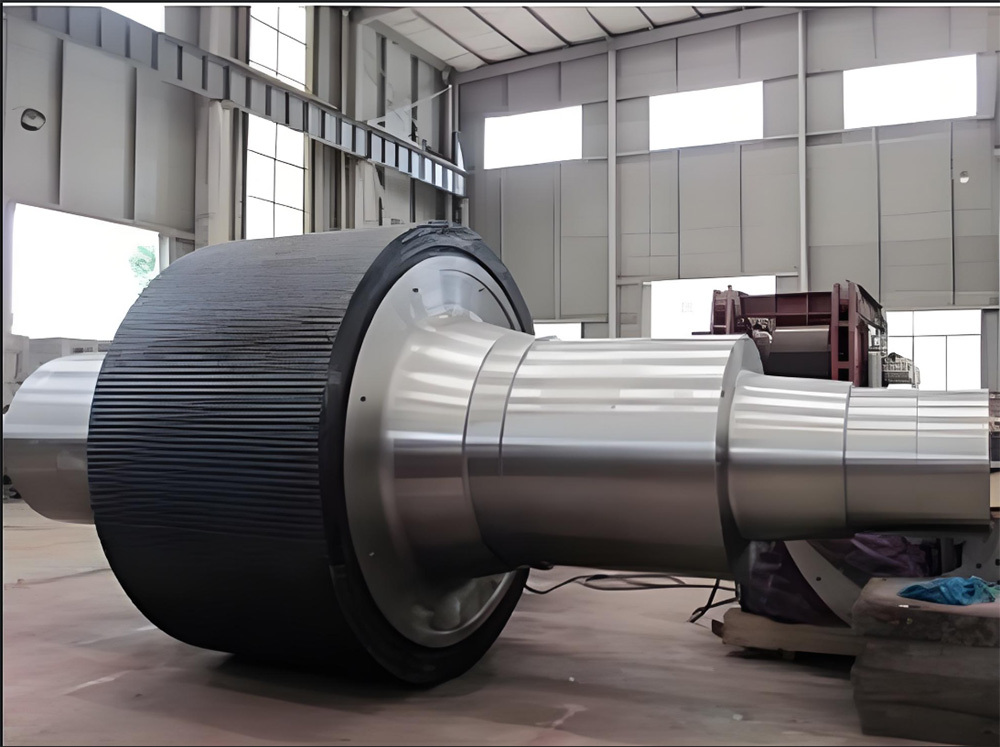
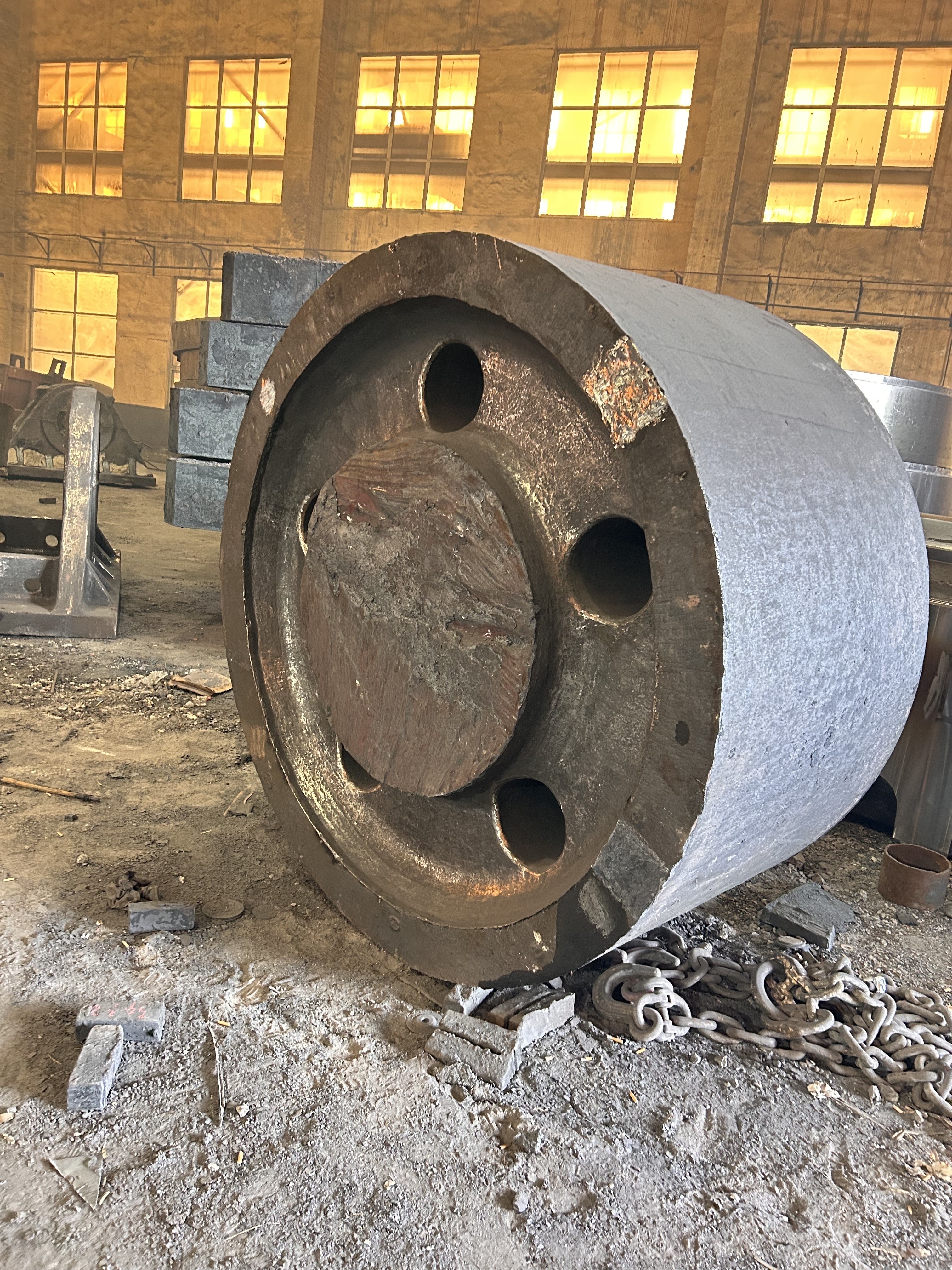
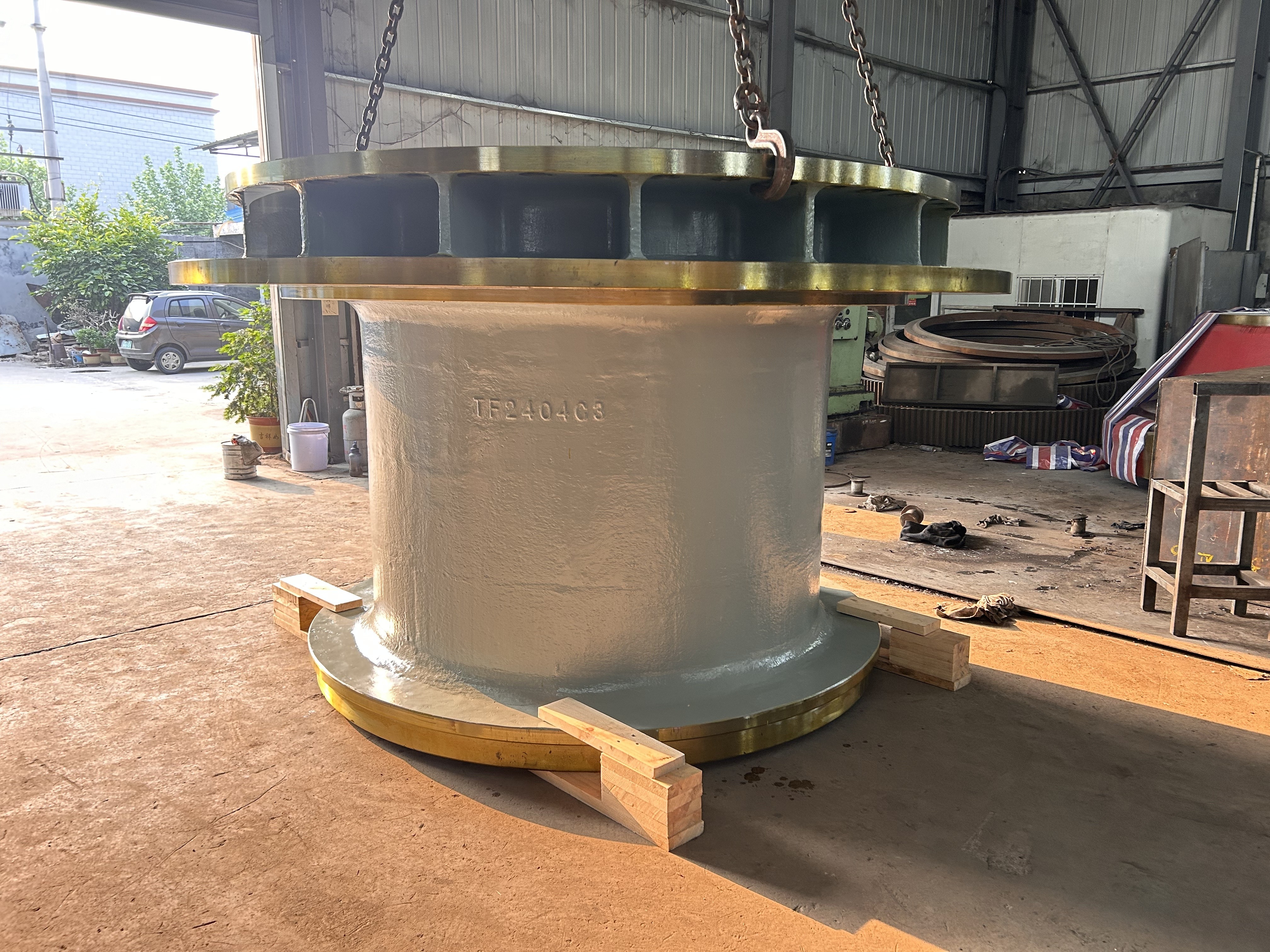
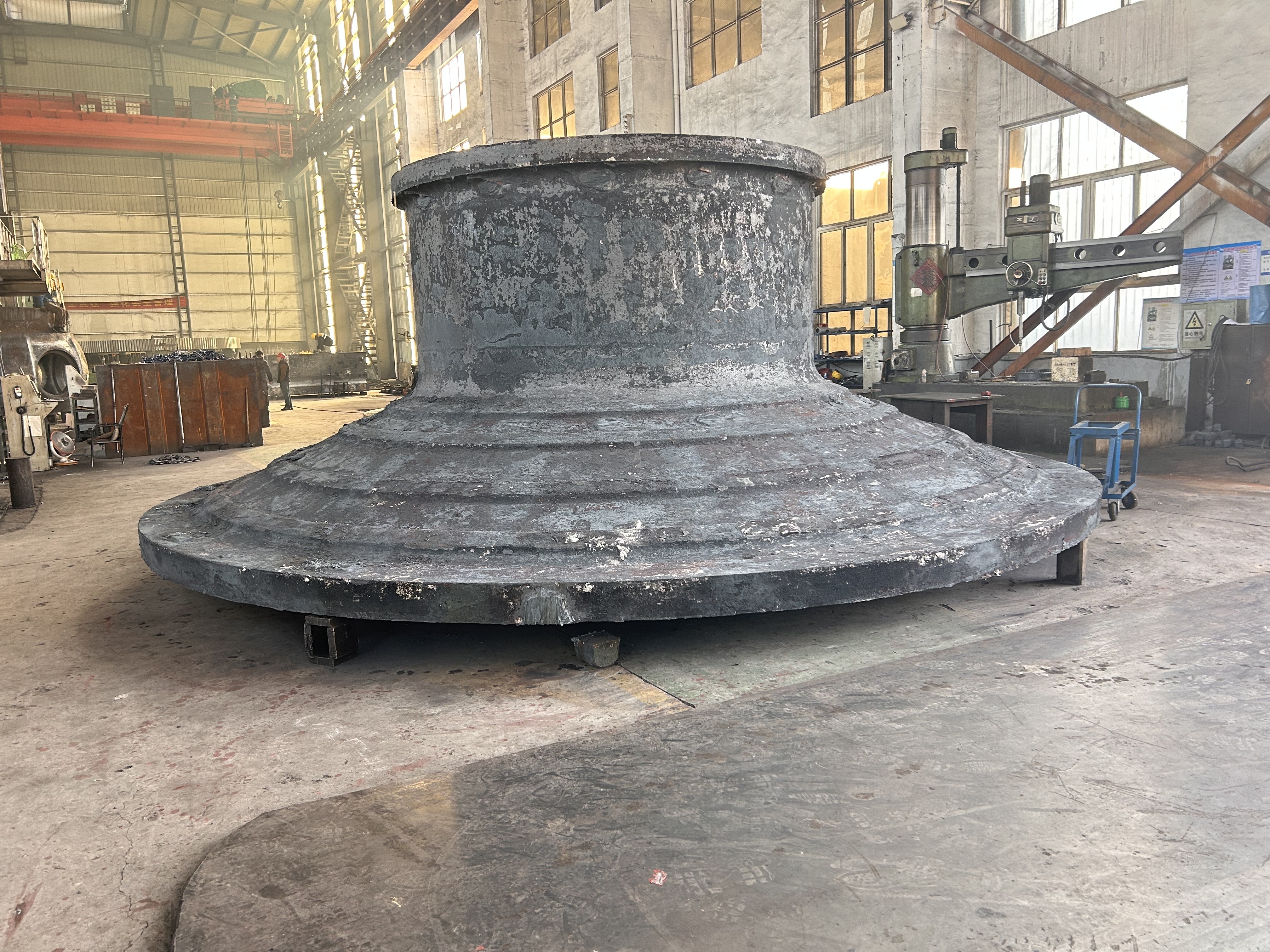
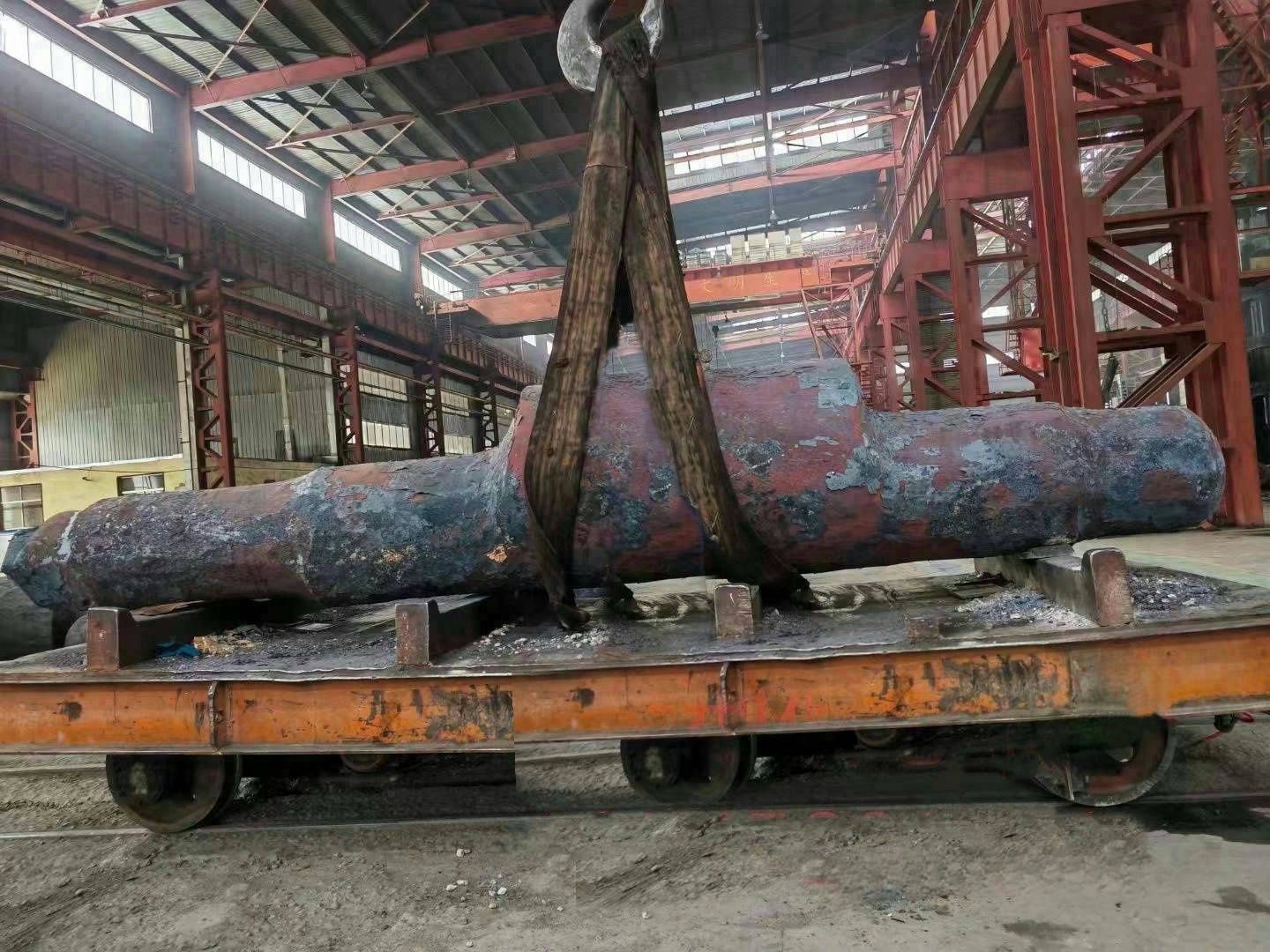
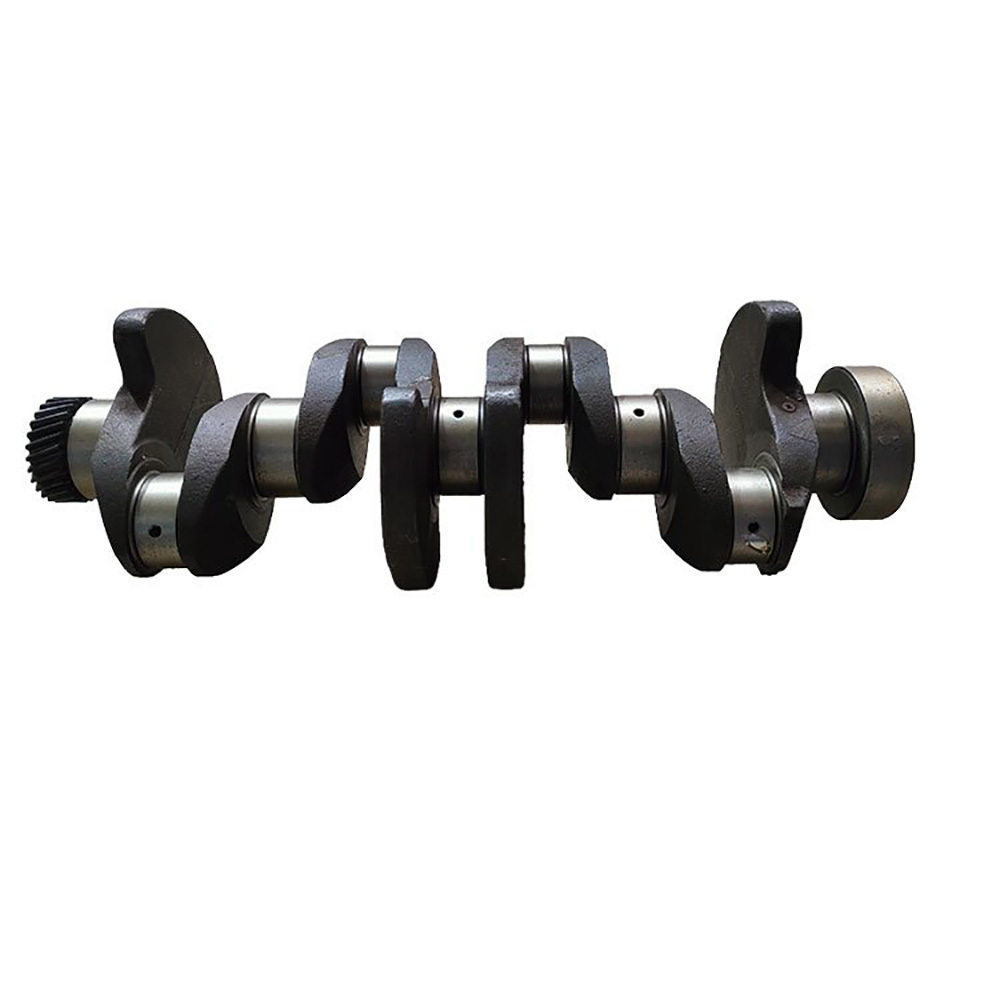
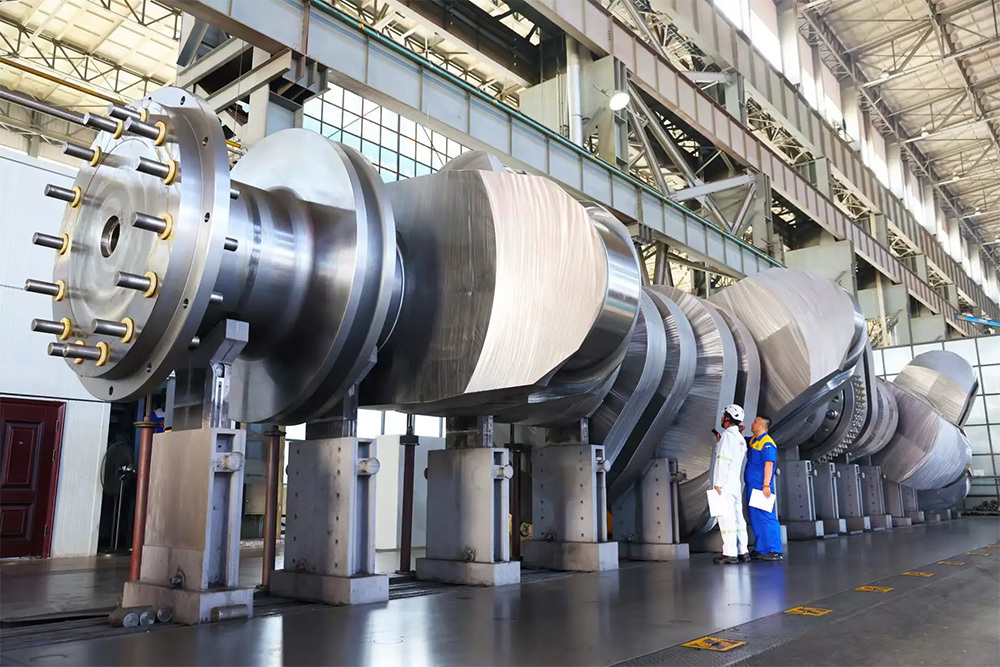
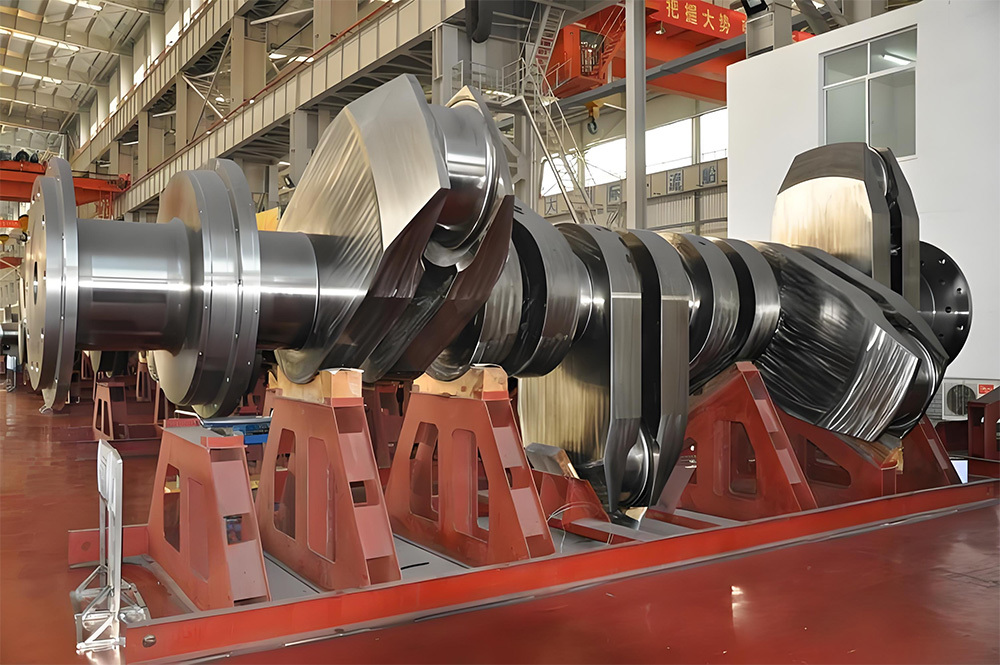
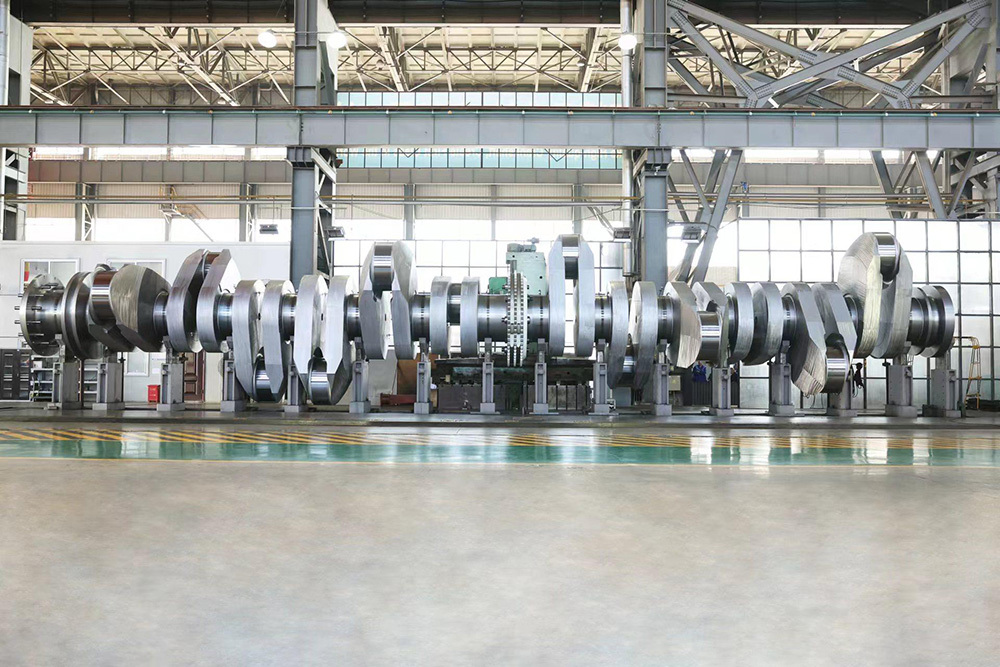
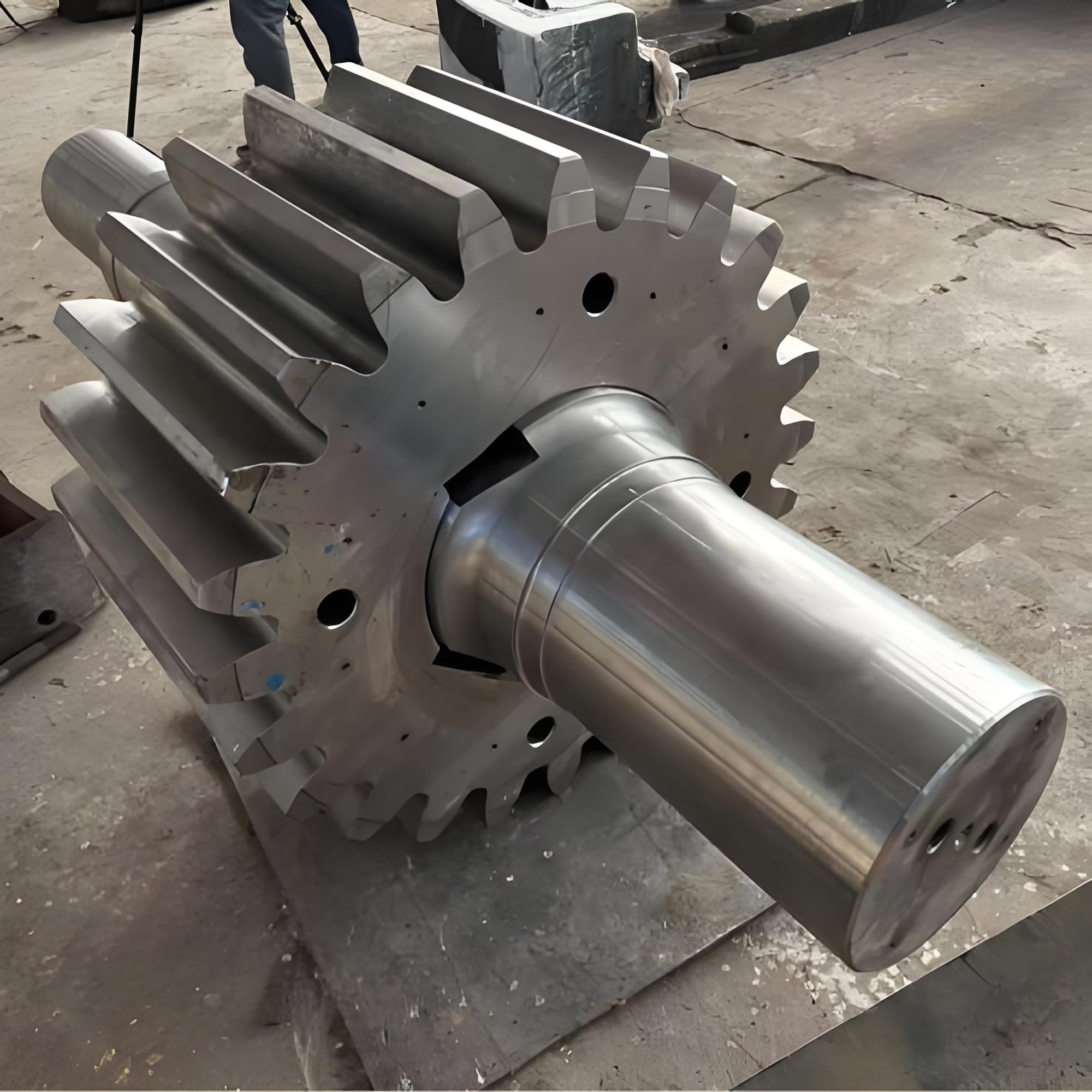
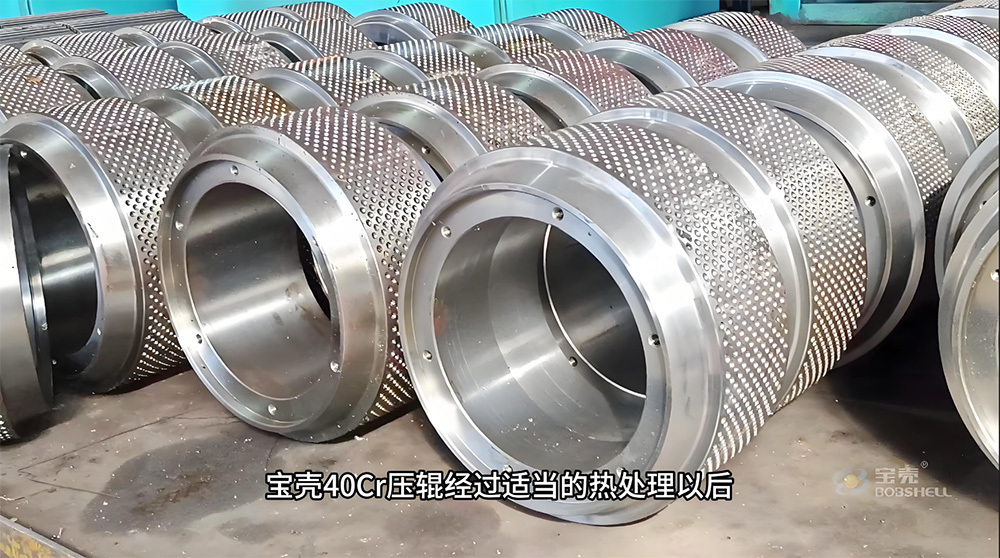
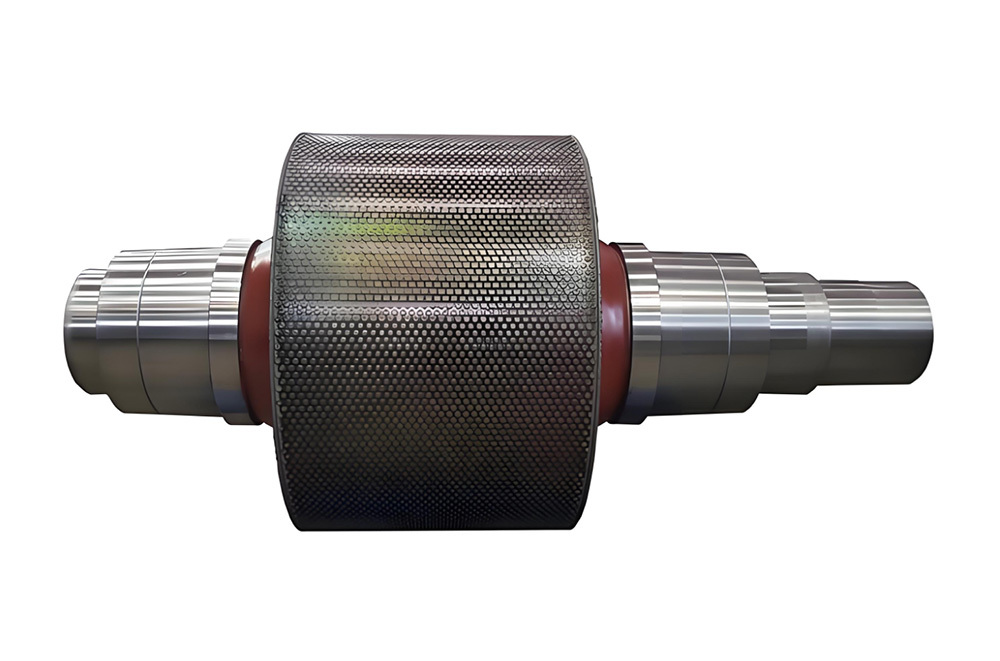
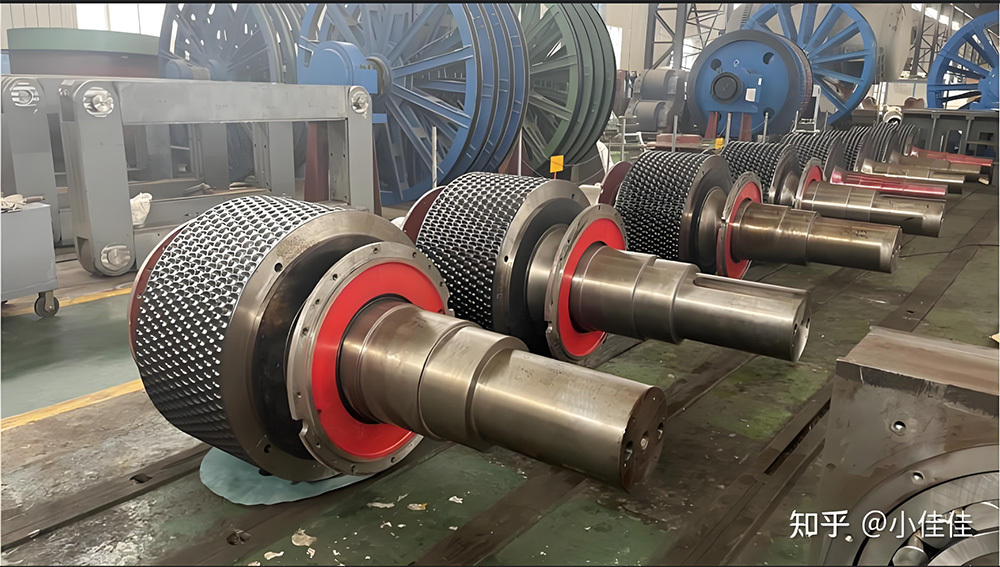
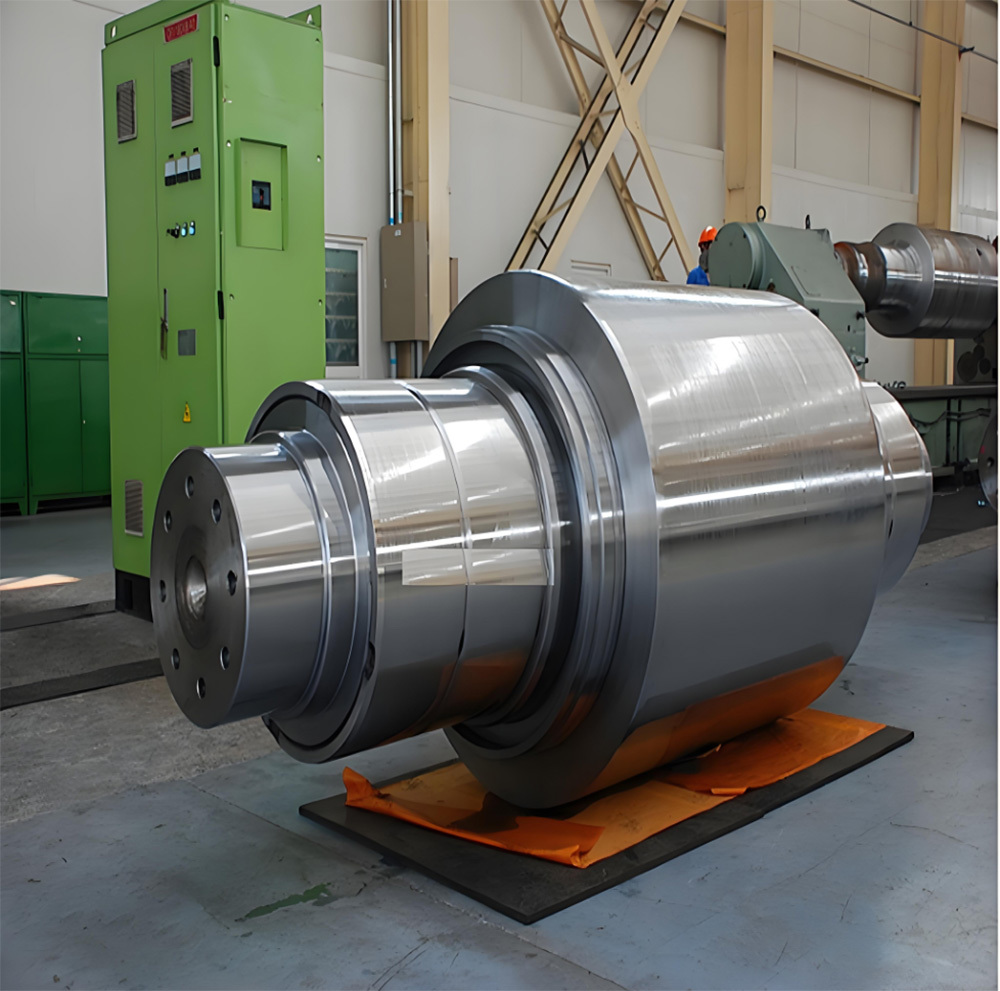
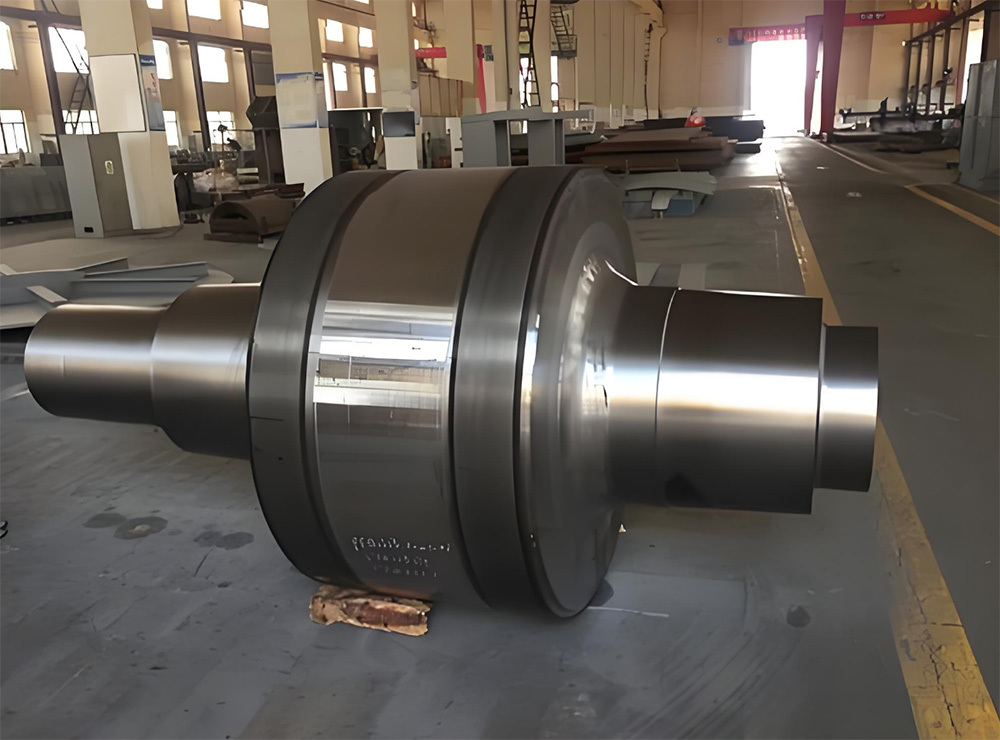
The crankshaft is the core rotating component of the engine. Its function is to convert the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion and drive the vehicle's transmission system, generator, compressor, and other accessories through output torque. It withstands cyclically varying gas pressure, inertial forces, and centrifugal forces, requiring high strength, rigidity, wear resistance, and good balance. It is a key component that determines engine performance and lifespan.
Crankshaft Classification
1. By structural form:
- Integral crankshaft: The main journal and connecting rod journal are formed as one piece, with a simple structure and high reliability, suitable for medium- to high-speed diesel engines.
- Built-up crankshaft: Manufactured in segments and then assembled, facilitating maintenance, commonly used in large low-speed diesel engines.
2. By engine type:
- Inline crankshaft (e.g., L-type): The number of connecting rod journals equals the number of cylinders, compact structure, mostly used in passenger cars.
- V-type crankshaft (e.g., V6, V8): The number of connecting rod journals is half the number of cylinders, suitable for high-power engines.
- Horizontally opposed crankshaft: Used in special layout engines (e.g., Porsche Boxer engine), with good balance.
3. By material and process:
- Forged crankshaft: Made of medium carbon steel (45 steel) or alloy steel (40CrMo), with high fatigue strength, used in high-performance engines.
- Cast crankshaft: Made of ductile cast iron (QT700-2), low cost, suitable for medium and small power engines.
Specifications
1. Dimensional parameters:
- Main journal diameter: φ50-φ300mm (increasing with power).
- Connecting rod journal diameter: φ40-φ280mm.
- Length: 0.3-3m (depending on the number and arrangement of cylinders).
2. Materials and performance:
- Hardness: Surface quenching HRC 50-62, core HRC 25-40.
- Fatigue strength: Forged steel ≥600MPa, ductile iron ≥400MPa.
3. Precision requirements:
- Journal roundness ≤0.01mm, coaxiality ≤0.03mm, surface roughness Ra ≤0.8μm.
Design Parameters
1. Mechanical design:
- Bending and torsional strength: Must meet 1.5 times the maximum engine torque safety factor.
- Transition fillet radius: R ≥3mm to reduce stress concentration and avoid fatigue cracks.
2. Dynamic balance:
- Counterweight design offsets centrifugal force, vibration amplitude ≤0.02mm (G6.3 dynamic balance grade).
3. Lubrication and cooling:
- Oil passage layout: Through the main journal and connecting rod journal to ensure high-pressure lubrication.
- Hollow structure: Reduces weight and optimizes heat dissipation.
Application Scope
1. Internal combustion engine field:
- Construction machinery (e.g., excavators), passenger cars, commercial vehicles, ships, generator sets.
2. Special applications:
- Aircraft engines, motorcycles, agricultural machinery (tractors).
3. Industry demands:
- High reliability (e.g., military vehicles), economy (commercial vehicles), high performance (racing engines).
Important Features
1. High strength and fatigue resistance:
- Forging process ensures continuous metal flow lines, surface strengthening improves lifespan.
2. Precision manufacturing:
- CNC grinding and online inspection technology achieve micron-level accuracy.
3. Lightweight design:
- Topology optimization or hollow structure reduces weight and improves fuel efficiency.
4. Modular design and maintainability:
- Built-up design facilitates replacement of worn parts, reducing maintenance costs.
5. Environmental adaptability:
- Surface coatings (e.g., nitriding, hard chrome plating) enhance corrosion resistance.
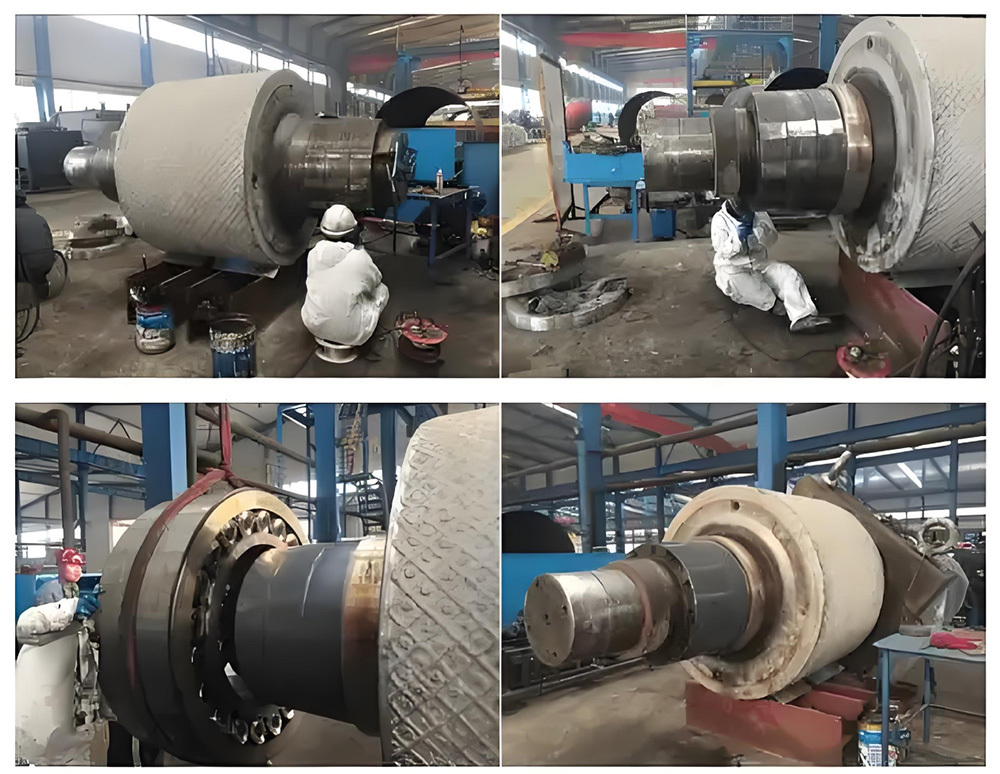
Process Introduction
1. Blank manufacturing:
- Forging: Hot die forging press forming, optimized metal flow lines.
- Casting: Ductile cast iron air impact molding, high precision, low cost.
2. Heat treatment:
- Quenching and tempering: Quenching plus high-temperature tempering to optimize strength and toughness.
- Surface induction hardening: Medium-frequency quenching forms a hardened layer (depth 1.5-3mm).
3. Machining process:
- External milling: CNC disc milling cutter intermittent cutting to improve efficiency.
- Tracking grinding: CNC coordinated grinding of main and connecting rod journals completed in one setup.
4. Strengthening technology:
- Rounded corner rolling: Roller pressing of rounded corners, lifespan increased by 120%-230%.
- Shot peening strengthening: Surface compressive stress layer enhances fatigue resistance.
5. Quality inspection:
- Ultrasonic flaw detection + magnetic particle inspection to check for cracks, dynamic balancing test to verify vibration.
Keywords
Previous: Mining crankshaft
Next: Marine crankshaft
















Crankshaft
Contact Information
Product Categories
Related Products
Related Products
Ball mill
Ball mill
Rod Mill
(Semi) Autogenous Mill
Mining Hoisting
Single-rope Winding Mine Hoist
Multi-rope friction mine hoist
Well Drilling Hoist
Supporting Equipment
Mining Washing and Selection
Selective Crusher
Centrifuge
-

WLL Series Coal Slime Scraper Discharge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZY Series Dual-Mass Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

WZL Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

TWZ Series Horizontal Vibrating Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

LLS-900 Sludge Centrifugal Dehydrator
-

ML Series Coal Slurry Centrifugal Dewatering Machine
-

LL Series Vertical Centrifugal Dehydrator
Flotation machine
Filter machine
Grading Machine
Mining Auxiliary Equipment
Gear Reducer Series
-

Vertical mill gearbox
-

Special reducer for scraper machine
-

Industry-specific gear reducer
-

Bevel Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Parallel shaft reducer
-

Industrial General Gearbox Series
-

Helical Gear - Bevel Gear Reduction Motor
-

Helical Gear Reduction Motor
-

Planetary Gear Reducer
-

Cylindrical Gear Reducer
Category One
Category Two
Crusher Series
Rotary Crusher
Jaw Crusher
Impact Crusher
Cone Crusher
Ball Press Machine
High-pressure briquetting machine
Medium and High Pressure Briquetting Machine
Rotary kiln
-

Cement kiln (rotary kiln)
-

Light gray kiln (self-alkali steam calcination kiln)
-
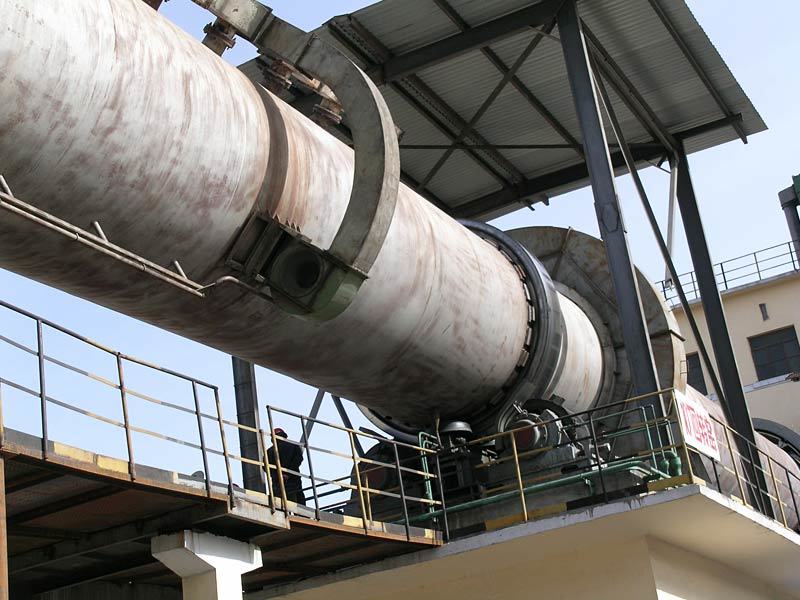

Chemical kiln
-

Oxidation Cooling Kiln
-

Oxidative roasting rotary kiln (oxidation kiln)
-

Lithium Carbonate Rotary Kiln
-
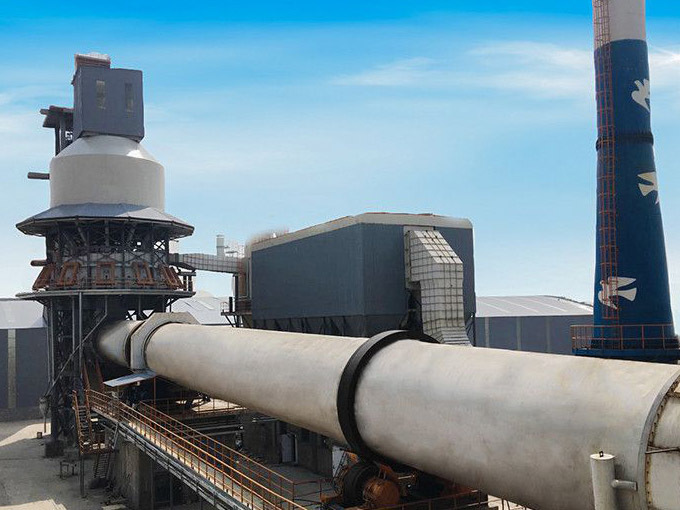

Lime Rotary Kiln
-
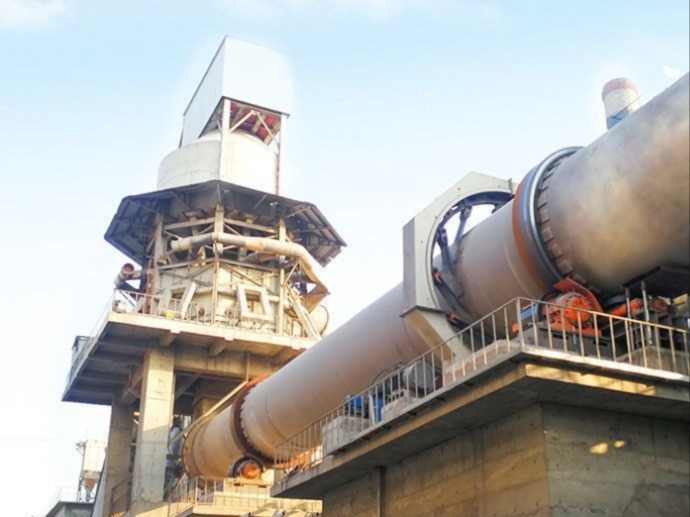

Metal Magnesium Rotary Kiln
-

Architectural Lightweight Aggregate Rotary Kiln
-
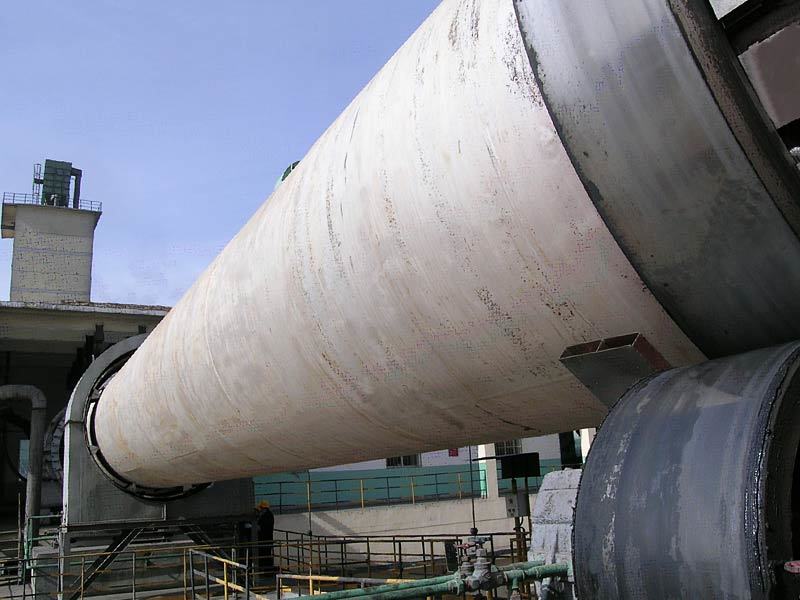

Cement Rotary Kiln
Cast and forged parts
Large castings
Large Forgings
Transmission Accessories
Gear Coupling
Gear
Electro-hydraulic control system
Automation Control
-

GPRS Remote Expert Diagnostic System
-

Metallurgical Electrical Control Equipment
-

Automated Control System for Mineral Processing and Coal Washing
-

Local System Upgrade
-
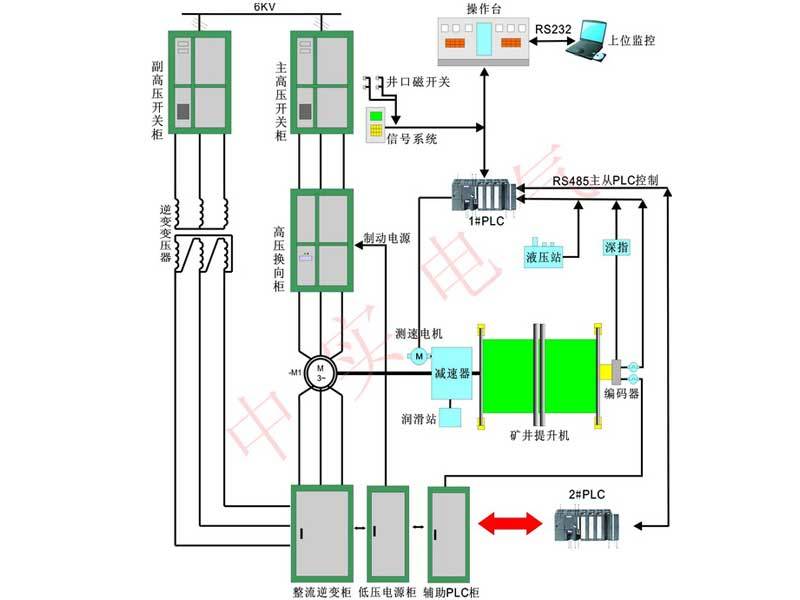
Doubly-Fed Variable-Frequency Electric Control System
-
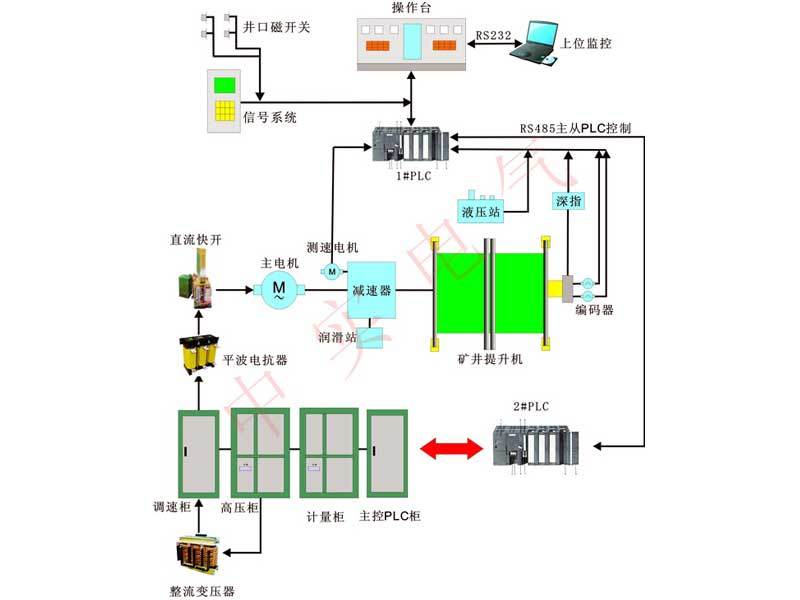
Fully digital DC control system
-
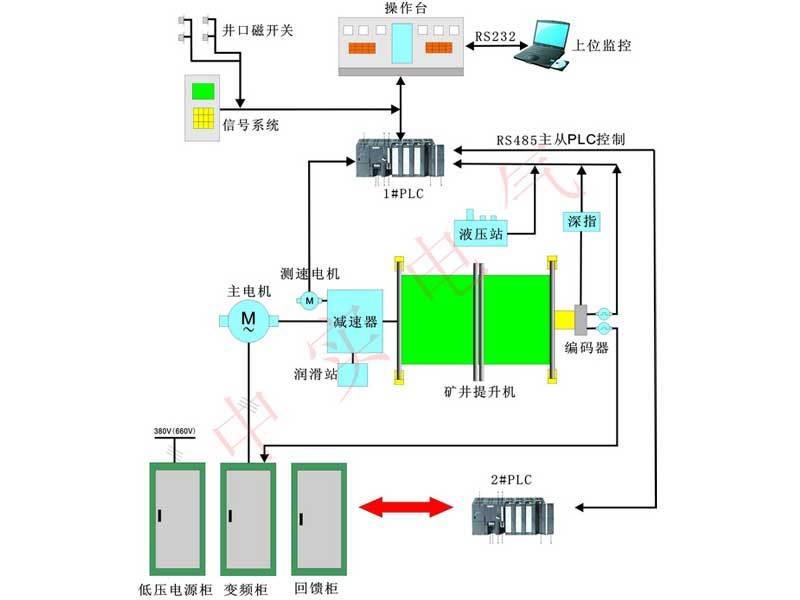
Fully digital low-voltage variable frequency feedback
-
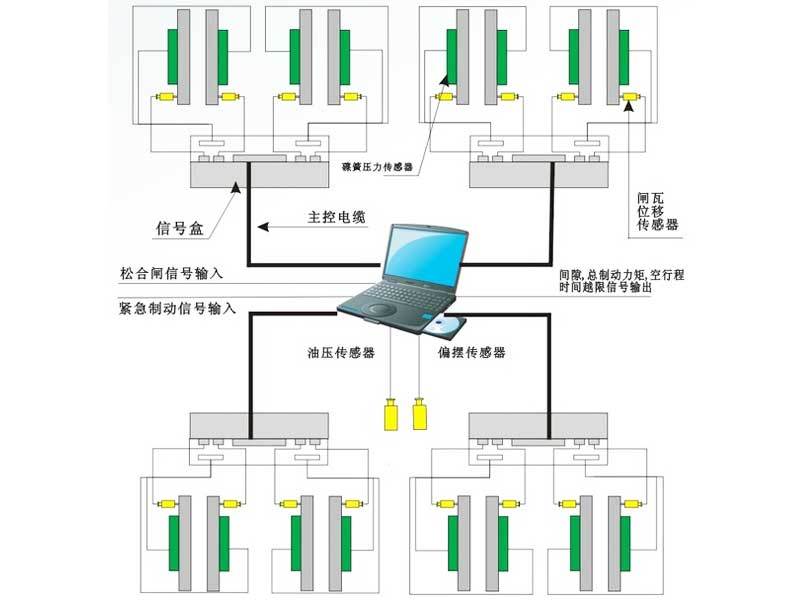
Disc Brake Online Inspection System
-

Rotary Kiln Control System
Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic system
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic System
-

Hydraulic Station
-
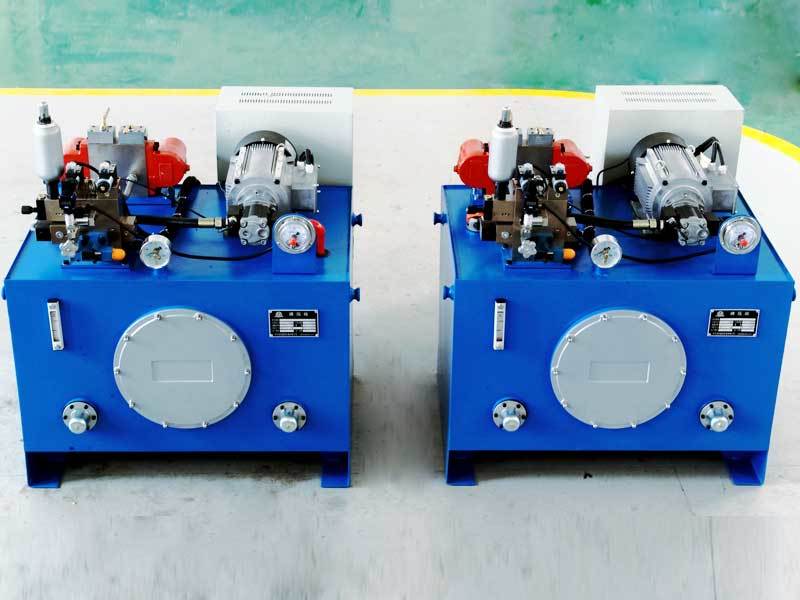

Variable-frequency servo hydraulic system
-

E119A/E119S, E118A/E118S Explosion-Proof Secondary Brake Hydraulic Station
-
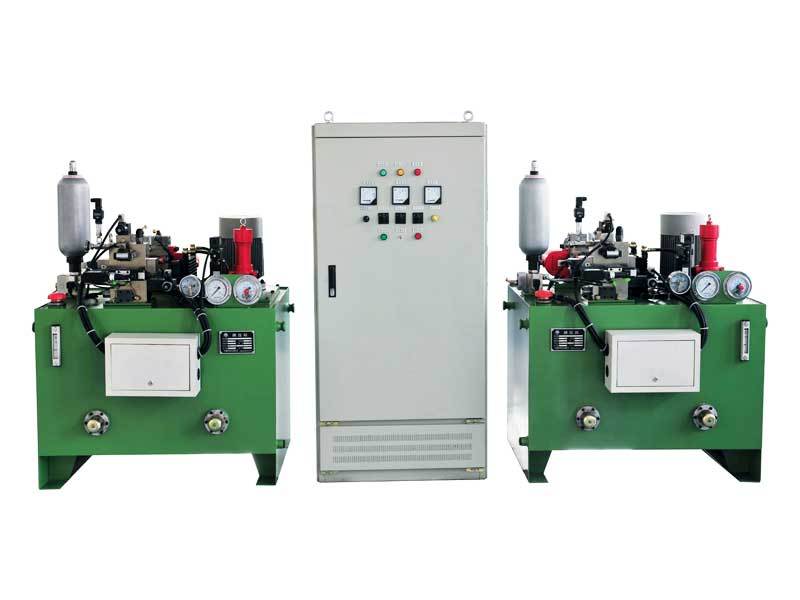

Constant-Deceleration Electro-Hydraulic Braking Control System
-
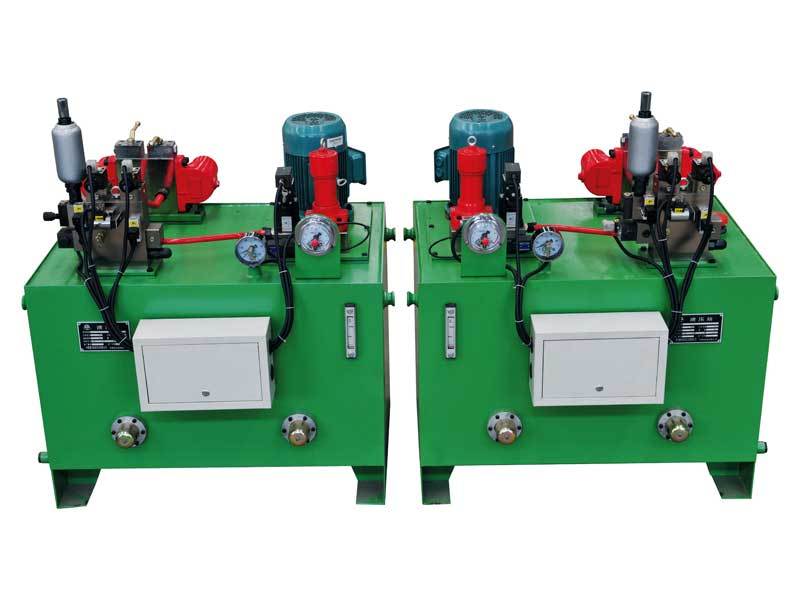

TE160/TE161/TE162/TE163 Insert-Mounted Control Dual-Stage Braking Hydraulic Station
Hydraulic cylinder
Other accessories
Large welded components
-
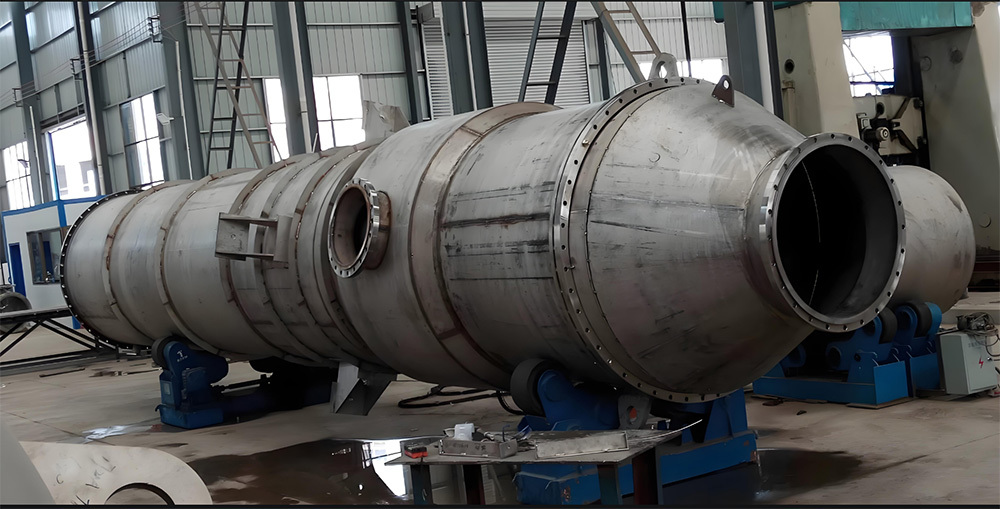

Large kiln body riveted and welded components
-

Large furnace riveted and welded components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
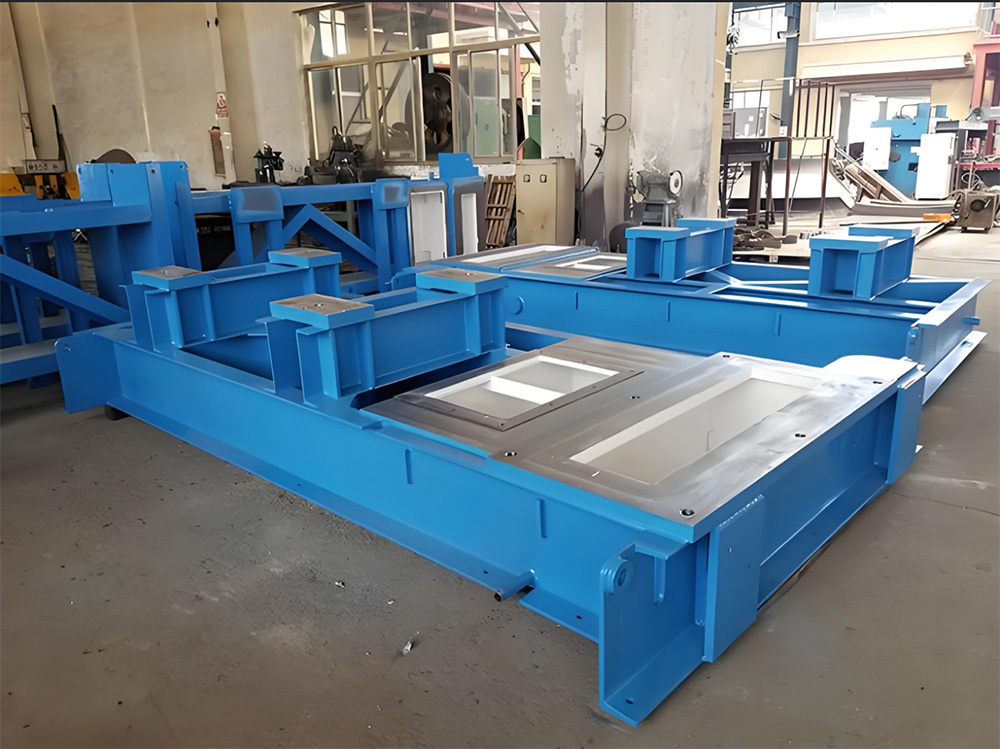

Large steel ladle riveted and welded components
-
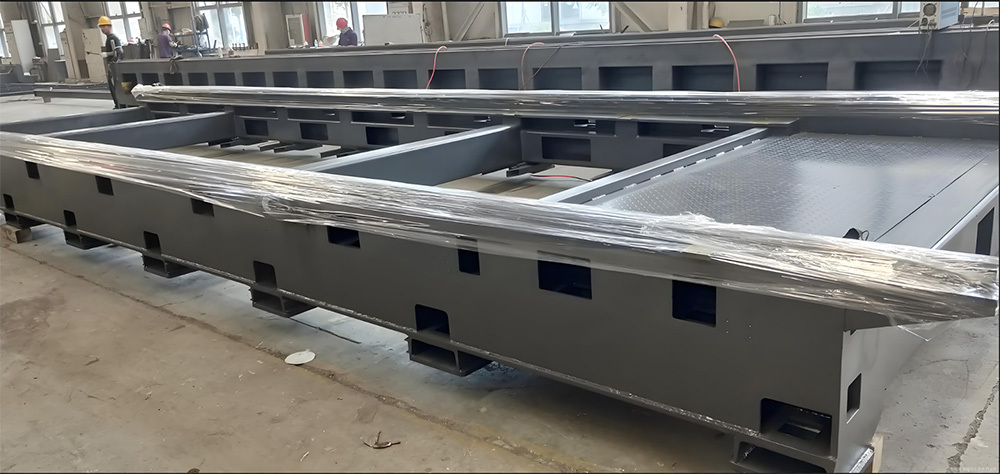

Large base
-
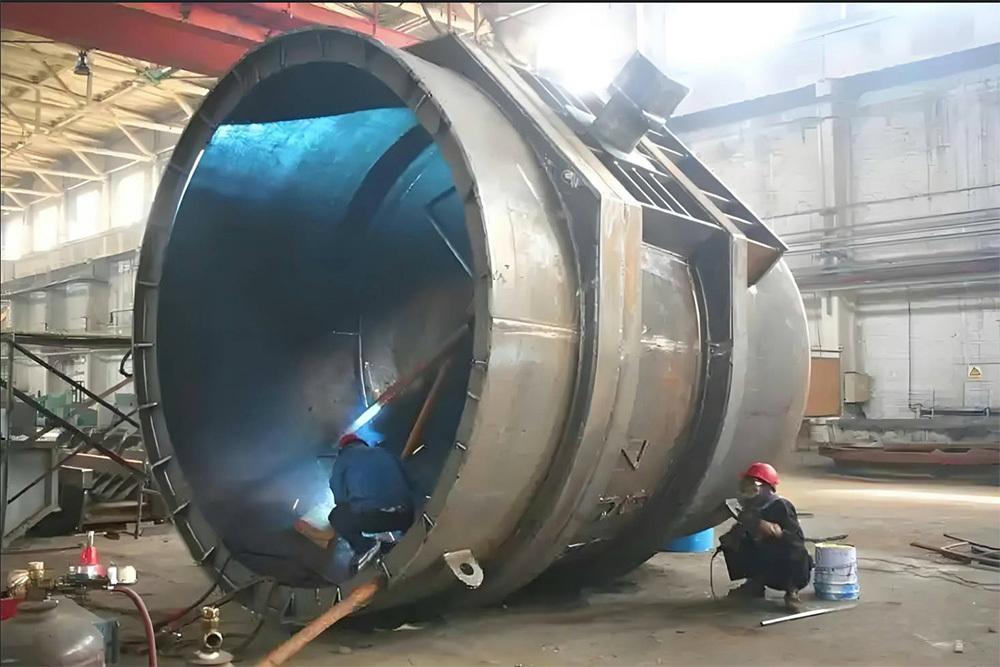

Large Riveted and Welded Components
-
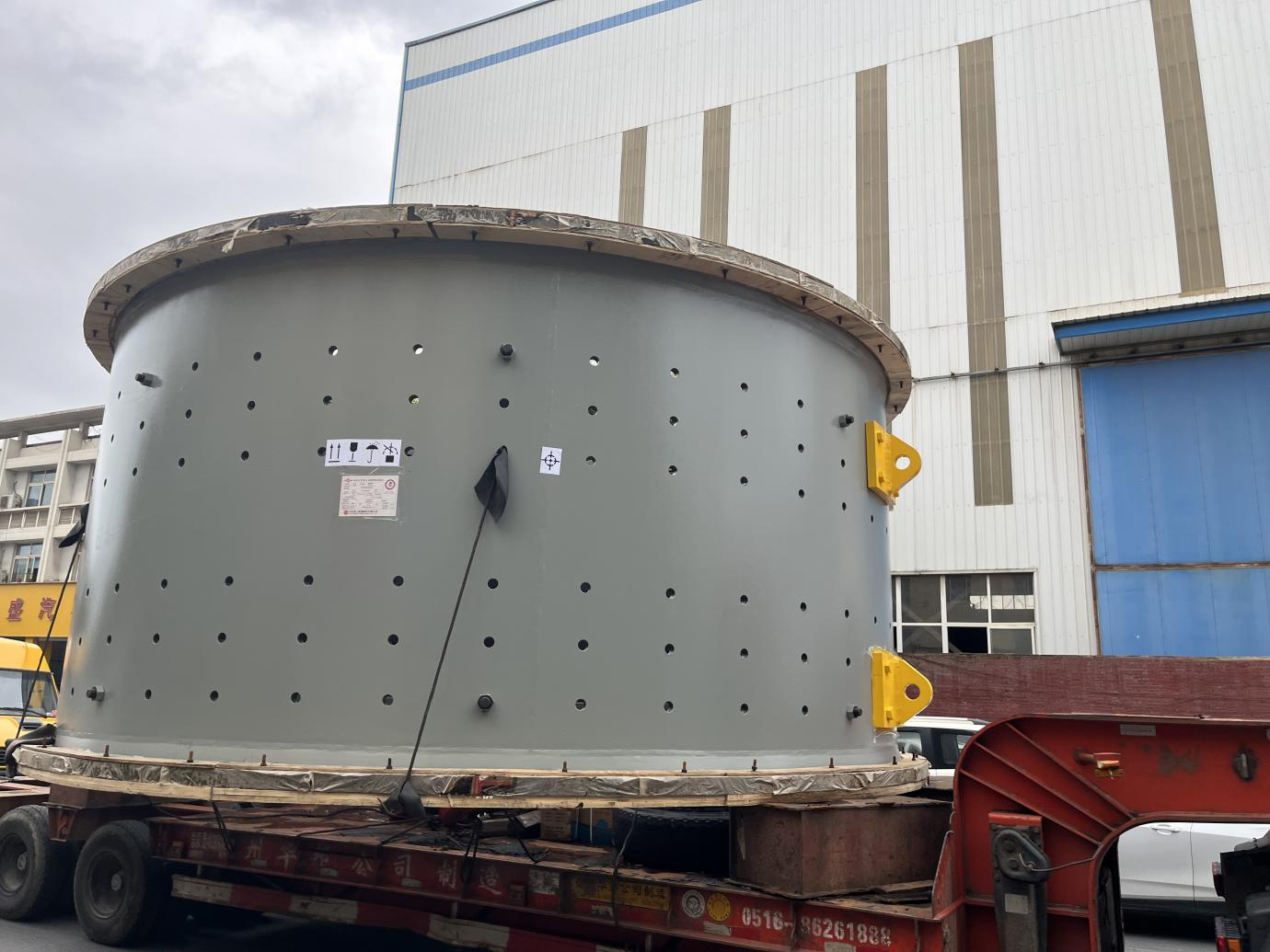

Ball Mill Cylinder
Wear-resistant products
-

Eccentric Crusher Jaw Plate
-

New-Type High-Pressure Roller Wear-Resistant Surfacing Welding Technology
-

Bus Alloy Bushings
-

Large ball mill ZGMN13CR2 lining plate
-

Medium-chromium alloy liner plate
-

High-manganese steel product series
-

High-precision cast iron parts
-

Low-carbon martensitic steel jaw plate
-

Large Self-Grinding Mill Cylinder Lining Plates
Engineering Plastics
-

Modified PP sheave and guide wheel lining blocks for elevators
-
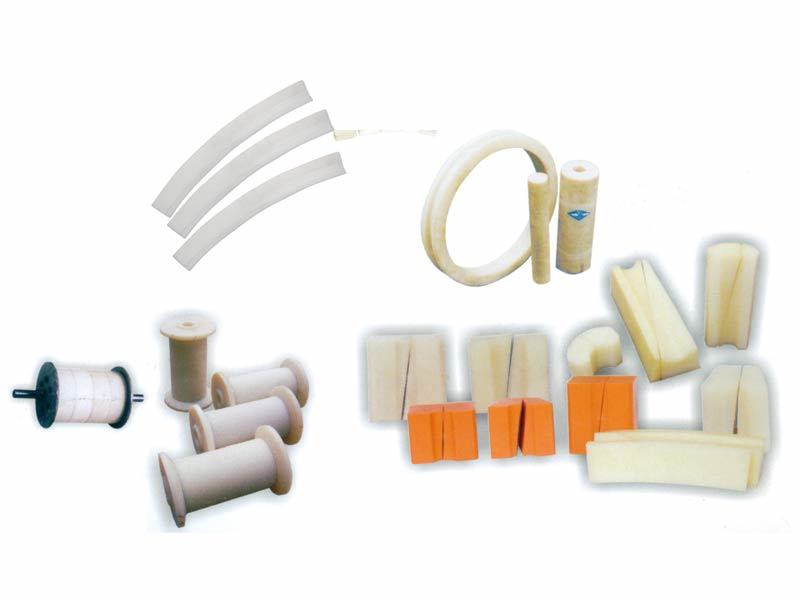

Nylon products
-
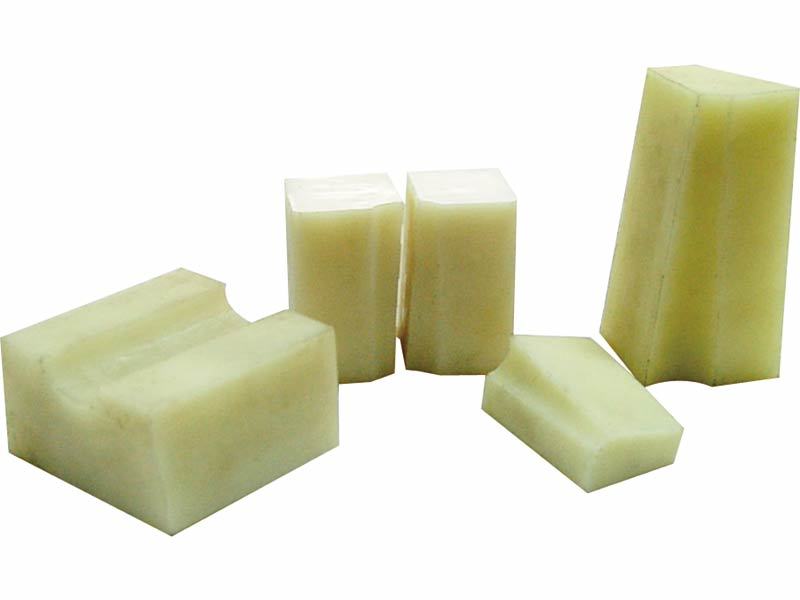

Polyurethane Products
-
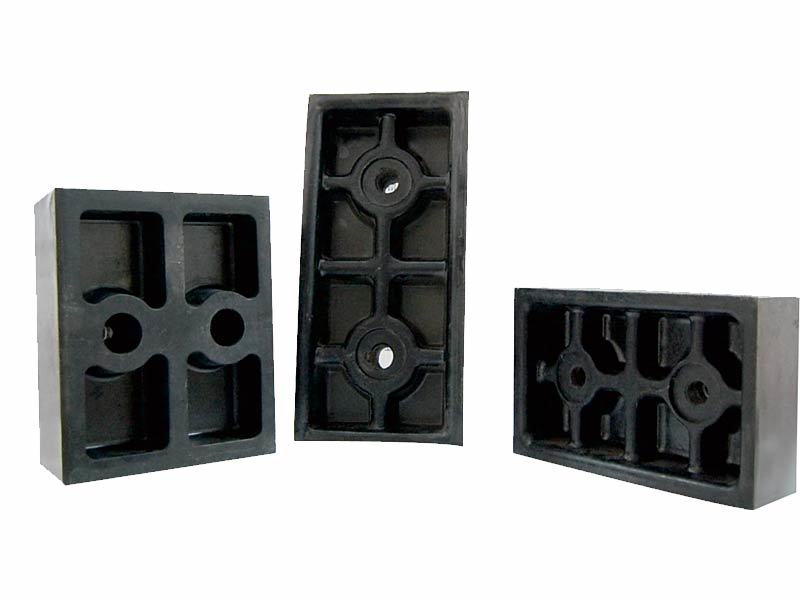

Multi-rope hoist phenolic press blocks, fixing blocks
-
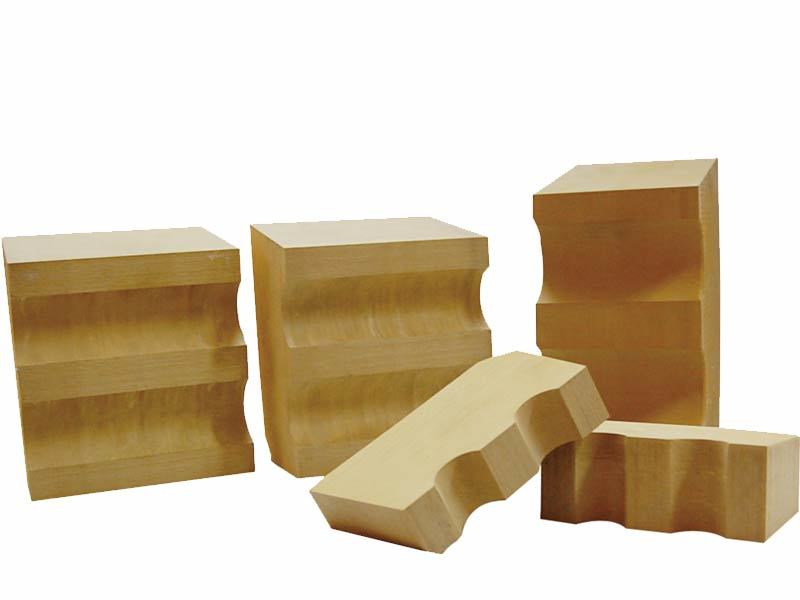

Germany-imported — LUWIPLAST GELB848 Friction Pads
-

Single-rope mine hoist plastic lining板
-

WSM-3 New Eco-Friendly, Non-Asbestos Brake Blocks (Elevator Braking System)
-

KP-09 Ultra-High Molecular Wheel Sheave Lining Pads
-

GDM326 Imported Material High-Performance Friction Pads
Roller shaft
crane sheave
Contact Us
No.99 Hengshan Road, Jianxi District, Luoyang City, Henan Province

sweep
CITICTLC
Learn more about dynamic information